华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 116-126.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240256
硝酸盐基中低温储热相变材料的制备及热物性调控
安周建, 李璐, 毛帅, 刘立功, 杜小泽, 张东
- 兰州理工大学 能源与动力工程学院,甘肃 兰州 730050
-
收稿日期:2024-05-27出版日期:2025-03-25发布日期:2024-08-23 -
作者简介:安周建(1990—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事储能材料及储能技术研究。E-mail: anzhoujian@lut.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(52206087);甘肃省重点研发计划项目(23YFGA0066);甘肃省教育厅产业支撑计划项目(2022CYZC-21);兰州理工大学博士科研启动经费项目(061907);兰州理工大学红柳优秀青年人才资助项目
Preparation and Thermal Property Regulation of Nitrates Based Phase Change Material for Low and Medium Temperature Thermal Energy Storage
AN Zhoujian, LI Lu, MAO Shuai, LIU Ligong, DU Xiaoze, ZHANG Dong
- School of Energy and Power Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,Gansu,China
-
Received:2024-05-27Online:2025-03-25Published:2024-08-23 -
About author:安周建(1990—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事储能材料及储能技术研究。E-mail: anzhoujian@lut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52206087);the Key R & D Program of Gansu Province(23YFGA0066);the Industrial Support Plan Project of Gansu Provincial Education;Department(2022CYZC-21)
摘要:
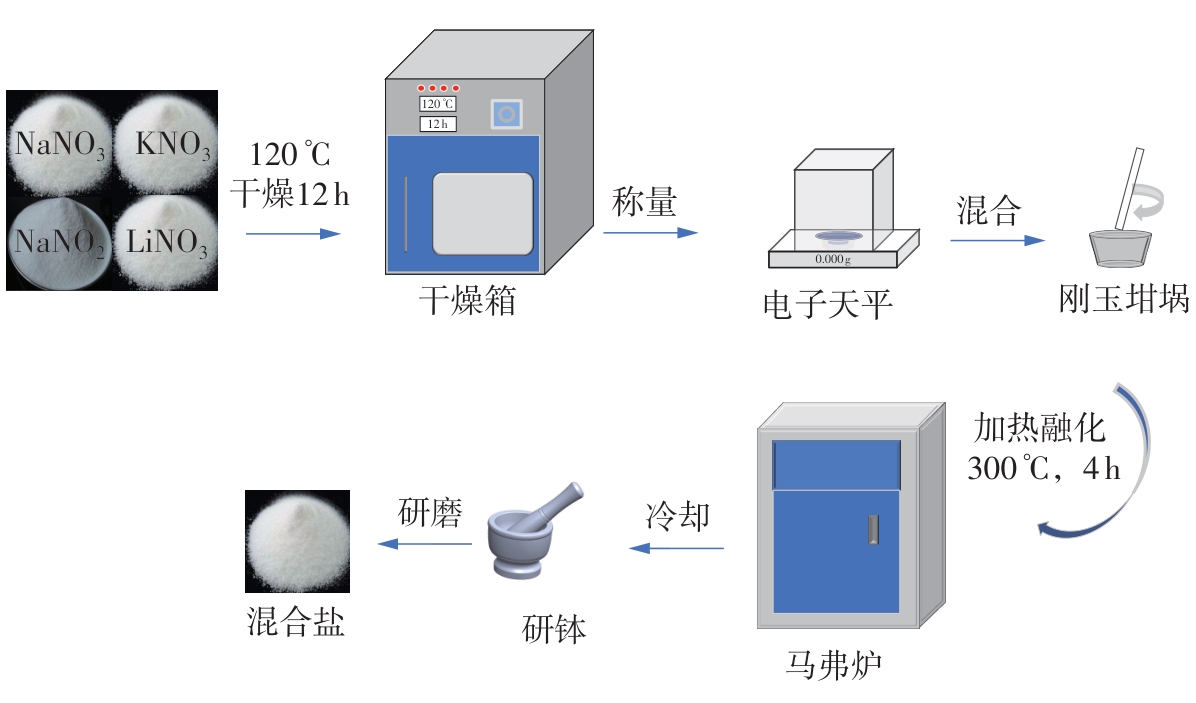
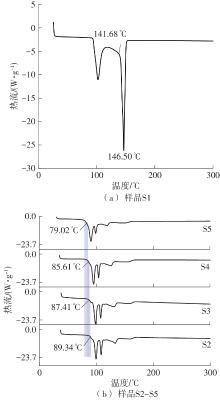
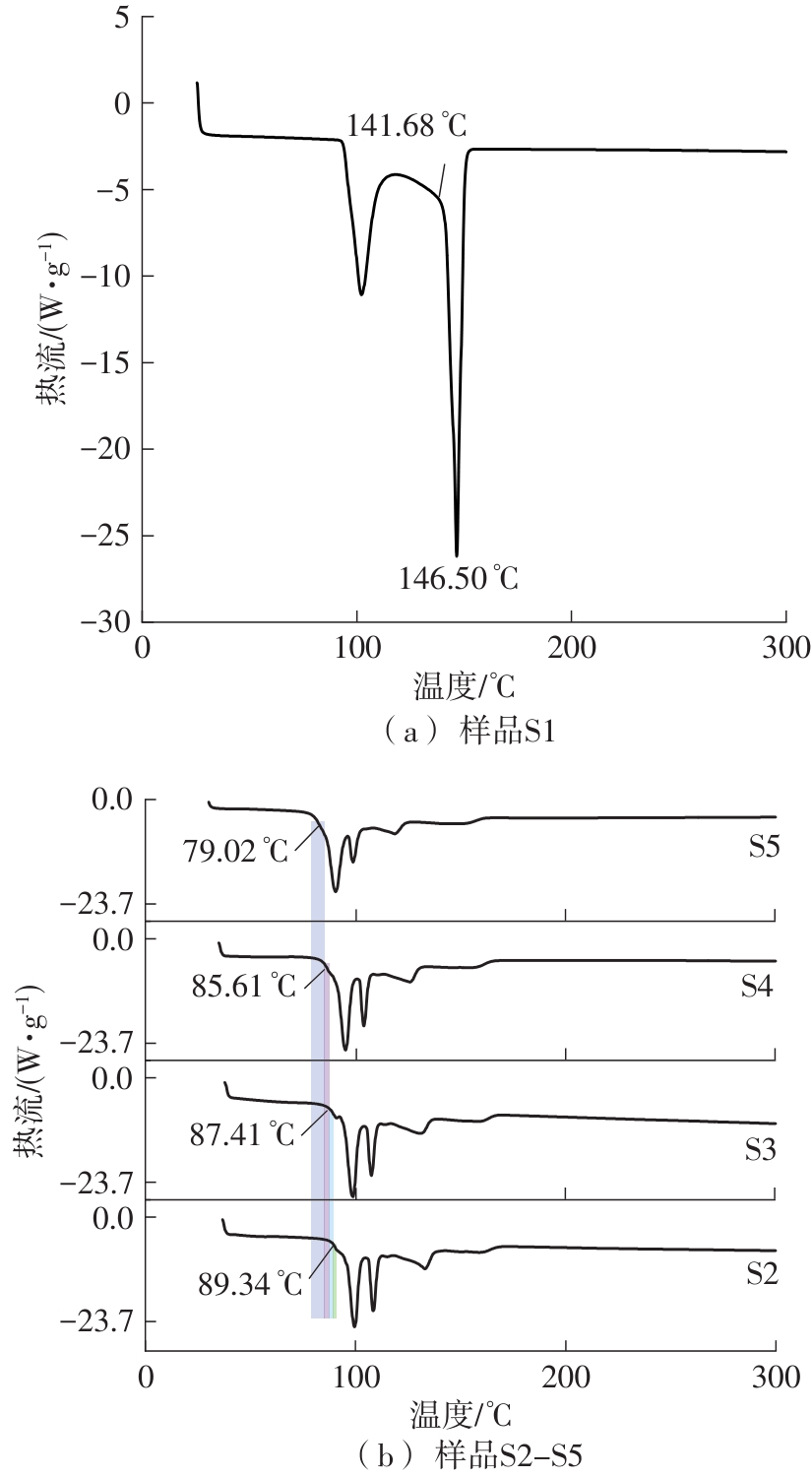
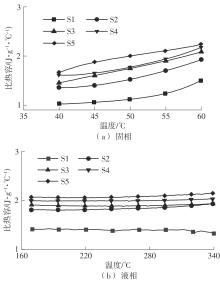
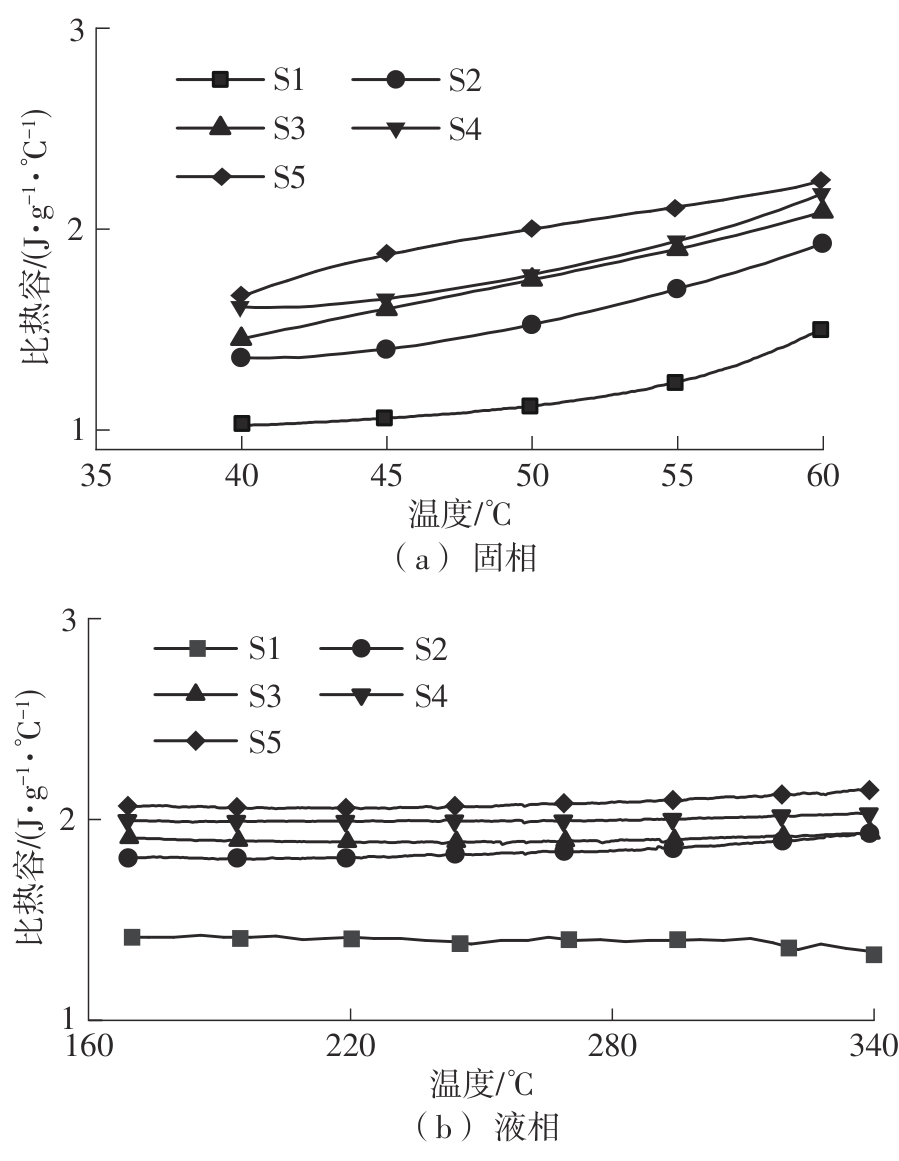
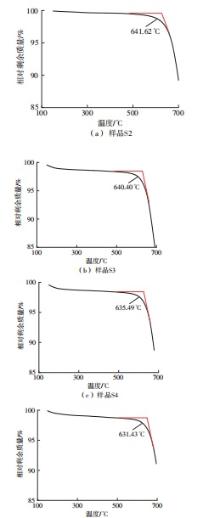
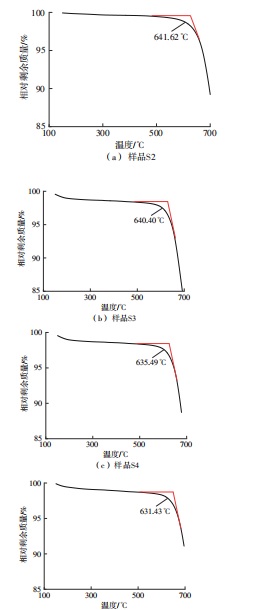
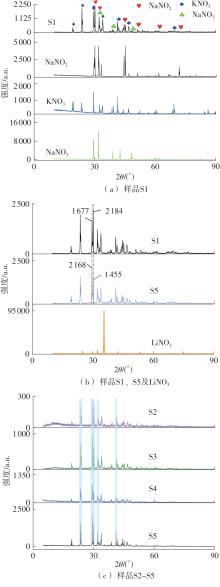
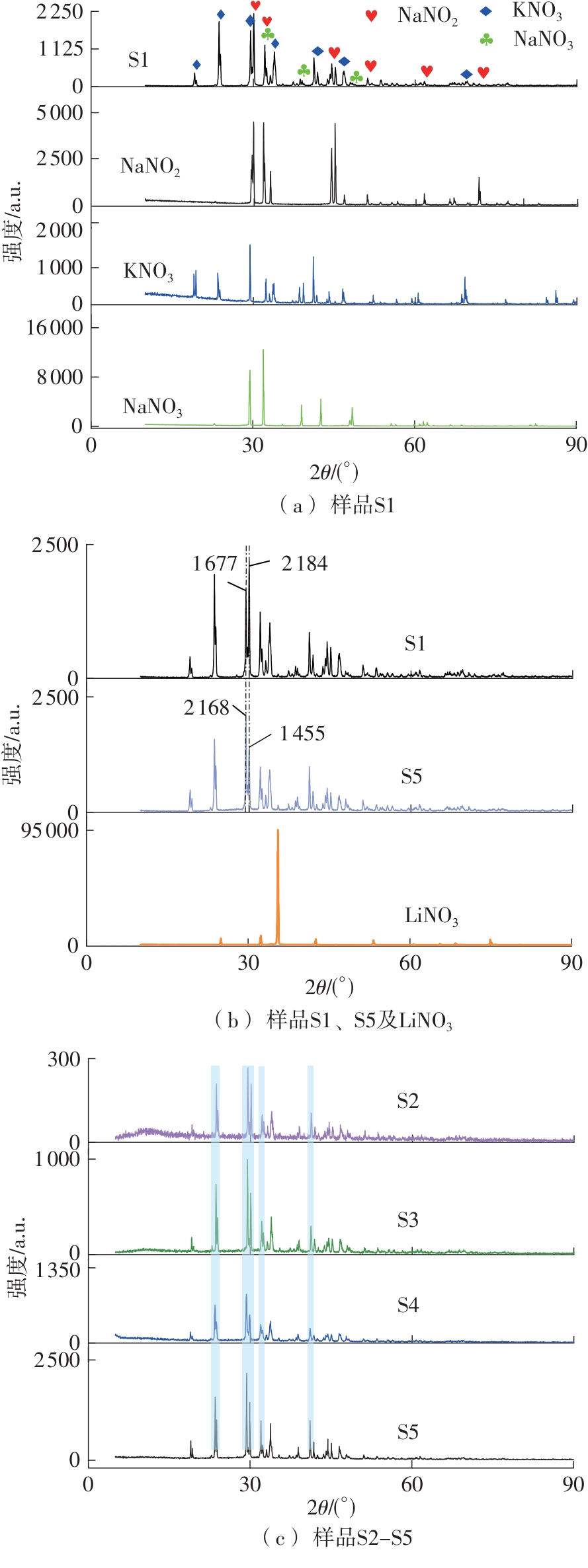
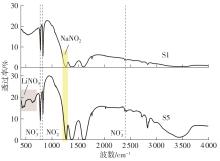
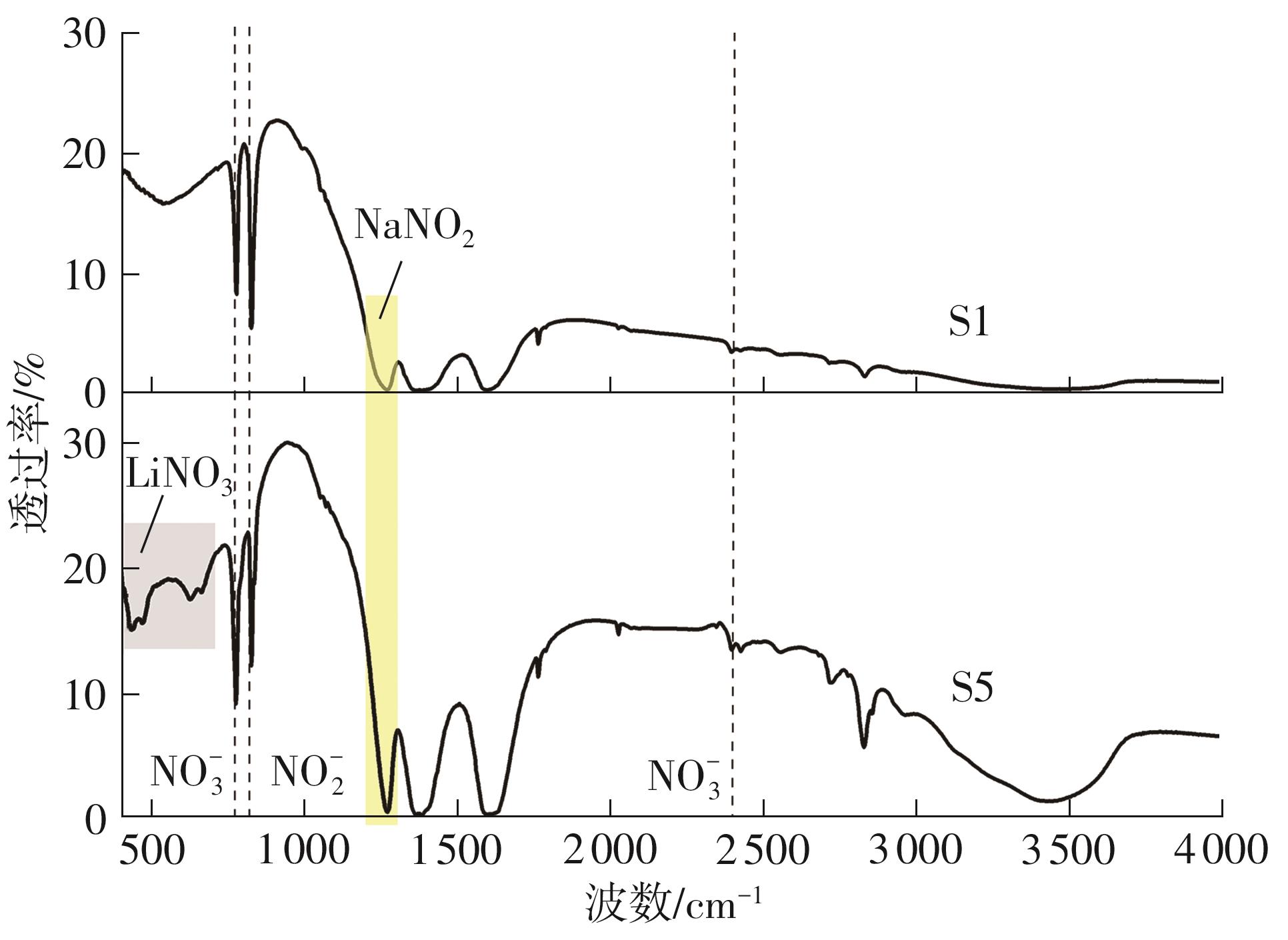
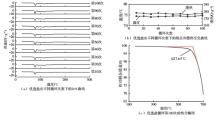
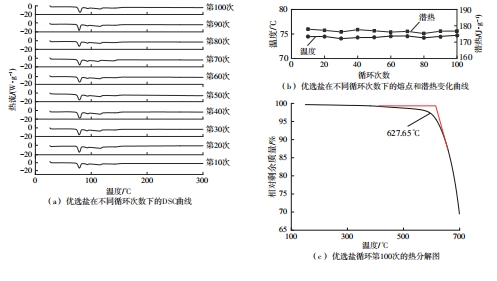
利用相变材料储热的方法对工业领域中低温余热进行回收、储存以及再利用,是实现能源梯次利用,提高能源利用效率的重要方法。相变材料的物性是决定储热系统性能的关键因素。因此,开发具有适宜相变温度、高低温循环稳定性较好的相变材料,对于实现高效余热回收具有重要的意义。基于此,该文采用静态熔融法,合成了一种新的相变材料NaNO3-KNO3-NaNO2-LiNO3,通过差热分析、热重分析、X射线衍射分析、傅里叶变换红外光谱分析等方法,对该材料的熔点、潜热、比热容和循环稳定性等热物理性能进行了一系列表征,筛选出配比m(NaNO3)∶m(KNO3)∶m(NaNO2)∶m(LiNO3) = 6.32∶47.83∶36.10∶9.75的熔盐作为最终的优选盐。实验结果表明:优选盐具有显著的性能优势,其熔点低至79.02 ℃,潜热为176.71 J/g,固相和液相的平均比热容分别为1.96和2.09 J/(g·℃),分解温度达到600 ℃以上,展现出宽温度范围的适用性;经过100次高低温循环测试后,优选盐仍表现出良好的热循环稳定性。该研究为中低温余热回收及储热系统提供了一种新型的相变储能材料,对相关领域的能源优化和节能减排具有重要的意义。
中图分类号:
引用本文
安周建, 李璐, 毛帅, 刘立功, 杜小泽, 张东. 硝酸盐基中低温储热相变材料的制备及热物性调控[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 53(3): 116-126.
AN Zhoujian, LI Lu, MAO Shuai, LIU Ligong, DU Xiaoze, ZHANG Dong. Preparation and Thermal Property Regulation of Nitrates Based Phase Change Material for Low and Medium Temperature Thermal Energy Storage[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(3): 116-126.
| 1 | 黄晟,王静宇,郭沛,等 .碳中和目标下能源结构优化的近期策略与远期展望[J].化工进展,2022,41(11):5695-5708. |
| HUANG Sheng, WANG Jingyu, GUO Pei,et al .Short-term strategy and long-term prospect of energy structure optimization under carbon neutrality target[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2022,41(11):5695-5708. | |
| 2 | ALVA G, LIU L, HUANG X,et al .Thermal energy storage materials and systems for solar energy applications[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2017,68:693-706. |
| 3 | 魏小兰,林国庆,丁静,等 .硝酸熔盐纳米流体比热容提高的模拟与实验研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(9):46-55. |
| WEI Xiaolan, LIN Guoqing, DING Jing,et al .Simulation and experiment investigation into specific heat capacity enhancement of nitrate molten salt nanofluid[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2021,49(9):46-55. | |
| 4 | ZHOU Y, LI J, WANG G,et al .Assessing the short-to medium-term supply risks of clean energy minerals for China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,215:217-225. |
| 5 | ZHANG Z, DING T, ZHOU Q,et al .A review of technologies and applications on versatile energy storage systems[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2021,148:111263/1-31. |
| 6 | DELOVATO N, SUNDARNATH K, CVIJOVIC L,et al .A review of heat recovery applications for solar and geothermal power plants[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2019,114:109329/1-19. |
| 7 | WOOLLEY E, LUO Y, SIMEONE A .Industrial waste heat recovery:a systematic approach[J].Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments,2018,29:50-59. |
| 8 | DADI D, INTRONA V, BENEDETTI M .Decarbonization of heat through low-temperature waste heat recovery:proposal of a tool for the preliminary evaluation of technologies in the industrial sector[J].Sustainability,2022,14(19):12626/1-28. |
| 9 | GIORDANO L, BENEDETTI M .A methodology for the identification and characterization of low-temperature waste heat sources and sinks in industrial processes:application in the Italian dairy sector[J].Energies,2022,15:155/1-33. |
| 10 | 吴玉庭,任楠,马重芳 .熔融盐显热蓄热技术的研究与应用进展[J].储能科学与技术,2013,2(6):586-592. |
| WU Yuting, REN Nan, MA Chongfang .Research and application of molten salts for sensible heat storage[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2013,2(6):586-592. | |
| 11 | MAGENDRAN S S, KHAN F S A, Mubarak N M,et al .Synthesis of organic phase change materials (PCM) for energy storage applications:a review[J].Nano-Structures and Nano-Objects,2019,20:100399/1-18. |
| 12 | 何媚质,杨鲁伟,张振涛 .有机-无机复合相变材料的研究进展[J].化工进展,2018,37(12):4709-4718. |
| HE Meizhi, YANG Luwei, ZHANG Zhentao .Research progress of organic-inorganic composite phase change materials[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2018,37(12):4709-4718. | |
| 13 | KALIDASAN B, PANDEY A K, SAIDUR R,et al .Nano additive enhanced salt hydrate phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J].International Materials Reviews,2023,68(2):140-183. |
| 14 | LIN Y, ALVA G, FANG G .Review on thermal performances and applications of thermal energy storage systems with inorganic phase change materials[J].Energy,2018,165:685-708. |
| 15 | PAN G, WEI X, YU C,et al .Thermal performance of a binary carbonate molten eutectic salt for high-temperature energy storage applications[J].Applied Energy,2020,262:114418/1-12. |
| 16 | HUA H, YASUDA K, KONISHI H,et al .Electrochemical formation of Nd-Ni alloys in molten CaCl2-NdCl3 [J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2021,168(3):032506/1-6. |
| 17 | 左芳菲,韩伟,姚明宇 .熔盐储能在新型电力系统中应用现状与发展趋势[J].热力发电,2023,52(2):1-9. |
| ZUO Fangfei, HAN Wei, YAO Mingyu .Application status and development trend of molten salt energy sto-rage in novel power systems[J].Thermal Power Ge-neration,2023,52(2):1-9. | |
| 18 | NAZIR H, BATOOL M, OSORIO F J B,et al .Recent developments in phase change materials for energy storage applications:a review[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2019,129:491-523. |
| 19 | HAMEED G, GHAFOOR M A, YOUSAF M,et al .Low temperature phase change materials for thermal energy storage:current status and computational per-spectives[J].Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments,2022,50:101808/1-22. |
| 20 | 张灿灿,吴玉庭,鹿院卫 .低熔点混合硝酸熔盐的制备及性能分析[J].储能科学与技术,2020,9(2):435-439. |
| ZHANG Cancan, WU Yuting, LU Yuanwei .Preparation and comparative analysis of thermophysical properties on low melting point mixed nitrate molten salts[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2020,9(2):435-439. | |
| 21 | SHI H, ZHOU H, MENG H,et al .Analysis of flowing and heat transfer of commercial molten nitrate in porous foundation material[J].Journal of Thermal Science,2023,32(4):1455-1465. |
| 22 | LU W, LIU G, XIONG Z,et al .An experimental investigation of composite phase change materials of ternary nitrate and expanded graphite for medium-temperature thermal energy storage[J].Solar Energy,2020,195:573-580. |
| 23 | ZHANG P, CHENG J, JIN Y,et al .Evaluation of thermal physical properties of molten nitrate salts with low melting temperature[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2018,176:36-41. |
| 24 | WANG Q, YANG L, SONG J .Preparation,thermal conductivity,and applications of nano-enhanced phase change materials (NEPCMs) in solar heat collection:a review[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2023,63:107047/1-33. |
| 25 | ZHU J, LENG G, YE F,et al .Form-stable LiNO3-NaNO3-KNO3-Ca(NO3)2/calcium silicate composite phase change material (PCM) for mid-low temperature thermal energy storage[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2015,106:165-172. |
| 26 | FERNÁNDEZ A G, USHAK S, GALLEGUILLOS H,et al .Thermal characterisation of an innovative quaternary molten nitrate mixture for energy storage in CSP plants[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2015,132:172-177. |
| 27 | BONK A, BRAUN M, BAUER T .Phase diagram,thermodynamic properties and long-term isothermal stability of quaternary molten nitrate salts for thermal energy storage[J].Solar Energy,2022,231:1061-1071. |
| 28 | BROSSEAU D, KELTON J W, Det al RAY .Testing of thermocline filler materials and molten-salt heat transfer fluids for thermal energy storage systems in parabolic trough power plants[J].Journal of Solar Energy Engineering,2005,127(1):109-116. |
| 29 | CHRISTENSEN A N, NORBY P, HANSON J C,et al .Phase transition of KNO3 monitored by synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction[J].Journal of Applied Crystallography,1996,29(3):265-269. |
| 30 | WANG T, MANTHA D, REDDY R G .Novel low melting point quaternary eutectic system for solar thermal energy storage[J].Applied Energy,2013,102:1422-1429. |
| 31 | LI L, YU H, WANG X,et al .Thermal analysis of melting and freezing processes of phase change materials (PCMs) based on dynamic DSC test[J].Energy and Buildings,2016,130:388-396. |
| 32 | KWASI-EFFAH C C, EGWARE H O, OBANOR A I,et al .Development and characterization of a quaternary nitrate based molten salt heat transfer fluid for concentrated solar power plant[J].Heliyon,2023,9(5):e16096/1-12. |
| 33 | 崔贤岱 .熔融盐相变材料分子动力学模拟研究[D].武汉:武汉理工大学,2022. |
| 34 | NARESH G, RAJASEKHAR A, BHARALI J,et al .Homogeneous molten salt formulations as thermal energy storage media and heat transfer fluid[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2022,50:104200/1-8. |
| 35 | REN N, WU Y, MA C,et al .Preparation and thermal properties of quaternary mixed nitrate with low mel-ting point[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2014,127:6-13. |
| 36 | JIN Y, CHENG J, AN X,et al .Accurate viscosity measurement of nitrates/nitrites salts for concentrated solar power[J].Solar Energy,2016,137:385-392. |
| 37 | RAZZAGHPANAH Z, SARUNAC N .Natural convection heat transfer from a bundle of heated circular cylinders with staggered arrangement immersed in molten solar salt[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2020,156:119900/1-15. |
| 38 | AHMAD N N B, YUNOS N B, MUHAMMAD W N A B W,et al .Effect of lithium nitrate and calcium nitrate composition on the thermal properties of quaternary molten salts mixture for heat transfer application[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2017,914:012027/1-9. |
| 39 | ALJAERANI H A, SAMYKANO M, PANDEY A K,et al .Thermophysical properties enhancement and characterization of CuO nanoparticles enhanced HITEC molten salt for concentrated solar power applications[J].International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer,2022,132:105898/1-9. |
| 40 | XIONG Y, WANG Z, XU P,et al .Experimental investigation into the thermos-physical properties by dispersing nanoparticles to the nitrates[J].Energy Procedia,2019,158:5551-5556. |
| 41 | BONK A,SAU S, URANGA N,et al .Advanced heat transfer fluids for direct molten salt line-focusing CSP plants[J].Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2018,67:69-87. |
| 42 | TULIMON M F, MUHAMMAD W N A W, MOHAMAD M N A,et al .Characterization and thermal properties of nitrate based molten salt for heat reco-very system[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2017,914:012016/1-6. |
| 43 | 何聪,鹿院卫,宋文兵,等 .新型相同钠离子混合熔盐相图预测及物性测量[J].储能科学与技术,2021,10(5):1729-1734. |
| HE Cong, LU Yuanwei, SONG Wenbing,et al.The phase diagram prediction and experimental study of ternary same cation systems[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2021,10(5):1729-1734. | |
| 44 | RAADE J W, PADOWITZ D .Development of molten salt heat transfer fluid with low melting point and high thermal stability[J].Journal of Solar Energy Engineering,2011,133(3):031013/1-6. |
| 45 | QIAN T, LI J, MIN X,et al .Diatomite:a promi-sing natural candidate as carrier material for low,middle and high temperature phase change material[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2015,98:34-45. |
| 46 | LIN Q, XU Y, YANG X,et al .Thermal stability and microstructure of sodium nitrite in multicomponent molten salts:an experimental analysis[J].Solar Energy,2024,283:113008/1-10. |
| 47 | 倪海欧,孙泽,路贵民,等 .NaNO3-KNO3-NaNO2三元混合相变熔盐结构与物性的分子动力学模拟[J].储能科学与技术,2017,6(4):669-674. |
| NI Haiou, SUN Ze, LU Guimin,et al .Molecular dynamics simulation of structure and physical properties of NaNO3-KNO3-NaNO2 ternary phase-change molten salts [J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2017,6(4):669-674. | |
| 48 | OROZCO M A, ACURIO K, VÁSQUEZ-AZA F .Thermal storage of nitrate salts as phase change mate-rials (PCMs)[J].Materials,2021,14:7223/1-18. |
| [1] | 楼波, 周达恒, 夏骏. 氯化镧的脱水/吸附反应动力学分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(8): 71-79. |
| [2] | 魏小兰, 林国庆, 丁静, 等. 硝酸熔盐纳米流体比热容提高的模拟与实验研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(9): 46-55. |
| [3] | 曹贤武, 韦创, 何光建, 等. 四元共聚热塑性聚酰亚胺的合成与表征[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(4): 73-79. |
| [4] | 李亚军 张锦文. 低温相变蓄冷材料热物性的高精度预测模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(9): 131-138. |
| [5] | 廖俊旭 鲁浩 戴康徐 曹华 赵鸿斌 韩利芬 徐勇军 方玉堂. 含氮润滑油添加剂的摩擦学性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(7): 70-78. |
| [6] | 李静 陈旭阳 雷汝白 张定 樊春雷. Bi-In-Sn-Sb四元合金界面材料热性能研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(11): 39-46. |
| [7] | 肖新颜 张登科. 异佛尔酮二异氰酸酯改性蒙脱土改性沥青的性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(2): 116-121. |
| [8] | 殷素红 高凡 郭辉 杨旭. 石灰重构钢渣过程中的物相变化[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(6): 47-52. |
| [9] | 肖新颜 张登科 晏英 朱文强. 有机蒙脱土/环氧树脂改性沥青材料的性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(2): 139-143,150. |
| [10] | 高学农 胡小冬 陈思婷 方玉堂. 五水硫代硫酸钠相变蓄热材料的制备[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 42(2): 8-13,20. |
| [11] | 刘述梅 冯猛 孙志松 赵建青 袁彦超. 螺环-双环笼状磷酸酯的合成与性质[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 42(10): 25-30. |
| [12] | 叶君 李文浩 熊犍. 低pH 值下DACMC 的制备、结构及热性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(6): 127-132. |
| [13] | 肖新颜 蔡锡松 万彩霞. 交联型 FSiPUA 乳液的制备及涂膜性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(10): 13-19. |
| [14] | 高学农 李得伦 孙滔 曹昕 何文祥. 石蜡/膨胀石墨复合相变材料控温电子散热器的性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(1): 7-12. |
| [15] | 李辉 付时雨 彭林才 詹怀宇. 漆酶的层层自组装固定化及其酶学性质[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(9): 158-164. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||