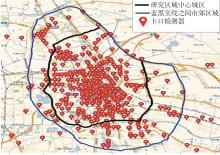
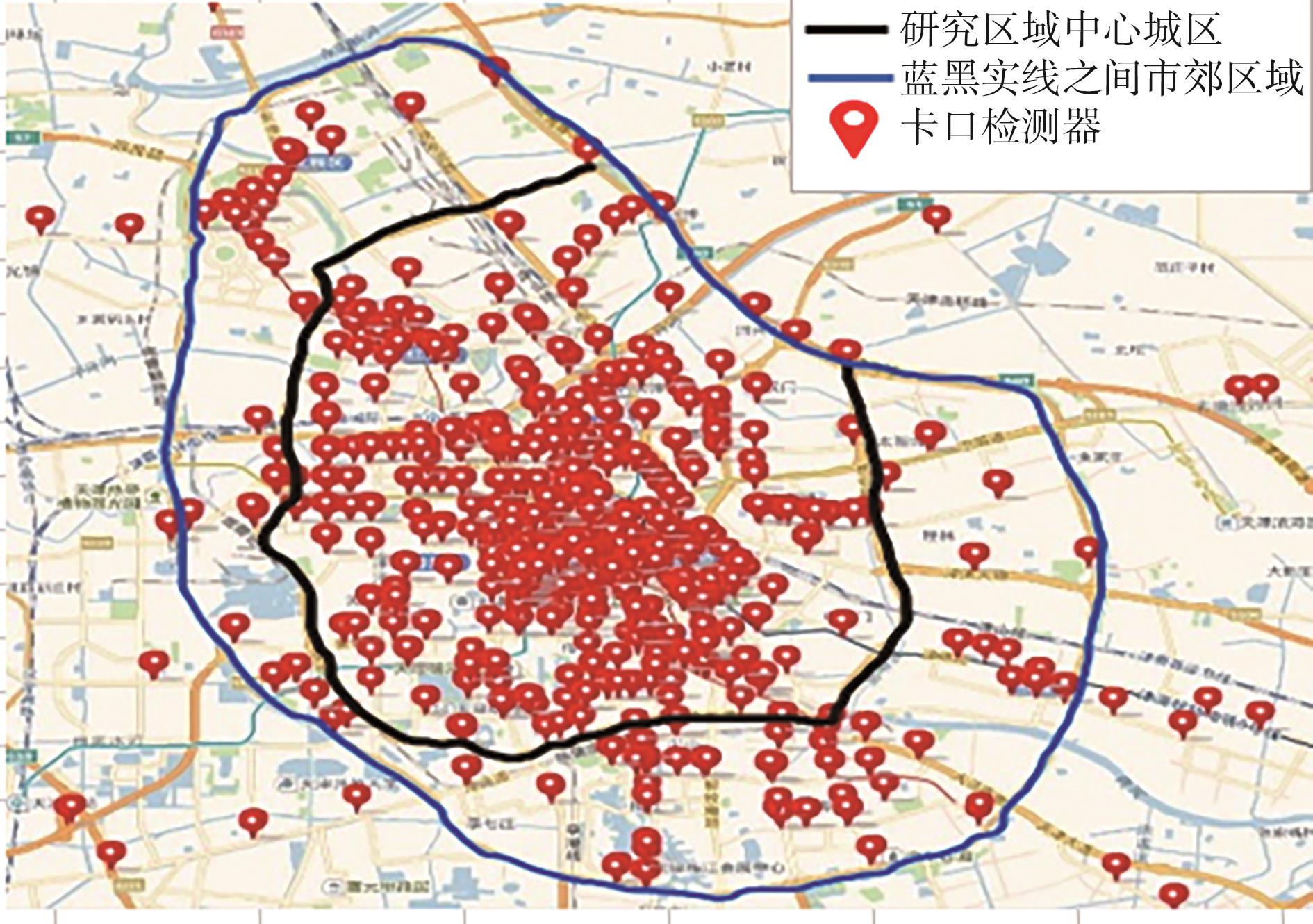
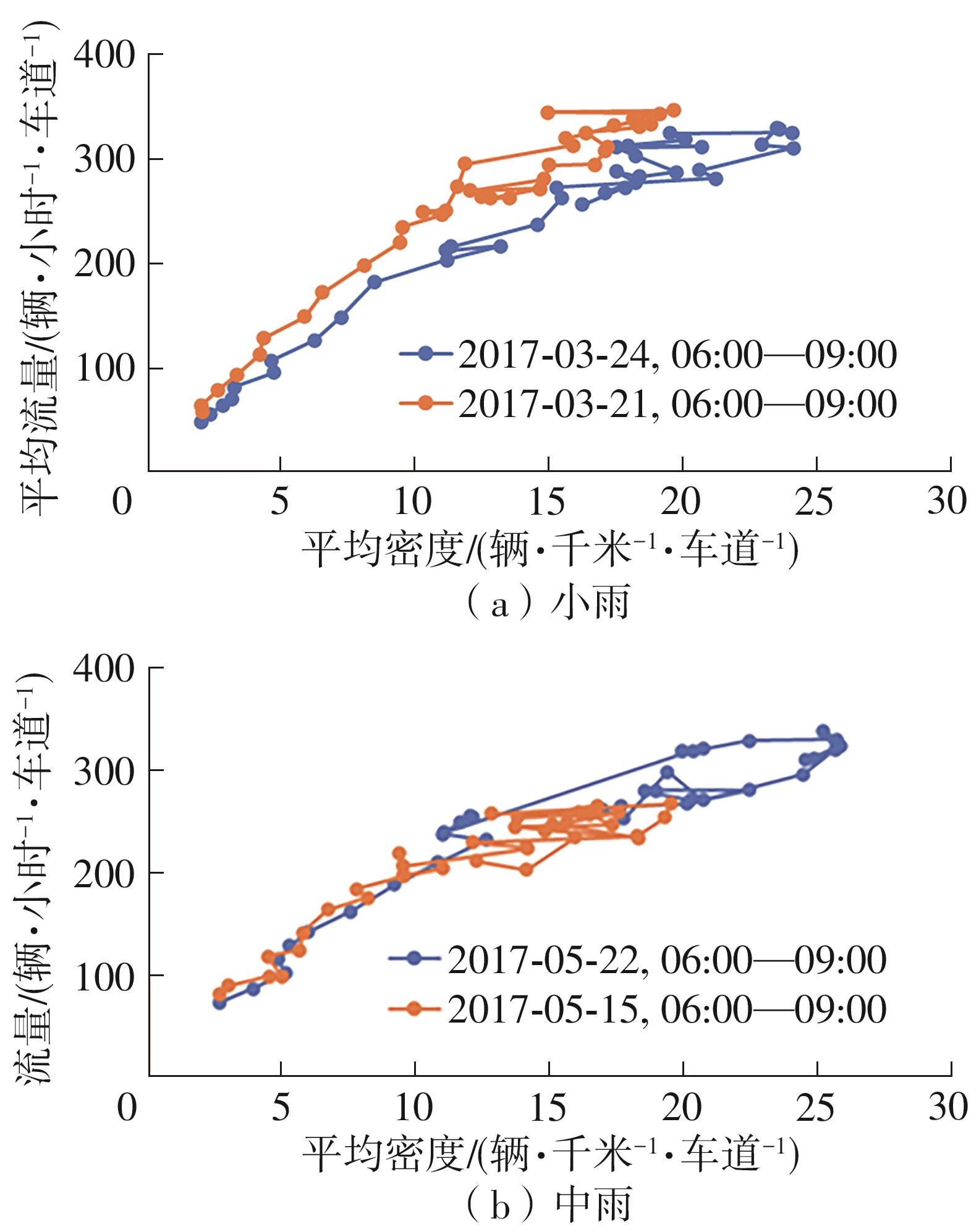
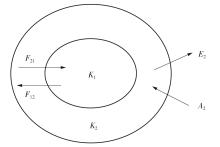
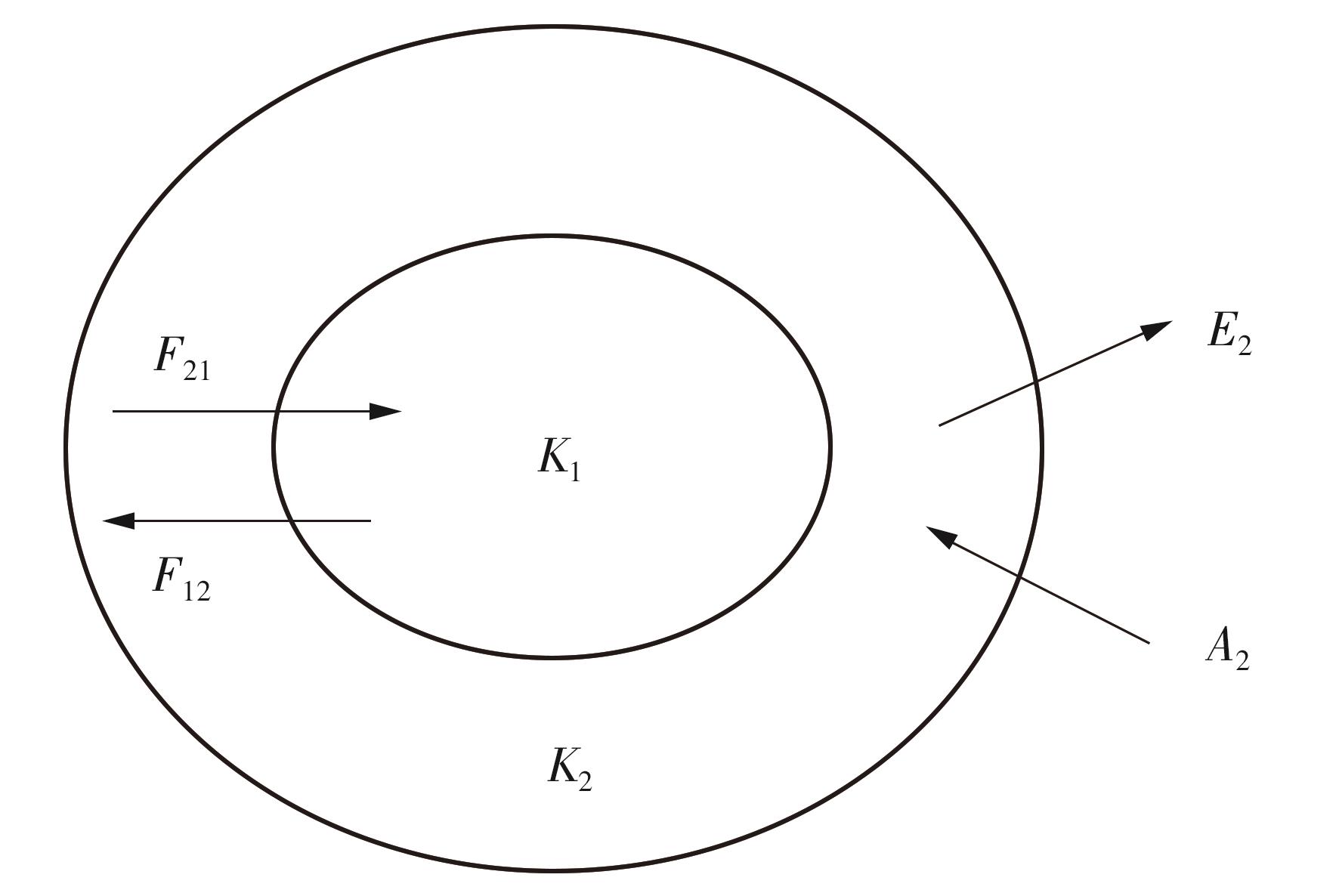
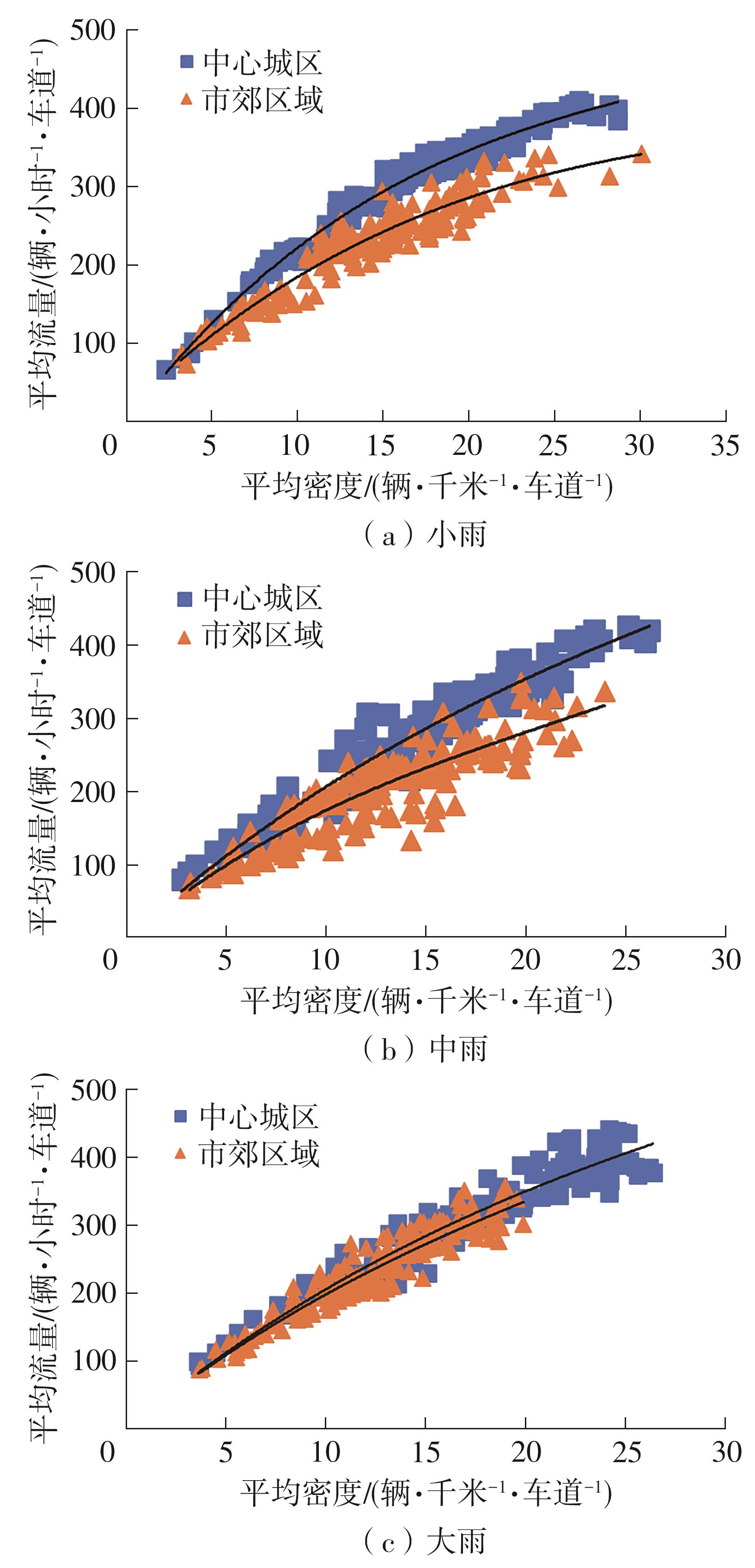
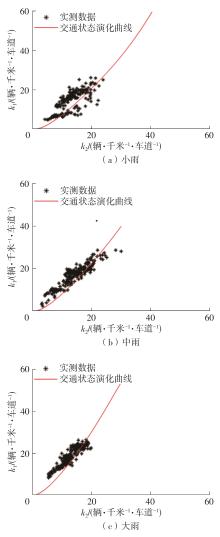
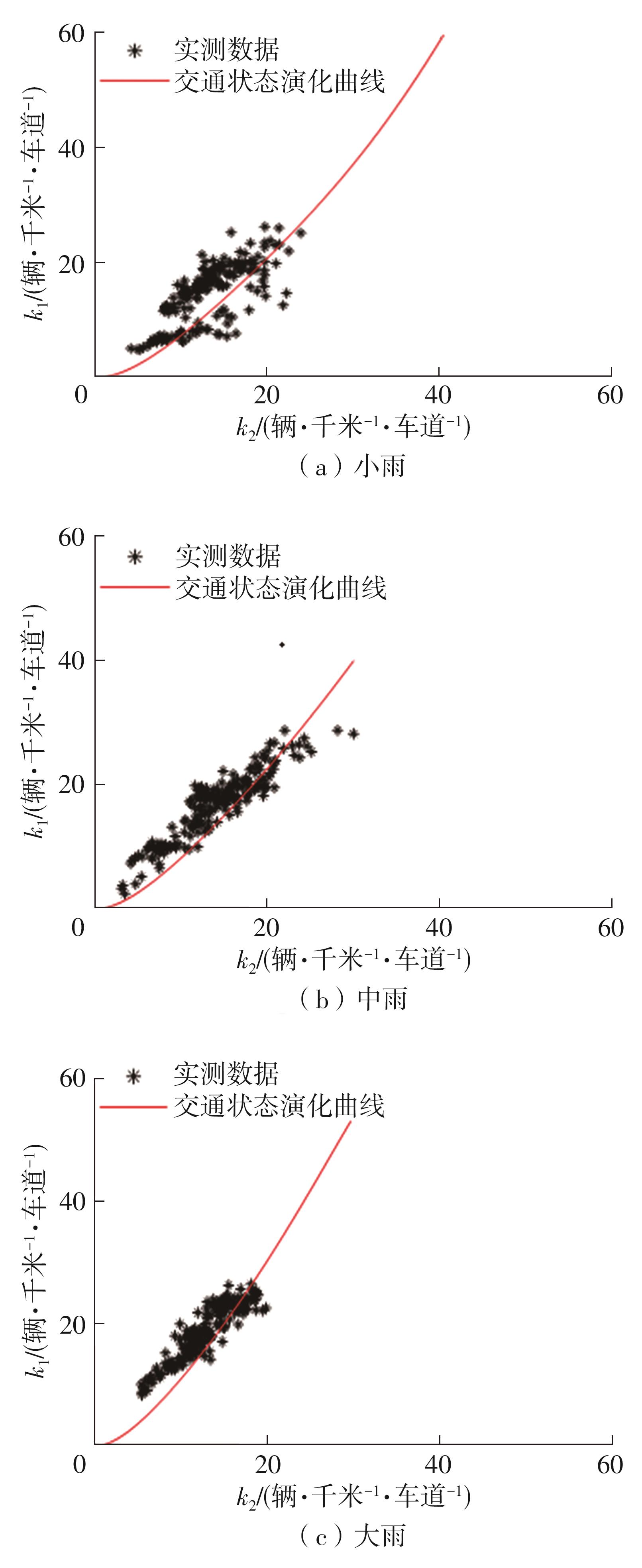
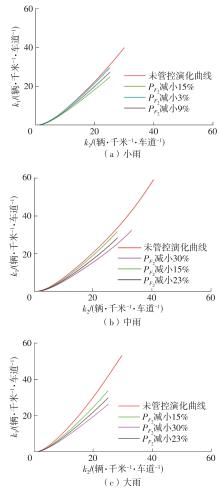
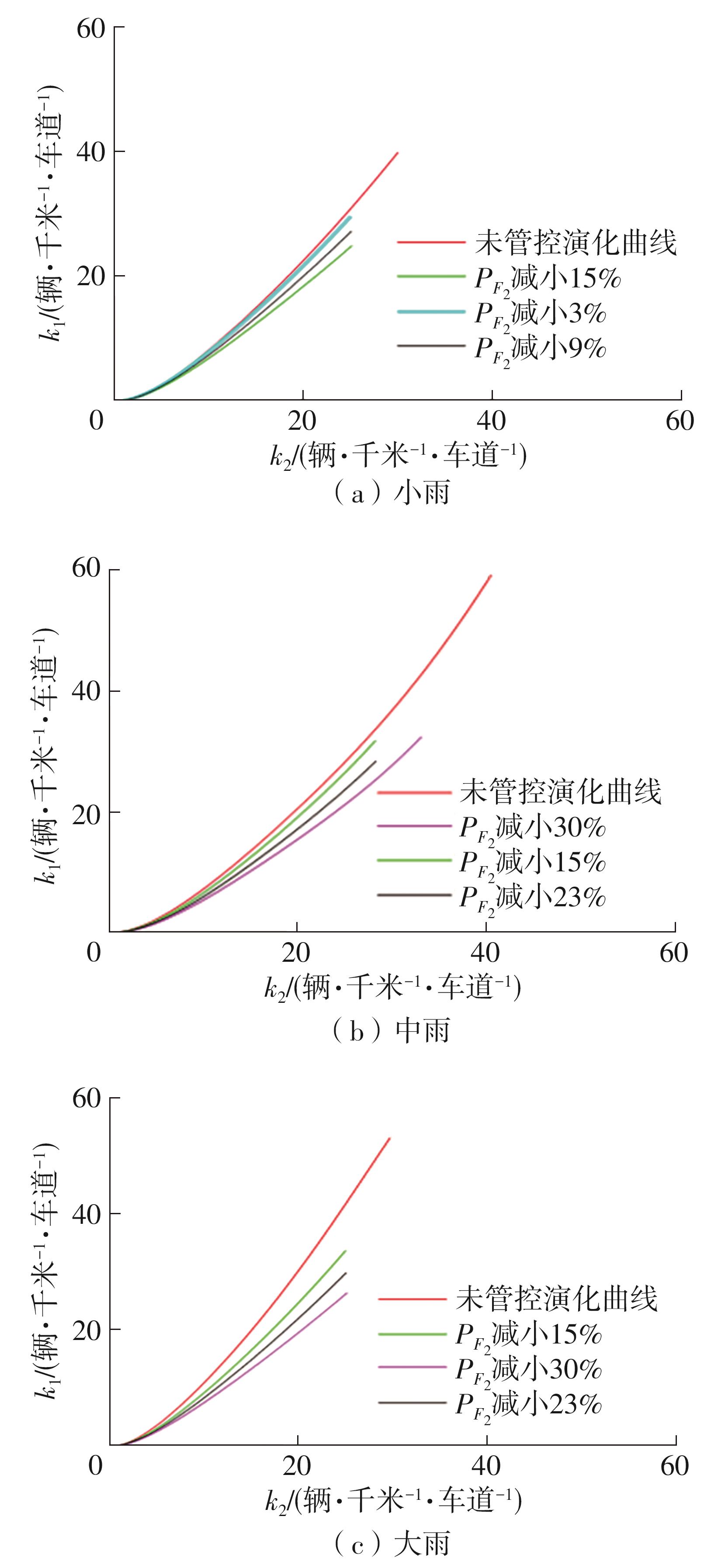
| 1 |
张存保,万平,梅朝辉,等 .雨天环境下高速公路交通流特性及模型研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2013,5(3):63-67.
|
|
ZHANG Cunbao, WAN Ping, MEI Chaohui,et al .Traffic flow characteristics and models of freeway under rain weather[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology,2013,5(3):63-67.
|
| 2 |
罗京,刘建蓓,郭腾峰,等 .降雨对高速公路交通流特征的影响[J].公路交通科技,2015,32(7):134-139.
|
|
LUO Jing, LIU Jianbei, GUO Tengfeng,et al .Impact of rainfall in expressway traffic flow characteristics[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2015,32(7):134-139.
|
| 3 |
BILLOT R, FAOUZI N E E, VUYST F D .Multilevel assessment of the impact of rain on drivers behavior[J].Journal of Transportation Research Record,2009(1):134-142.
|
| 4 |
杨中良,林瑜,高霄 .恶劣天气条件下城市快速路通行能力研究[J].交通信息与安全,2010,28(1):75-78.
|
|
YANG Zhongliang, LIN Yu, GAO Xiao .Urban expressway capacity under adverse weather conditions[J].Journal of Transport Information and Safety,2010,28(1):75-78.
|
| 5 |
龚大鹏,宋国华,黎明,等 .降雨对城市道路行程速度的影响[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2015,15(1):218-225.
|
|
GONG Dapeng, SONG Guohua, LI Ming,et al .Impact of rainfalls on travel speed on urban roads[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2015,15(1):218-225.
|
| 6 |
KEYVAN-EKBATANI M, PAPAGEORGIOU M, PAPAMICHAIL I .Urban congestion gating control based on reduced operational network fundamental diagrams[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2013,33:74-87.
|
| 7 |
KEYVAN-EKBATANI M, KOUVELAS A, PAPAMI-CHAIL I,et al .Exploiting the fundamental diagram of urban networks for feedback-based gating[J].Tramsportation Research Part B:Methodological,2012,46(10):1393-1403.
|
| 8 |
KOUVELAS A, SAEEAMANESH M, GEROLIMINIS N .Enhancing model-based feedback perimeter control with data-driven online adaptive optimization[J].Tramsportation Research Part B:Methodological,2017,96:26-45.
|
| 9 |
GEROLIMINIS N, HADDAD J, RAMEZANI M. Optimal perimeter for two urban regions with macroscopic fundamental diagram:a model predictive approach[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2013,14(1):348-359.
|
| 10 |
YANG KD, ZHENG N, MENENDEZ M .Optimal perimeter control synthesis for two urban regions with aggregate boundary queue dynamics[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2017,96:1-25.
|
| 11 |
YILDIRIMOGLU M, SIRMATEL II, GEROLIMINIS N .Hierarchical control of heterogeneous large-scale urban road networks via path assignment and regional route guidance[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2019,118:106-123.
|
| 12 |
ABOUDOLAS K, GEROLIMINIS N .Perimeter and boundary flow control in multi-reservoir heterogeneous[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2013,56(12):265-281.
|
| 13 |
KOUVELAS A, SAEEDMANESH M, GEROLIMINIS N .Enhancing model-based feedback perimeter control with data-driven online adaptive optimization[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2017,96:26-45.
|
| 14 |
RAMEZANI M, HADDAD J, GEROLIMINIS N .Dynamics of heterogeneity in urban networks:aggregated traffic modeling and hierarchical control[J].Tramsportation Research Part B:Methodological,2015,74:1-19.
|
| 15 |
HAJIAHMADI M, HADDAD J, DE SCHUTTER B,et al .Optimal hybrid perimeter and switching plans control for urban traffic networks[J].Control Systems Technology,IEEE Transactions on Control System Technology,2015,23(2):464-478.
|
| 16 |
廖南楠 .基于MFD的城市路网交通拥堵特性及门限控制方法研究[D].南京:东南大学,2017.
|
| 17 |
赵靖,马万经,汪涛,等 .基于宏观基本图的相邻子区协调控制方法[J].交通运输系统工程与信息. 2016,16(1):78-84.
|
|
ZHAO Jing, MA Wanjing, WANG Tao,et al .Coordinated perimeter flow control for two subareas with macroscopic fundamental diagram[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2016,16(1):78-84.
|
| 18 |
LI Yishun, XU Jianmin, SHEN Lvou .A perimeter control Strategy for oversaturated network preventing queue spillback[J].Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences,2012,43:418-427.
|
| 19 |
李轶舜,徐建闽,王琳虹 .过饱和交通网络的多层边界主动控制方法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) 2012,40(7):27-32.
|
|
LI Yi-shun, XU Jian-min, WANG Lin-hong .Active multi-layer perimeter control strategy of oversaturated traffic networks[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2012,40(7):27-32.
|
| 20 |
李长城 .不良天气下的高速公路交通流特性及引导控制研究[D].北京:北京工业大学,2015.
|