华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (8): 41-48.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210527
所属专题: 2022年食品科学与技术
湿热处理环境下咖啡酸/绿原酸对板栗淀粉消化和回生性能的影响
陈瑾 何大伟 陈玲†
- 华南理工大学 食品科学与工程学院/广东省天然产物绿色加工与产品安全重点实验室/淀粉与植物蛋白深加工 教育部工程研究中心,广东 广州 510640
Effect of Caffeic Acid/Chlorogenic Acid on Digestion and Retrogradation Properties of Chestnut Starch Under Heat-Moisture Treatment
CHEN Jin HE Dawei CHEN Ling
- School of Food Science and Engineering / Guangdong Province Key Laboratory for Green Processing of Natural Products and Product Safety / Engineering Research Center of Starch and Vegetable Protein Processing of the Ministry of Education, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, Guangdong, China
摘要:
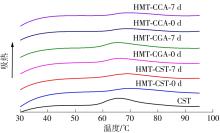
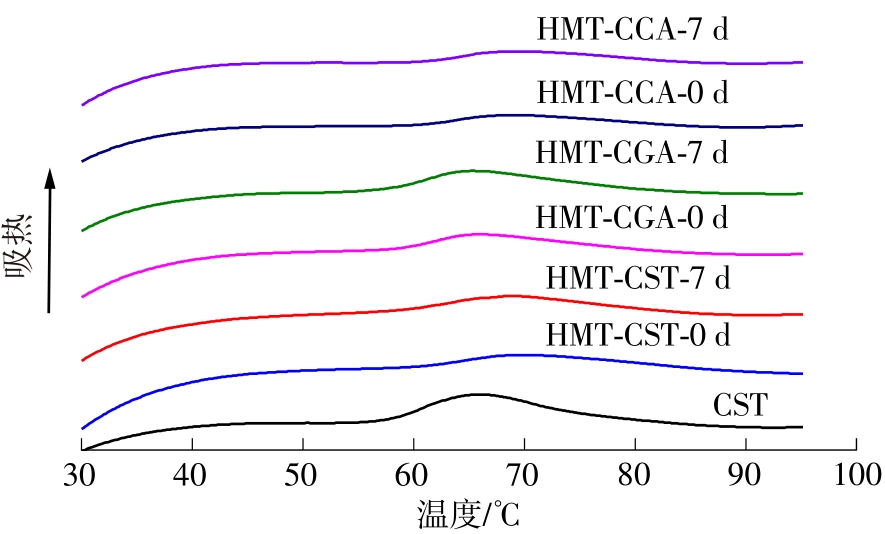
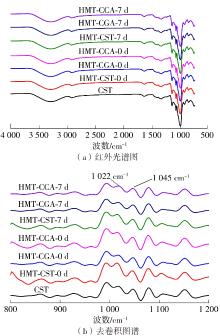
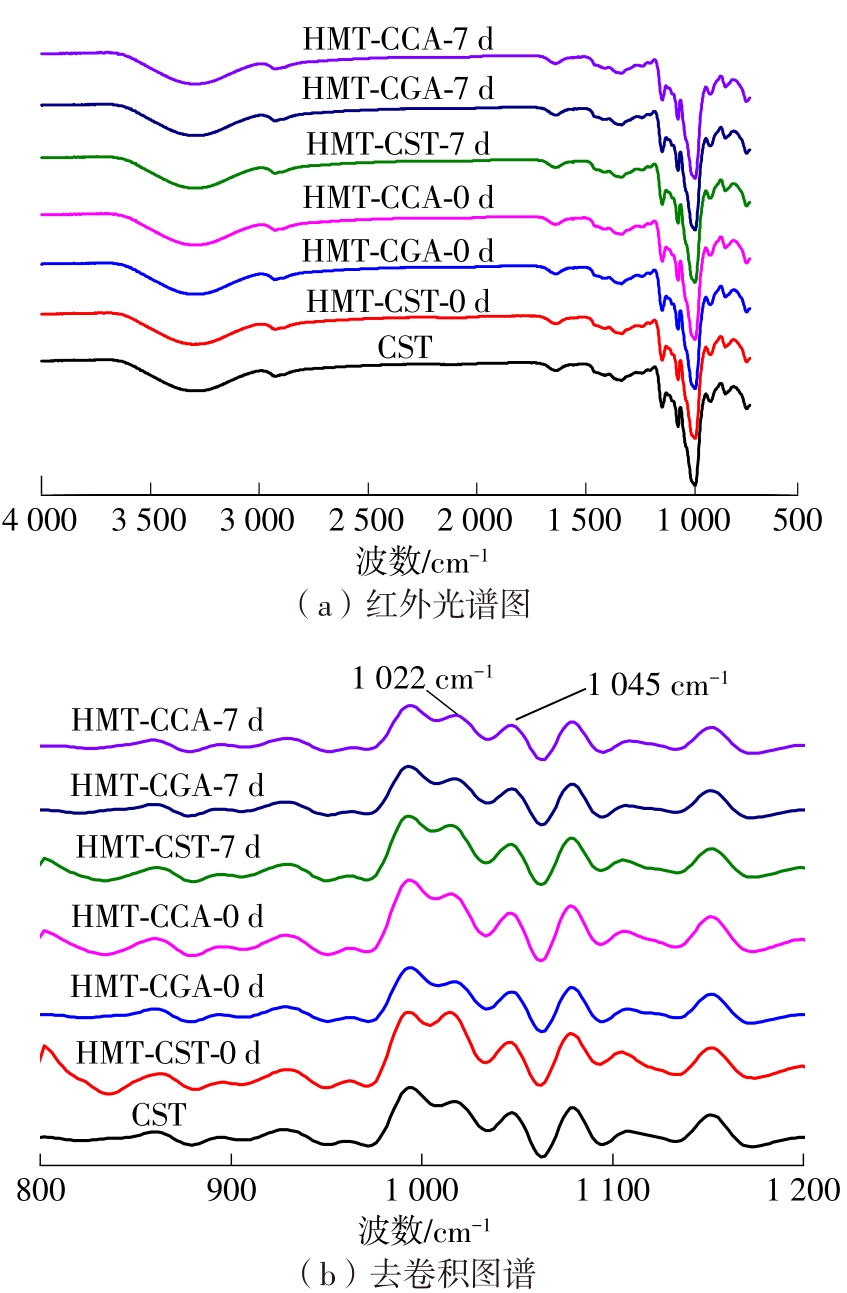
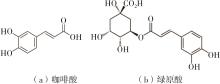
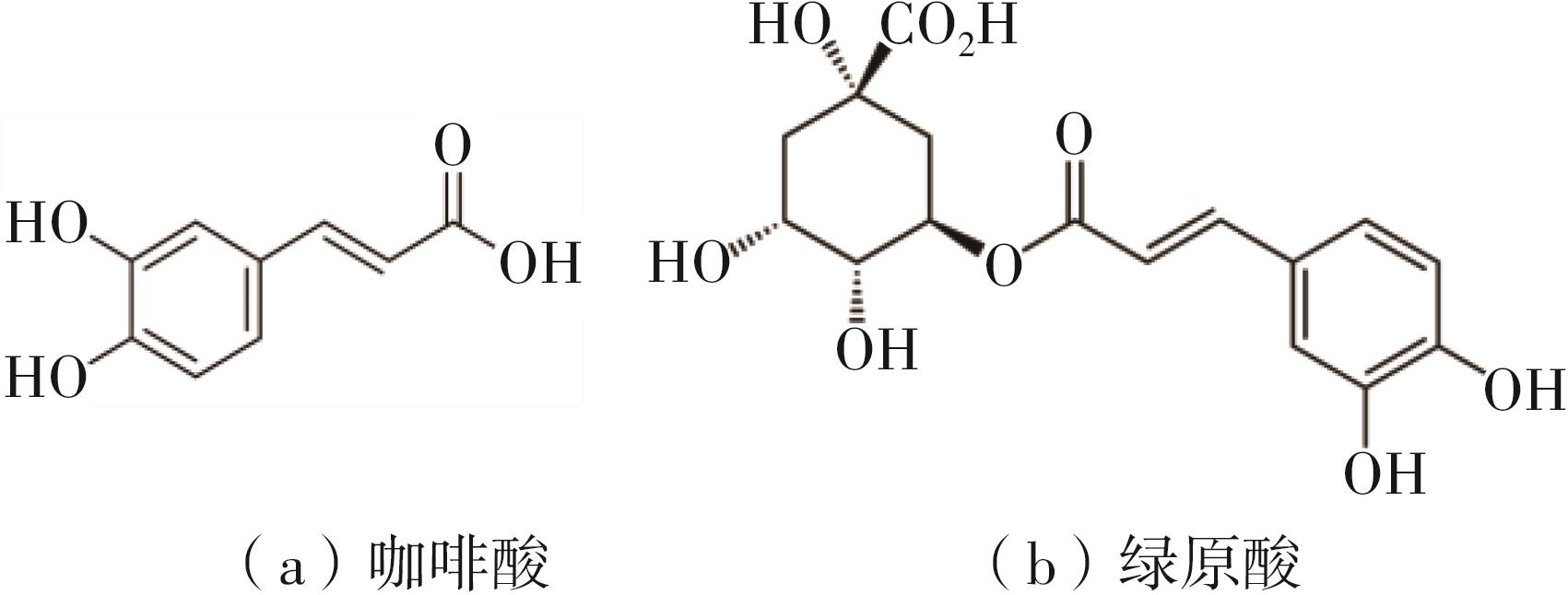
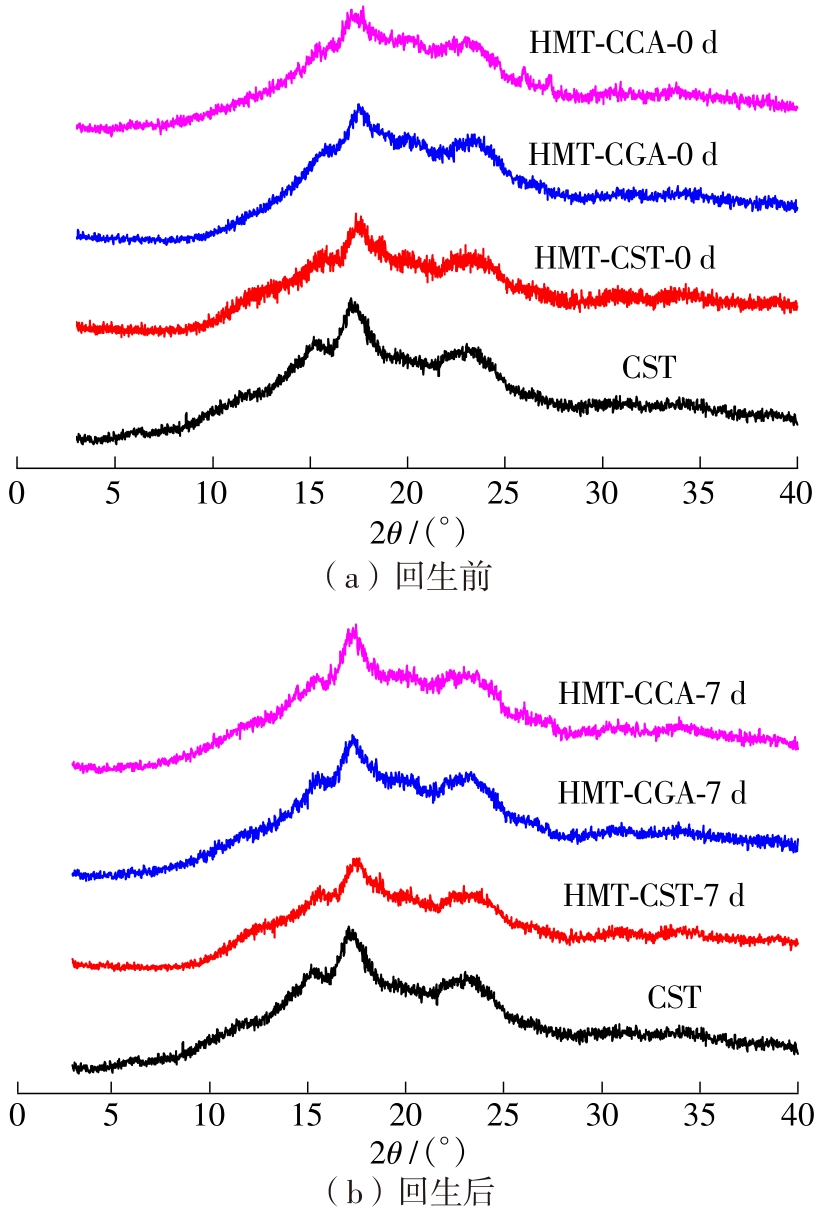
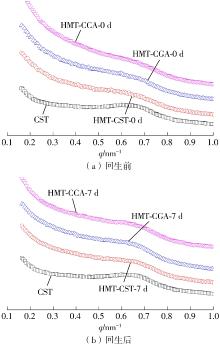
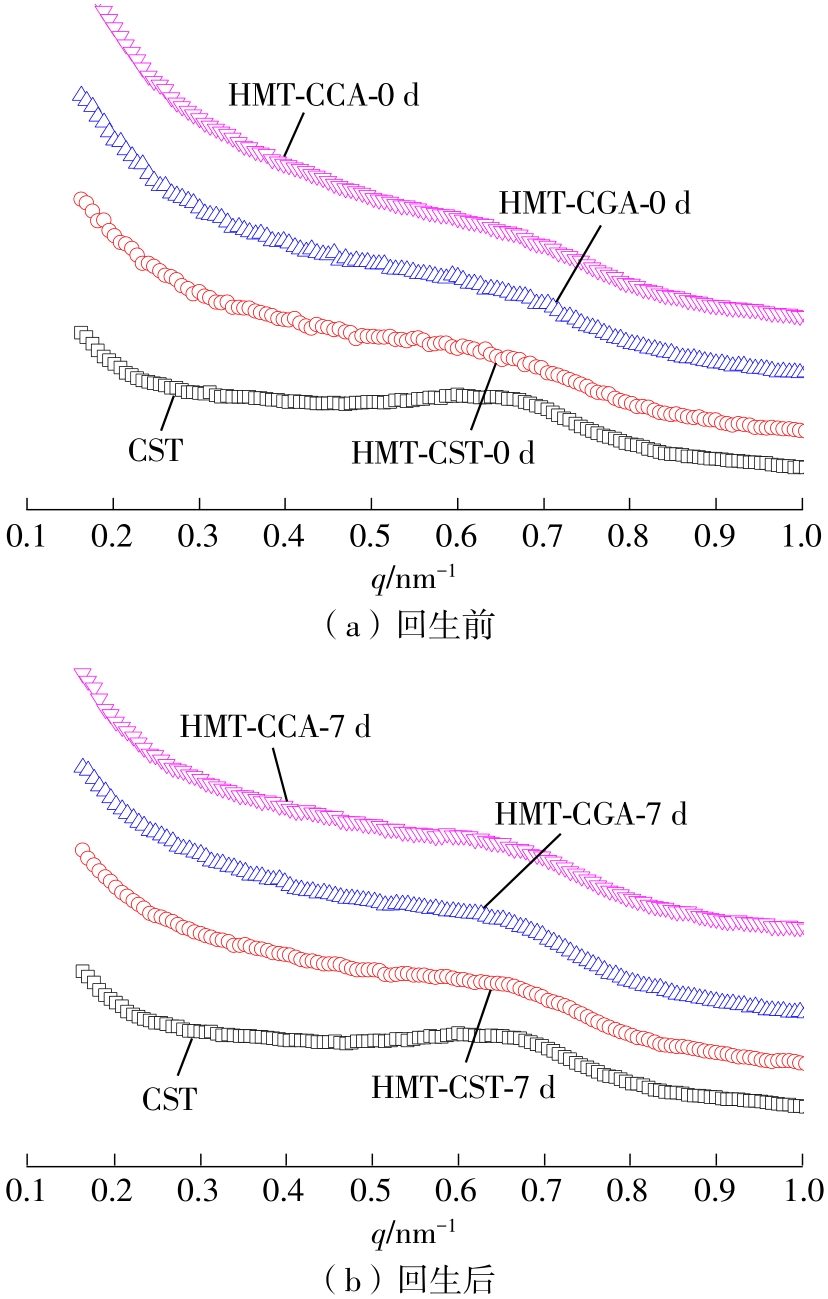
作为种植面积和产量居世界前列的我国特色经济林果实,板栗是重要的休闲食品和食品辅料之一,深受消费者青睐。但板栗中淀粉含量较高,经加工后快消化淀粉含量显著升高,容易导致人体血糖紊乱,进而增加2型糖尿病和肥胖等慢性代谢性疾病的患病风险;此外,板栗在储藏过程中存在板栗淀粉易回生的问题,影响了板栗食品的加工品质。有鉴于此,为提高板栗制品的营养功能和加工品质,采用湿热处理协同多酚复合改性板栗淀粉,利用现代分析仪器研究咖啡酸/绿原酸结构对板栗淀粉-多酚复合物多尺度结构以及消化、回生性能的影响。结果表明:在湿热处理过程中添加咖啡酸/绿原酸会显著降低板栗淀粉的消化性能,板栗淀粉、湿热处理板栗淀粉、湿热处理板栗淀粉-绿原酸复合物、湿热处理板栗淀粉-咖啡酸复合物的抗酶解成分含量分别为15.53%、17.77%、19.72%、22.73%;相比于绿原酸,分子体积更小的咖啡酸更易与板栗淀粉形成短程有序结构及V型结晶等抗酶解结构域;低温储藏7 d会促使湿热处理板栗淀粉及其多酚复合物发生回生,回生过程中淀粉分子链会聚集重排形成更多、更有序的短程有序结构和结晶结构,但总体回生现象不明显。相对于湿热处理板栗淀粉,多酚化合物的加入会阻碍淀粉分子形成长程有序结晶结构,继而抑制淀粉颗粒的回生性能,提高其储藏稳定性。其中相对于绿原酸,咖啡酸的添加使板栗淀粉同时具有良好的抗消化和抗回生性能,可为创制高品质及营养健康的板栗淀粉类食品提供新途径和技术支撑。
中图分类号: