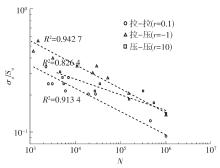
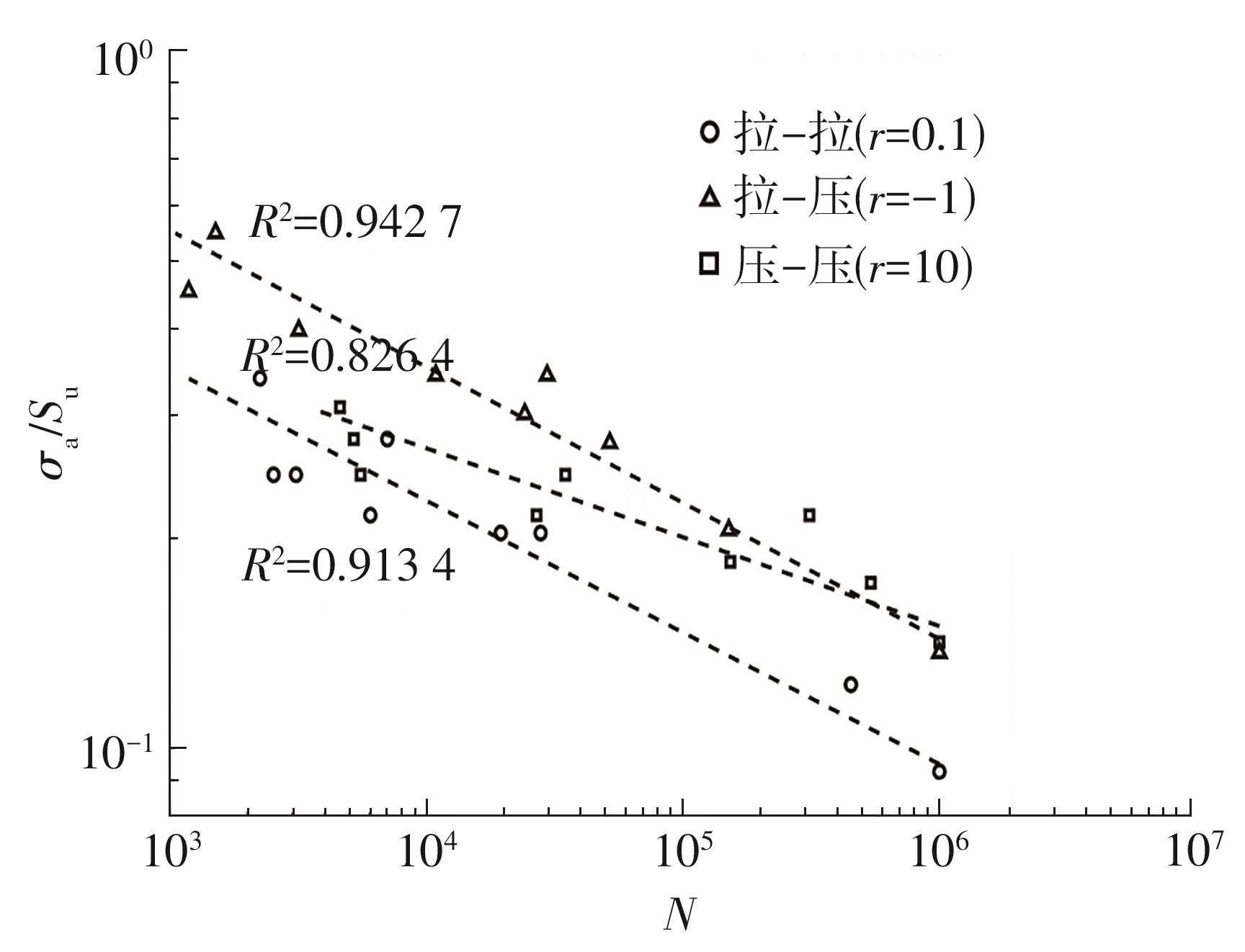
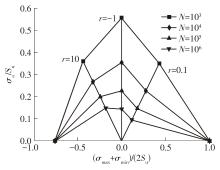
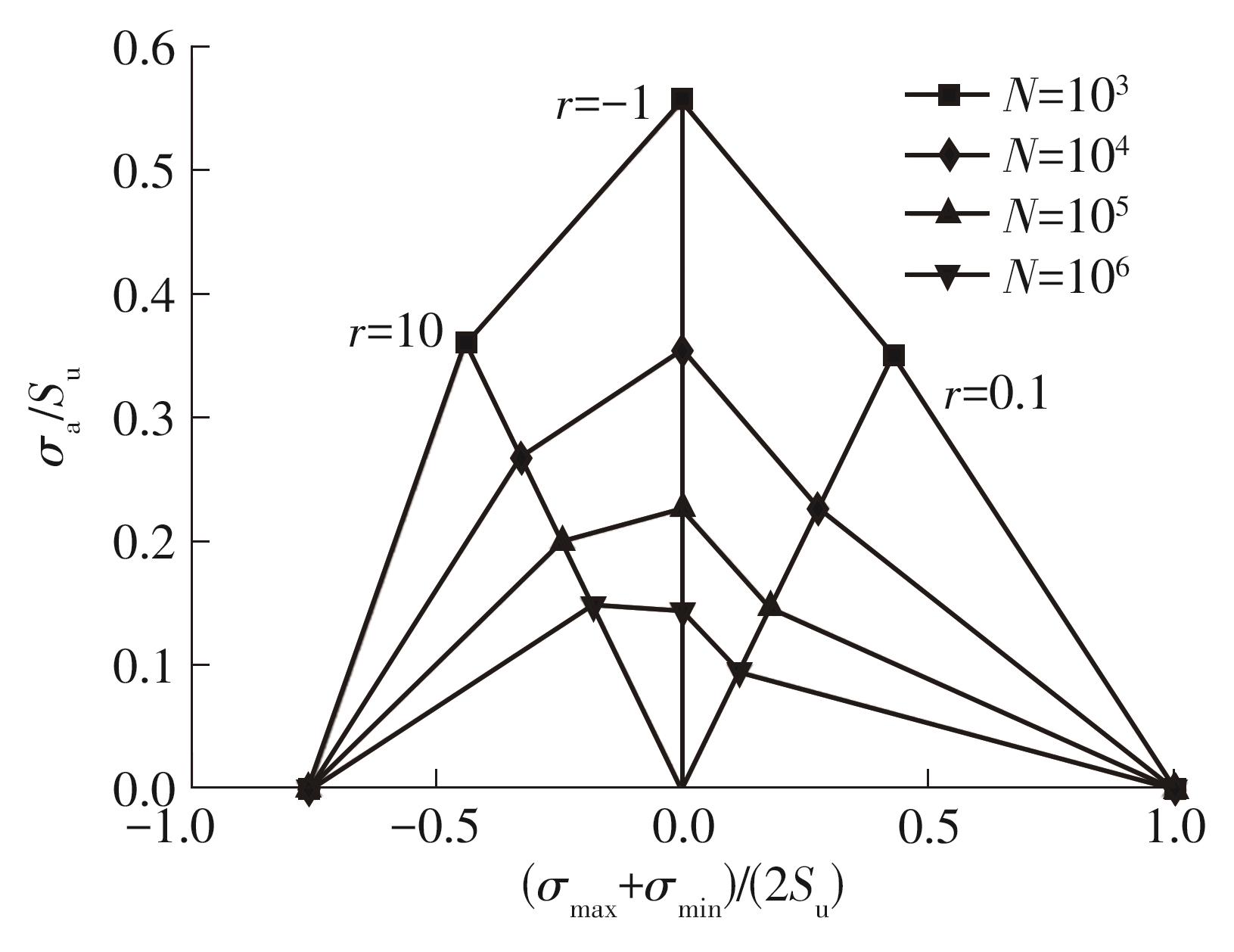
| 1 |
单青 .新型复合横担在特高压输电铁塔中的应用研究[D].北京:华北电力大学,2017.
|
| 2 |
FERDOUS W, MANALO A, PEAURIL J,et al .Testing and modelling the fatigue behavior of GFRP composites—Effect of stress level, stress concentration and frequency[J].Engineering Science and Technology,an International Journal,2020,23(5):1223-1232.
|
| 3 |
JAGANNATHAN N, ANILCHANDRA A R, MANJU-NATHA C M .A study on the fatigue performance of a glass fiber-epoxy polymer nanocomposite under random loads[J].Nanocomposites,2015,1(3):138-144.
|
| 4 |
孔令美,郑威,高泉喜,等 .玻纤增强树脂基复合材料的疲劳性能研究[J].化工新型材料,2015,43(7):177-179.
|
|
KONG Lingmei, ZHENG Wei, GAO Quanxi,et al .Study of the fatigue characteristic of glass fiber reinforced resin composites[J].New Chemical Materials,2015,43(7):177-179.
|
| 5 |
GANESAN C, JOANNA P S .Fatigue life and residual strength prediction of GFRP composites:an experimental and theoretical approach[J].Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures,2018,15(7):e72/1-16.
|
| 6 |
STOJKOVIĆ N, FOLIĆ R, PASTERNAK H .Mathematical model for the prediction of strength degradation of composites subjected to constant amplitude fatigue[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2017,103:478-487.
|
| 7 |
PAKDEL H, MOHAMMADI B .Stiffness degradation of composite laminates due to matrix cracking and induced delamination during tension-tension fatigue[J].Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2019,216:106489/1-11.
|
| 8 |
GAO J X, YUAN Y P .Probabilistic modeling of stiffness degradation for fiber reinforced polymer under fatigue loading[J].Engineering Failure Analysis,2020,116:104733/1-12.
|
| 9 |
THOR M, SAUSE M G R, HINTERHÖLZLR M .Mechanisms of origin and classification of out-of-plane fiber waviness in composite materials—a review[J].Journal of Composites Science,2020,4(3):130-168.
|
| 10 |
VIEIRA P R, CARVALHO E M L, VIEIRA J D,et al .Experimental fatigue behavior of pultruded glass fiber reinforced polymer composite materials[J].Composites Part B:Engineering,2018,146:69-75.
|
| 11 |
IQBAL M A .Fatigue life of pultruded and hand lay-up GFRP exposed to different environmental conditions[D].Maine:The University of Maine,2002.
|
| 12 |
POST N L .Modeling the residual strength distribution of structural GFRP composite materials subjected to constant and variable amplitude tension-tension fatigue loading[D].Virginia:Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University,2005.
|
| 13 |
刘浩龙 .考虑孔隙及尺寸效应的碳纤维/树脂基复合材料疲劳研究[D].南京:南京航空航天大学,2019.
|
| 14 |
YUAN Y, YAO X, NIU K,et al .Compressive failure of fiber reinforced polymer composites by imperfection[J].Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,118:106-116.
|
| 15 |
BASQUIN O H .The exponential law of endurance tests[C]∥ Proceedings of the American Society for Testing and Materials.Philadelphia:American Society for Testing and Materials,1910:625-630.
|
| 16 |
VASSILOPOULOS A P, MANSHADI B D, KELLER T .Influence of the constant life diagram formulation on the fatigue life prediction of composite materials[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2010,32(4):659-669.
|
| 17 |
PHILIPPIDIS T P, VASSILOPOULOS A P. Life prediction methodology for GFRP laminates under spectrum loading[J].Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing,2004,35:657-666.
|
| 18 |
POST N L, CASE S W, LESKO J J .Modeling the variable amplitude fatigue of composite materials:a review and evaluation of the state of the art for spectrum loading[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2008,30(12):2064-2086.
|
| 19 |
REIFSNIDER K L, HENNEKE E G, STINCHCOMB W W,et al .Damage mechanics and NDE of composite laminates[M]∥HASHIN Z,HERAKOVICH C T.Mechanics of composite materials:recent advances.New York:Pergamon Press Ltd,1983:399-420.
|
| 20 |
寇海霞 .复合材料风电叶片刚度退化模型研究[D].兰州:兰州理工大学,2019.
|
| 21 |
SHIRI S, YAZDANI M, POURGOL-MOHAMMAD M .A fatigue damage accumulation model based on stiffness degradation of composite materials[J].Materials & Design,2015,88:1290-1295.
|
| 22 |
廉伟,姚卫星 .复合材料层压板剩余刚度-剩余强度关联模型[J].复合材料学报,2008,25(5):151-156.
|
|
LIAN Wei, YAO Weixing .Residual stiffness residual strength coupled model of composite laminates[J]Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2008,25(5):151-156.
|