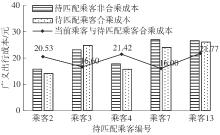
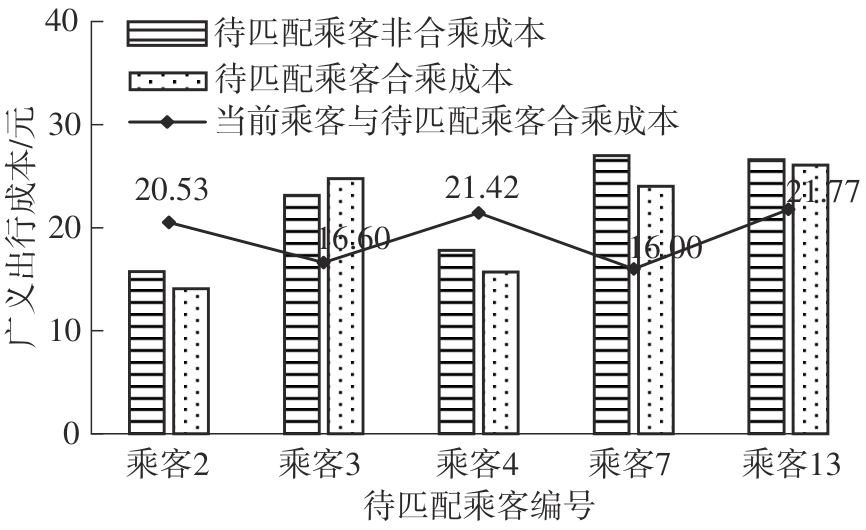
| 1 |
LI W, PU Z, LI Y,et al .Characterization of ridesplitting based on observed data:a case study of Chengdu,China[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2019,100:330-353.
|
| 2 |
LIN J, HUANG S, JIAU M .An evolutionary multiobjective carpool algorithm using set-based operator based on simulated binary crossover[J].IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics,2019,49(9):3432-3442.
|
| 3 |
ZHANG X, ZHANG X .A set-based differential evolution algorithm for QoS-oriented and cost-effective ridesharing[J].Applied Soft Computing,2020,96:106618/1-11.
|
| 4 |
BROWN A E .Who and where rideshares?Rideshare travel and use in Los Angeles[J].Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice,2020,136:120-134.
|
| 5 |
de SOUZA SILVA L A, de ANDRADE M O, ALVES MAIA M L .How does the ride-hailing systems demand affect individual transport regulation?[J].Research in Transportation Economics,2018,69(SI):600-606.
|
| 6 |
缪格,袁鹏程 .基于优化遗传算法的网约车合乘模型[J].计算机系统应用,2022,31(12):287-293.
|
|
Ge MIU, YUAN Peng-cheng .Ride-sharing model of online car-hailing based on optimized genetic algorithm[J].Computer Systems & Applications,2022,31(12):287-293.
|
| 7 |
曹弋,周泽禹,李金洋 .考虑驾乘人员公平性的网约出租车合乘路径优化模型[J].控制理论与应用,2022,39(7):1281-1288.
|
|
CAO Yi, ZHOU Ze-yu, LI Jin-yang .Optimization model of ride-sharing path for taxis online considering passenger fairness[J].Control Theory & Applications,2022,39(7):1281-1288.
|
| 8 |
JIAO G P, RAMEZANI M .Incentivizing shared rides in e-hailing markets:dynamic discounting[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2022,144:103879/1-19.
|
| 9 |
FENG H, RUICHUN H, SENGBIN Y,et al .Research on optimization model of taxi-carpooling expenses based on the passengers’ personalized demand[C]∥ Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS2015).WuHan:IEEE,2015:246-249.
|
| 10 |
李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,等 .网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J].吉林大学学报(工学版),2022,52(3):578-584.
|
|
LI Xing-hua, FENG Fei-yu, CHENG Cheng,et al .Choice preference analysis and modeling of ridesplitting service[J].Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2022,52(3):578-584.
|
| 11 |
ZHANG H, ZHAO J .Mobility sharing as a preference matching problem[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2019,20(7):2584-2592.
|
| 12 |
薛守强,宋瑞,安久煜,等 .感知乘客心理的出租车动态合乘优化方法[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21(2):205-210,250.
|
|
XUE Shouqiang, SONG Rui, AN Jiuyu,et al .Dynamic shared taxi optimization method considering passengers perceptions[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021,21(2):205-210,250.
|
| 13 |
王志建,郭健,张强.考虑乘客信任程度的营运车辆合乘线路规划[J].计算机应用研究,2023,40(4):996-999.
|
|
WANG Zhijian, GUO Jian, ZHANG Qiang .Planning of ride-sharing routes for operating vehicles considering degree of passenger trust[J].Application Research of Computers,2023,40(4):996-999.
|
| 14 |
彭子烜,魏然,单文轩,等 .基于稳定匹配的网约车合乘优化[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2023,42(12):106-112.
|
|
PENG Zixuan, WEI Ran, SHAN Wenxuan,et al .Ride sharing optimization based on stable matching [J].Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science),2023,42(12):106-112.
|
| 15 |
贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽 .终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J].吉林大学学报(工学版),2022,52(3):564-571.
|
|
JIA Hong-fei, SHAO Zi-han, YANG Li-li .Ride⁃sharing matching model and algorithm of online car-hailing under condition of uncertain destination[J].Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2022,52(3):564-571.
|
| 16 |
MOHAMED M J,RYE T, FONZONE A .Operational and policy implications of ridesourcing services:a case of uber in London,UK[J].Case Studies on Transport Policy,2019,7(4):823-836.
|
| 17 |
彭子烜,崔林,郭志伟,等 .网约车合乘均衡匹配与激励策略[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2024,52(2):95-103.
|
|
PENG Zixuan, CUI Lin, GUO Zhiwei,et al .Taxi-sharing matching equilibrium under peer-passenger incentive mechanism [J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2024,52(2):95-103.
|
| 18 |
袁振洲,陈思媛,吴玥琳,等 .考虑行驶时间不确定性的合乘路径鲁棒优化方法[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2022,22(5):233-242.
|
|
YUAN Zhen-zhou, CHEN Si-yuan, WU Yue-lin,et al .Robust optimization of carpooling routing problem under travel time uncertainty[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2022,22(5):233-242.
|
| 19 |
宗刚,曾庆华,魏素豪 .基于时间价值的交通出行方式选择行为研究[J].管理工程学报,2020,34(3):142-150.
|
|
ZONG Gang, ZENG Qinghua, WEI Suhao .Research on traffic mode choice behavior based on commuting ravel time value[J].Journal of Industrial Engineering/ Engineering Management,2020,34(3):142-150.
|
| 20 |
汪景,邵雨晨,胡华,等 .快慢车模式下早高峰时空乘车路径选择研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2024,24(2):225-233.
|
|
WANG Jing, SHAO Yuchen, HU Hua,et al .Spatio-temporal ride path selection in morning peak for express-local trains[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2024,24(2):225-233.
|
| 21 |
赵明钰,吕军威 .基于灰色关联度理论的合乘出行意愿影响因素分析[J].物流工程与管理,2023,45(3):111-114,135.
|
|
ZHAO Ming-yu, LV Jun-wei .Analysis of influencing factors of carpooling willingness based on grey relational theory[J].Logistics Engineering and Management,2023,45(3):111-114,135.
|
| 22 |
张薇,何瑞春,肖强,等 .考虑乘客心理的出租车合乘决策方法研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2015,15(2):17-23.
|
|
ZHANG Wei, HE Rui-chun, XIAO Qiang,et al .A method of taxi pooling mode decision-making with passenger psycholog[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2015,15(2):17-23.
|
| 23 |
倪亚洲,薛运强,刘彤,等 .基于非集计模型的公交票价弹性研究[J].交通标准化,2013(11):66-67.
|
|
NI Ya-zhou, XUE Yun-qiang, LIU Tong,et al .Study of bus fare elasticities based on disaggregate model[J].Traffic Engineering,2013(11):66-67.
|
 ), ZHAI Manrong, WANG Yuanze, MAO Jianxu
), ZHAI Manrong, WANG Yuanze, MAO Jianxu