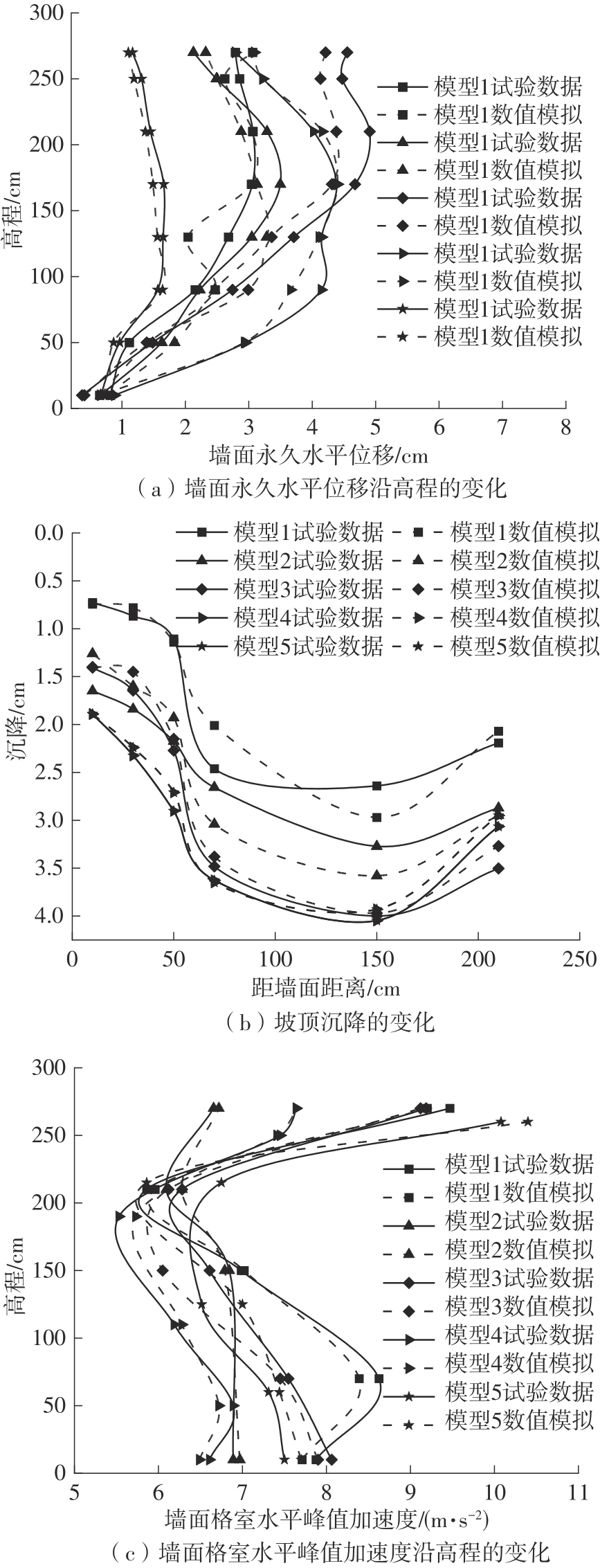
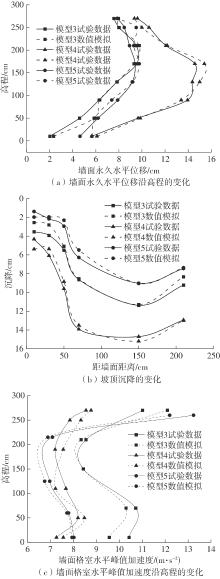
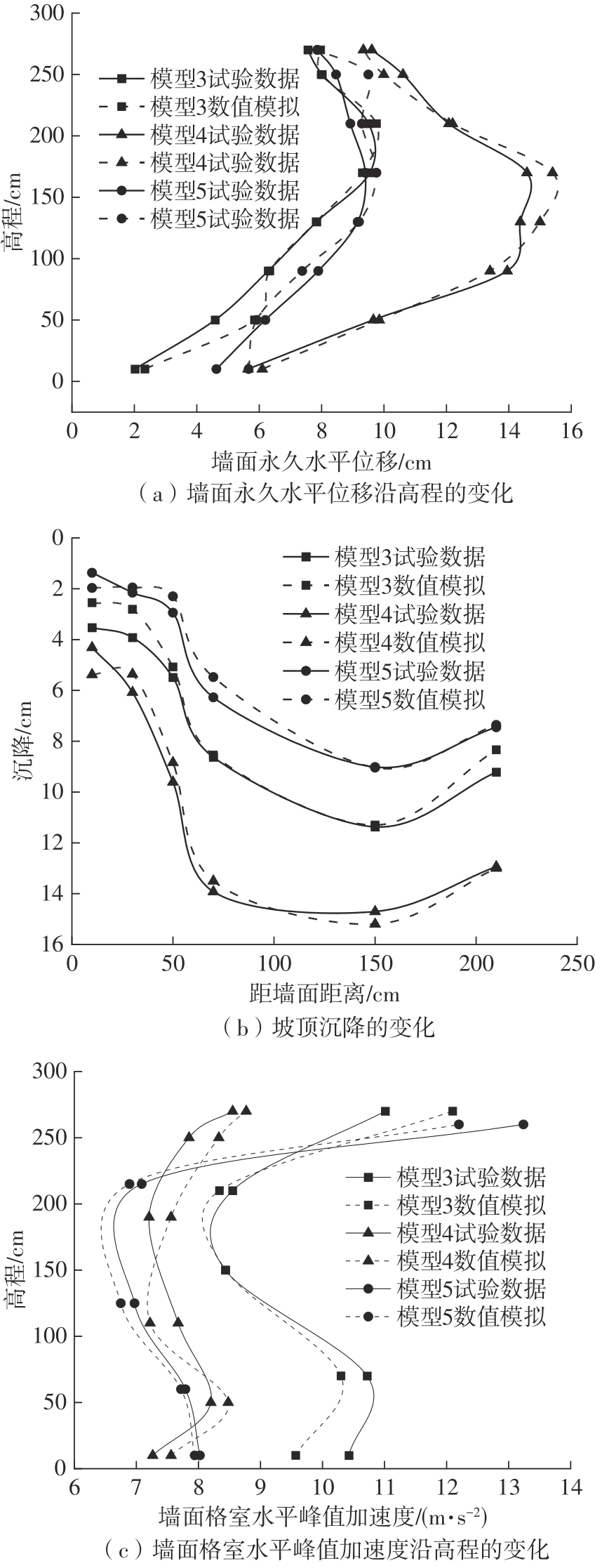
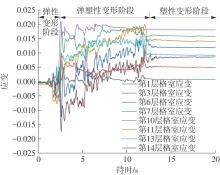
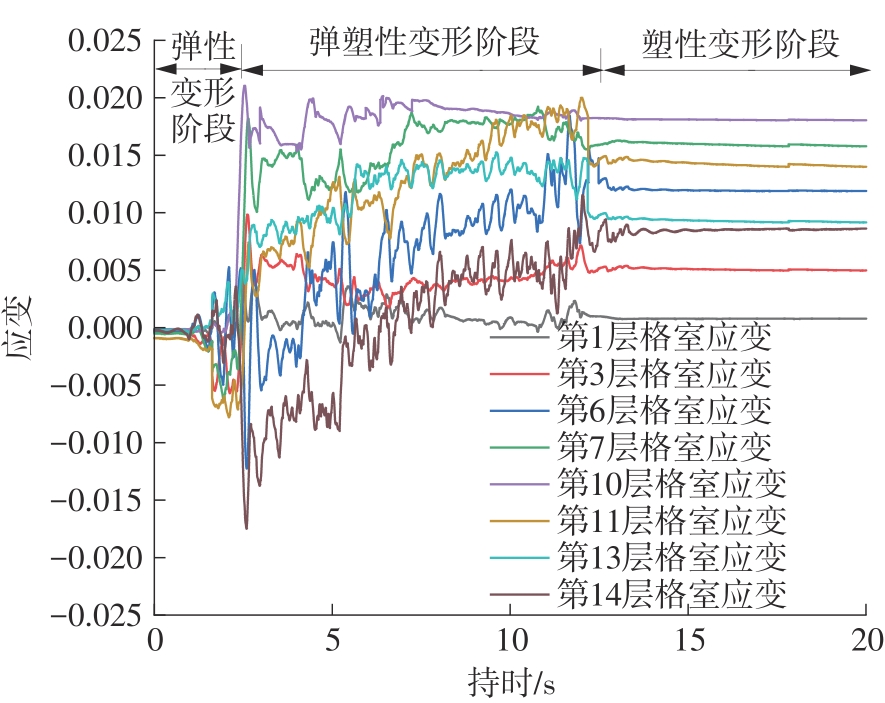
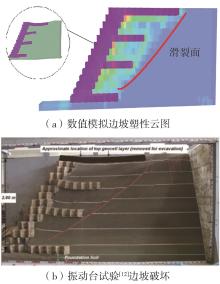
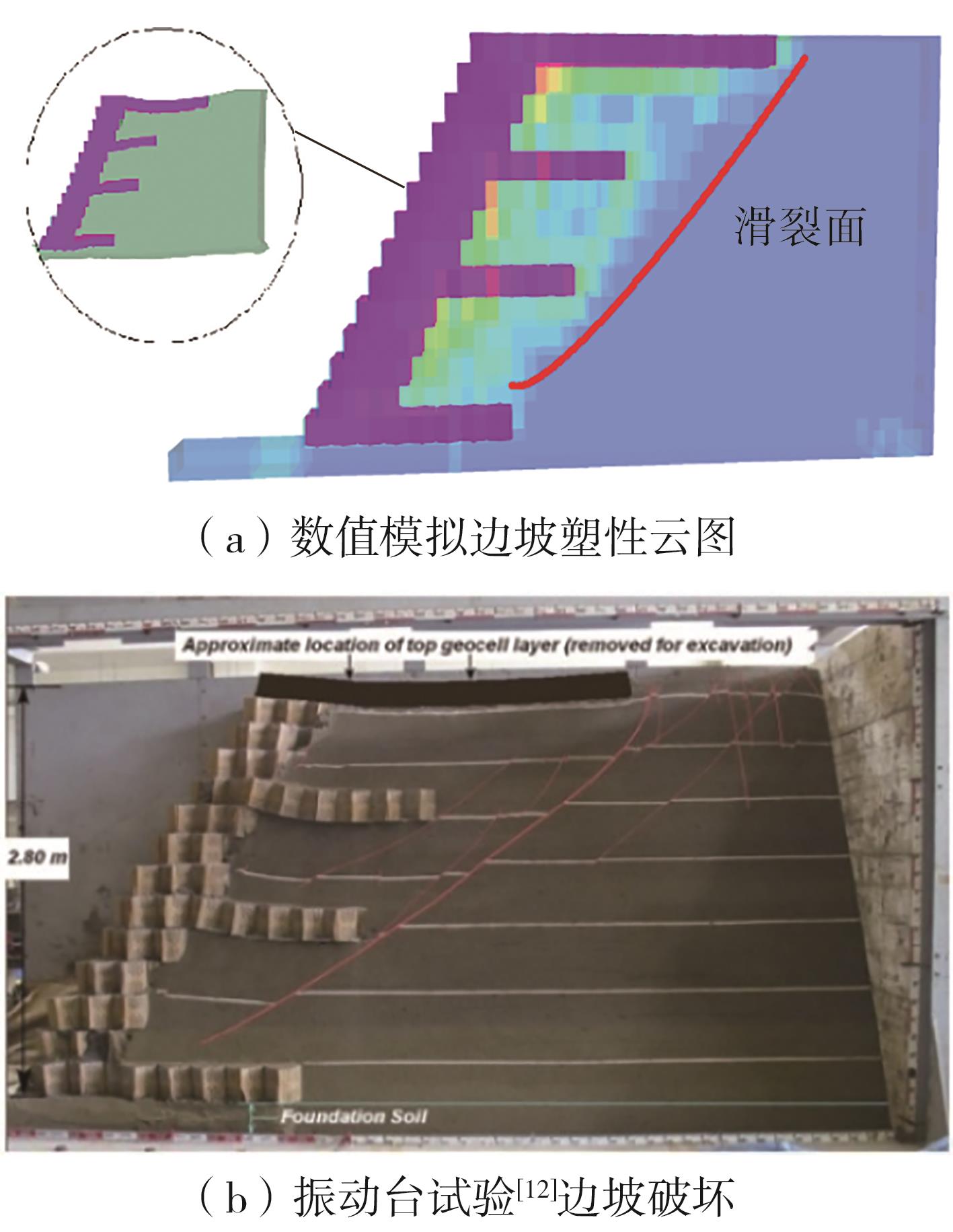
| 1 |
赵飞,俞松波,李博,等 .地震作用下岩质边坡大型振动台试验研究进展[J].地球学报,2022,47(12):4498-4512.
|
|
ZHAO Fei, YU Songbo, LI Bo,et al .Research advances on large-scale shaking table test for rock slopes under earthquake[J].Earth Science,2022,47(12):4498-4512.
|
| 2 |
LIN P, LIU X L, HU S Y,et al .Large deformation analysis of a high steep slope relating to the Laxiwa Reservoir,China[J].Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2016,49(6):2253-2276.
|
| 3 |
CHEN R H, CHIU Y M .Model tests of geocell retaining structures[J].Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2008,26(1):56-70.
|
| 4 |
SONG F, XIE Y L, YANG Y F,et al .Analysis of failure of flexible geocell-reinforced retaining walls in the centrifuge[J].Geosynthetics International,2014,21(6):342-351.
|
| 5 |
宋飞,谢永利,杨晓华,等 .填土面作用荷载时土工格室柔性挡墙破坏模式研究[J].岩土工程学报,2013,35(s1):152-155.
|
|
SONG Fei, XIE Yong-li, YANG Xiao-hua,et al .Failure mode of geocell flexible retaining wall with surcharge acting on backfill surface[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(s1):152-155.
|
| 6 |
SONG F, LIU H B, MA L Q,et al .Numerical analysis of geocell-reinforced retaining wall failure modes[J].Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2018,46(3):284-296.
|
| 7 |
NARIMAN K, GHAZAVI M .Static stability analysis of geocell-reinforced slopes[J].Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2021,49(3):852-863.
|
| 8 |
XIE Y L, YANG X H .Characteristics of a new-type geocell flexible retaining wall[J].Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2009,21(4):171-175.
|
| 9 |
CHEN R H, WU C P, HUANG F C,et al .Numerical analysis of geocell-reinforced retaining structures[J].Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2013,39(8):51-62.
|
| 10 |
屈战辉,谢永利,袁福发,等 .土工格室柔性挡墙极限主动土压力计算方法[J].交通运输工程学报,2010,10(1):24-28,35.
|
|
QU Zhan-hui, XIE Yong-li, YUAN Fu-fa,et al .Calculation method of active earth pressure under limitstate for geocell flexible retaining wall[J].Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2010,10(1):24-28,35.
|
| 11 |
WANG J P .Large-scale shaking table tests of reinforced soil retaining walls with geocell facing[D].New York:Columbia University,2007.
|
| 12 |
LING H I,DOV L, WANG J P,et al .Seismic response of geocell retaining walls:experimental studies[J].Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2009,135(4):515-524.
|
| 13 |
SONG F, LIU H B, YANG B,et al .Large-scale triaxial compression tests of geocell-reinforced sand[J].Geosynthetics International,2019,26(4):388-395.
|
| 14 |
蔡晓光,徐洪路,李思汉,等 .地震作用下返包式加筋土挡墙数值模拟[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(5):1416-1426.
|
|
CAI Xiaoguang, XU Honglu, LI Sihan,et al .Numerical simulation of reinforced soil retaining wall with wrapped face under seismic effects[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(5):1416-1426.
|
| 15 |
蒋建清,杨果林 .格宾加筋土挡墙抗震性能及数值分析[J].土木工程学报,2012,45(1):100-108.
|
|
JIANG Jianqing, YANG Guolin .Numerical analysis of seismic behaviour of gabion-reinforced soil retaining wall[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2012,45(1):100-108.
|
| 16 |
LIU H B, YANG G Q, LING H I .Seismic response of multi-tiered reinforced soil retaining walls[J].Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2014,43(61/62):1-12.
|
| 17 |
UIJAWAL K N, VENKATESWARLU H, HEGDE A .Vibration isolation using 3D cellular confinement system:a numerical investigation[J].Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2019,119(4):220-234.
|
| 18 |
左政,杨广庆,王贺,等 .土工格室规格对加筋土剪切性能的影响[J].岩土工程学报,2022,44(6):1053-1060.
|
|
ZUO Zheng, YANG Guang-qing, WANG He,et al .Effects of geocell size on shear behavior of reinforced soil[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2022,44(6):1053-1060.
|
| 19 |
王涛,韩煊,赵先宇,等 .FLAC 3D数值模拟方法及工程应用[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2015.
|
| 20 |
宋丹青,黄进,刘晓丽 .地震作用下层状岩质边坡动力响应[J].湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2021,48(5):113-120.
|
|
SONG Danqing, HUANG Jin, LIU Xiaoli .Dynamic response of layered rock slopes under earthquakes[J].Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences),2021,48(5):113-120.
|
| 21 |
言志信,郭斌,段建 .黄土边坡地震动力响应探讨[C]∥第三届全国工程安全与防护学术会议论文集.武汉:中国岩石力学与工程学会,2012:373-378.
|
| 22 |
曾新吾,韩开锋 .弹性波动力学基础[M].长沙:国防科技大学出版社,2012.
|
| 23 |
张祖武,姚令侃 .土岩界面地震波能量传递与耗散特性研究——以汶川8.0级地震为例[J].灾害学,2011,26(1):5-9.
|
|
ZHANG Zuwu, YAO Lingkan .Seismic waves scattering in rock interface and energy dissipation characteristics-taking M8.0 Wenchuan Earthquake as an example[J].Journal of Catastrophology,2011,26(1):5-9.
|
| 24 |
李昀,杨果林,林宇亮 .水平地震作用下加筋格宾挡土墙动力特性试验研究[J].岩土工程学报,2009,31(12):1930-1935.
|
|
LI Yun, YANG Guo-lin, LIN Yu-liang .Dynamic characteristics of reinforced gabion walls subjected to horizontal seismic loading[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2009,31(12):1930-1935.
|
| 25 |
张江伟,李小军,齐剑峰,等 .地震动参数对土坡地震响应的影响权重研究[J].振动与冲击,2018,37(6):225-230.
|
|
ZHANG Jiangwei, LI Xiaojun, QI Jianfeng,et al .Effect of influence weights of ground motion parameters on soil slope seismic responses[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2018,37(6):225-230.
|