华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 119-126.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220659
基于改进网络核密度和负二项回归的事故黑点鉴别
庄焱1 董春娇1 米雪玉2 王菁1 杨妙言1
- 1.北京交通大学 交通运输学院,北京 100044
2.华北理工大学 建筑工程学院,河北 唐山 063210
Identification of Accident Black Spots Based on Improved Network Kernel Density and Negative Binomial Regression
ZHUANG Yan1 DONG Chunjiao1 MI Xueyu2 WANG Jing1 YANG Miaoyan1
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation of Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
2.College of Civil and Architectural Engineering,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063210,Hebei,China
摘要:
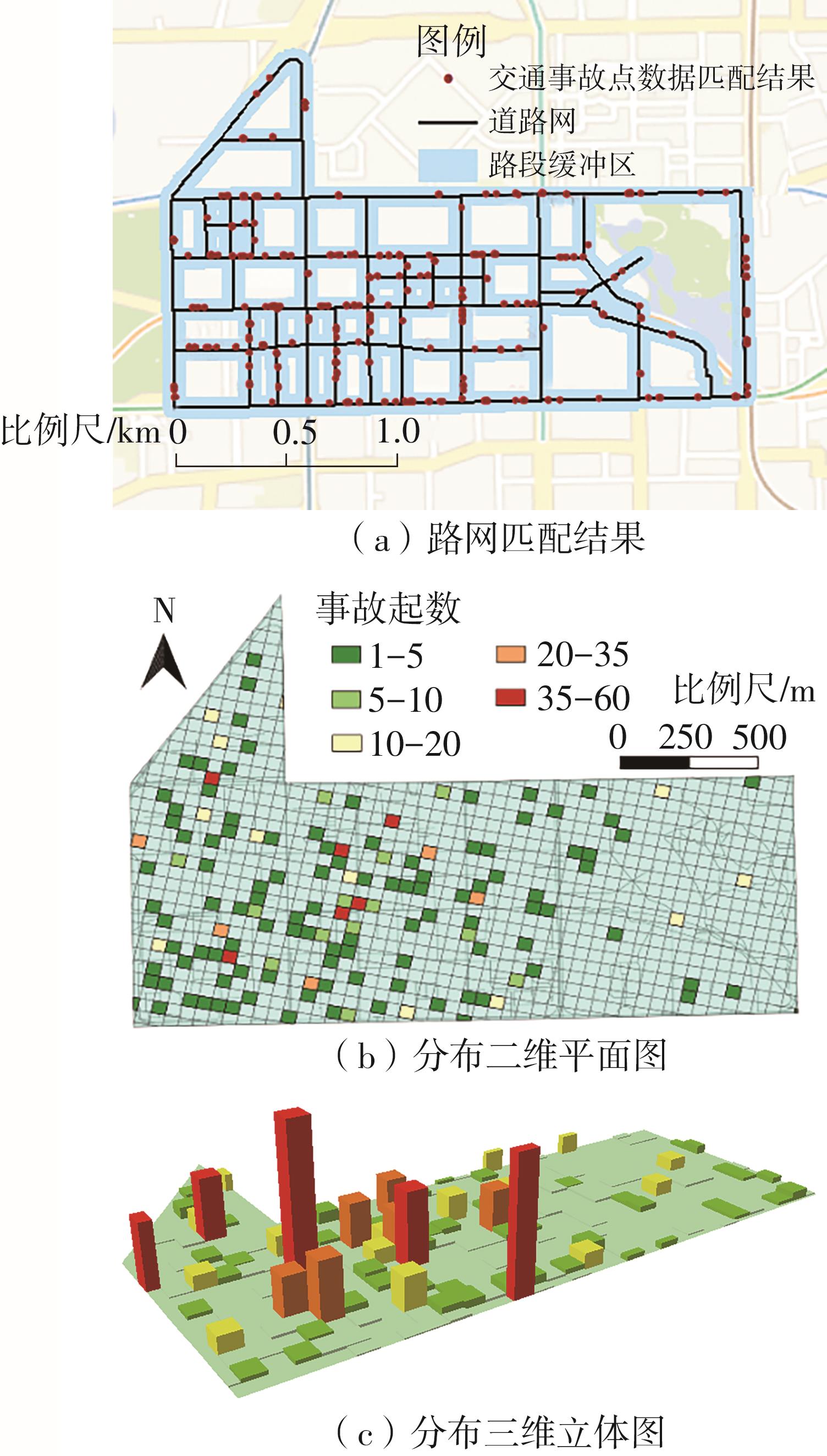
已有的交通事故黑点鉴别研究大多基于事故频数或事故率,并未考虑交通事故对不同发生地的影响特征。为了综合考虑交通事故在不同交通环境和路网特征下的差异影响,并解决交通事故数据中零值远超经典离散分布的零膨胀问题,本文提出一种考虑节点综合重要度的改进网络核密度估计法,并基于零膨胀负二项回归模型对城市交通事故黑点进行鉴别。首先,在拓扑路网中综合考虑事故发生地的交通环境和道路条件构建事故综合影响度指标,连同事故严重程度指数嵌入到传统网络核密度估计中,通过在道路网络上生成平滑的密度表面定性体现点事件的空间聚集性。在此基础上,构建基于零膨胀负二项回归鉴别模型,明晰事故高发区域边界范围,定量刻画不同严重等级的事故黑点路段空间分布特征。最后,以深圳市华强北街道为例进行实例分析。结果表明,在90%、80%和70%的阈值水平下本文提出的事故黑点鉴别法的有效搜索率均高于平面核密度估计法,且考虑节点综合影响度后,部分无道路区域不再被误识,模型准确率比传统网络核密度法分别提升了3.60%、5.31%和7.20%。
中图分类号: