华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 142-152.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230579
所属专题: 2024年交通运输工程
• 交通运输工程 • 上一篇
老年驾驶人认知驾驶能力评价及影响因素研究
- 1.北京工业大学 城市交通学院,北京 100124
2.北京警察学院 道路交通管理系,北京 102202
-
收稿日期:2023-09-14出版日期:2024-09-25发布日期:2024-01-05 -
通信作者:李洋(1979—),男,博士,高级工程师,主要从事交通管理和交通法规研究。 E-mail:yang_li009@163.com -
作者简介:陈兵硕(1995—),女,博士生,主要从事驾驶行为与安全研究。E-mail: bingshuo2018@163.com -
基金资助:北京市教育委员会科技计划项目(KM202014019001)
Study on Evaluation and Influencing Factors of Cognitive Driving Ability in Elderly Drivers
CHEN Bingshuo1( ), LI Yang2(
), LI Yang2( ), ZHAO Xiaohua1, LIU Xiaoming1
), ZHAO Xiaohua1, LIU Xiaoming1
- 1.School of Urban Transportation, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
2.Department of Road Traffic Management, Beijing Police College, Beijing 102202, China
-
Received:2023-09-14Online:2024-09-25Published:2024-01-05 -
Contact:李洋(1979—),男,博士,高级工程师,主要从事交通管理和交通法规研究。 E-mail:yang_li009@163.com -
About author:李洋(1979—),男,博士,高级工程师,主要从事交通管理和交通法规研究。E-mail: yang_li009@163.com -
Supported by:Beijing Municipal Education Commission Science and Technology Plan General Project(KM202014019001)
摘要:
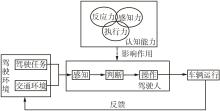
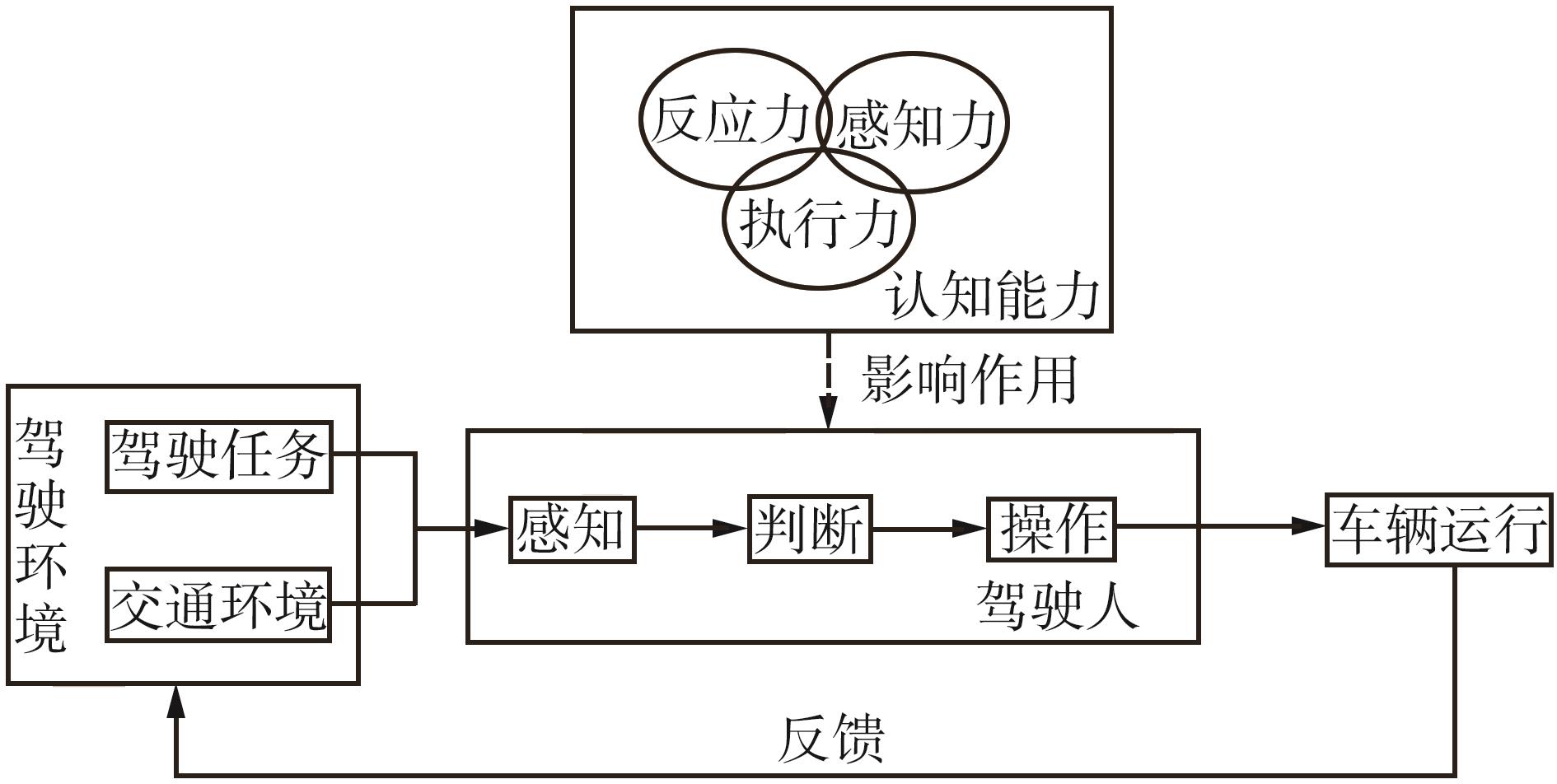
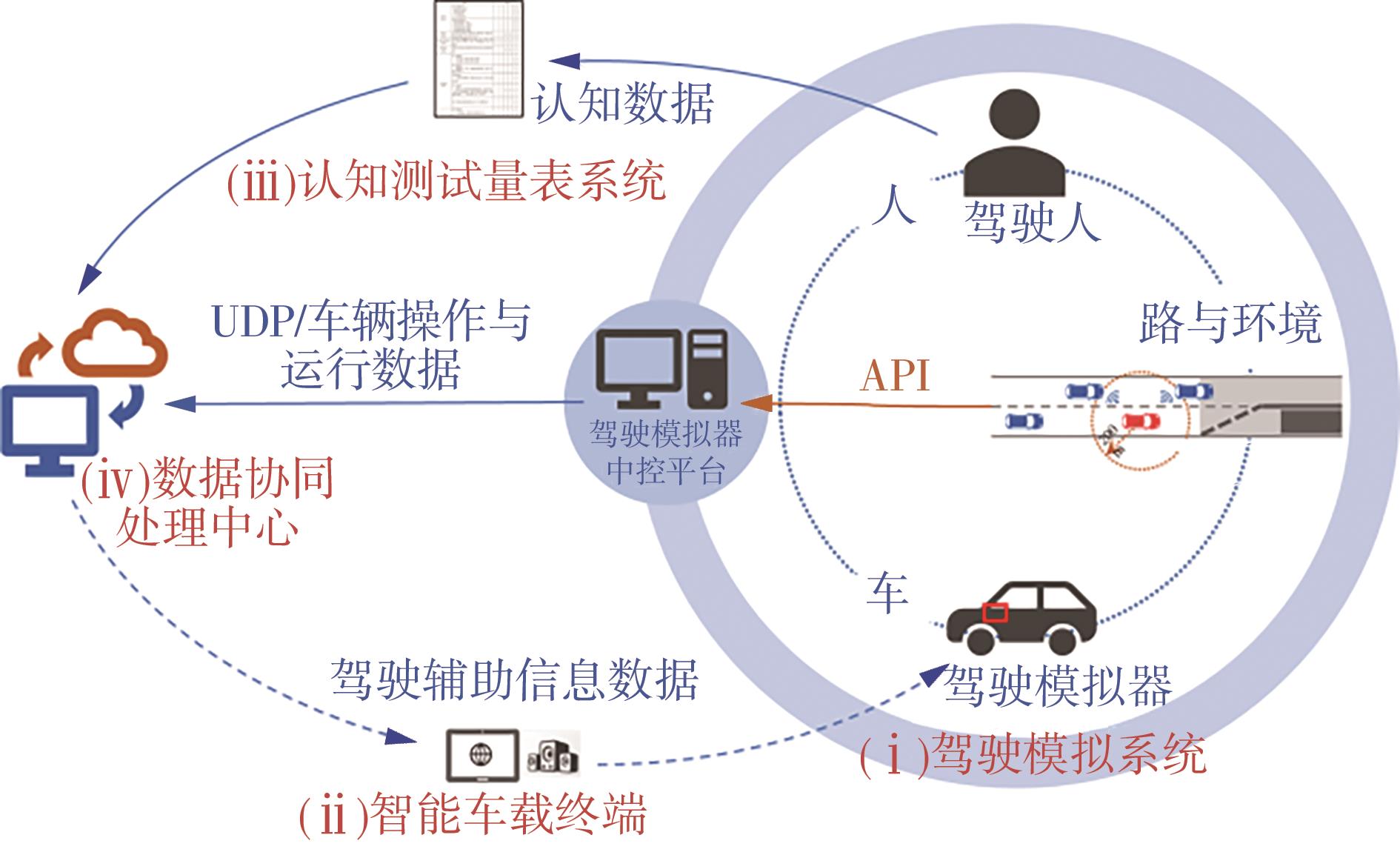
我国老年驾驶人数量持续增长,驾驶人结构的变化给交通安全带来了挑战。相比于其他年龄段驾驶人,老年人生心理功能逐渐衰退,更容易发生交通事故。认知功能与驾驶安全表现显著相关。从注意反应能力、执行处理能力、空间感知能力3项认知功能领域出发,研究老年人驾驶特征,设计驾驶模拟实验风险事件,获得认知驾驶行为数据,分析青年人、中年人、老年人驾驶行为特征的差异性;采用主客观结合的方法确定指标权重,提出认知驾驶行为指数计算方法;以驾驶人属性和认知功能为自变量,以认知驾驶行为指数为因变量,建立广义线性混合模型,探究不同因素对认知驾驶能力的影响。结果表明年龄、周驾驶频率、自我调节和TMT-B(Trail Making Test-B)与认知驾驶行为指数显著相关,MMSE(Mini-Mental State Examination)为边缘显著相关;老年驾驶人的认知驾驶行为指数受个体特质影响较大;相较于老年人,青年人认知驾驶行为指数更差,中年人更好;周驾驶频率低的人比周驾驶频率高的人认知驾驶行为指数更好;自我调节频率为低和中的驾驶人,比频率为高的驾驶人认知驾驶行为指数更好;TMT-B测量认知正常的驾驶人比认知障碍驾驶人的认知驾驶行为指数更好。该研究从交通事故的人因机理角度出发,探究老年驾驶人面对的认知挑战,提出老年人认知驾驶行为指数计算方法并解析影响因素,为简化老年人驾驶适宜性评价程序、制定驾驶安全干预策略提供参考。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈兵硕, 李洋, 赵晓华, 等. 老年驾驶人认知驾驶能力评价及影响因素研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(9): 142-152.
CHEN Bingshuo, LI Yang, ZHAO Xiaohua, et al. Study on Evaluation and Influencing Factors of Cognitive Driving Ability in Elderly Drivers[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(9): 142-152.
表2
实验事件及研究指标"
| 事件 | 事件内容 | 考察功能 | 分析指标 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
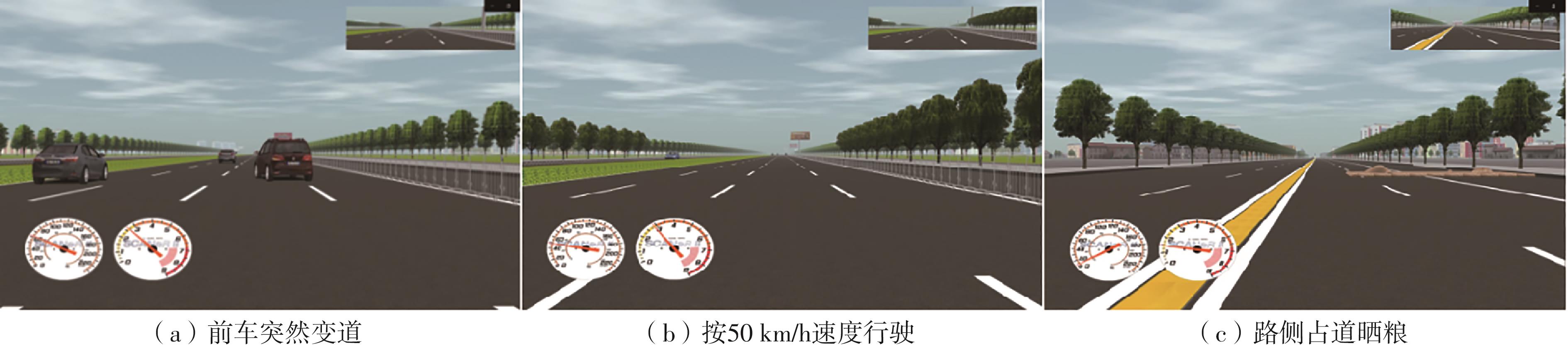
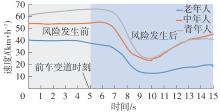
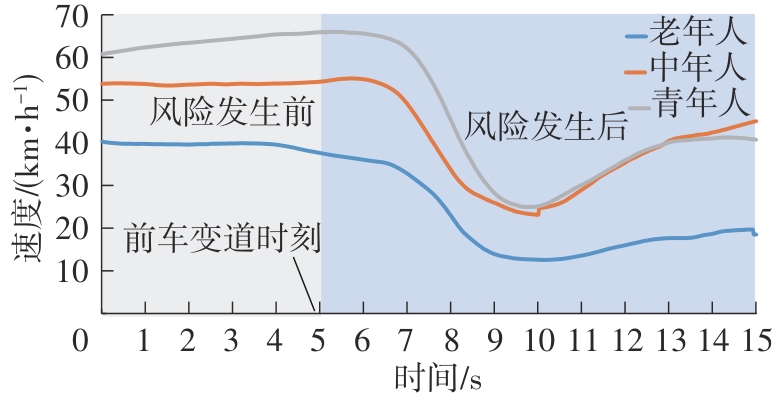
| 前车突然变道 | 城市道路上,当实验车行驶在指定路段上,与冲突车的碰撞时间为2.5 s时,右前方的冲突车突然向左变道到实验车正前方车道上 | 注意反应能力:驾驶人及时注意到前车变道的风险并迅速做出反应的能力 | 刹车反应时间:从前车左转向灯亮到被试踩下刹车的时间间隔 | 参考文献[ 参考文献[ |
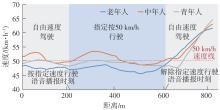
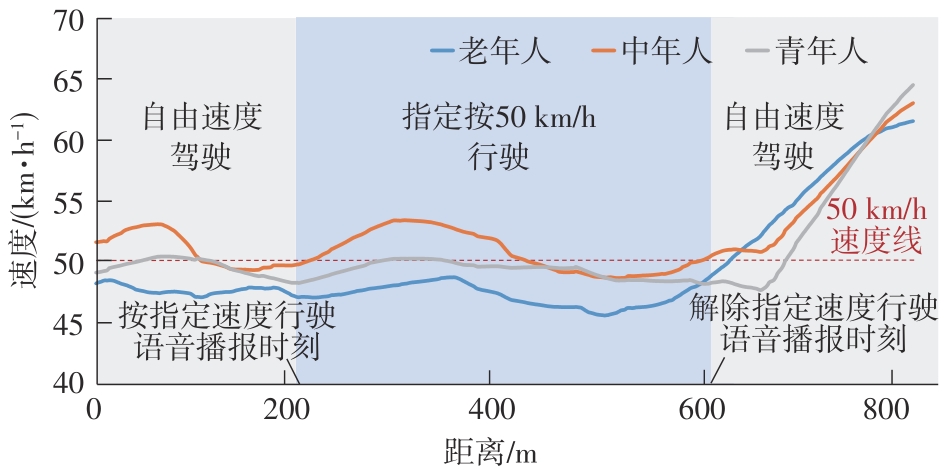
按50 km/h 行驶 | 城市道路上,当实验车行驶到该事件路段区域的起点时,导航语音提醒驾驶人“前方道路请按50 km/h的速度行驶”。当实验车驶出该事件路段区域时,导航语音提醒驾驶人“前方道路解除50 km/h的速度要求” | 执行处理能力:驾驶人实现预定目标(按50 km/h速度驾驶)的控制操作能力 | 实际驾驶速度:在指定按50 km/h速度行驶的路段,被试实际的行驶速度 | 参考文献[ 参考文献[ 参考文献[ |
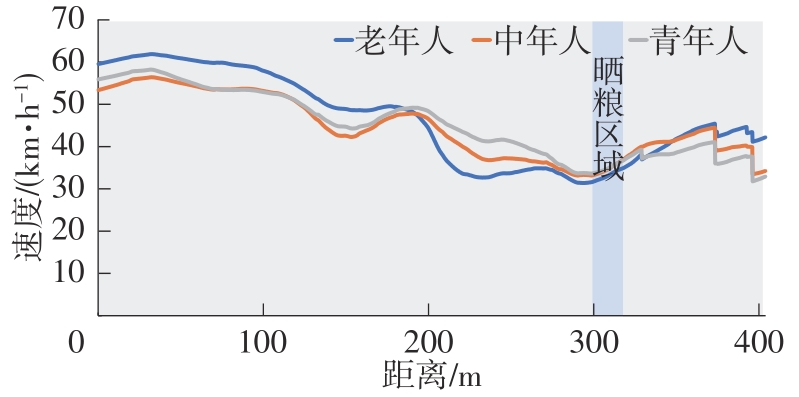
| 路侧占道晒粮 | 农村道路上,当实验车行驶到指定路段上,发现右前方有一片占道晾晒的粮食,仅剩下一段狭窄的道路空间可驾驶通过 | 空间感知能力:驾驶人识别和解释感官信息,感知空间环境(车辆通过时不压到路面晾晒的谷物)的能力 | 横向安全距离:被试驾驶通过时,车轮距离路面晾晒的谷物的最小距离值 | 参考文献[ 参考文献[ |
表6
不同分类下认知驾驶行为指数值"
| 变量 | 认知驾驶行为指数值 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 子分类 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | |
| 年龄 | 青年人 | 0.009 | 0.351 | 0.150 | 0.117 |
| 中年人 | 0.080 | 0.332 | 0.205 | 0.078 | |
| 老年人 | 0.000 | 0.473 | 0.182 | 0.155 | |
周驾驶 频率 | 低 | 0.000 | 0.473 | 0.125 | 0.149 |
| 中 | 0.000 | 0.332 | 0.076 | 0.099 | |
| 高 | 0.080 | 0.230 | 0.046 | 0.065 | |
自我 调节 | 低 | 0.000 | 0.473 | 0.118 | 0.147 |
| 中 | 0.000 | 0.351 | 0.093 | 0.113 | |
| 高 | 0.000 | 0.305 | 0.090 | 0.110 | |
| TMT A | 认知正常 | 0.000 | 0.391 | 0.174 | 0.106 |
| 认知障碍 | 0.000 | 0.473 | 0.192 | 0.202 | |
| TMT B | 认知正常 | 0.009 | 0.473 | 0.099 | 0.125 |
| 认知障碍 | 0.000 | 0.332 | 0.120 | 0.141 | |
| MMSE | 认知正常 | 0.000 | 0.473 | 0.095 | 0.119 |
| 认知障碍 | 0.000 | 0.473 | 0.137 | 0.183 | |
表11
认知驾驶行为指数模型的固定效应解"
| 模型项 | 系数 | 标准误差 | t统计量 | 显著性 | 95% 置信区间 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||
| 截距 | -0.119 | 0.096 1 | -1.239 | 0.226 | -0.316 | 0.078 |
| 年龄=青年人 | -0.105 | 0.050 2 | -2.082 | 0.047*1) | -0.208 | -0.002 |
| 年龄=中年人 | 0.185 | 0.068 2 | 2.718 | 0.011*1) | 0.046 | 0.325 |
| 年龄=老年人 | 0b3) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 周驾驶频率=低 | 0.194 | 0.080 6 | 2.401 | 0.023*1) | 0.028 | 0.359 |
| 周驾驶频率=中 | 0.067 | 0.071 3 | 0.935 | 0.358 | -0.079 | 0.213 |
| 周驾驶频率=高 | 0b3) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 自我调节=低 | 0.163 | 0.057 | 2.85 | 0.008**2) | 0.046 | 0.279 |
| 自我调节=中 | 0.123 | 0.056 8 | 2.165 | 0.039*1) | 0.007 | 0.239 |
| 自我调节=高 | 0b3) | — | — | — | — | — |
| TMT B=认知正常 | 0.177 | 0.057 9 | 3.065 | 0.005**2) | 0.059 | 0.296 |
| TMT B=认知障碍 | 0b3) | — | — | — | — | — |
| MMSE=认知正常 | -0.119 | 0.058 4 | -2.043 | 0.051 | -0.239 | 0.000 |
| MMSE=认知障碍 | 0b3) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 1 | 老龄健康司 .2020年度国家老龄事业发展公报[EB/OL].(2021-10-15)[2023-08-15].. |
| 2 | 巩建国,刘晓晨,綦聪,等 .老年驾驶人驾驶安全特性与事故预防对策研究[J].综合运输,2023,45(1):34-38. |
| GONG Jianguo, LIU Xiaochen, QI Cong,et,al .Research on the safety characteristics and accident prevention measures of elderly drivers[J].Comprehensive Transportation,2023,45 (1):34-38. | |
| 3 | 沈永俊,谭旭 .结合功能测试与模拟驾驶的老年人驾驶适性评估[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版),2021,51(1):171-177. |
| SHEN Yongjun, TAN Xu .Combining functional testing with simulated driving to assess the driving adaptability of elderly people[J].Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition),2021,51 (1):171-177. | |
| 4 | SANDER M, OXLUND B, JESPERSEN A,et al .The challenges of human population ageing[J].Age and Ageing,2015,44(2):185-187. |
| 5 | 刘蕾 .老年机动车驾驶人的交通特点分析及交通安全对策研究[J].法制与社会,2017(21):176-177. |
| LIU Lei .Analysis of traffic characteristics and research on traffic safety countermeasures for elderly motor vehicle driver [J].Law and Society,2017(21):176-177. | |
| 6 | 刘文丽 .基于车辆行驶状态的驾驶员驾驶能力评价方法研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2019. |
| 7 | AKSAN N, ANDERSON S W, DAWSON J,et al .Cognitive functioning differentially predicts different dimensions of older drivers’ on-road safety[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2015,75:236-244. |
| 8 | DEPESTELE S, ROSS V, VERSTRAELEN S,et al .The impact of cognitive functioning on driving performance of older persons in comparison to younger age groups:a systematic review[J].Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour,2020,73:433-452. |
| 9 | BARJONET P .Traffic psychology today[M].New York:Springer Science & Business Media,2001. |
| 10 | CUENEN A, JONGEN E M M, BRIJS T,et al .The relations between specific measures of simulated driving ability and functional ability:new insights for assessment and training programs of older drivers[J].Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour,2016,39:65-78. |
| 11 | MATHIAS J L, LUCAS L K .Cognitive predictors of unsafe driving in older drivers:a meta-analysis[J].International Psychogeriatrics,2009,21(4):637-653. |
| 12 | PARK S, CHOI E S, LIM M H,et al .Association between unsafe driving performance and cognitive‐perceptual dysfunction in older drivers[J].Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,2011,3(3):198-203. |
| 13 | ANDREWS E C, WESTERMAN S J .Age differences in simulated driving performance:compensatory processes[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2012,45:660-668. |
| 14 | LEDGER S, BENNETT J M, CHEKALUK E,et al .Cognitive function and driving:important for young and old alike[J].Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour,2019,60:262-273. |
| 15 | 张殿业,金键,杨京帅 .老年人驾驶反应行为分析[J].交通运输工程与信息学报,2004(3):1-5. |
| ZHANG Dianye, JIN Jian, YANG Jingshuai .Analysis of driving response behavior among elderly people[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information Technology,2004(3):1-5. | |
| 16 | 吴琼 .基于情感化的新能源老年代步车内饰设计研究[D].济南:山东大学,2020. |
| 17 | 姜凯 .登山杖长度对登山动作影响的生物力学研究[D].金华:浙江师范大学,2019. |
| 18 | ANDREWS E C, WESTERMAN S J .Age differences in simulated driving performance:compensatory processes[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2012,45:660-668. |
| 19 | 李猛杰,李璐璐,德新玲,等 .沧州地区公路客货运司机安全驾驶能力评价指标体系构建研究[J].时代汽车,2022(22):174-176. |
| LI Mengjie, LI Lulu, DE Xinling,et al .Research on the construction of safety driving ability evaluation index system for highway passenger and freight drivers in cangzhou region[J].Times Automotive,2022 (22):174-176. | |
| 20 | LAJUNEN T, SUMMALA H .Driving experience,personality,and skill and safety-motive dimensions in drivers’ self-assessments[J].Personality and Individual Differences,1995,19(3):307-318. |
| 21 | SUNDSTRÖM A .The validity of self-reported driver competence:relations between measures of perceived driver competence and actual driving skill[J].Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour,2011,14(2):155-163. |
| 22 | 倪涛 .认知分心状态下纵向驾驶权切换策略研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2020. |
| 23 | 郭凤香 .基于风险感知的老年驾驶人行为特性研究[D].昆明:昆明理工大学,2019. |
| 24 | 杨艳群,樵婷,郑新夷 .基于数据包络分析的高速公路指路标志地名数研究[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(6):137-146. |
| YANG Yanqun, QIAO Ting, ZHENG Xinyi .Number of place names of freeway guide signs based on data envelopment analysis[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2020,33(6):137-146. | |
| 25 | YANG L, BIAN Y, ZHAO X,et al .Experimental research on the effectiveness of navigation prompt messages based on a driving simulator:a case study[J].Cognition,Technology & Work,2021,23(3):439-458. |
| 26 | 高原 .无线近红外脑功能成像仪及驾驶疲劳研究[D].成都:电子科技大学,2017. |
| 27 | 冯树民,吴迪,孙雅丽 .基于自然驾驶数据的典型风险场景致因分析[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2022,41(1):13-21. |
| FENG Shumin, WU Di, SUN Yali .Cause analysis of typical critical scenarios based on naturalistic driving data[J].Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Science),2022,41(1):13-21. | |
| 28 | 高岩,苏虎,金炜东 .面向驾驶安全教育的虚拟交通环境设计与实现[J].系统仿真学报,2014,26(10):2481-2485. |
| GAO Yan, SU Hu, JIN Weidong .Design and lmplement of virtual traffic environments for driving safety[J].Journal of System Simulation,2014,26(10):2481-2485. | |
| 29 | SUN M K .Executive functioning:perspectives on neurotrophic activity and pharmacology[J].Behavioural Pharmacology,2018,29(7):592-604. |
| 30 | 詹静静 .青年与老年驾驶人车辆操控行为特征及差异性研究[D].安徽:合肥工业大学,2018. |
| 31 | 姜景文 .智能汽车激光点云与视觉图像融合三维目标检测与跟踪算法研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2023. |
| 32 | PAPANDONATOS G D, OTT B R, DAVIS J D,et al .Clinical utility of the trail-making test as a predictor of driving performance in older adults[J].Journal of the American Geriatrics Society,2015,63(11):2358-2364. |
| 33 | BIERNACKI M P, LEWKOWICZ R .Evidence for the role of personality in the cognitive performance of older male drivers[J].Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour,2020,69:385-400. |
| 34 | 王亚兵 .基于驾驶模拟器的驾驶能力评估及其应用研究[D].北京:北方工业大学,2021. |
| 35 | 贺玉龙,陈兵硕,高鹏旺,等 .基于未确知测度理论的高速公路交通安全评价[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(2):8-12. |
| HE Yulong, CHEN Bingshuo, GAO Pengwang,et al .Expressway traffic safety evaluation based on unascertained measurement theory[J].Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science Edition),2021,40 (2):8-12. | |
| 36 | 温建敏,张西寨,丁剑锋,等 .基于层次分析和未确知测度的冲击地压风险评价[J].矿业研究与开发,2021,41(7):98-103. |
| WEN Jianmin, ZHANG Xizhai, DING Jianfeng,et al .Risk assessment of rockburst based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Unascertained Measures[J].Mining Research and Development,2021,41(7):98-103. | |
| 37 | BROWN H, PRESCOTT R .Applied mixed models in medicine[M].London:John Wiley & Sons,2000. |
| 38 | ROSS L A, CLAY O J, EDWARDS J D,et,al .Do older drivers at-risk for crashes modify their driving over time?[J].The Journals of Gerontology Series B:Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences,2009,64(2):163-170. |
| 39 | PAYYANADAN R P, MAUS A, SANCHEZ F A,et al .Using trip diaries to mitigate route risk and risky driving behavior among older drivers[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2017,106:480-491. |
| 40 | REGER M A, WELSH R K, WATSON G S,et al .The relationship between neuropsychological functioning and driving ability in dementia:a meta-analysis[J].Neuropsychology,2004,18(1):85-93. |
| 41 | SELANDER H, WRESSLE E, SAMUELSSON K .Cognitive prerequisites for fitness to drive:norm values for the TMT,UFOV and NorSDSA tests[J].Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy,2020,27(3):231-239. |
| 42 | 邱大鹏 .基于老龄驾驶行为的汽车人机交互适老化设计研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2020. |
| [1] | 武彪, 任洪泽, 郑联庆, 朱西产, 马志雄. 基于自然驾驶行为的智能驾驶复杂场景构建方法[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 53(2): 38-47. |
| [2] | 任文浩, 赵晓华, 陈晨, 付强. 网联碰撞预警信息系统对雾天高速公路驾驶行为的影响[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 53(2): 27-37. |
| [3] | 何庆龄, 裴玉龙, 董春彤, 等. 基于混合策略改进ASO-LSSVM的风险驾驶行为分类识别[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(9): 131-141. |
| [4] | 付强, 赵晓华, 李海舰, 等. 跟驰事件下网联混驾编队的运行特征及生态安全影响[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(8): 65-75. |
| [5] | 高龙凯, 赵晓华, 欧居尚, 等. 基于Unity3D的立体复合高速公路标志系统优化设计[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(5): 20-30. |
| [6] | 边扬, 张钰, 赵晓华, 等. 行人过街事件网联HUD预警系统对驾驶行为的影响[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(4): 114-125. |
| [7] | 张婷, 陈丰, 李璜, 等. 基于驾驶行为的快速路交织区发光标线效果评估[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(11): 106-117. |
| [8] | 赵晓华, 董文慧, 李佳, 等. 基于驾驶行为的隧道交通标志影响特征及作用机理[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(4): 88-100. |
| [9] | 郭淼, 赵晓华, 姚莹, 等. 基于驾驶行为和交通运行状态的事故风险研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(9): 29-38. |
| [10] | 赵晓华, 朱红臻, 边扬, 等. 基于扩展TPB模型的老年驾驶人自我调节行为研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(3): 28-37. |
| [11] | 黄玲, 黄子虚, 吴泽荣, 等. 不同行为模型框架下的数据驱动类人驾驶模型比较[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(10): 1-10. |
| [12] | 杨丽平, 边扬, 赵晓华, 等. 导航播报措辞复杂度对驾驶行为的影响[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(3): 139-148. |
| [13] | 边扬, 俞洁, 赵晓华, 等. 导航播报措辞对驾驶行为的综合影响研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(11): 30-37,54. |
| [14] | 符锌砂 杜锦涛 何石坚.
提示距离和初始速度对高速出口驾驶行为的影响
[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(11): 1-9. |
| [15] | 曹宝贵 杨兆升. 一种改进的车辆跟驰动力学模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(10): 96-99,131. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||