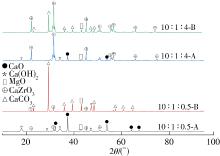
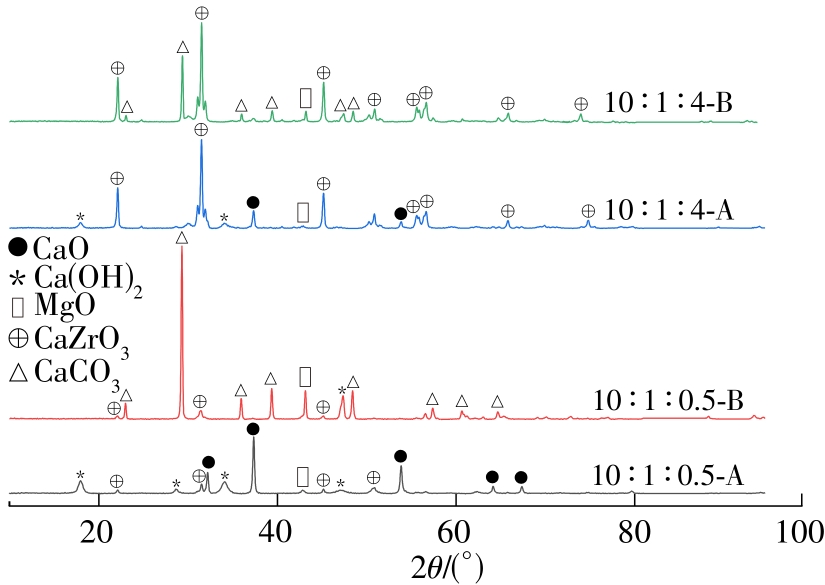
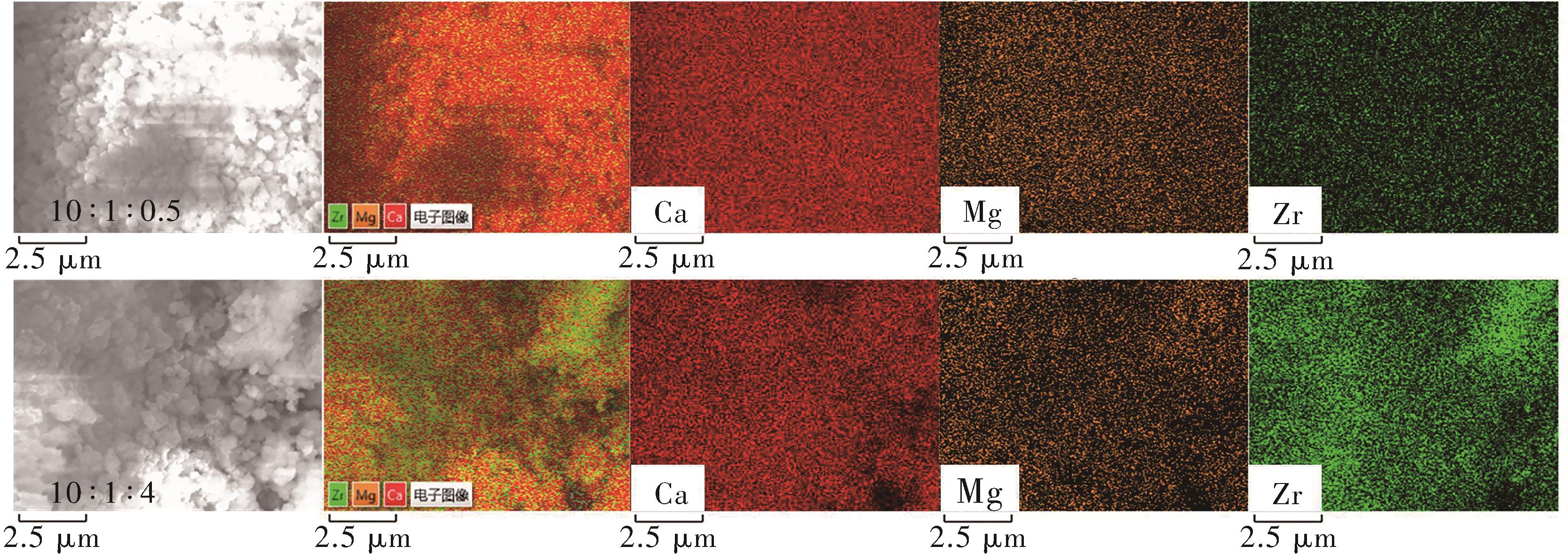
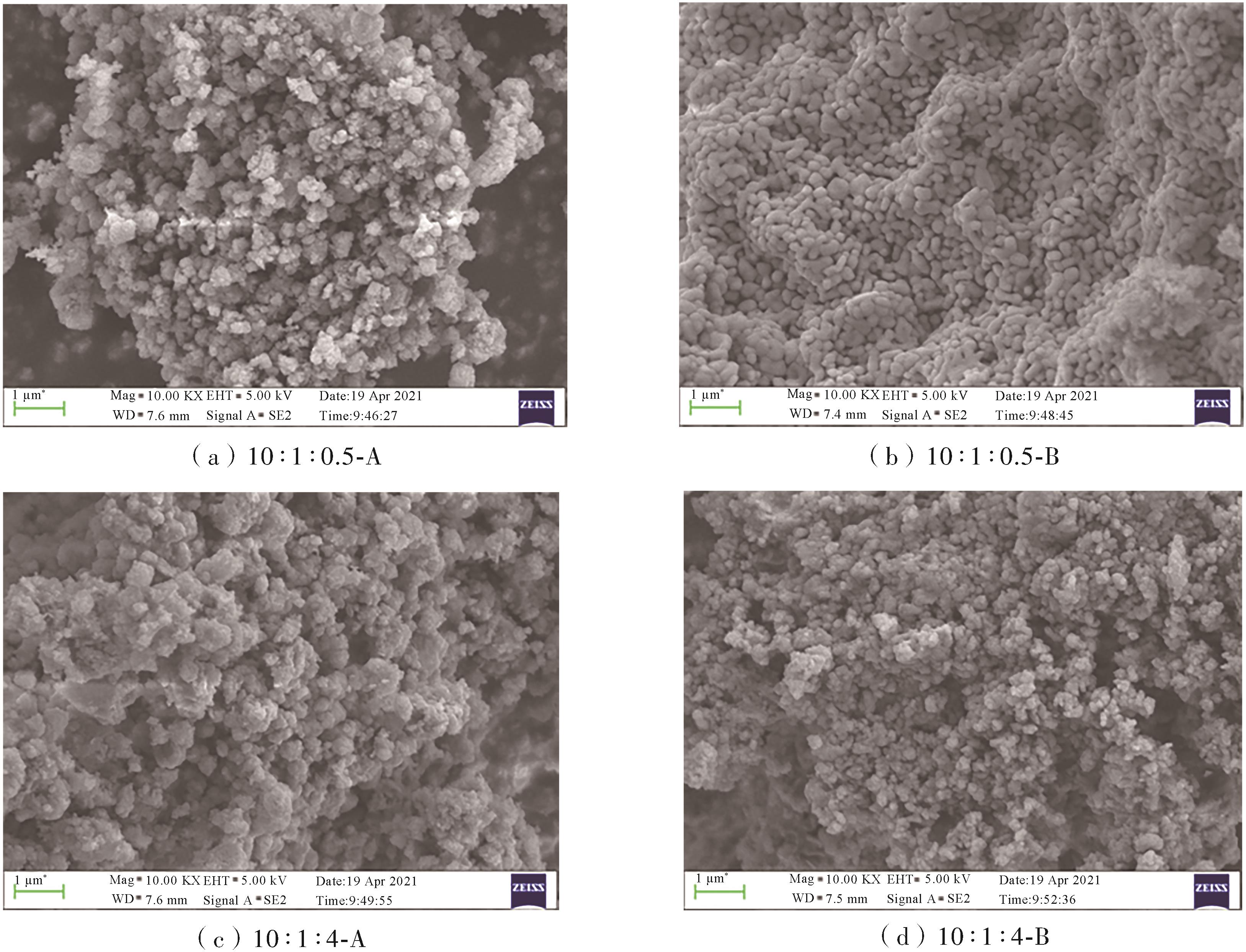
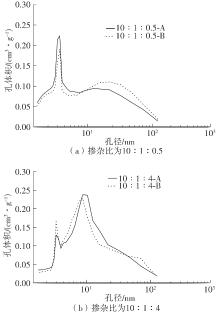
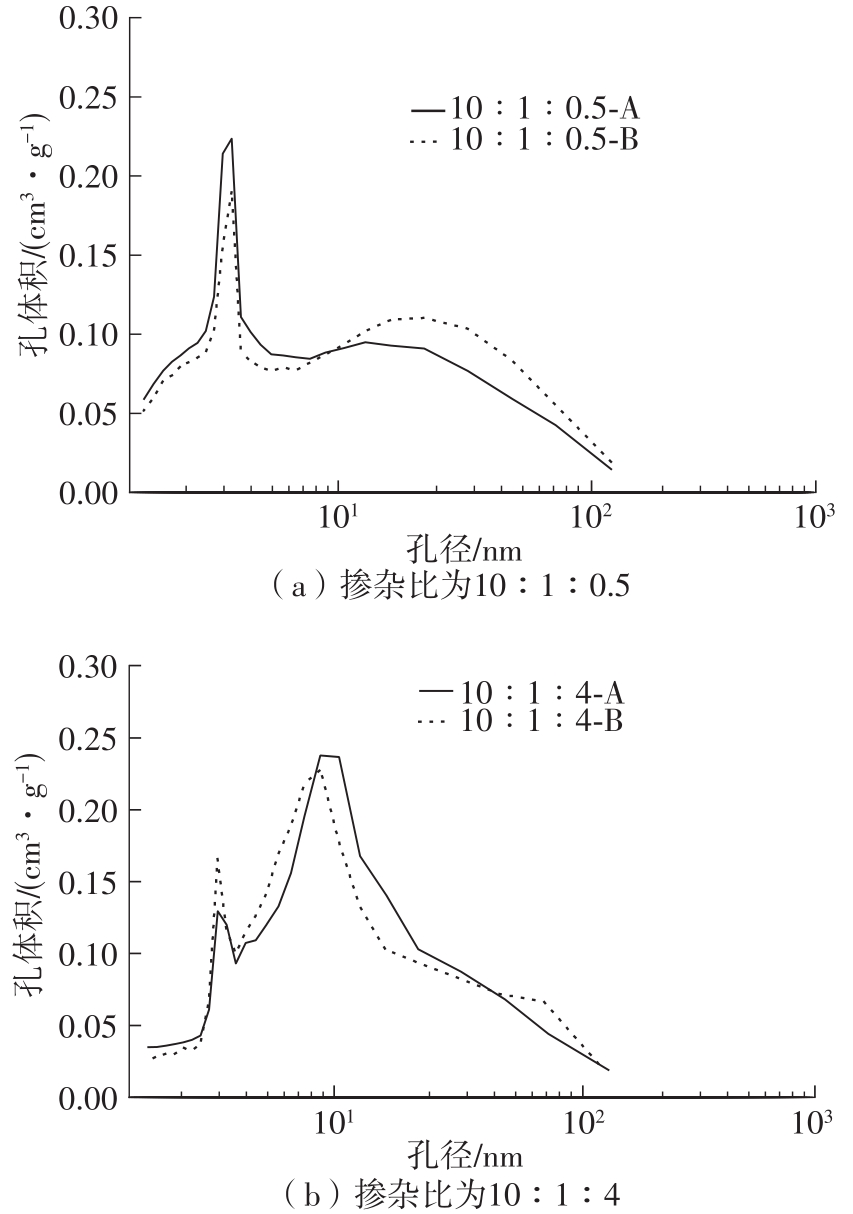
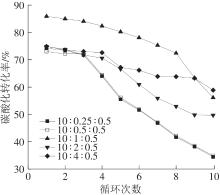
| 1 |
莫永强,李洪亮,方书起,等 .城市生活垃圾气化制合成气研究进展[J].现代化工,2021,41(5):73-77.
|
|
MO Yongqiang, LI Hongliang, FANG Shuqi,et al .Research progress in preparing syngas through gasification of municipal solid waste[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2021,41(5):73-77.
|
| 2 |
廖艳芬,张曼玉,陈顺凯,等 .基于FLUENT的垃圾热解气MILD燃烧研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(2):9-16.
|
|
LIAO Yanfen, ZHANG Manyu, CHEN Shunkai,et al .Study on MILD combustion of MSW pyrolysis gas based on FLUENT[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2021,49(2):9-16.
|
| 3 |
廖艳芬,陈顺凯,张曼玉,等 .有机固废热解气MILD燃烧的数值分析[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(7):28-35,46.
|
|
LIAO Yanfen, CHEN Shunkai, ZHANG Manyu,et al .Numerical analysis of MILD combustion of organic solid waste pyrolysis gas[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2020,48(7):28-35,46.
|
| 4 |
MA X, LI Y, DUAN L,et al .CO2 capture performance of calcium-based synthetic sorbent with hollow core-shell structure under calcium looping conditions[J].Applied Energy,2018,225(1):402-412.
|
| 5 |
LIU X, SHI J, HE L,et al .Modification of CaO-based sorbents prepared from calcium acetate for CO2 capture at high temperature[J].Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2017,25(5):572-580.
|
| 6 |
SU C, DUAN L, DONAT F,et al .From waste to high value utilization of spent bleaching clay in synthesizing high-performance calcium-based sorbent for CO2 capture[J].Applied Energy,2018,210:117-126.
|
| 7 |
张雷,张力,闫云飞,等 .掺杂Ce、Zr对CO2钙基吸附剂循环特性的影响[J].化工学报,2015,66(2):612-617.
|
|
ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Li, YAN Yunfei,et,al .Effect of Ce,Zr on cyclic performance of CaO-based CO2 sorbents[J].CIESC Journal,2015,66(2):612-617.
|
| 8 |
GRASA G S, ABANADES J C .CO2 capture capacity of CaO in long series of carbonation/calcination cycles[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2006,45(26):8846-8851.
|
| 9 |
韩蕙宇,石俊飞,徐龙,等 .掺杂Mg、La对高温CO2钙基吸附剂循环特性的影响[J].天然气化工(C1化学与化工),2018,43(6):68-74.
|
|
HAN Huiyu, SHI Junlong, XU Long,et al .Effect of doping Mg or La on cyclic performance of CaO-based adsorbents for CO2 capture at high temperature[J].Natural Gas Chemical Industry,2018,43(6):68-74.
|
| 10 |
GUO H, KOU X, ZHAO Y,et al .Effect of synergistic interaction between Ce and Mn on the CO2 capture of calcium-based sorbent:textural properties,electron donation,and oxygen vacancy[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,334:237-246.
|
| 11 |
NAWAR A,ALI M, MAHMOOD M,et al .Effect of structural promoters on calcium based sorbents from waste derived sources[J].Materials Today Communications,2020,24:101075/1-8.
|
| 12 |
牛佳宁,张登峰,金悦,等 .电石水解制备复合钙基吸附剂及其循环吸附CO2的特性[J].过程工程学报,2014,14(2):340-344.
|
|
NIU Jianing, ZHANG Dengfeng, JIN Yue,et al .Preparation of calcium-based composite sorbent by hydrolysis of calcium carbide and its multi-cyclic CO2 capture performance[J].The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering,2014,14(2):340-344.
|
| 13 |
张珏伟 .改性钙基、镁基小球循环捕获烟气CO2性能的研究[D].徐州:中国矿业大学,2019.
|
| 14 |
王艳,张书廷,张于峰,等 .城市生活垃圾低温热解产气特性的实验研究[J].燃料化学学报,2005,33(1):62-67.
|
|
WANG Yan, ZHANG Shuting, ZHANG Yufeng,et al .Gas formation characteristics during low temperature pyrolysis of municipal household garbage[J].Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2005,33(1):62-67.
|
| 15 |
唐诗,诸林,范峻铭,等 .钙基CO2吸收剂改性研究进展[J].现代化工,2015,35(2):44-48.
|
|
TANG Shi, ZHU Lin, FANG Junming,et al .Research progress in modified Ca-based sorbents for cyclic CO2 capture[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2015,35(2):44-48.
|
| 16 |
陈健,段伦博,卞若愚,等 .钙基中空微球的碳酸化性能及其动力学分析[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版),2019,49(4):757-763.
|
|
CHEN Jian, DUAN Lunbo, BIAN Ruoyu,et al .Analysis of carbonation and kinetic performance of CaO hollow microspheres[J].Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition),2019,49(4):757-763.
|
| 17 |
孙荣岳,李英杰,刘长天,等 .白泥循环煅烧/碳酸化捕集CO2的反应特性[J].煤炭学报,2013,38(4):675-680.
|
|
SUN Rongyue, LI Yingjie, LIU Changtian,et al .CO2 capture behavior of white mud during its calcination/carbonation cycles[J].Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(4):675-680.
|