华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 20-28.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240455
共享单车与需求响应公交耦合优化研究
许航, 李欣, 袁昀
- 大连海事大学 交通运输工程学院,辽宁 大连 116026
Research on the Joint Optimization of Shared Bikes and Demand-Responsive Connector
XU Hang, LI Xin, YUAN Yun
- Transportation Engineering College,Dalian Maritime University,Dalian 116026,Liaoning,China
摘要:
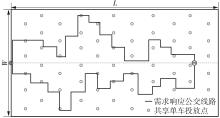
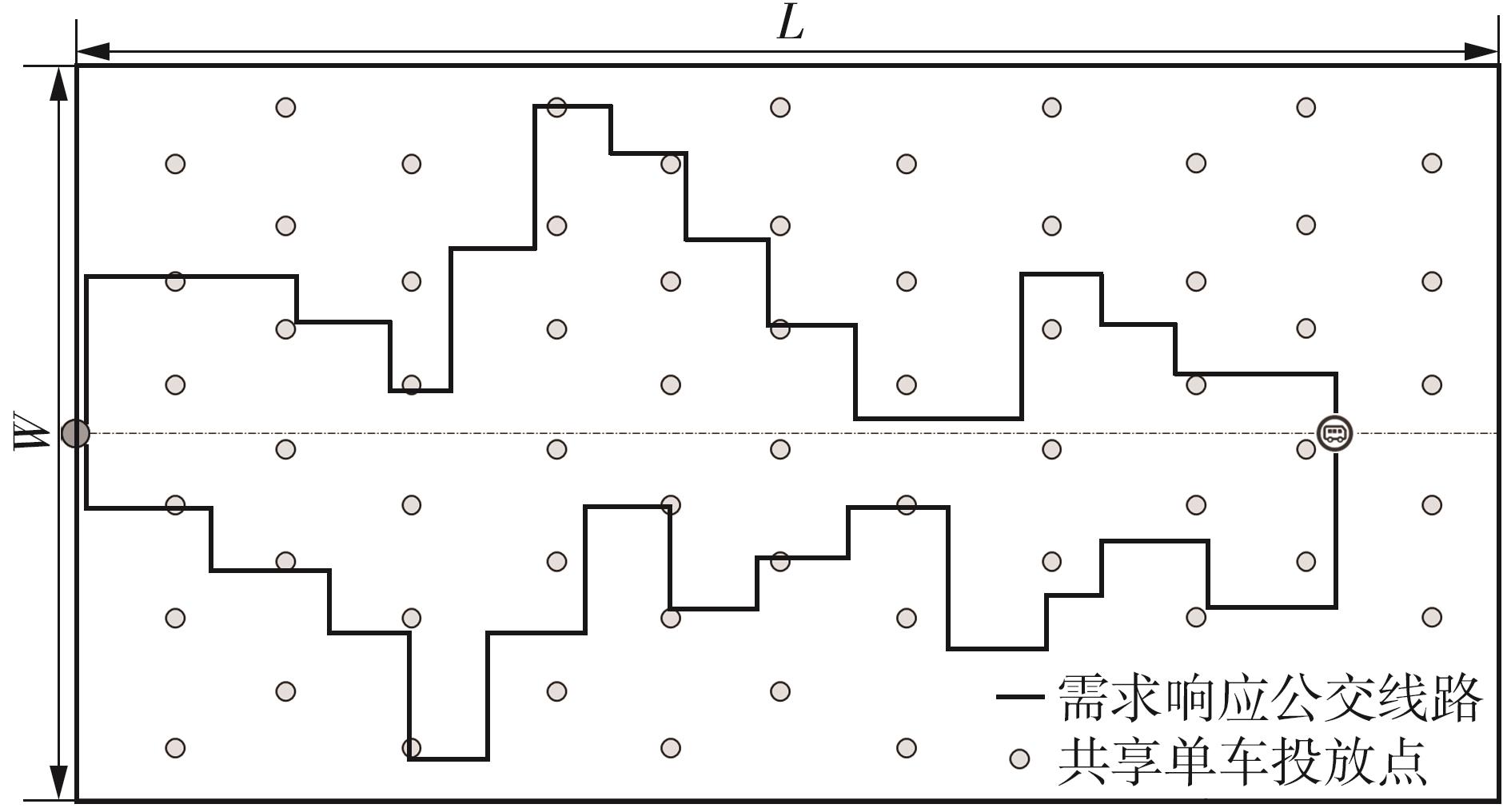
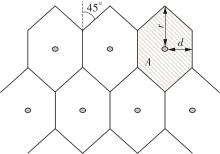
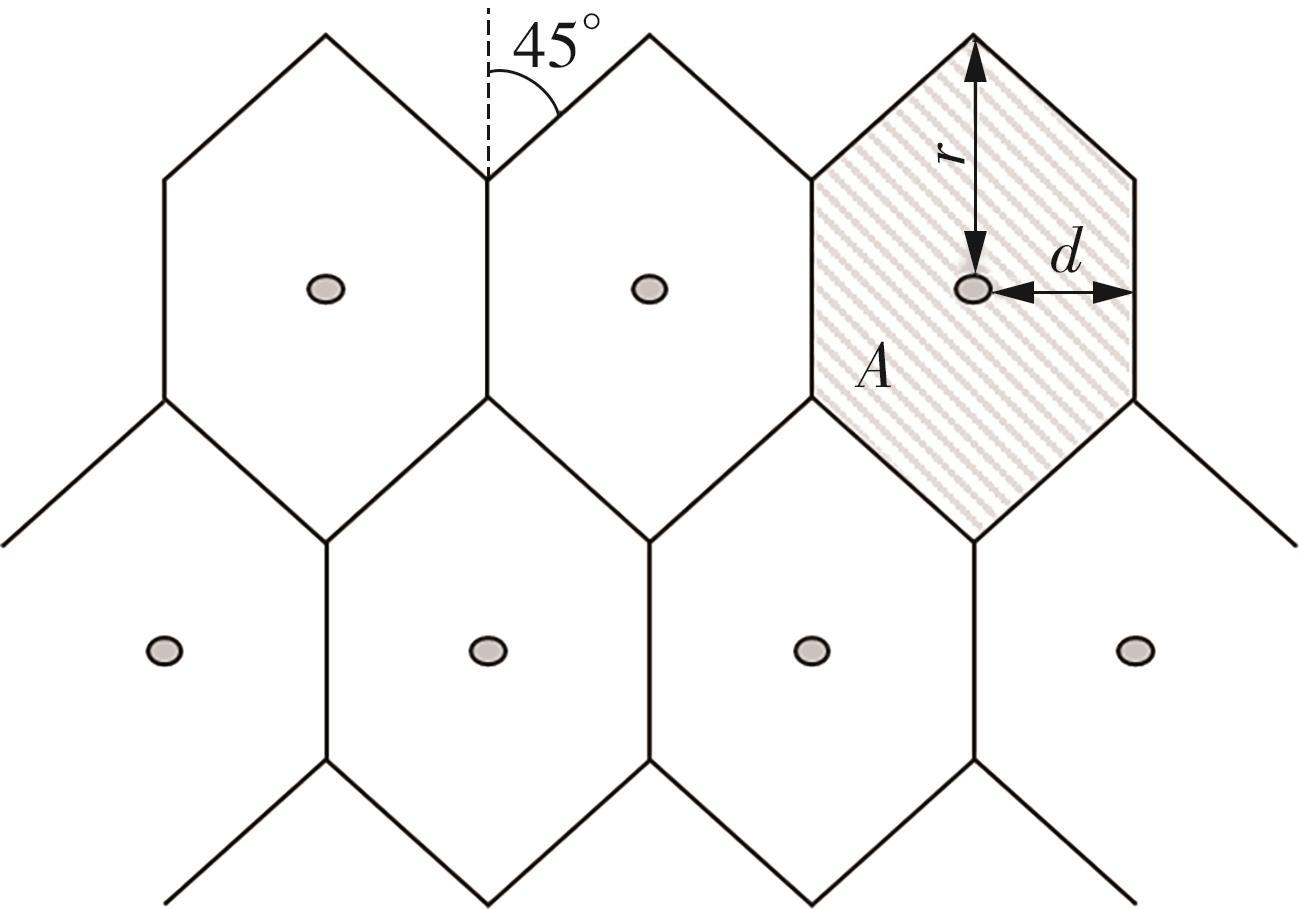
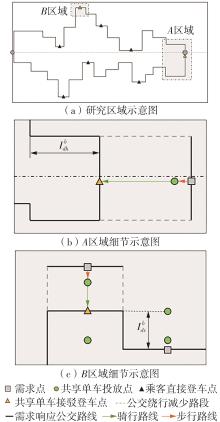
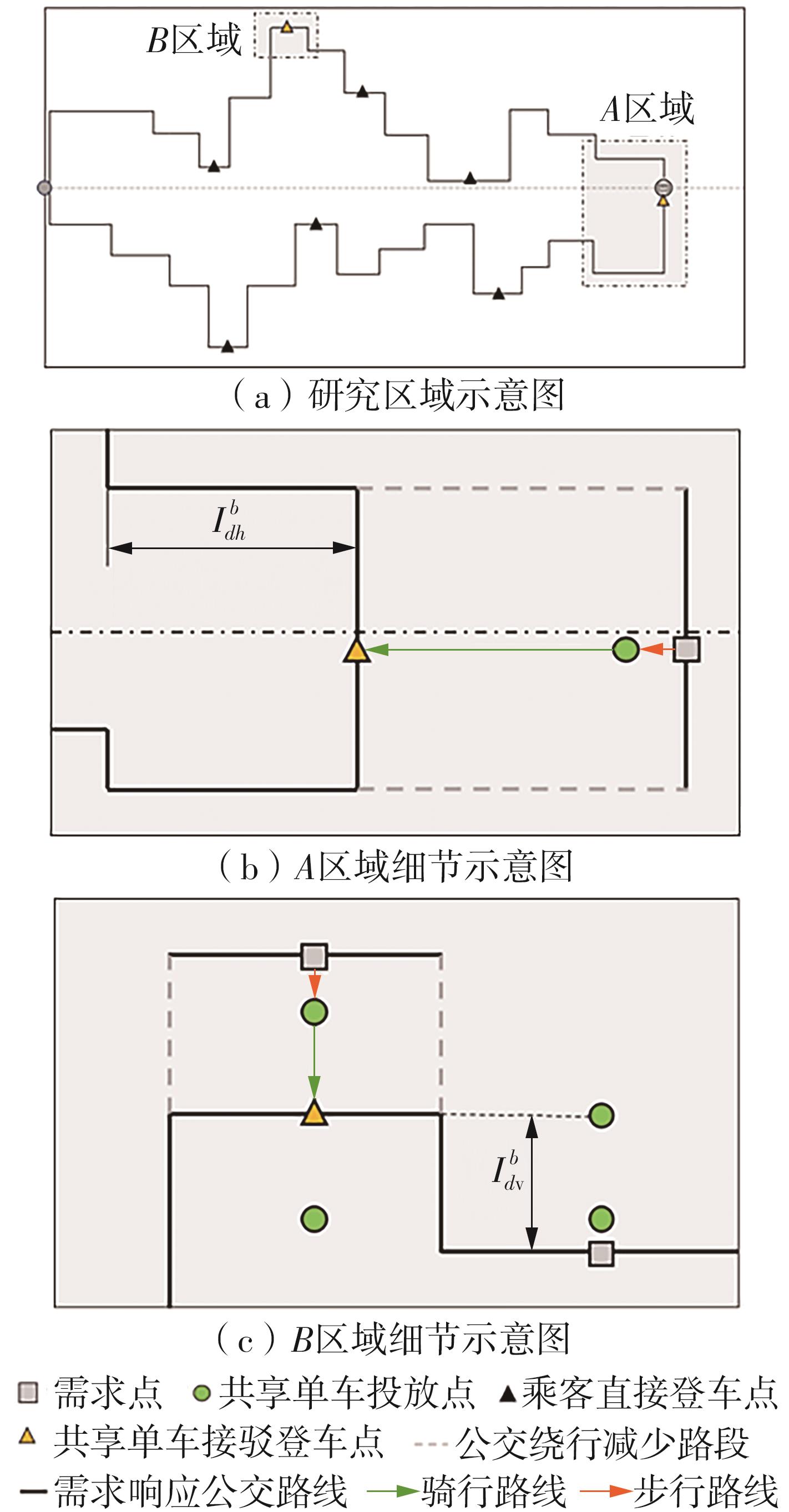
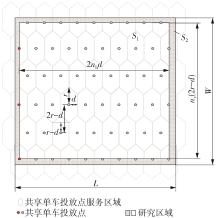
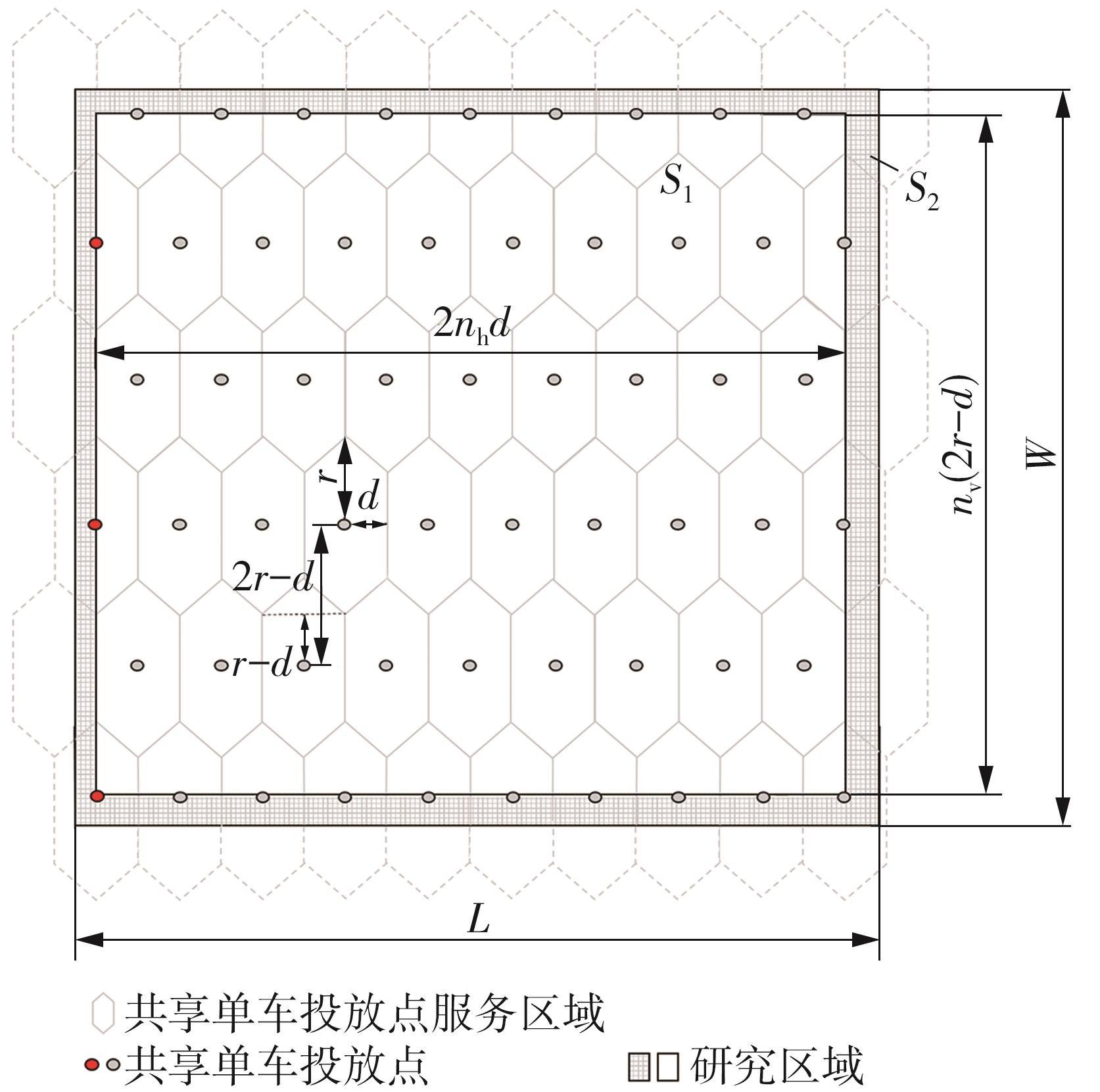
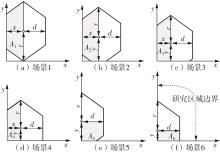
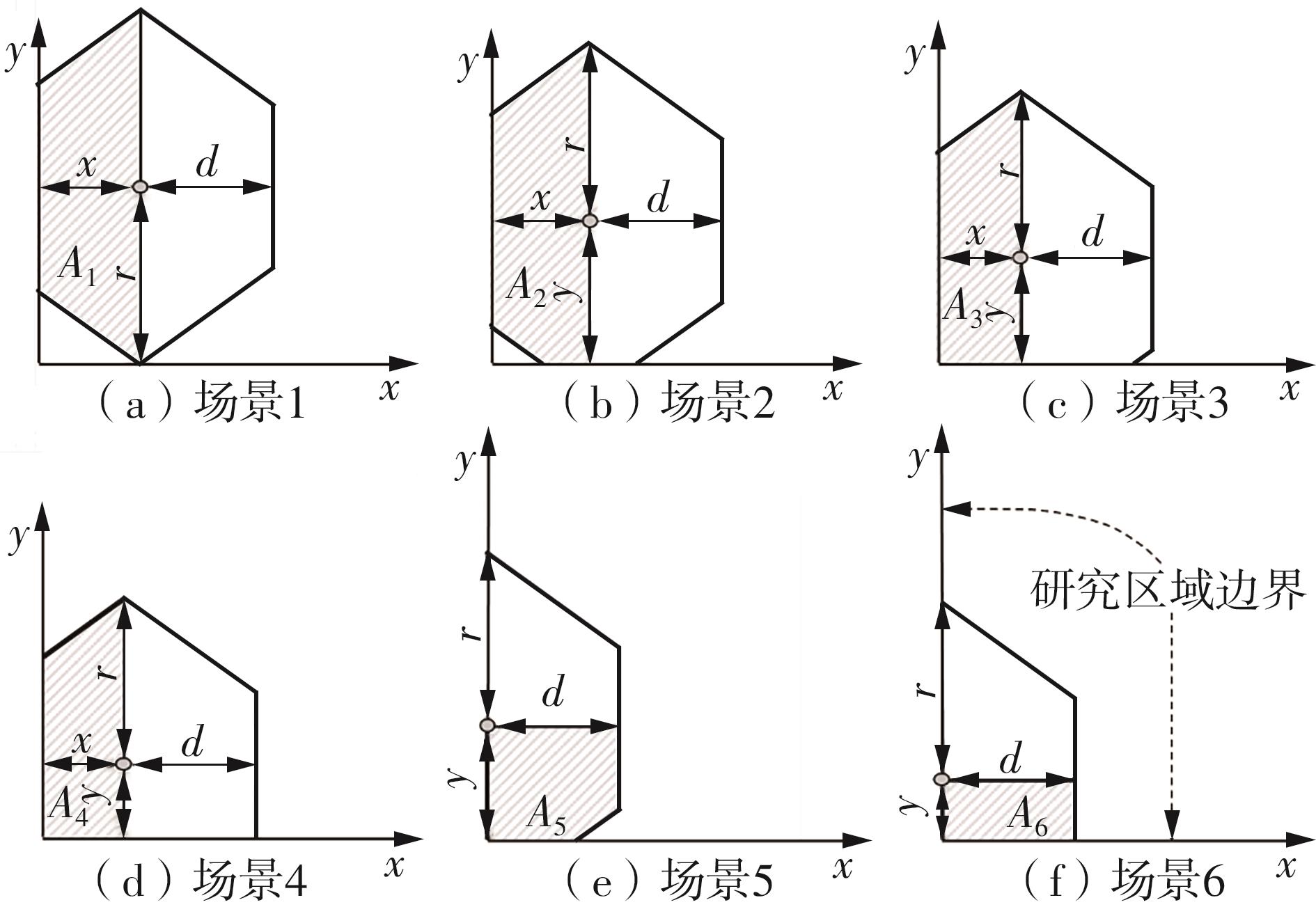
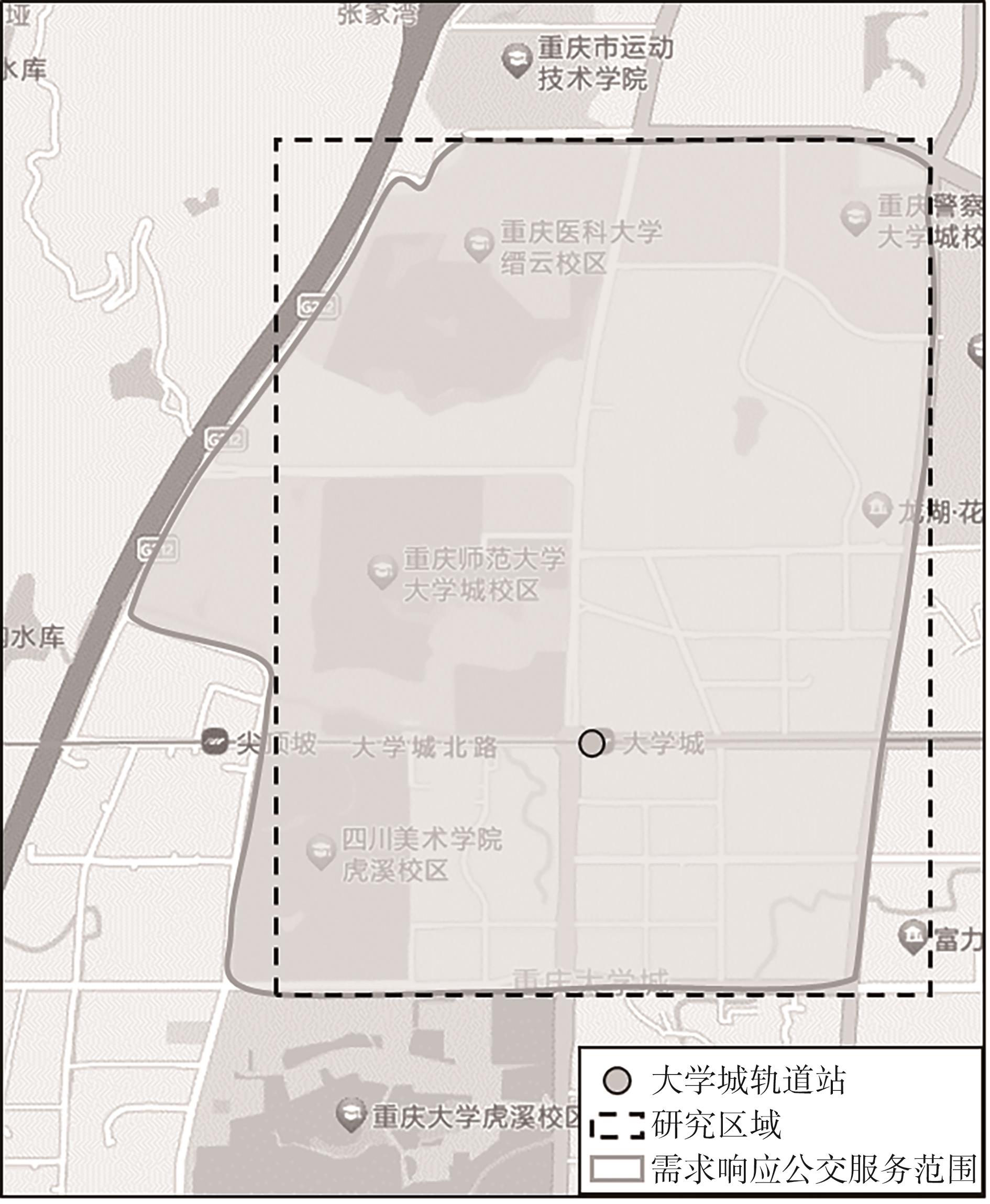
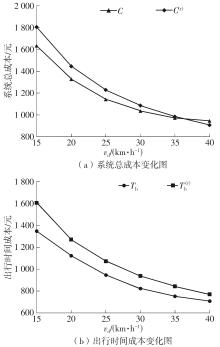
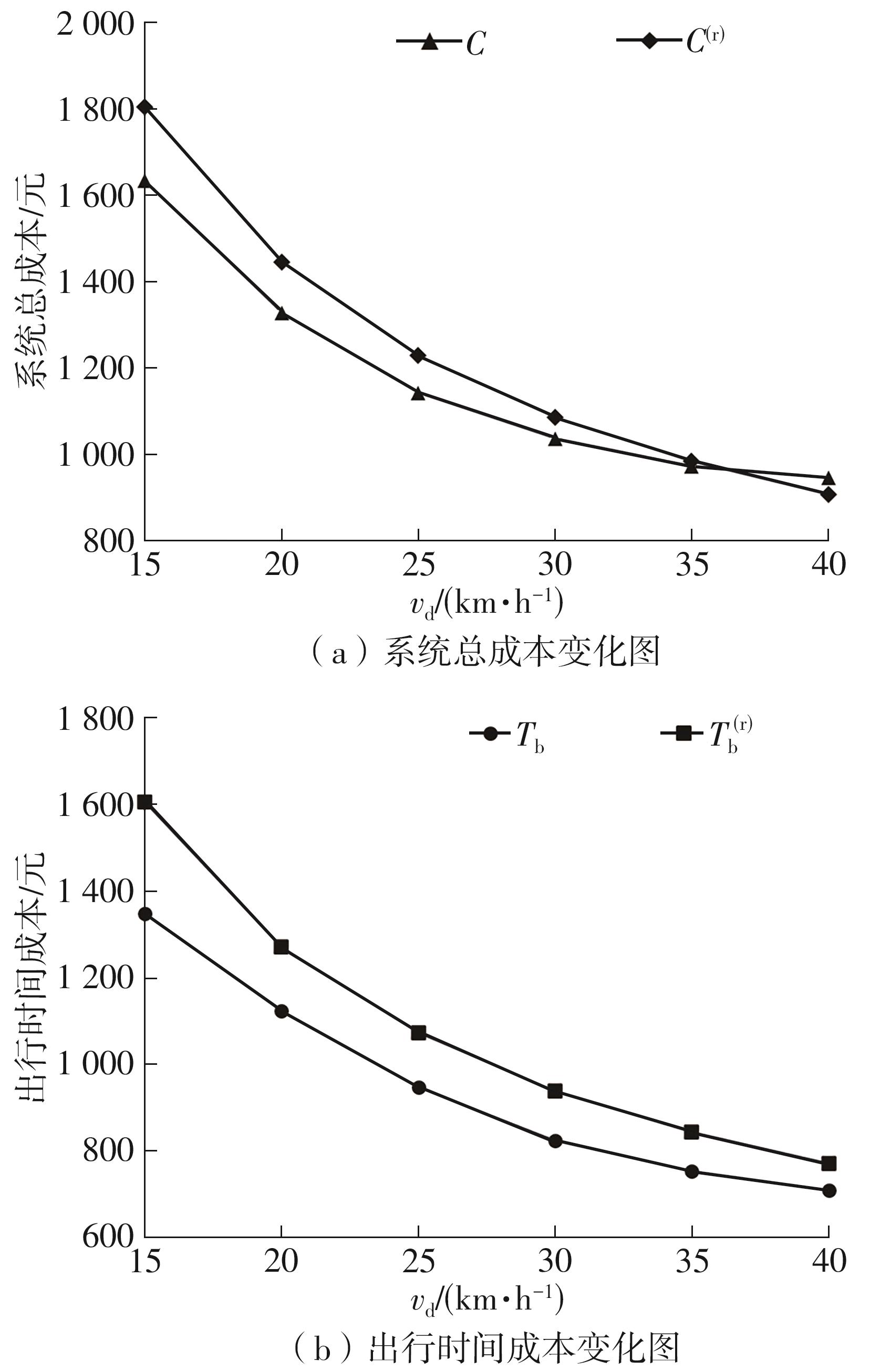
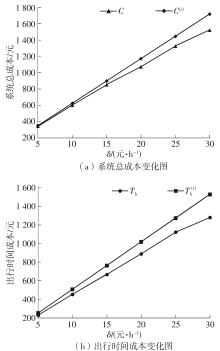
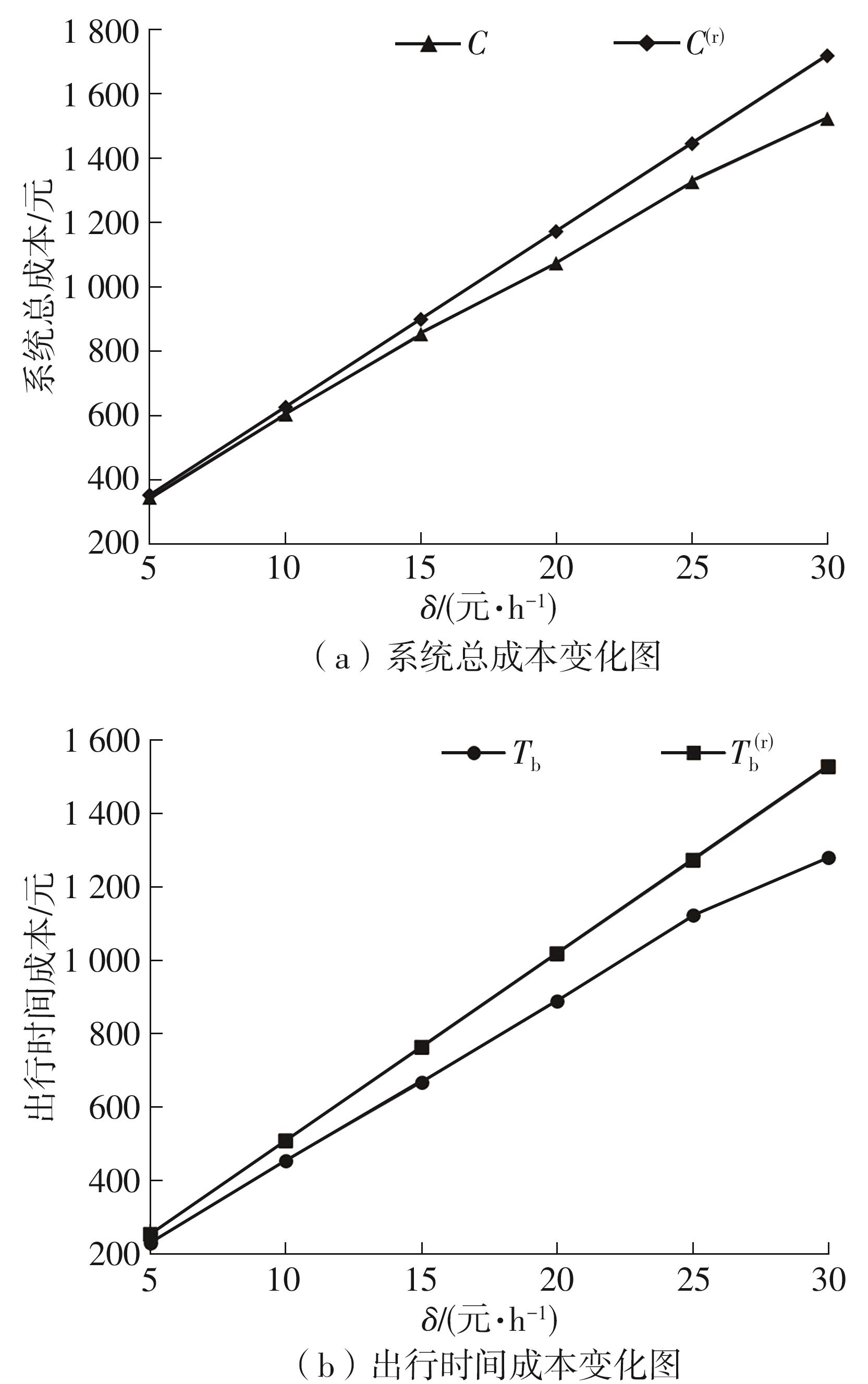
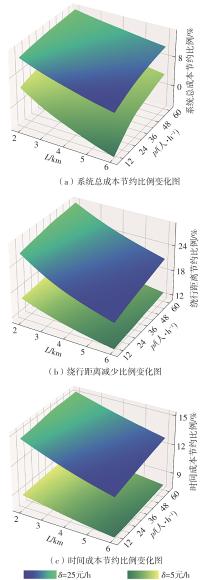
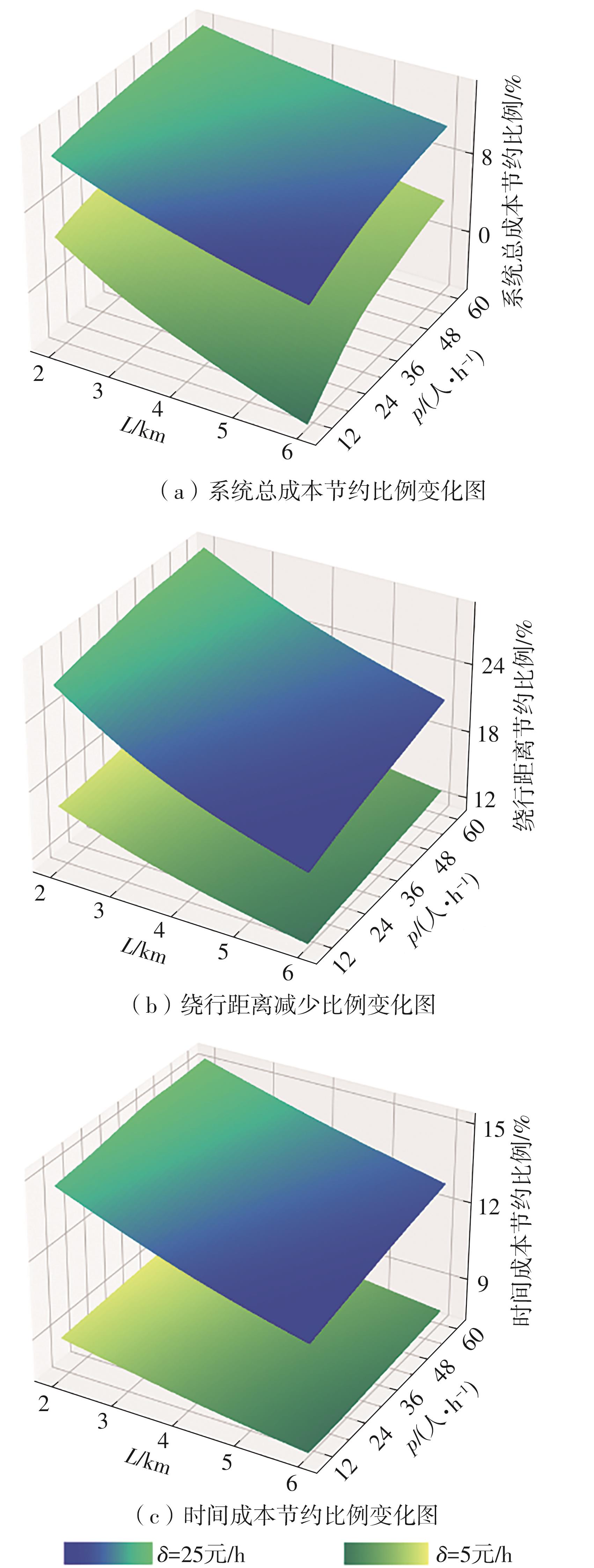
需求响应公交作为一种灵活的公共交通模式,能够根据乘客需求提供个性化的公交服务,已在国内外城市广泛应用。然而其在实际运营中却面临着服务效率与运营成本博弈的难题,以及难以实现“门到门”服务的难题。对此,提出一种共享单车接驳需求响应公交的联合出行模式,通过整合共享单车与需求响应公交的优势,实现两种交通方式的耦合优化,从而提高公共交通的整体服务效率与服务水平。基于连续近似方法,将离散的需求点与共享单车投放点连续化,推导计算公交运营成本、共享单车成本以及乘客出行时间成本,以最小化系统总成本为目标,对联合出行系统进行优化。为了验证所提出的联合出行系统的有效性,以重庆市大学城片区为案例进行实证研究,通过模拟联合出行系统在不同场景下的运营情况,将其与无共享单车接驳的传统需求响应公交系统进行对比。结果表明:联合出行系统可有效解决需求响应公交的运营难题,与传统需求响应公交系统相比,联合出行系统最高可降低14.8%的系统总成本、15.2%的出行时间成本和29%的公交车辆绕行。证明在需求响应公交系统中,引入共享单车作为接驳工具,能够显著降低公交运营成本,减少乘客的出行时间,同时减少公交车辆不必要的绕行,优化了公交运营路线,大幅提升了公共交通的服务效率与服务水平。
中图分类号: