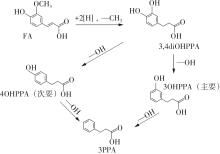
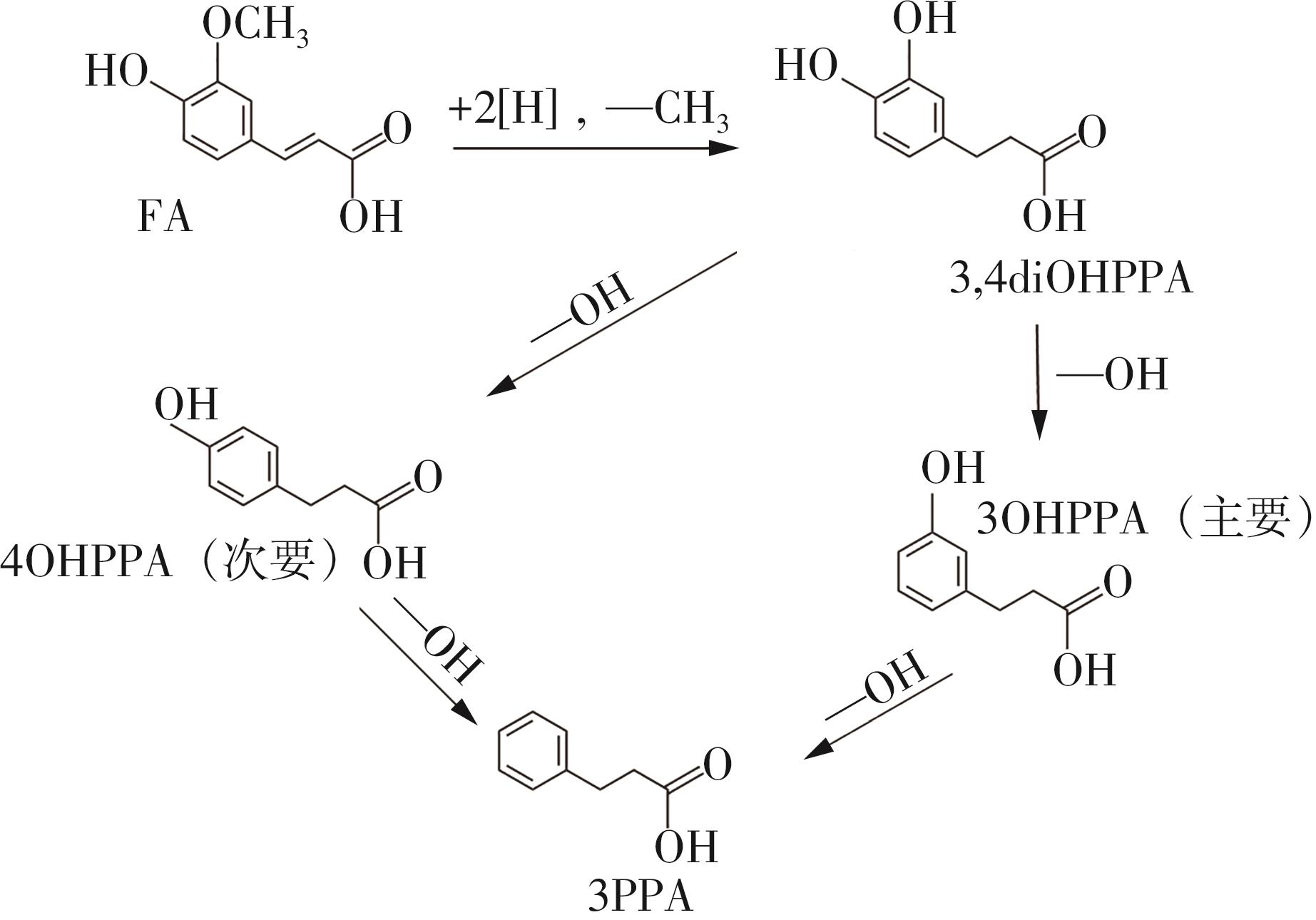
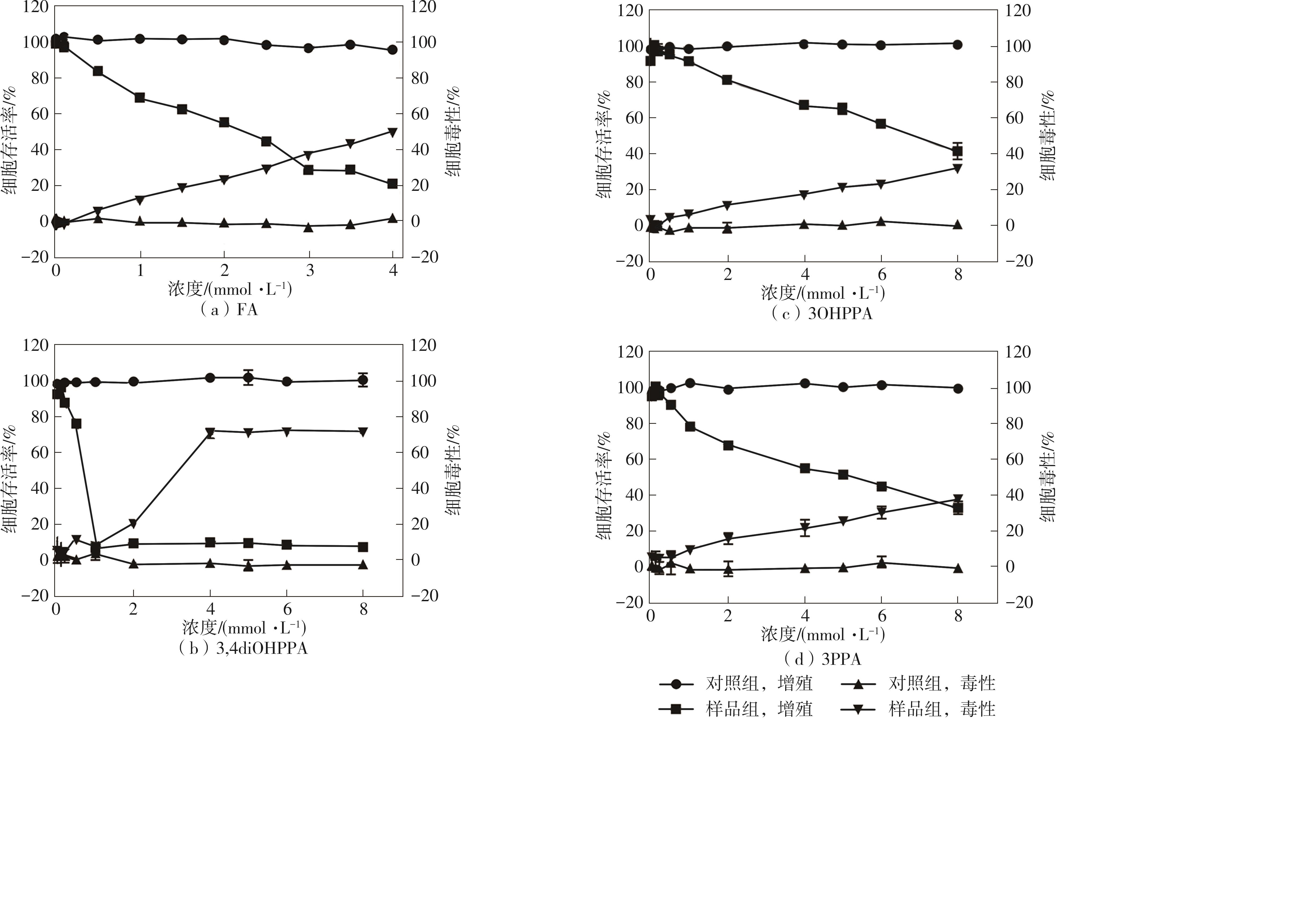
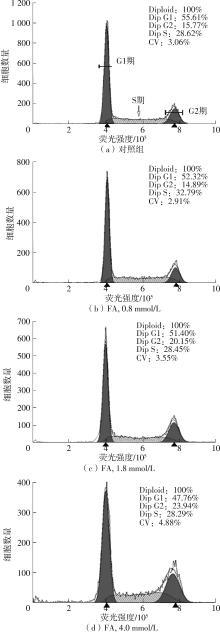
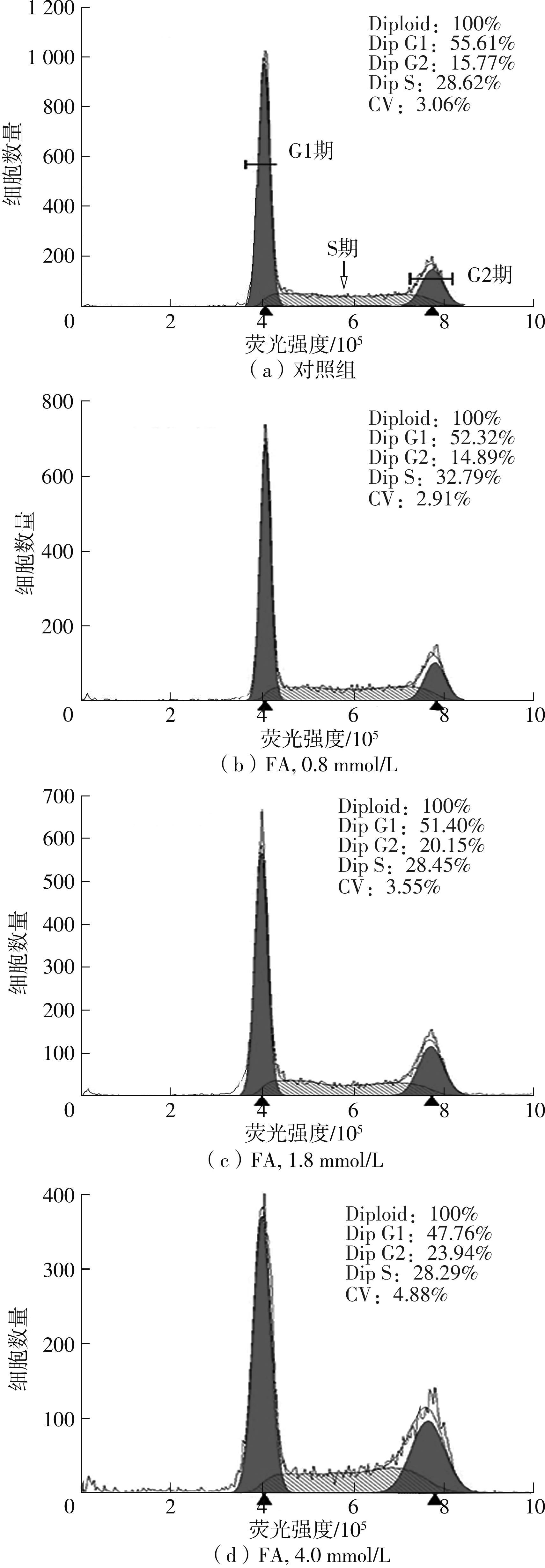
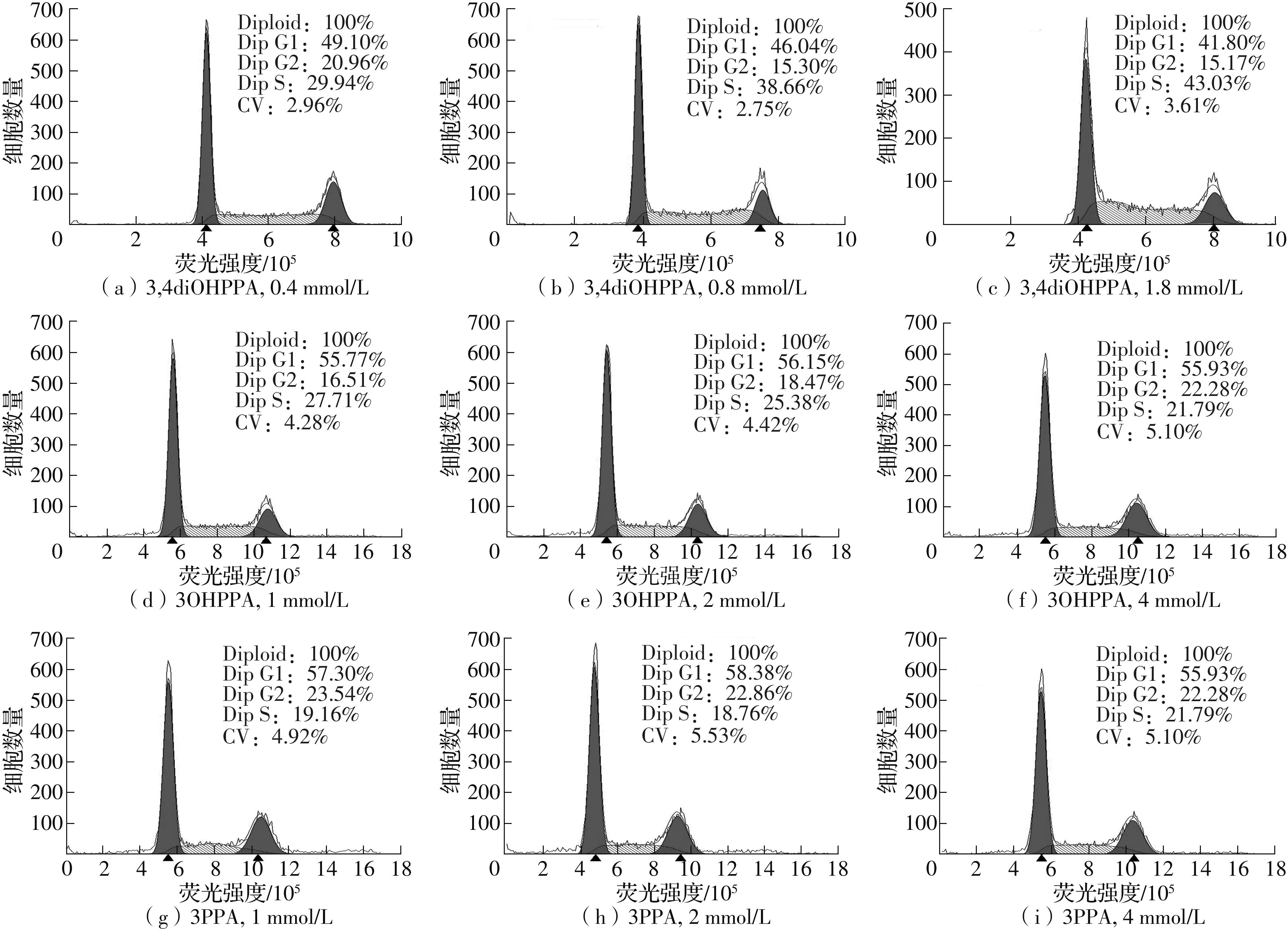
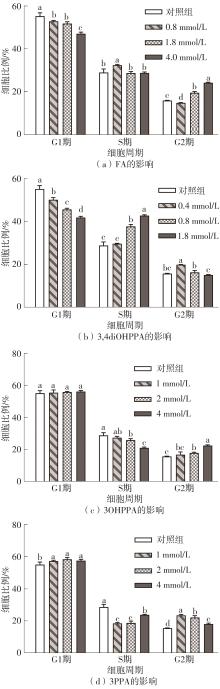
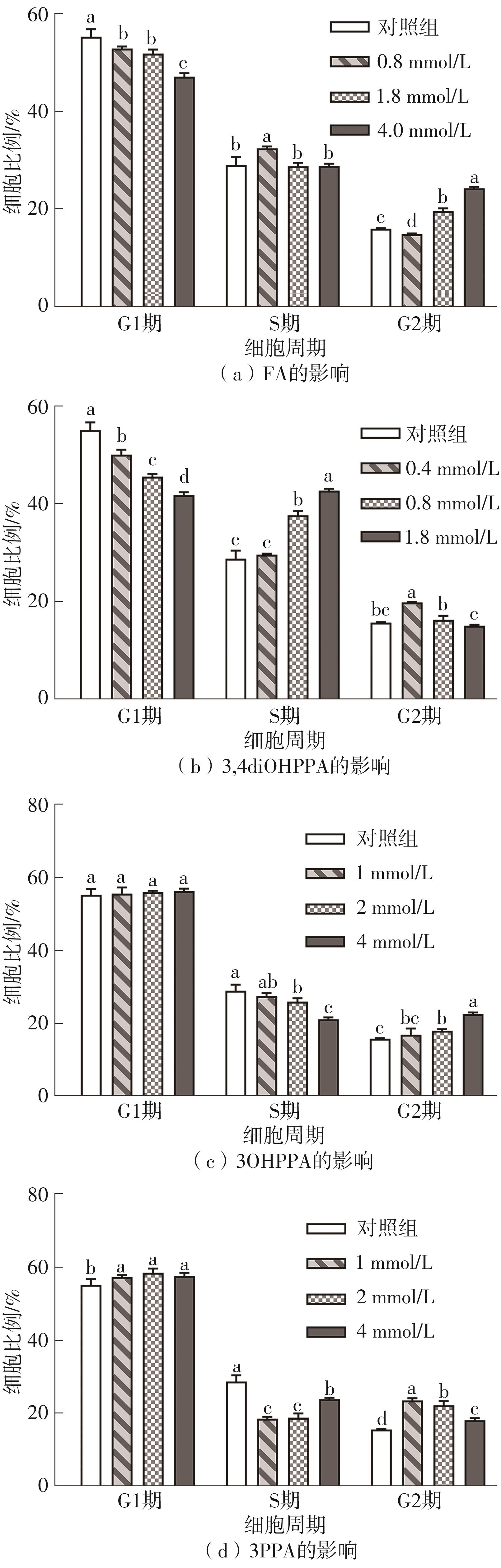
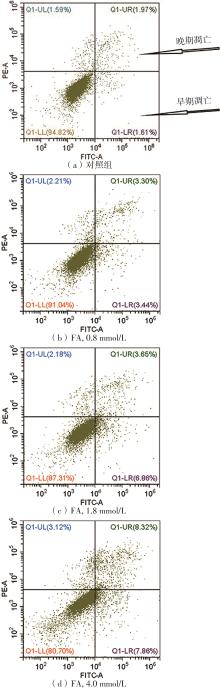
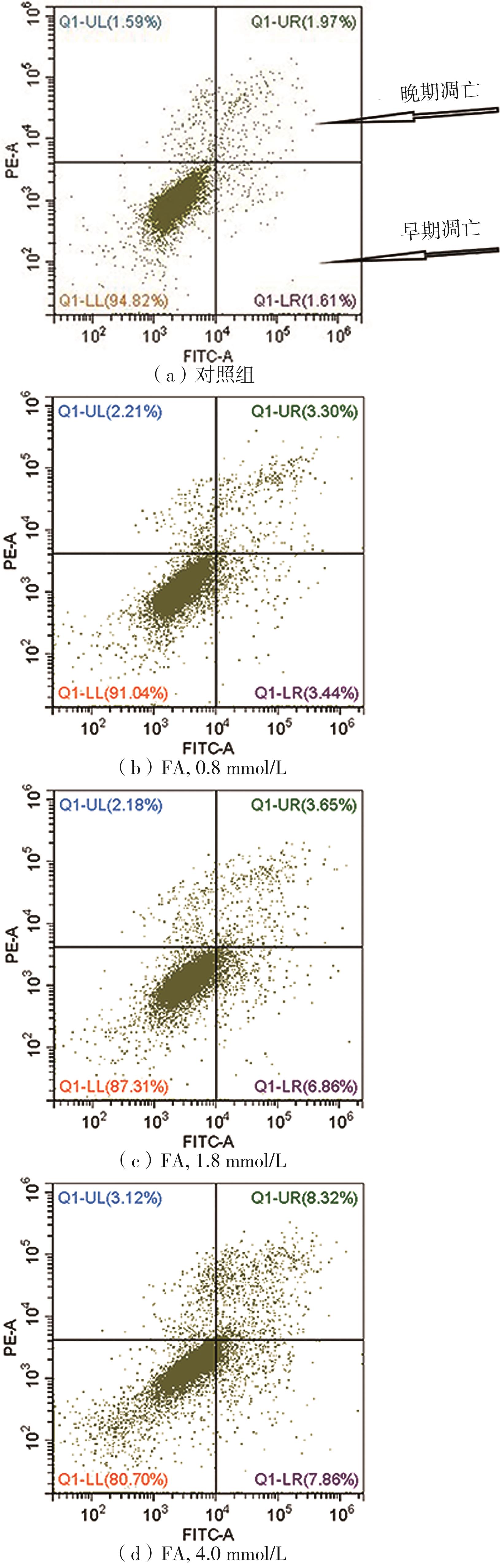
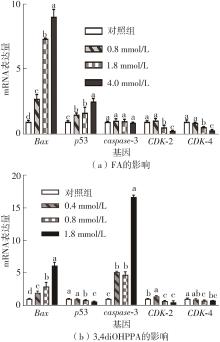
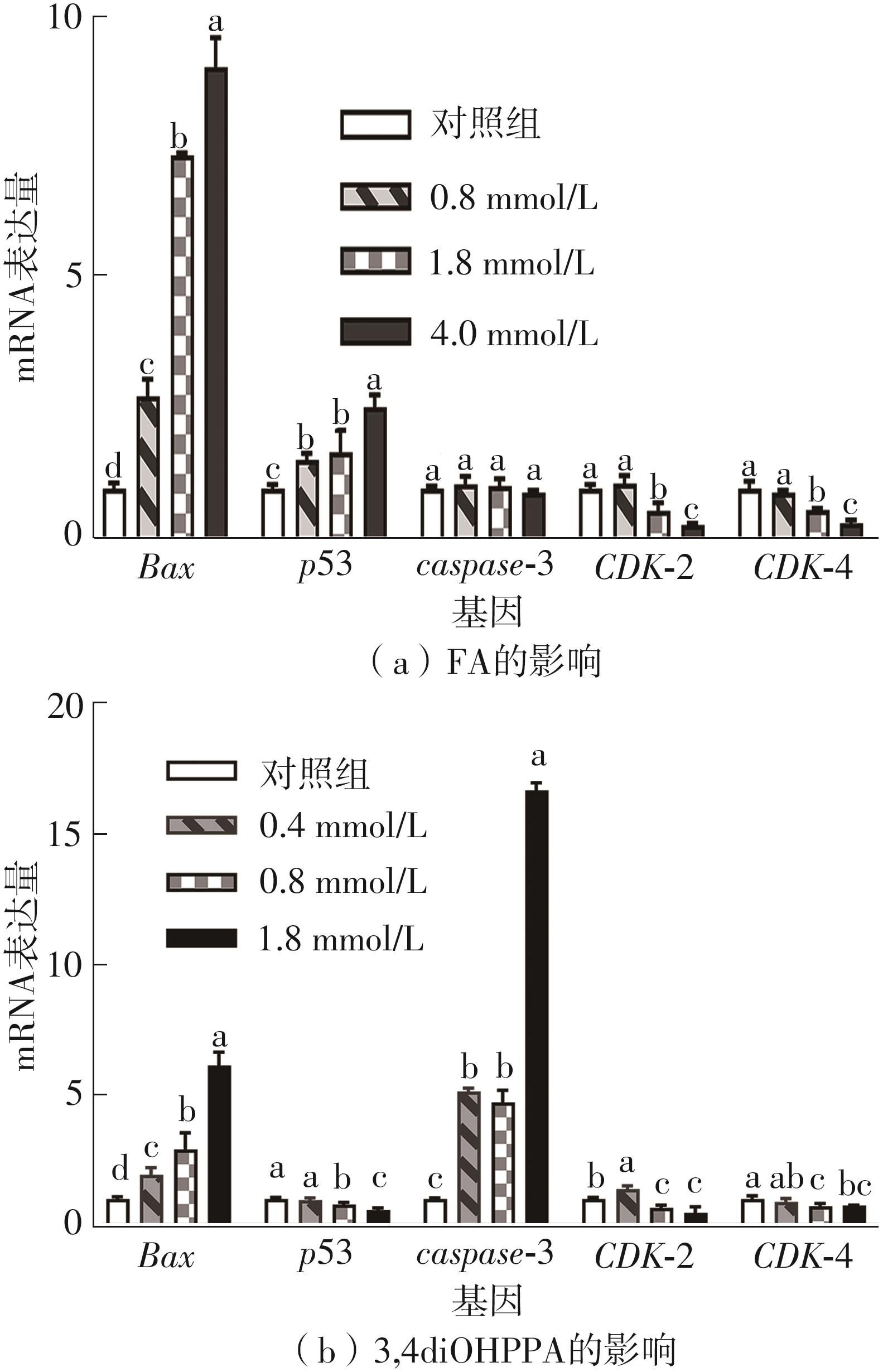
| 1 |
BARONE E, CALABRESE V, MANCUSO C .Ferulic acid and its therapeutic potential as a hormetin for age-related diseases[J].Biogerontology,2009,10(2):97-108.
|
| 2 |
CHOWDHURY S, GHOSH S, DAS A K,et al .Ferulic acid protects hyperglycemia-induced kidney damage by regulating oxidative insult,inflammation and autophagy[J].Frontiers in Pharmacology,2019,10:3389.
|
| 3 |
GIZAWY H A EL, BOSHRA S A, MOSTAFA A,et al . Pimenta dioica (L.) Merr. bioactive constituents exert anti-SARS-CoV-2 and anti-inflammatory activities: molecular docking and dynamics,in vitro,and in vivo studies[J].Molecules,2021,26(19):5844.
|
| 4 |
CHOI J H, PARK J K, KIM K M,et al .In vitro and in vivo antithrombotic and cytotoxicity effects of ferulic acid[J].Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology,2018,32(1):1002.
|
| 5 |
JUNG E H, KIM S R, HWANG I K,et al .Hypoglycemic effects of a phenolic acid fraction of rice bran and ferulic acid in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(24):9800-9804.
|
| 6 |
MANCUSO C, SANTANGELO R .Ferulic acid: pharmacological and toxicological aspects[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,2014,65:185-195.
|
| 7 |
LI D, RUI Y X, GUO S D,et al .Ferulic acid: a review of its pharmacology,pharmacokinetics and derivatives[J].Life Sci,2021,284:119921.
|
| 8 |
RECHNER A R, KUHNLE G, BREMNER P,et al .The metabolic fate of dietary polyphenols in humans[J].Free Radical Bio Med,2002,33(2):220-235.
|
| 9 |
CHESSON A, PROVAN G J, RUSSELL W R,et al .Hydroxycinnamic acids in the digestive tract of livestock and humans[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,1999,79(3):373-378.
|
| 10 |
ZHAO Z H, MOGHADASIAN M H .Chemistry,natural sources,dietary intake and pharmacokinetic properties of ferulic acid:a review[J].Food Chem,2008,109(4):691-702.
|
| 11 |
BRAUNE A, BUNZEL M, YONEKURA R,et al .Conversion of dehydrodiferulic acids by human intestinal microbiota[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(8):3356-3362.
|
| 12 |
ANSON N M, SELINHEIMO E, HAVENAAR R,et al.Bioprocessing of wheat bran improves in vitro bioaccessibility and colonic metabolism of phenolic compounds[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(14):6148-6155.
|
| 13 |
RUSSELL W R, SCOBBIE L, CHESSON A,et al .Anti-inflammatory implications of the microbial transformation of dietary phenolic compounds[J].Nutrition and Cancer-An International Journal,2008,60(5):636-642.
|
| 14 |
CELIK E E, GOKMEN V, FOGLIANO V .Soluble Antioxidant compounds regenerate the antioxidants bound to insoluble parts of foods[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(43):10329-10334.
|
| 15 |
ZHENG S L, ZHANG H, LIU R H,et al .Do short chain fatty acids and phenolic metabolites of the gut have synergistic anti-inflammatory effects? - New insights from a TNF-alpha-induced Caco-2 cell model[J].Food Res Int,2021,139:109833/1-13.
|
| 16 |
ADOM K K, LIU R H .Rapid peroxyl radical scavenging capacity (PSC) assay for assessing both hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2005,53(17):6572-6580.
|
| 17 |
WOLFE K L, LIU R H .Cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) assay for assessing antioxidants,foods,and dietary supplements[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(22):8896-8907.
|
| 18 |
FELICE D L, SUN J, LIU R H .A modified methylene blue assay for accurate cell counting[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2009,1(1):109-118.
|
| 19 |
BI H C, KRAUSZ K W, MANNA S K,et al .Optimization of harvesting,extraction,and analytical protocols for UPLC-ESI-MS-based metabolomic analysis of adherent mammalian cancer cells[J].Anal Bioanal Chem,2013,405(15):5279-5289.
|
| 20 |
ZHANG X W, ZHANG M W, DONG L H,et al .Phytochemical profile,bioactivity,and prebiotic potential of bound phenolics released from rice bran dietary fiber during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(46):12796-12805.
|
| 21 |
KIKUZAKI H, HISAMOTO M, HIROSE K,et al .Antioxidant properties of ferulic acid and its related compounds[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2002,50(7):2161-2168.
|
| 22 |
GRAF E .Antioxidant potential of ferulic acid[J].Free Radic Biol Med,1992,13(4):435-448.
|
| 23 |
AFSHARI A R, MOLLAZADEH H, HENNEY N C,et al .Effects of statins on brain tumors:a review[J].Semin Cancer Biol,2021,73:116-133.
|
| 24 |
D’ARCY M S .Cell death:a review of the major forms of apoptosis,necrosis and autophagy[J].Cell Biol Int,2019,43(6):582-592.
|
| 25 |
ELMORE S .Apoptosis:a review of programmed cell death[J].Toxicol Pathol,2007,35(4):495-516.
|
| 26 |
董雅洁,高维娟 .bcl-2、bax、caspase-3在细胞凋亡中的作用及其关系[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(21):4828-4830.
|
|
DONG Yajie, GAO Weijuan .Effect of bcl-2,bax and caspase-3 on cell apoptosis and corresponding relationship[J].Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2012,32(21):4828-4830.
|
| 27 |
WAJANT H, PFIZENMAIER K, SCHEURICH P .Tumor necrosis factor signaling[J].Cell Death Differ,2003,10(1):45-65.
|
| 28 |
OTTO T, SICINSKI P .Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2017,17(2):93-115.
|
| 29 |
JIN Y, FAN Y, YAN E Z,et al .Effects of sodium ferulate on amyloid-beta-induced MKK3/MKK6-p38 MAPK-Hsp27 signal pathway and apoptosis in rat hippocampus[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2006,27(10):1309-1316.
|