华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 11-19.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240362
城市轨道交通限流背景下的协作疏解研究
王豹, 罗霞, 乔璇, 苏启明
- 西南交通大学 交通运输与物流学院,四川 成都 611756
Research on Collaborative Transfer Under the Condition of Urban Rail Transit Passenger Flow Control
WANG Bao, LUO Xia, QIAO Xuan, SU Qiming
- Southwest Jiaotong University,School of Transportation and Logistics,Chengdu 611756,Sichuan,China
摘要:
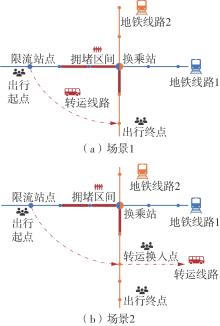
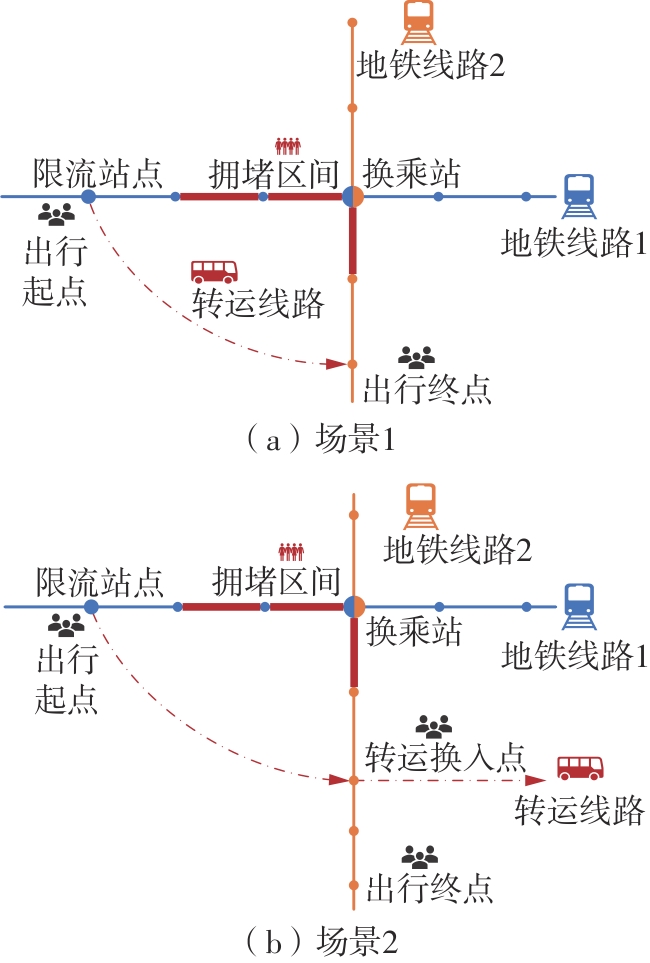
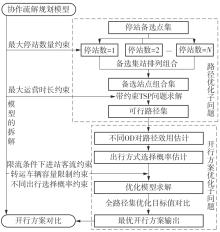
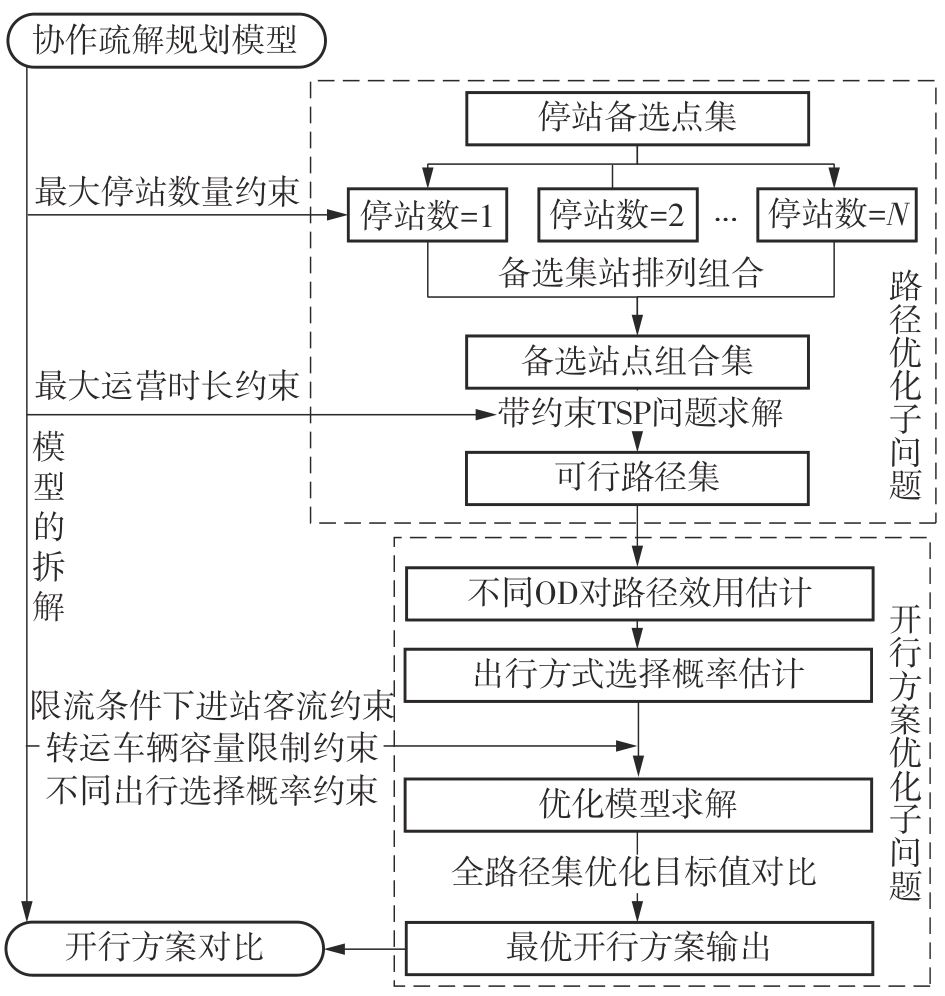
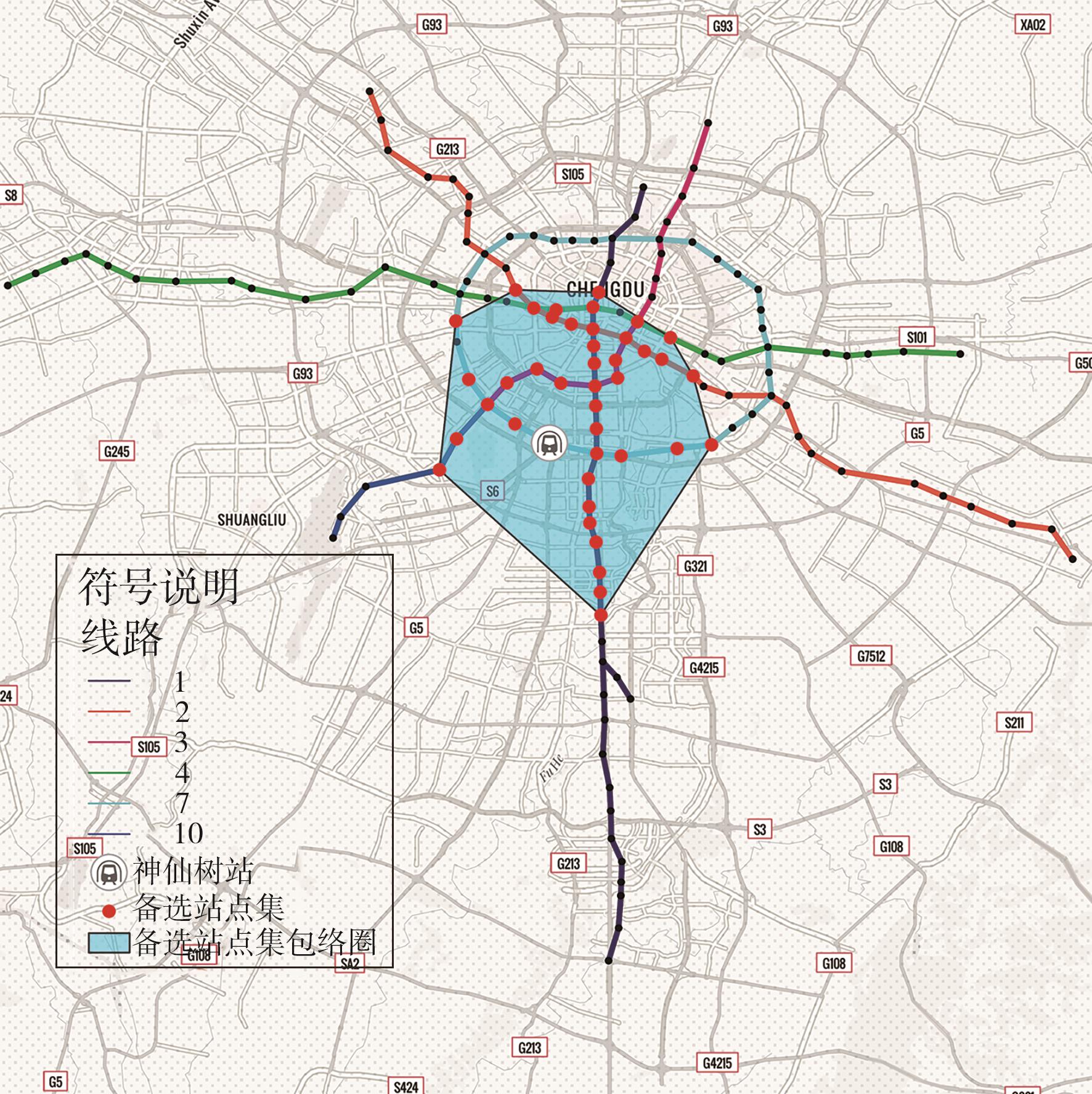
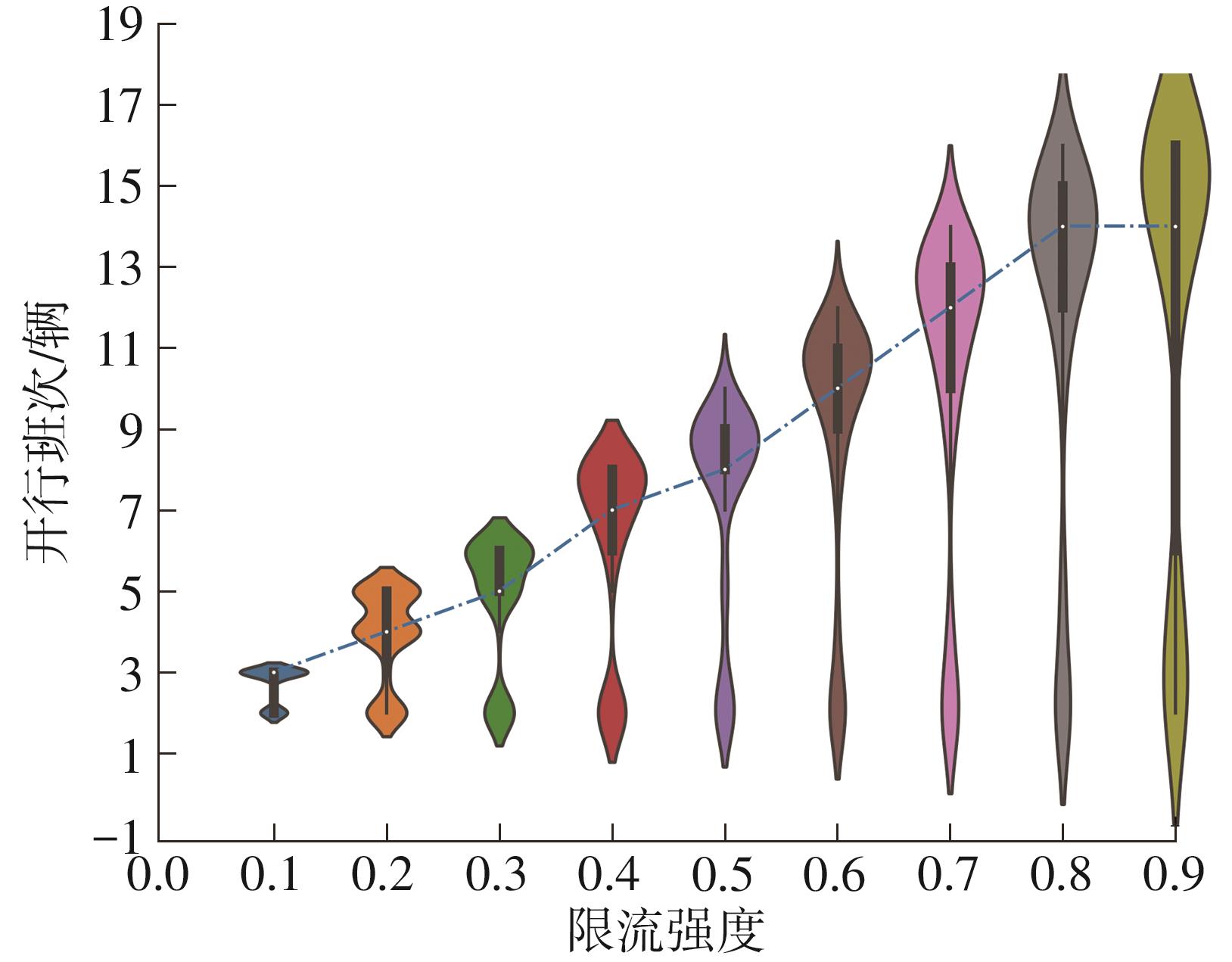
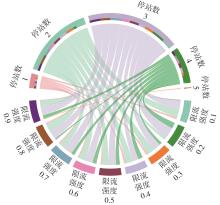
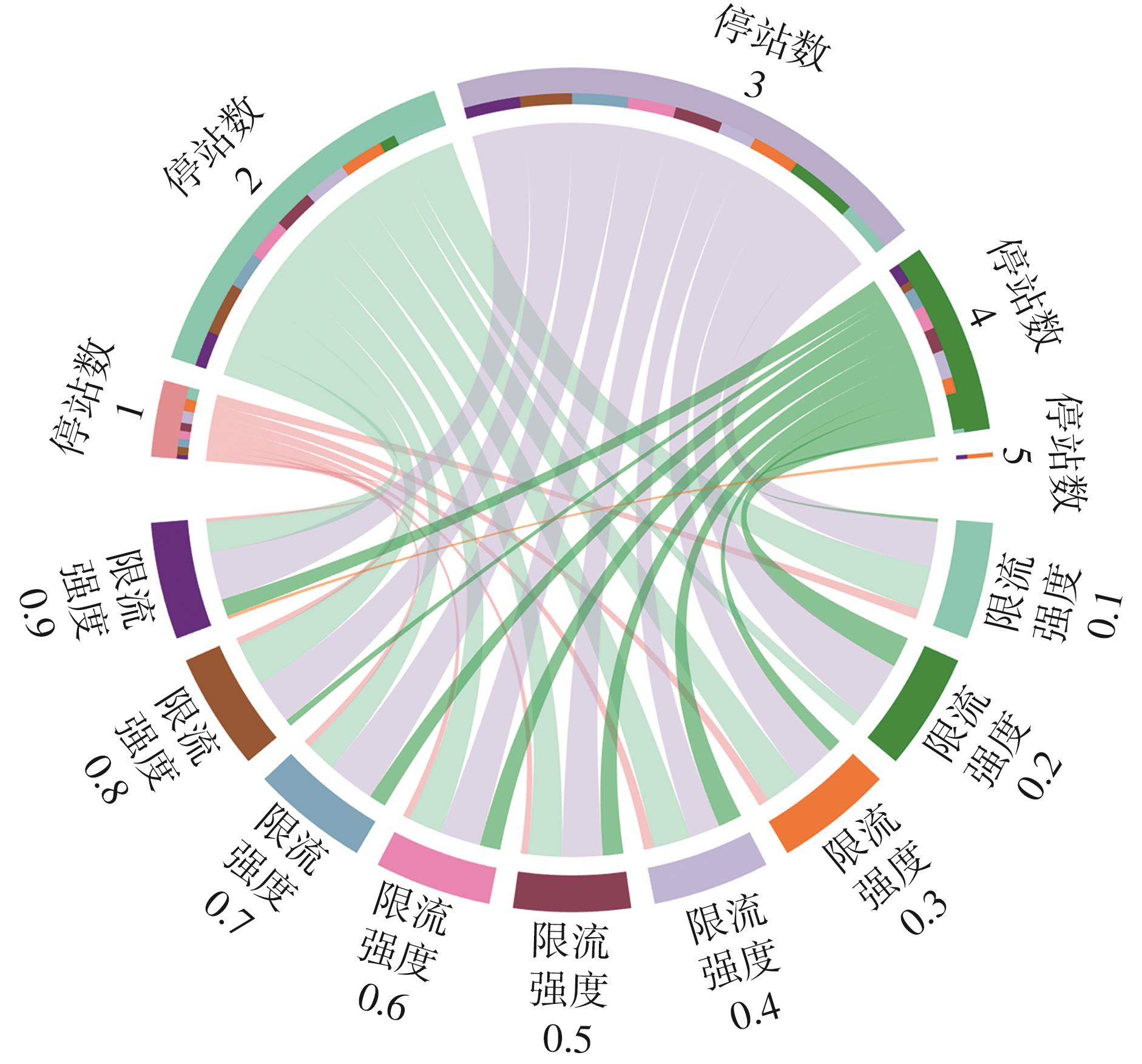
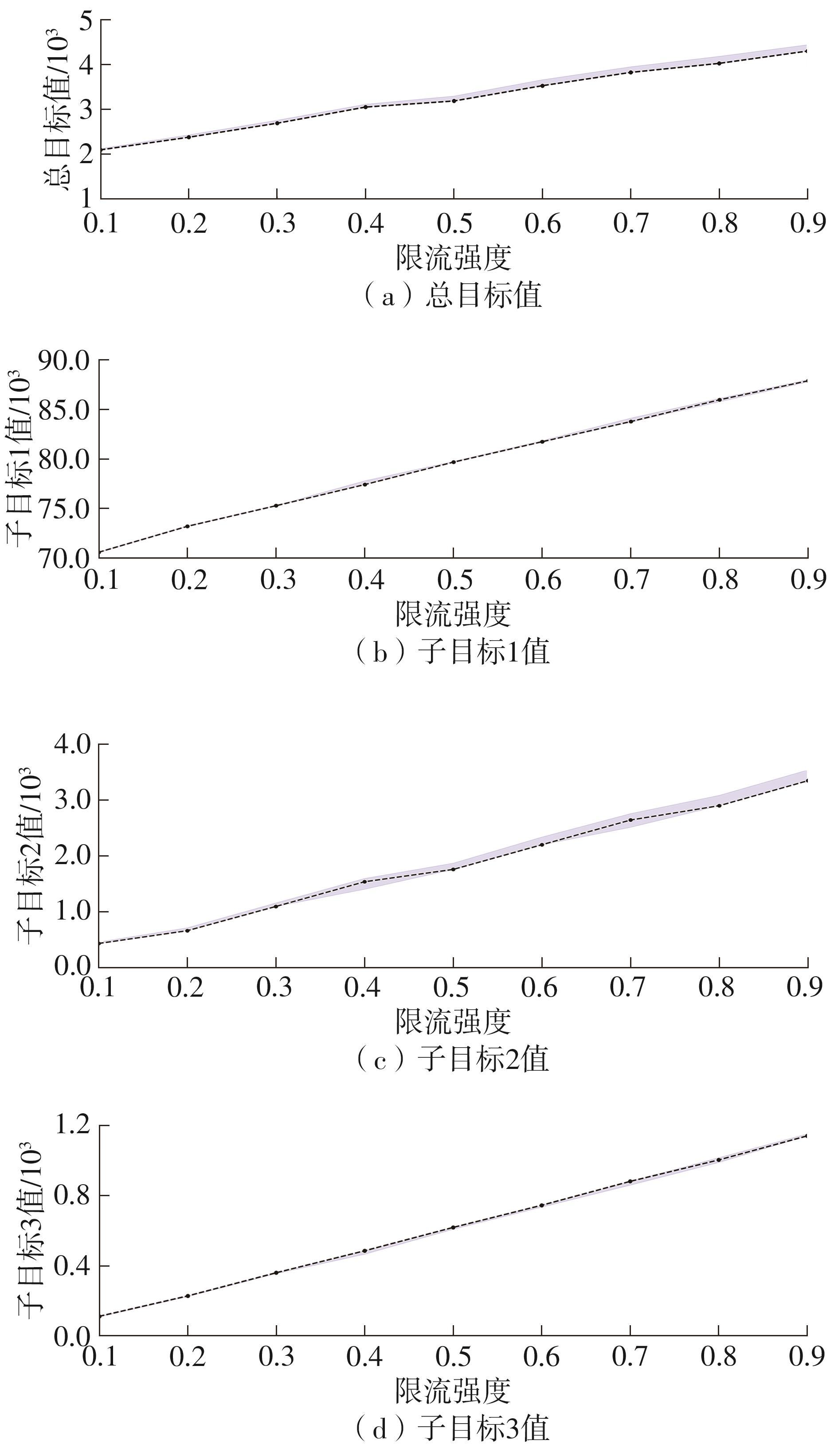
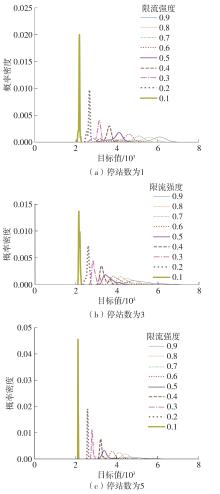
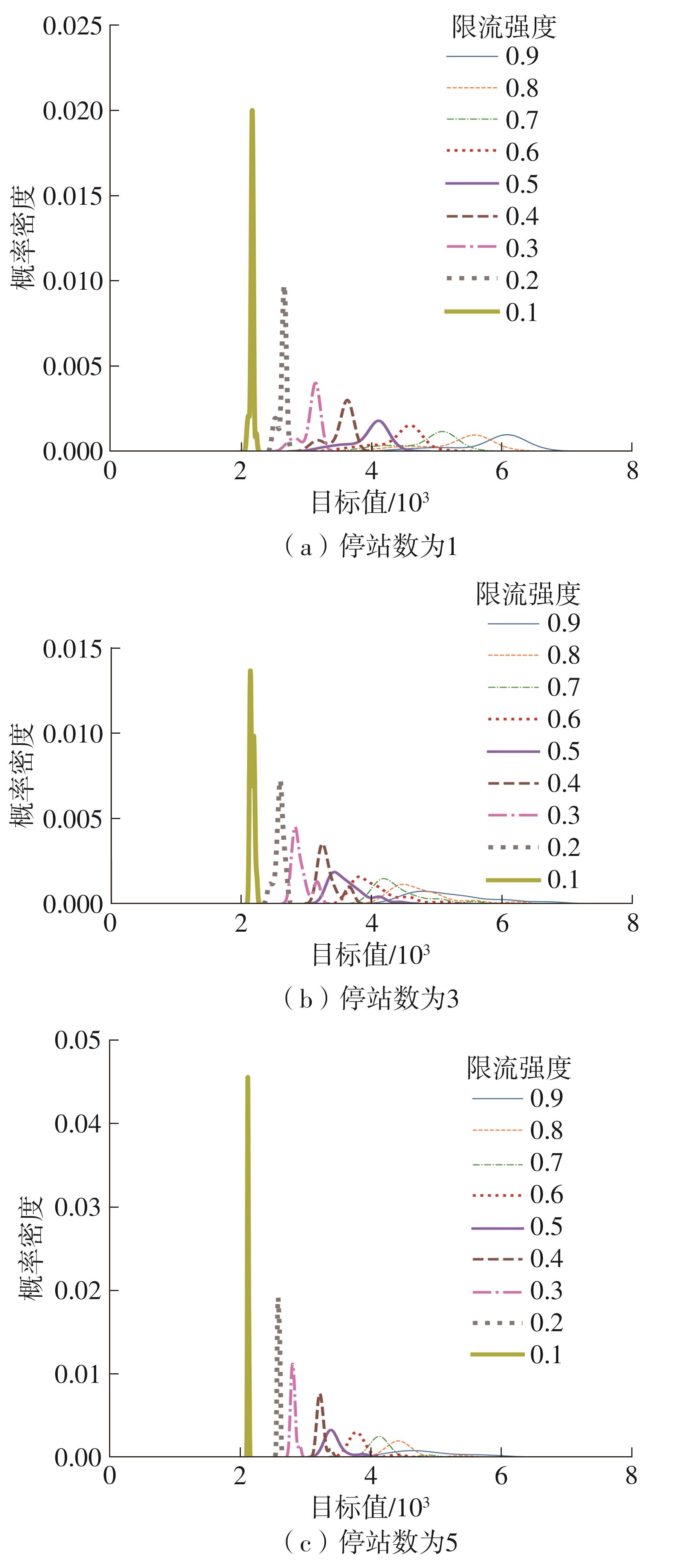
针对现阶段对城市轨道交通网络限流场景下的被限制客流转运关注不足等问题,对特定限流条件下转运车辆线路布设和运力配置进行研究。首先,分析量化不同转运线路条件下,乘客选择乘坐转运车辆的效用和选择概率。在此基础上,以最小化总期望旅行时间、最小化转运车辆开行成本、最大化轨道交通网络拥堵区间客流疏解量为目标,构建了限流场景下转运车辆线路设计和运力规划模型。为提高模型求解效率,将模型拆解为开行路径优化和开行方案优化两个子问题,把第1个子问题转换为旅行商问题,将获得的备选线路路径作为第2个子问题的输入进行模型求解。依托成都市轨道交通网络和早高峰时段的客流数据,验证不同限流强度下所提模型的有效性,讨论了转运线路对停站点数量和停靠站点选取的偏好。结果表明:目标值表现良好的线路多为停站点为2-3个的路径,在停靠站点的选取上高度集中,对3-4个特定路径的偏好显著;随着限流强度的逐步加强,偏好于选择停站数量较少、走行距离较短的线路以达到快速转运的需求,在开行班次的选取上,整体上呈现线性增长趋势,但当限流强度大于0.8时,单一线路难以满足转运需求,不再保持线性增长趋势。
中图分类号: