华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 52-59.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.250014
基于纵向摩擦测试模型的水泥刻槽路面抗滑性能
张大伟1, 叶俊涛1, 谢志禹2
- 1.浙江大学 结构工程研究所,浙江 杭州 310058
2.浙江科技大学 土木与建筑工程学院,浙江 杭州 310023
Skid Resistance of Cement Concrete Grooved Pavements Based on a Longitudinal Friction Testing Model
ZHANG Dawei1, YE Juntao1, XIE Zhiyu2
- 1.Institute of Structural Engineering,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
2.School of Civil Engineering and Architecture,Zhejiang University of Science and Technology,Hangzhou 310023,Zhejiang,China
摘要:
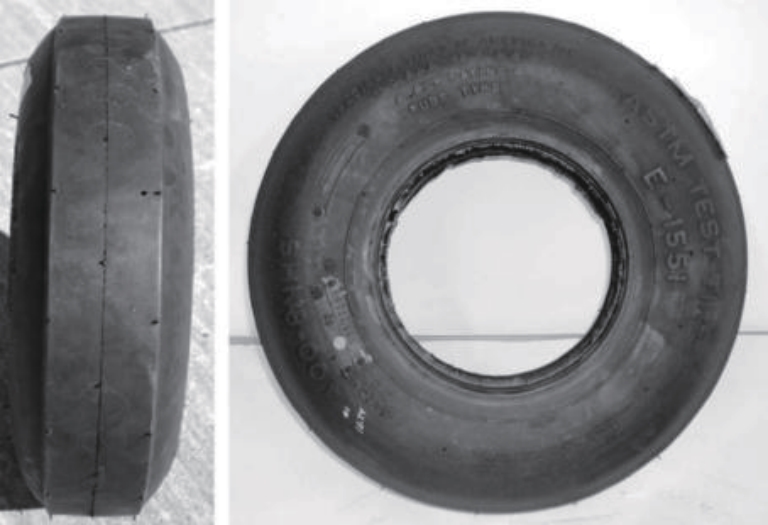
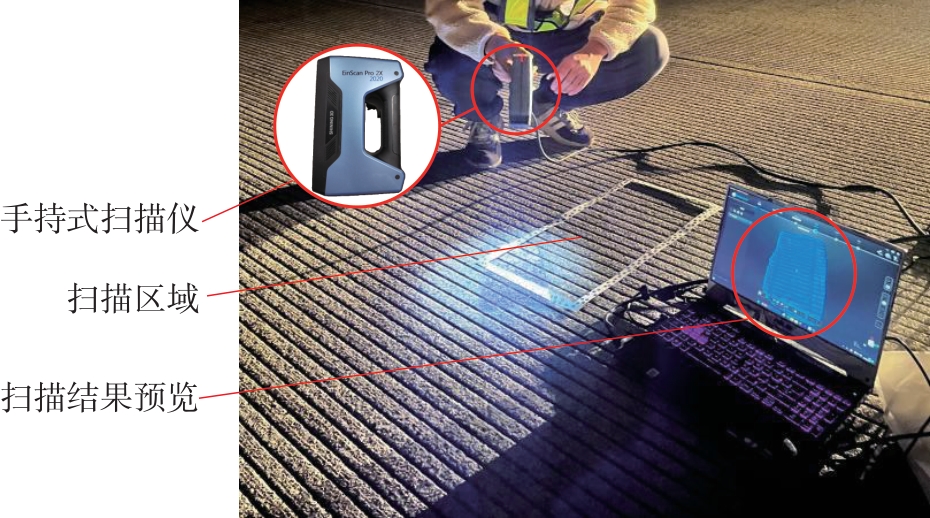
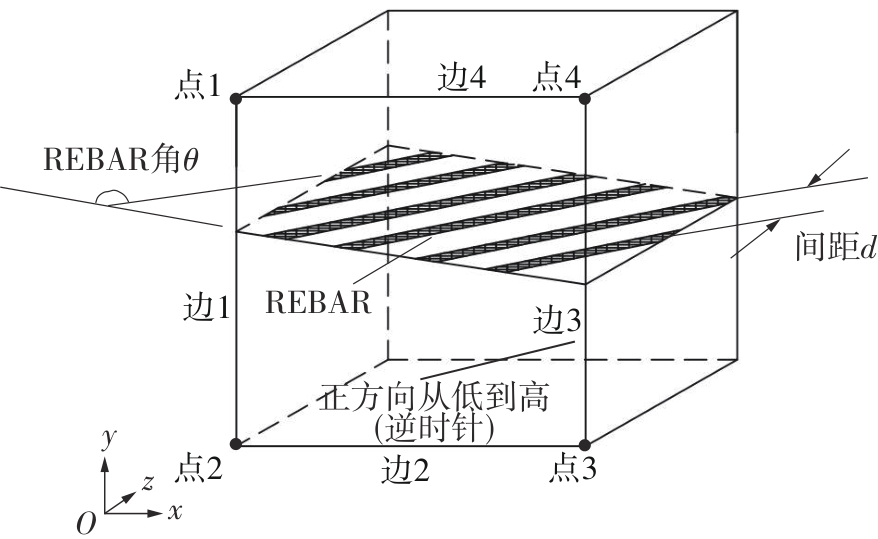
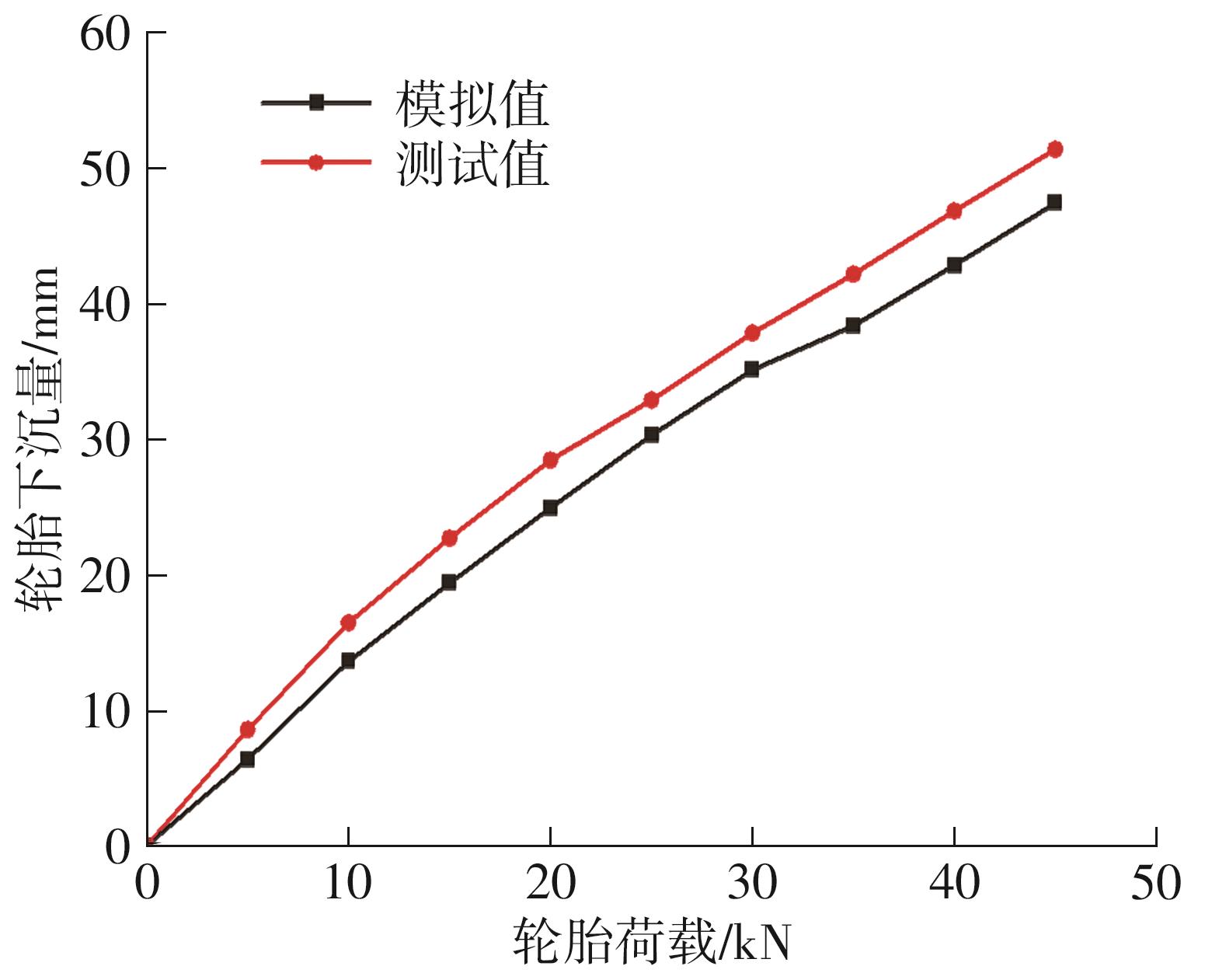
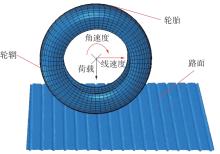
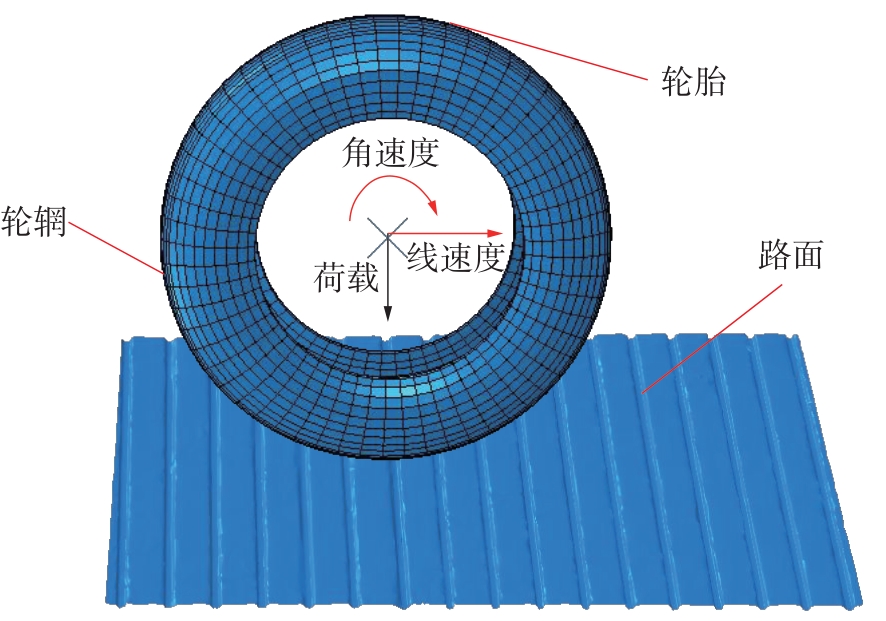
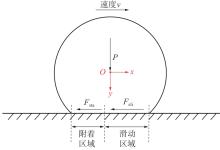
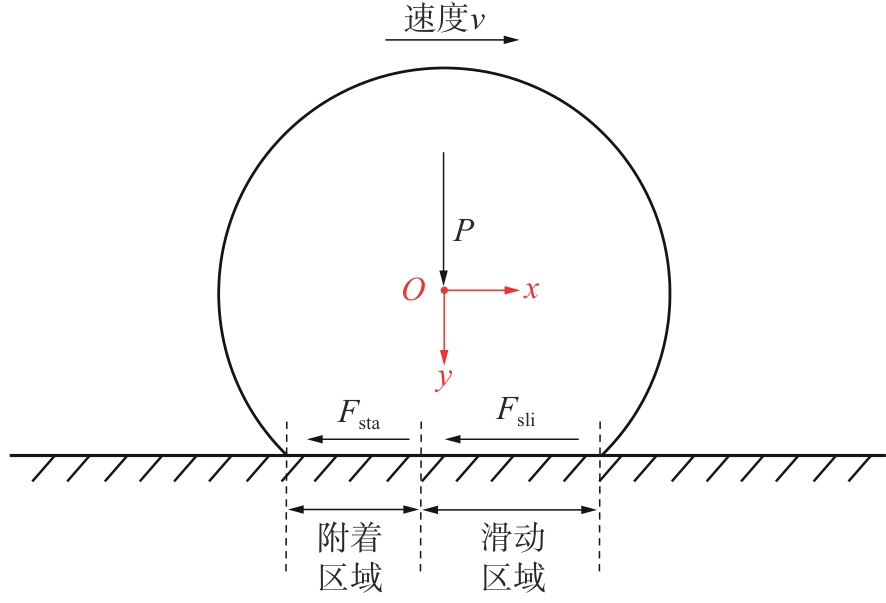
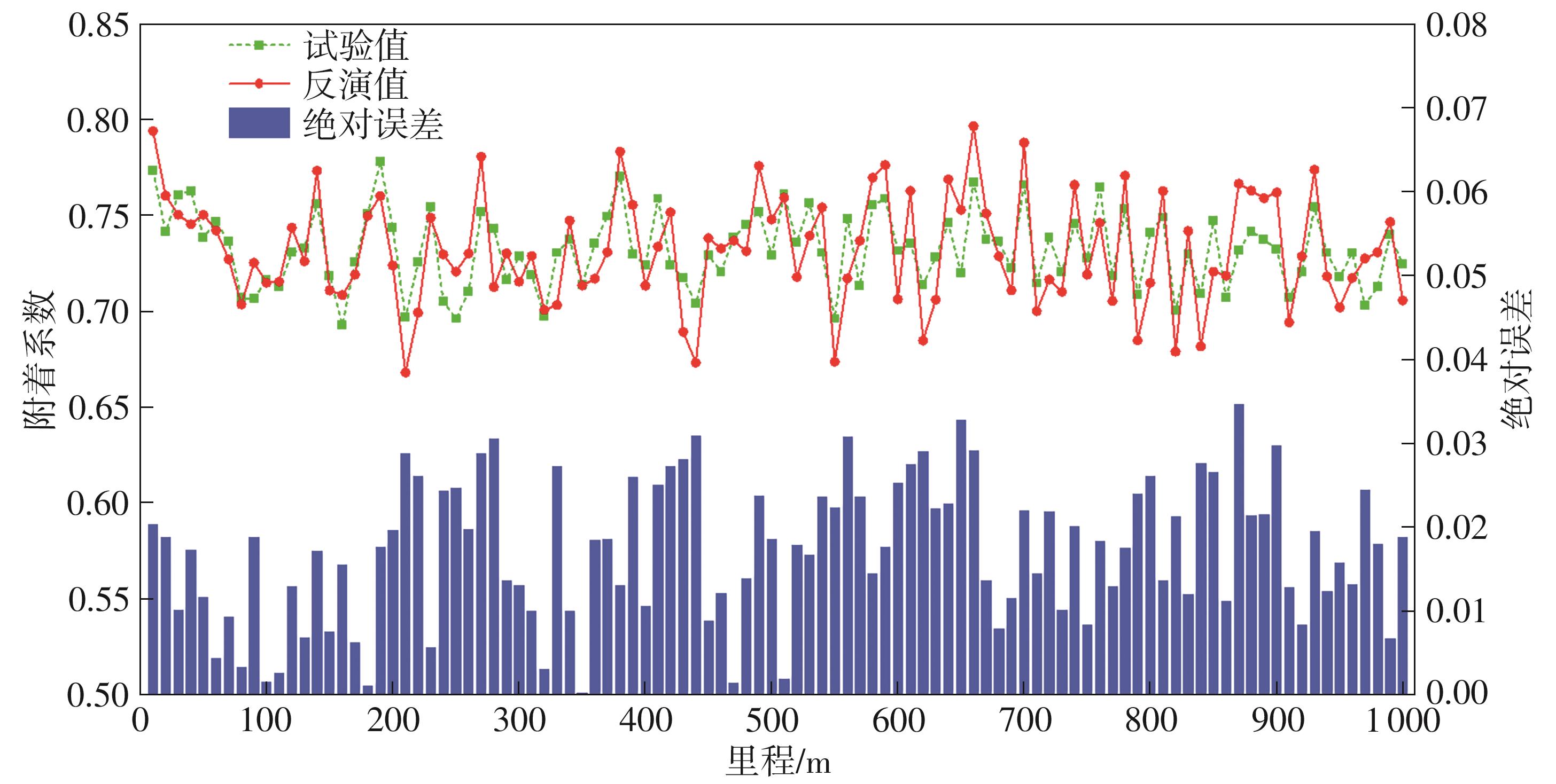
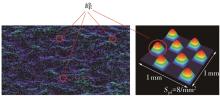
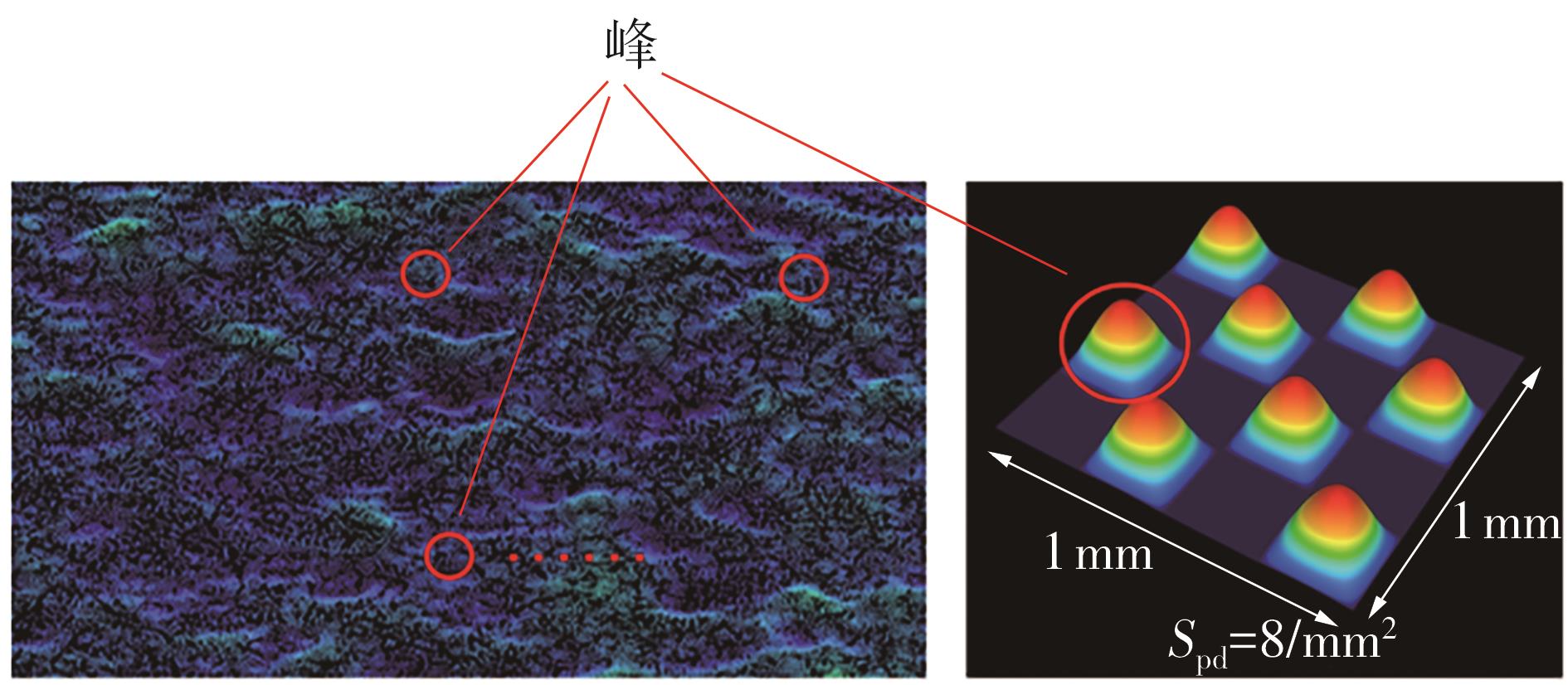
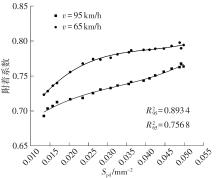
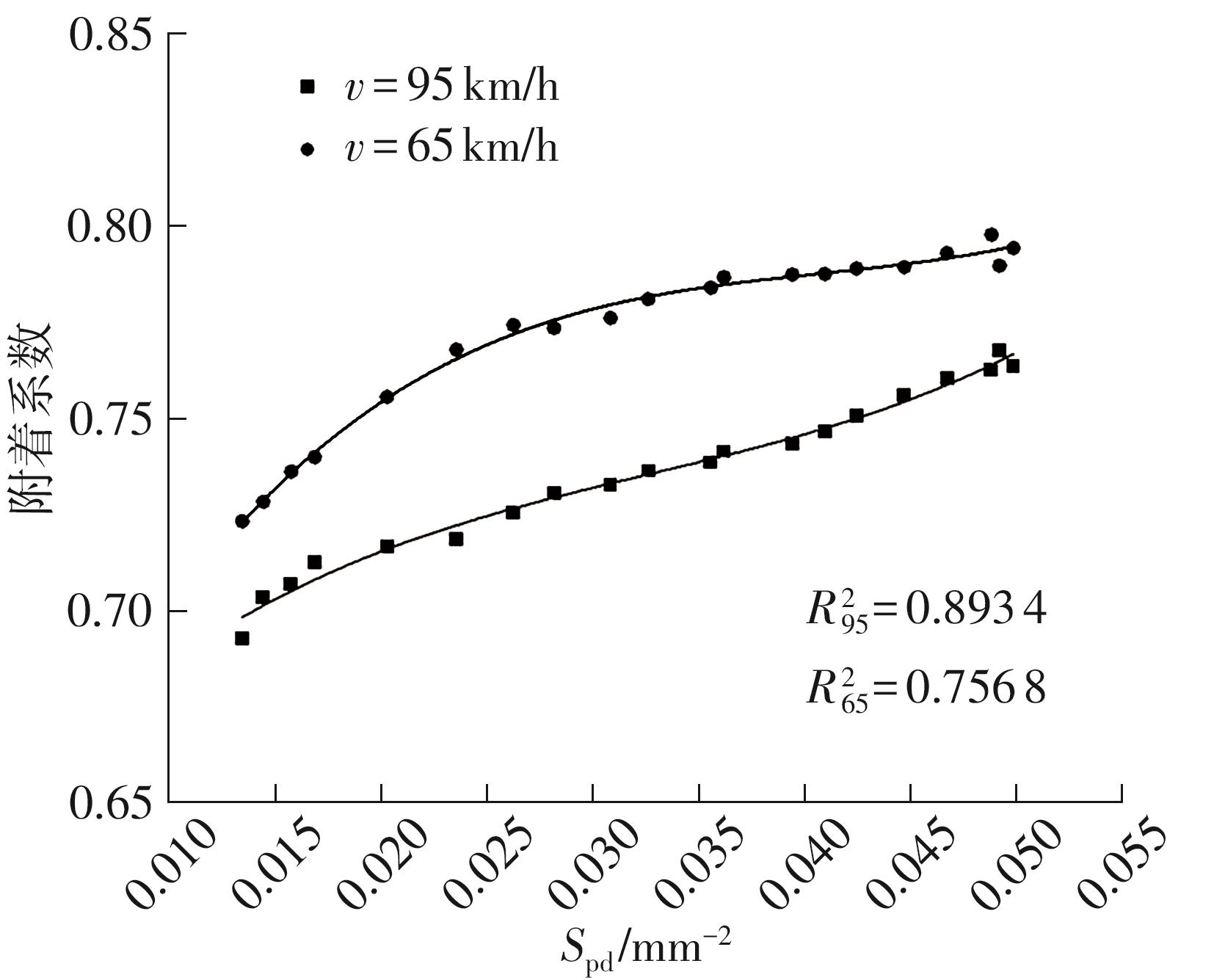
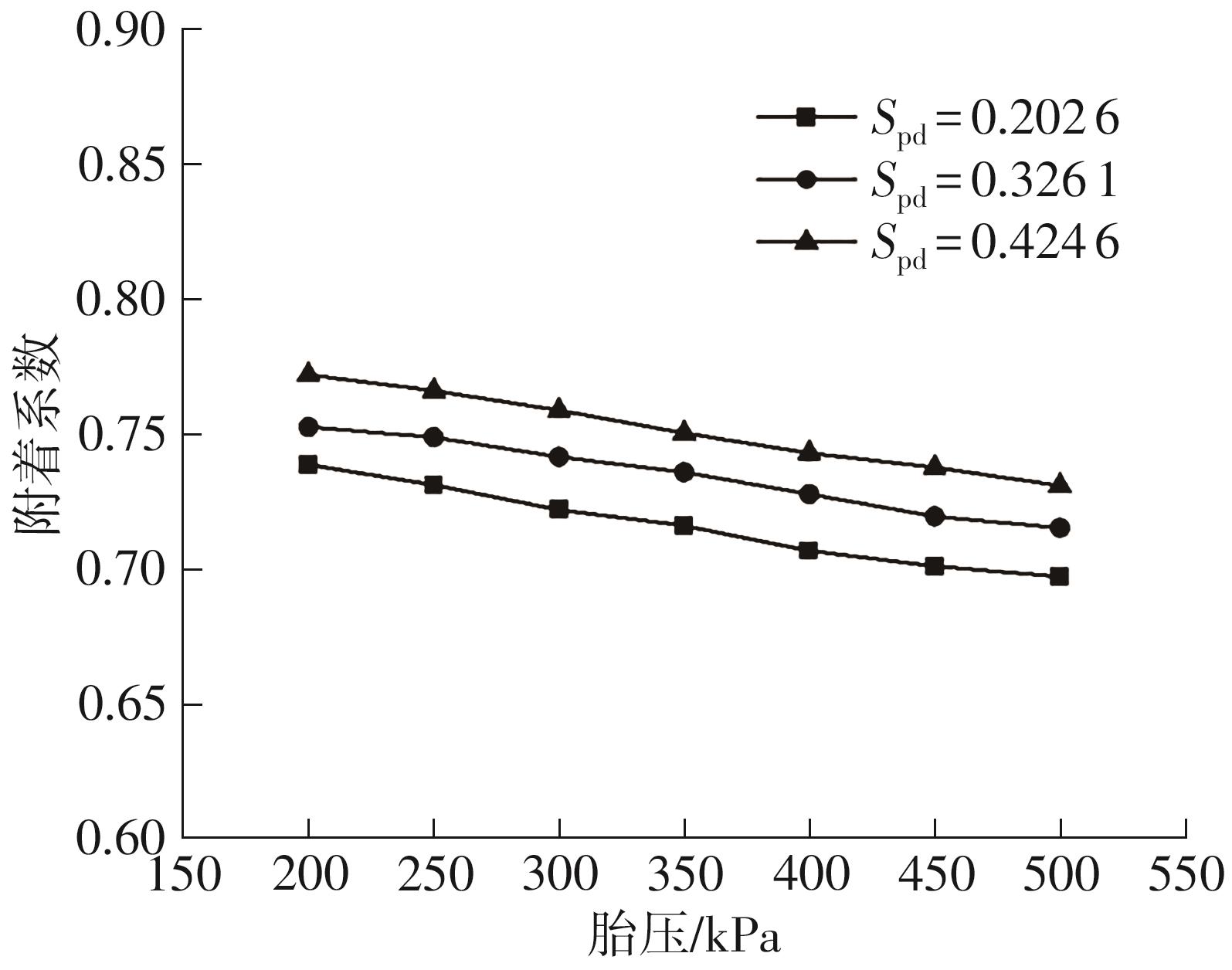
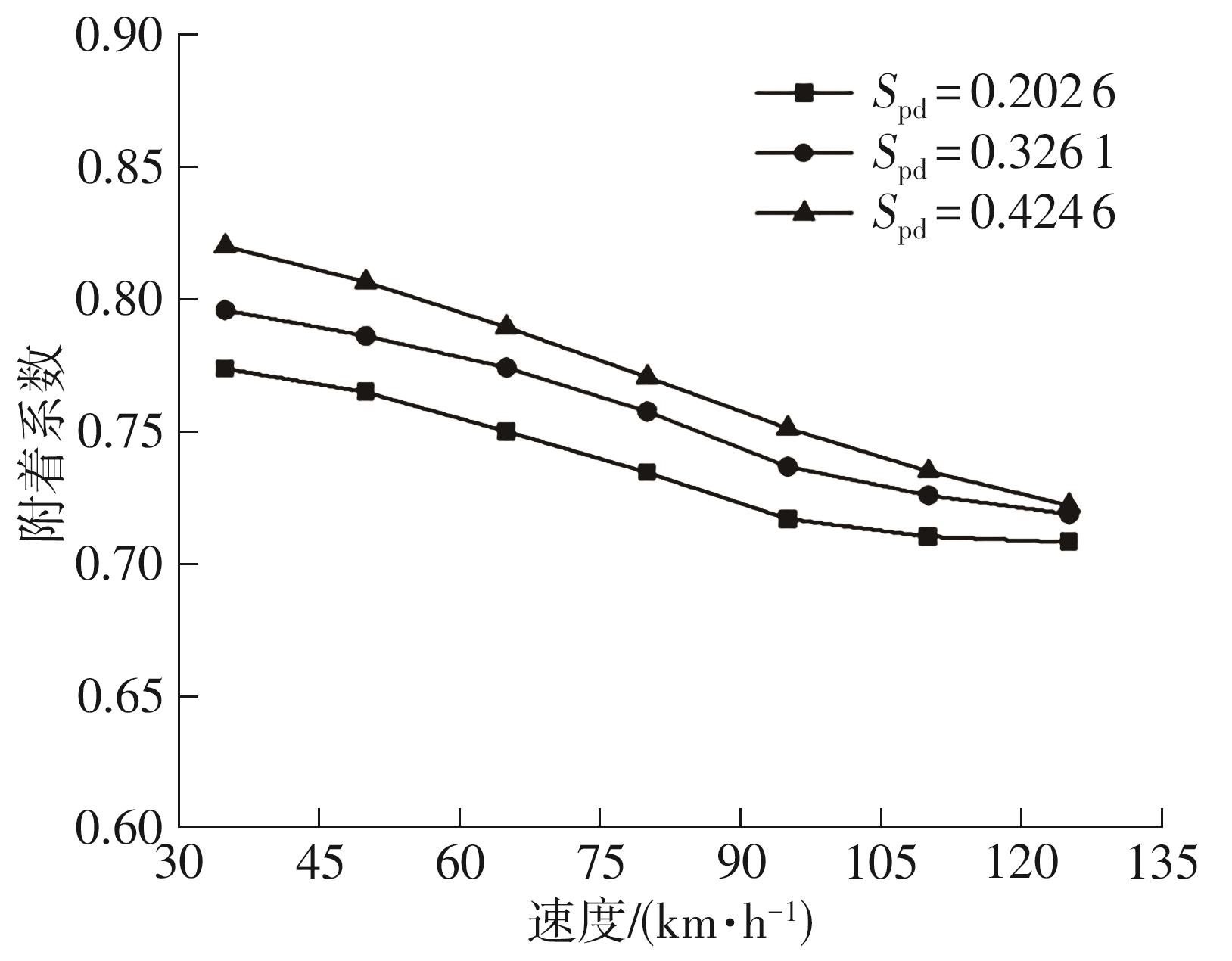
探明路面和轮胎因素与抗滑性能间的相互关系,对于降低因路面抗滑性能不足引发的交通事故率具有重要的意义。通过现场标准测试获得100个真实水泥混凝土刻槽路面测点的三维点云数据以及对应附着系数,并经过水平校正和降噪处理后逆向建模,建立了保留路面纹理的路面模型。然后,根据规范建立了纵向摩擦测试使用的光滑轮胎几何结构,根据厂家提供的数据建立材料模型,在Abaqus中装配建立轮胎-路面模型,通过与静压实验实验数据对比,验证轮胎模型的有效性。最后,通过对比有限元反演值与试验测量值,验证了模型的有效性,分析了路面纹理、胎压、速度对路面抗滑性能的影响。结果表明:该研究建立的轮胎模型能够反映真实工况,建立的轮胎-路面模型能够精准估计路面的附着系数,绝对误差低于0.05;随着路面峰顶点密度(Spd)的增大,附着系数在高速和低速状态下均呈现上升趋势,且低速时受Spd的影响更为显著;随着轮胎胎压的上升,各个测试点的附着系数均存在较为一致的下降趋势,附着系数降低幅度差异不显著。相较于速度,轮胎胎压对附着系数的影响较不显著;随着速度的升高,路面附着系数趋于稳定值,该稳定附着系数由路面的宏观纹理决定,而速度本身对附着系数的影响则相对有限。
中图分类号: