华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 1-10.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240519
• 能源、动力与电气工程 • 下一篇
基于MIC-PCA-LSTM模型的垃圾焚烧炉NO x 排放浓度预测
姚顺春1, 李龙千1, 刘文2, 李峥辉1, 周安鹂1, 李文静1, 陈姜宏1, 卢志民1
- 1.华南理工大学 电力学院,广东 广州 510640
2.广州环投花城环保能源有限公司,广东 广州 510830
Emission Concentration Prediction of NO x from Waste Incinerator Based on MIC-PCA-LSTM Model
YAO Shunchun1, LI Longqian1, LIU Wen2, LI Zhenghui1, ZHOU Anli1, LI Wenjing1, CHEN Jianghong1, LU Zhimin1
- 1.School of Electric Power,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangzhou Huantou Huacheng Environmental Protection Energy Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510830,Guangdong,China
摘要:
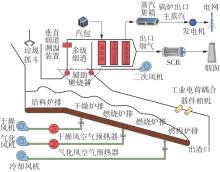
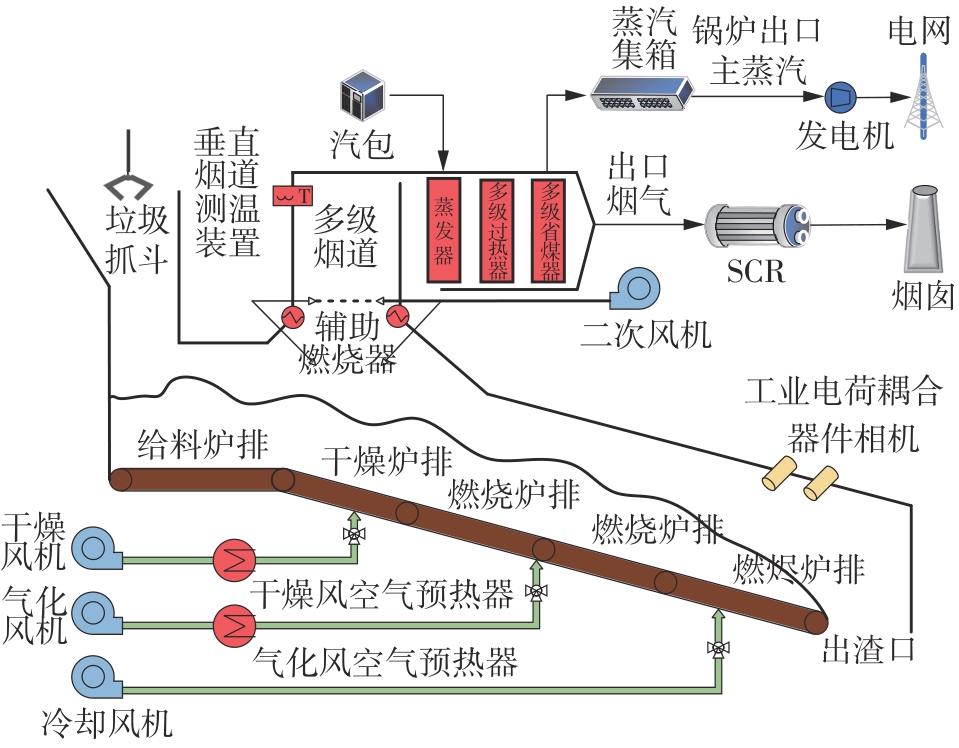
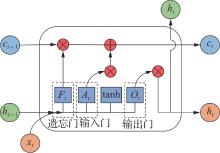
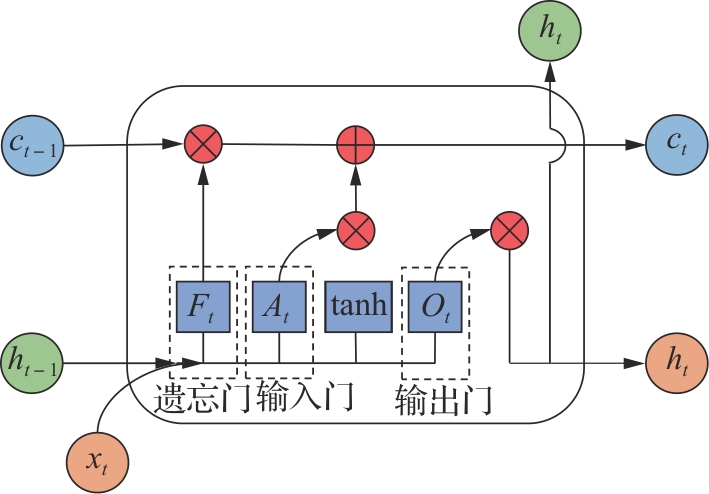
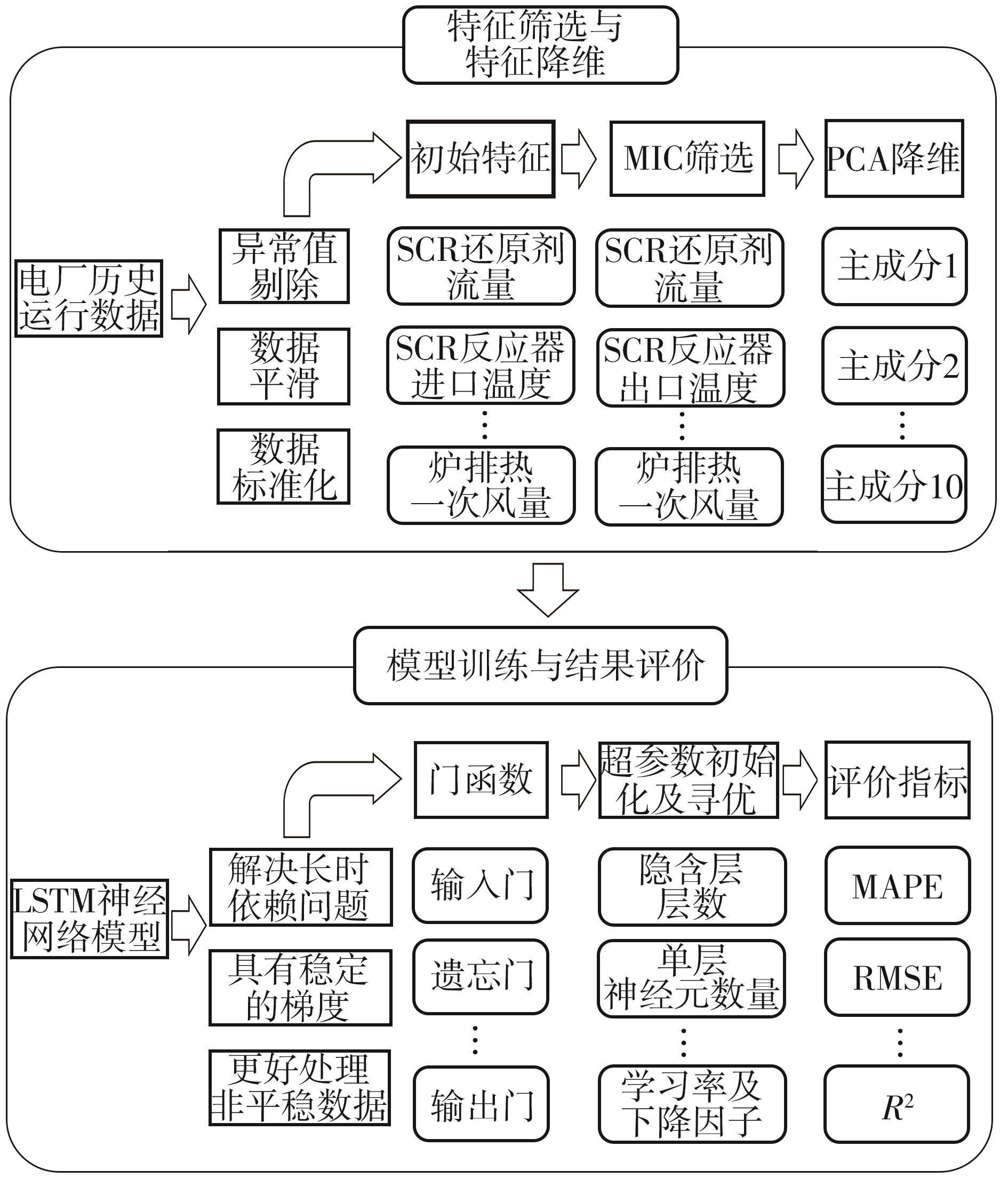
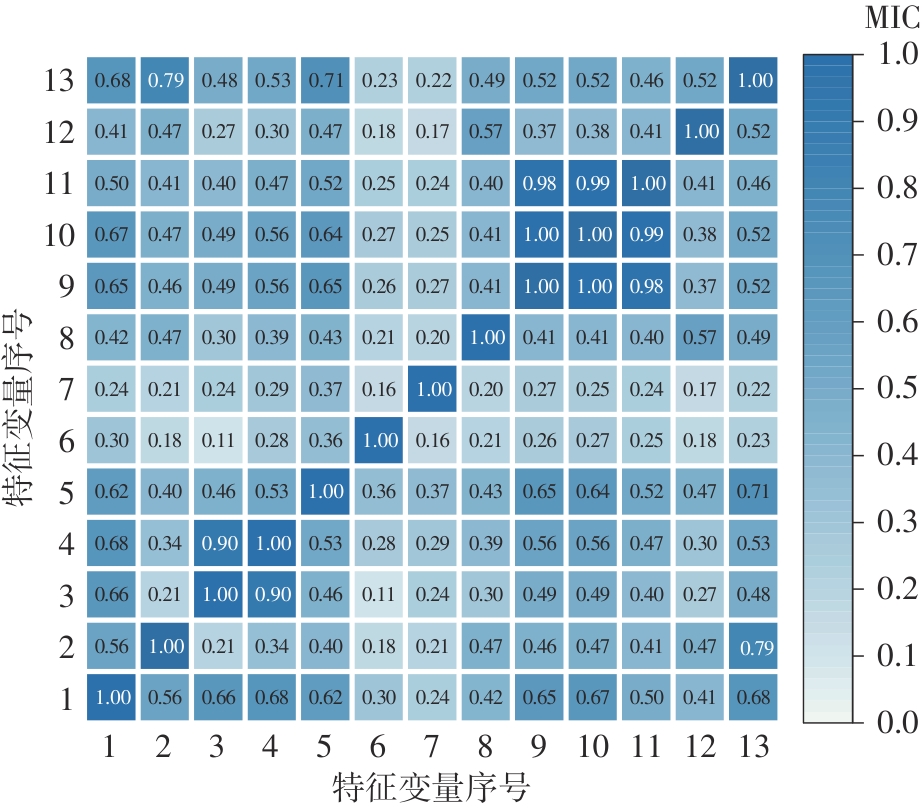
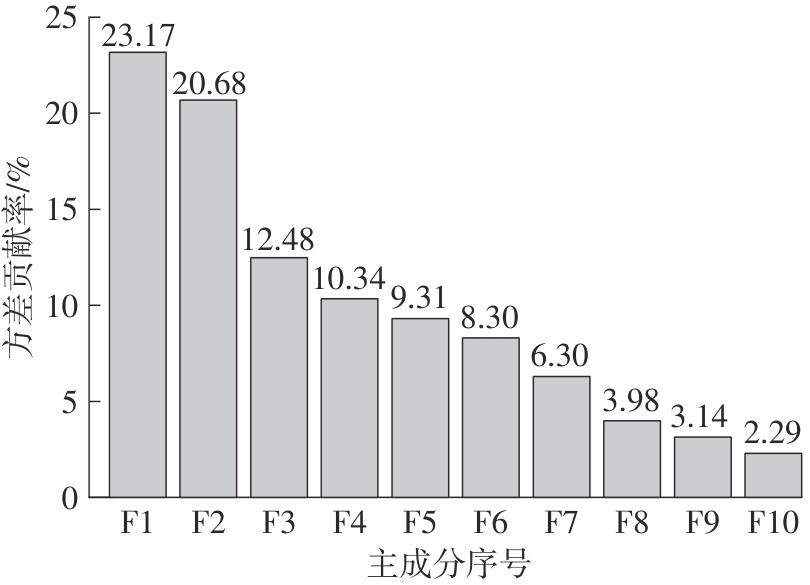
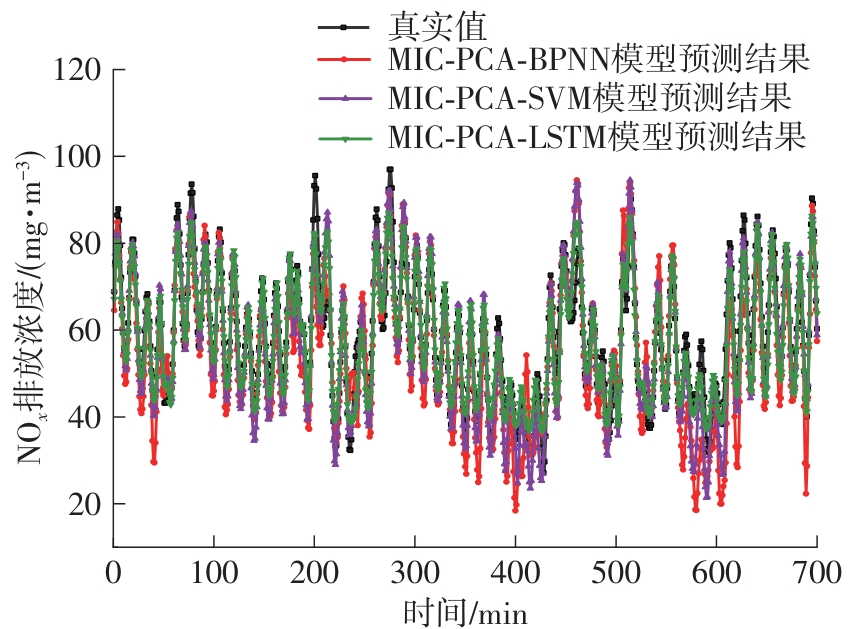
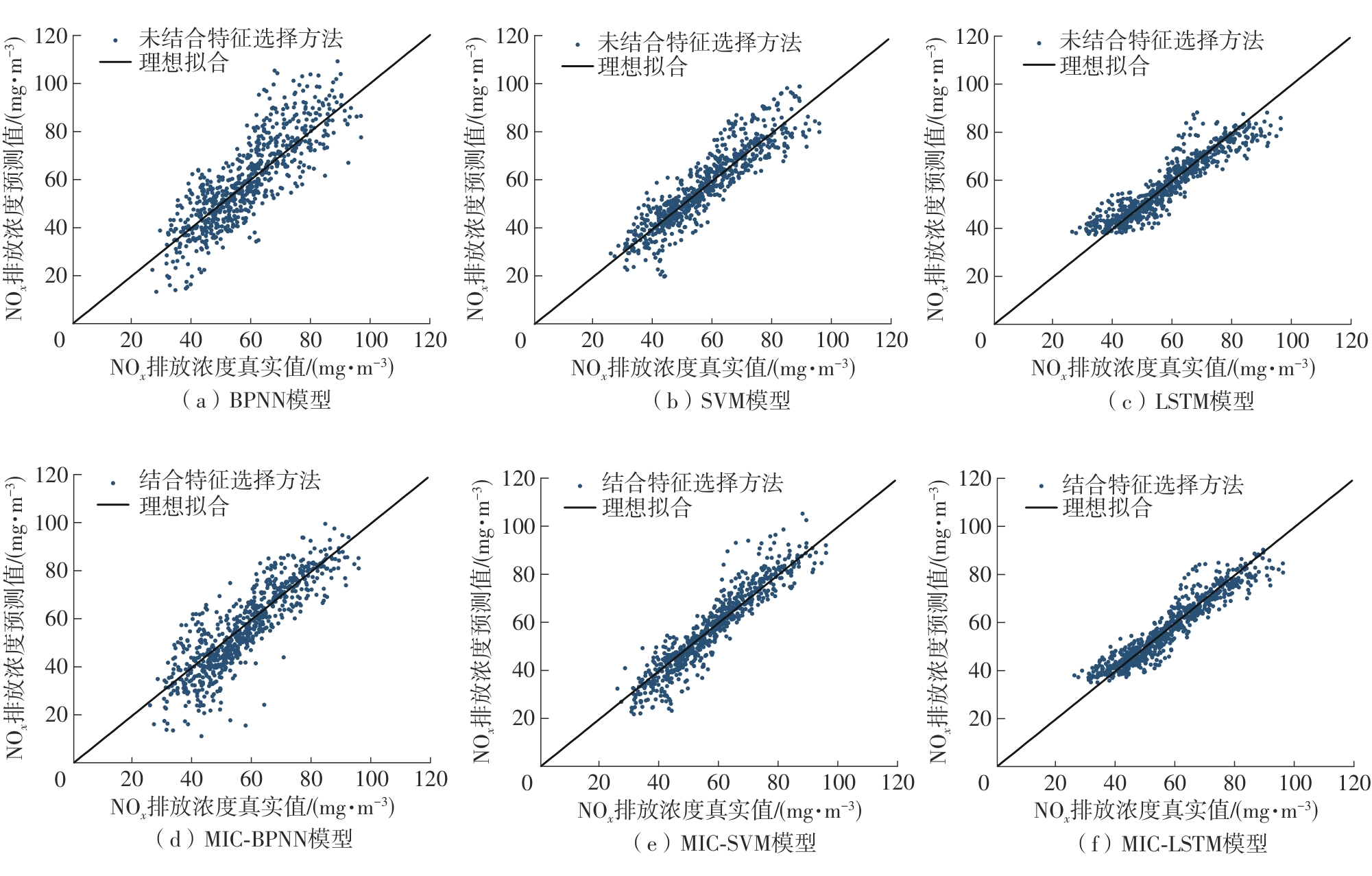
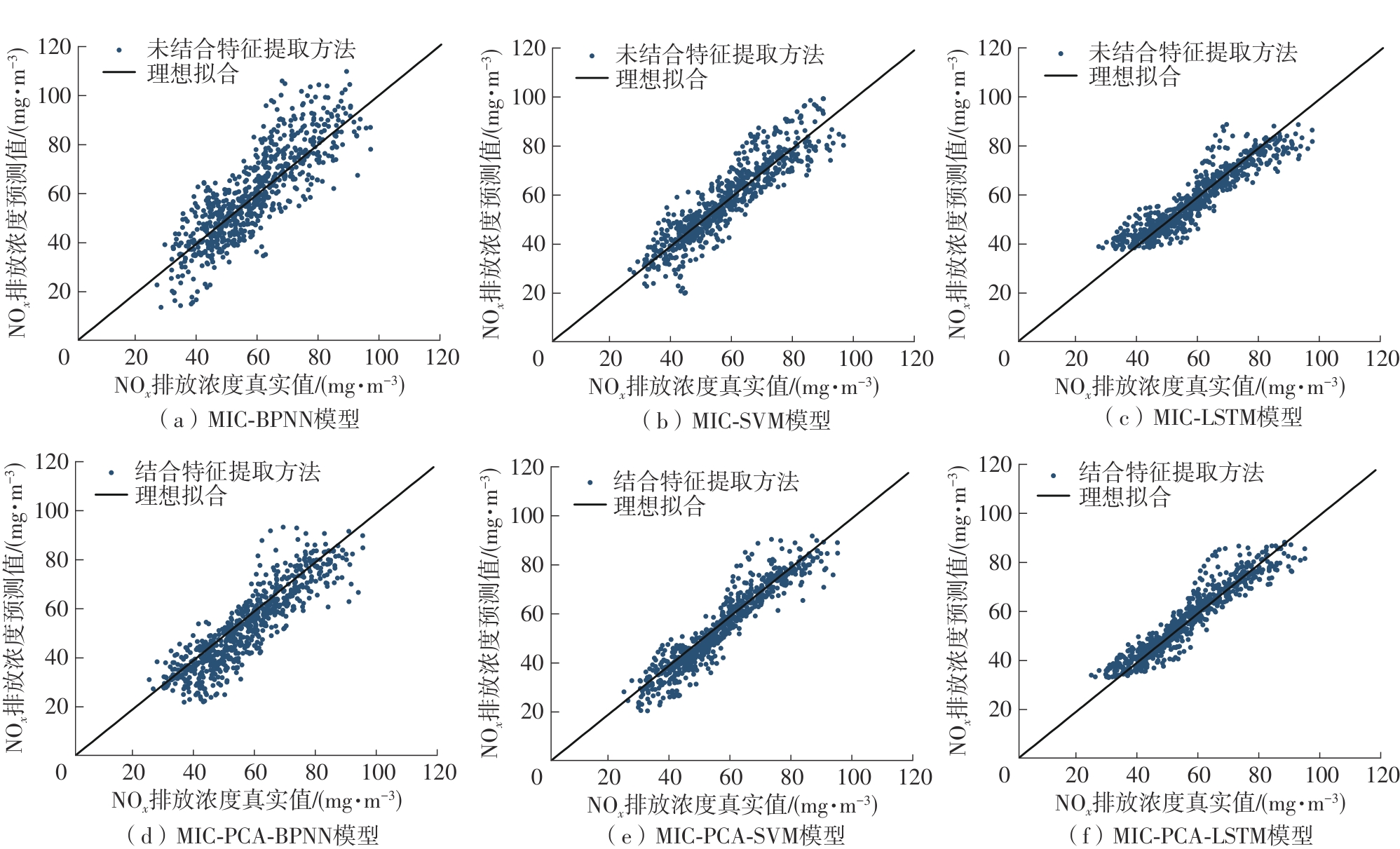
垃圾焚烧过程选择性催化还原(SCR)脱硝系统出口NO x 排放浓度的准确预测对提高数据质量和喷氨控制水平具有重要意义。垃圾焚烧过程存在显著的非线性、多变量耦合和时间序列特性,给NO x 排放浓度的精准预测带来了巨大挑战。针对此问题,该文将最大信息系数(MIC)、主成分分析(PCA)和长短期记忆(LSTM)神经网络相结合,提出了一种SCR脱硝系统出口NO x 排放浓度预测模型。首先,采用MIC方法计算各变量间的最大归一化互信息值,选择和NO x 排放浓度相关性较大的特征变量,再结合最大冗余原则剔除冗余变量。随后,基于PCA方法获得各主成分方差的累计贡献率,提取主成分特征,得到最优输入特征变量集。最后,利用LSTM神经网络建立SCR出口NO x 排放浓度预测模型。结果表明,相比反向传播神经网络模型和支持向量机模型,该文提出的模型具有最优的预测精度和泛化能力,其测试集平均绝对百分比误差为6.33%,均方根误差为4.71 mg/m3,决定系数为0.90。研究结果为实现垃圾焚烧过程SCR脱硝系统的喷氨智能控制提供了理论基础。
中图分类号: