华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 79-86.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240112
所属专题: 2024年力学
沥青组分与废木油相互作用行为的分子模拟
- 1.大连海事大学 交通运输工程学院,辽宁 大连 116026
2.密歇根理工大学 土木与环境工程学院,密歇根 霍顿 MI499 31
Molecular Simulation of Interaction Behavior Between Asphalt Components and Waste Wood Oil
ZHENG Zhi1( ), GUO Naisheng1(
), GUO Naisheng1( ), YOU Zhanping2
), YOU Zhanping2
- 1.College of Transportation Engineering,Dalian Maritime University,Dalian 116026,Liaoning,China
2.Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,Michigan Technological University,Houghton MI499 31,Michigan,USA
摘要:
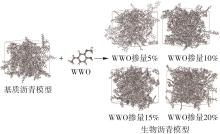
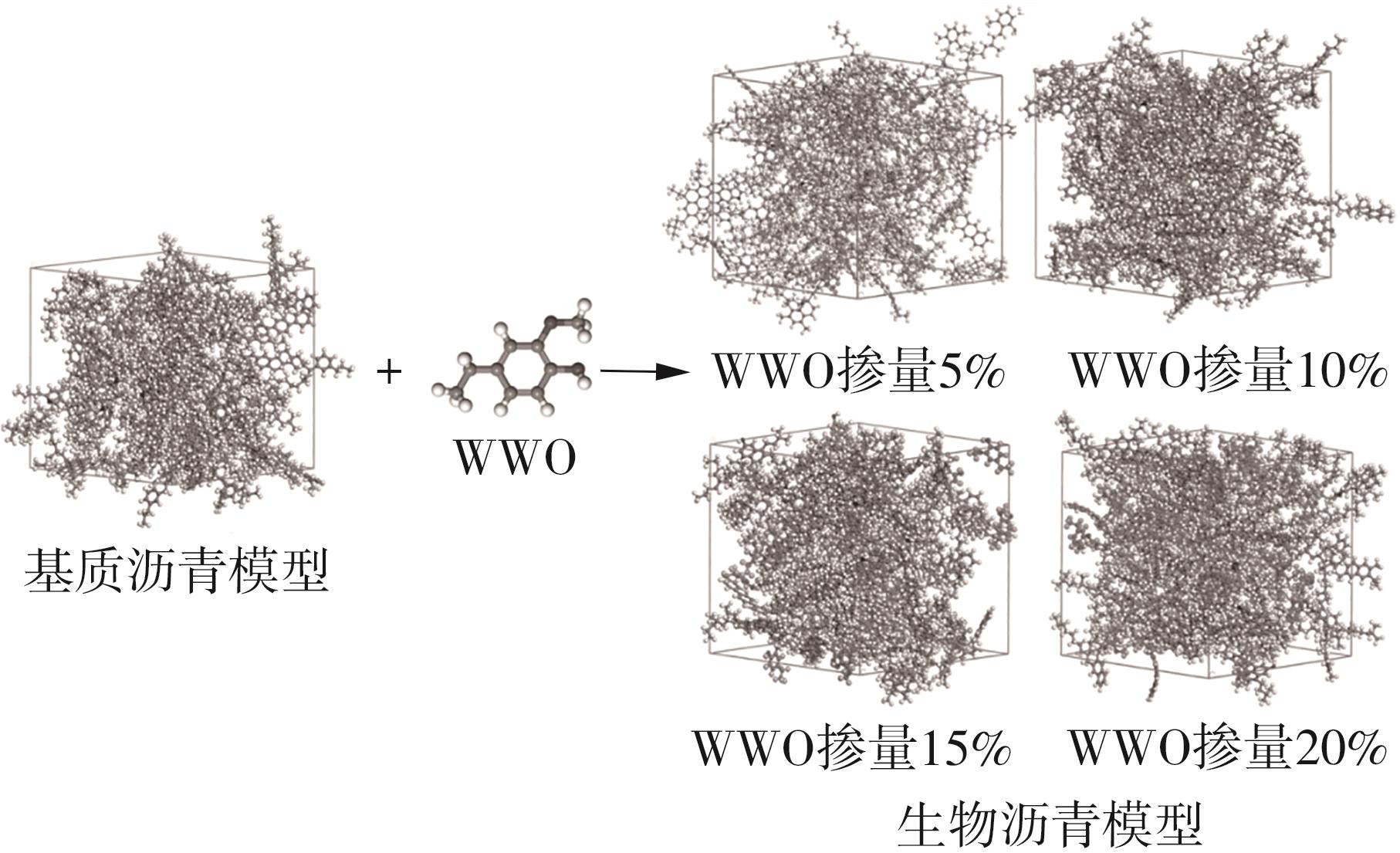
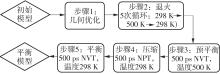
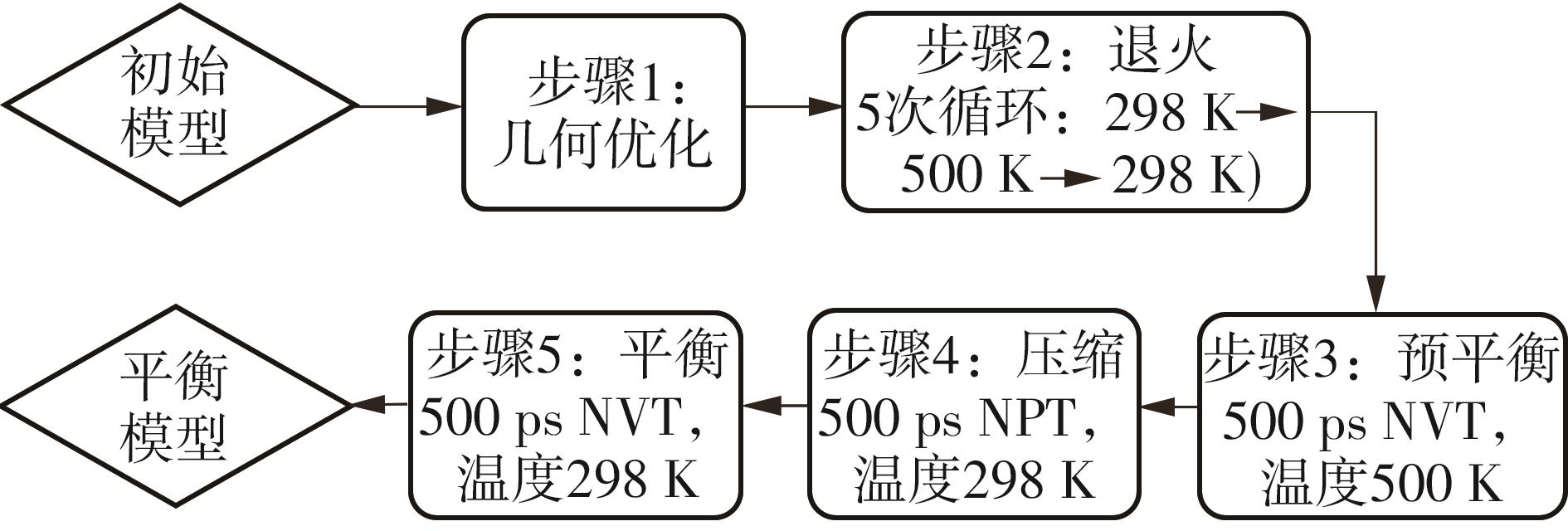
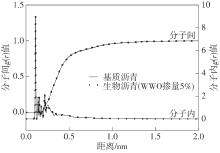
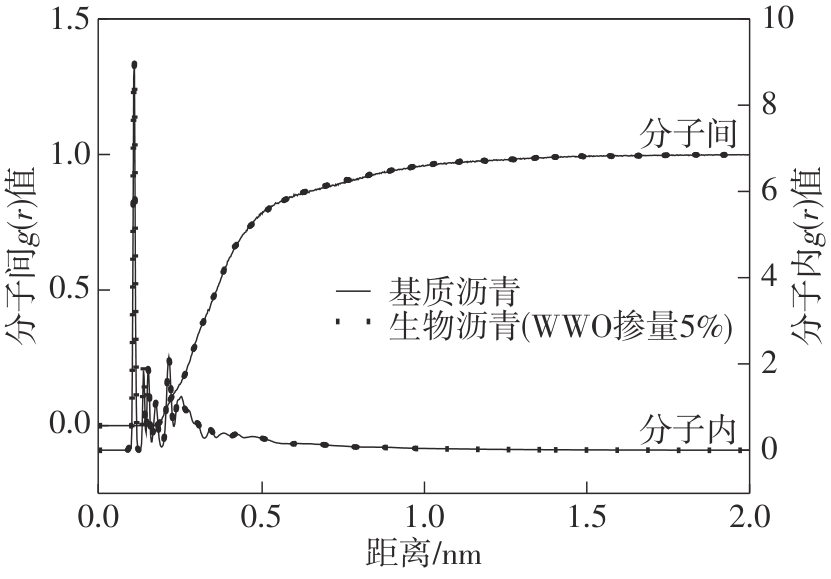
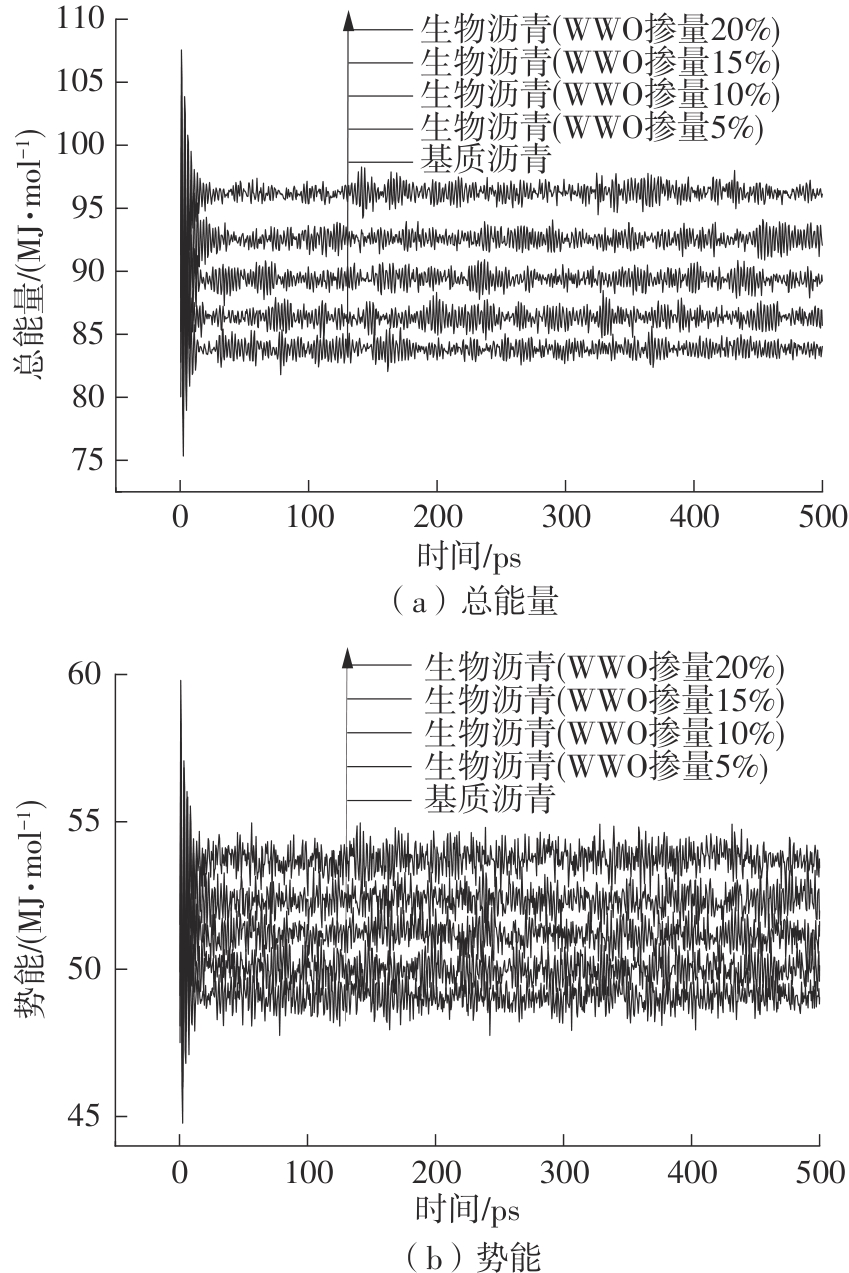
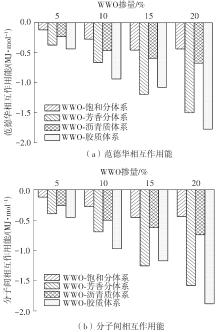
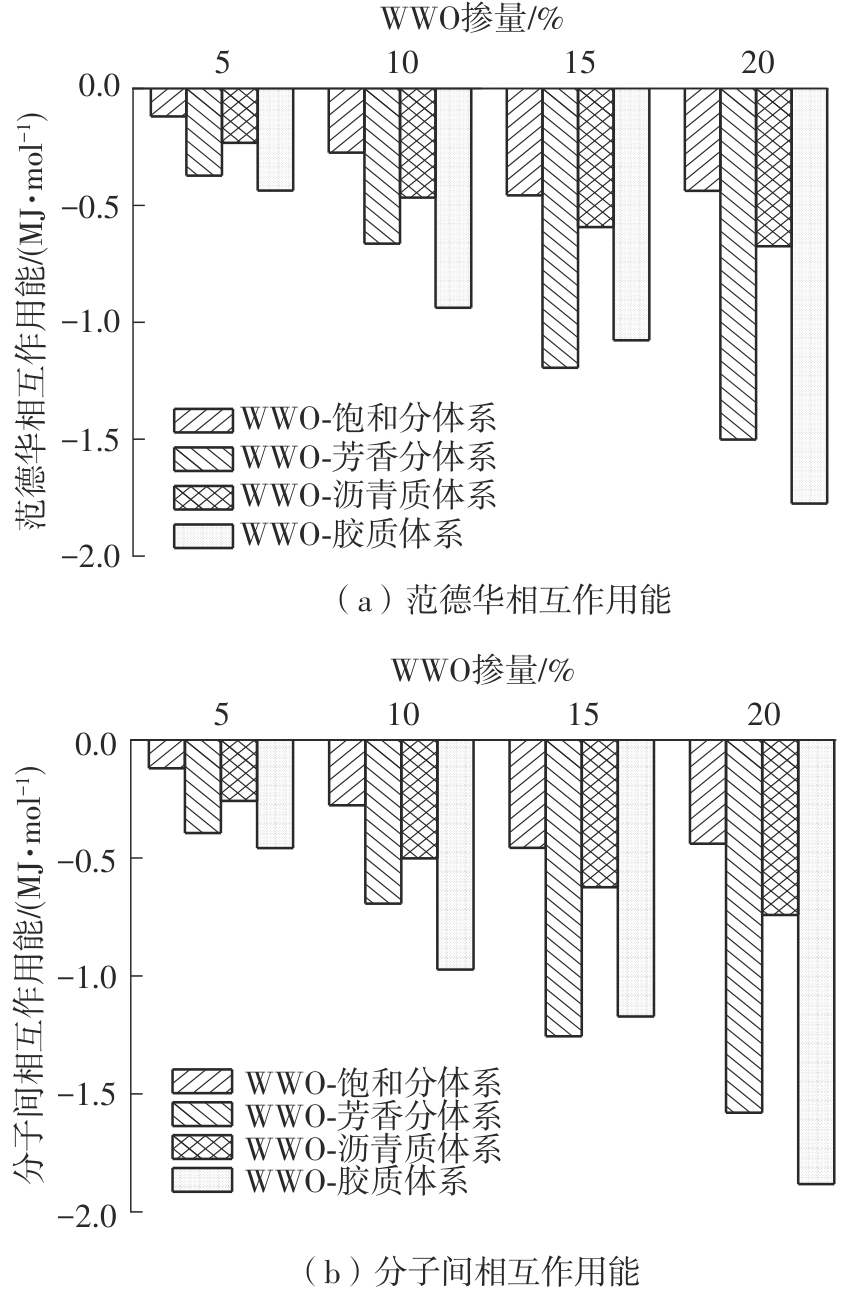
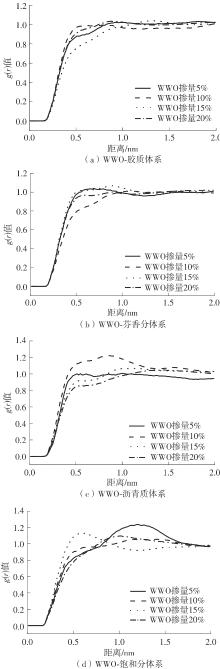
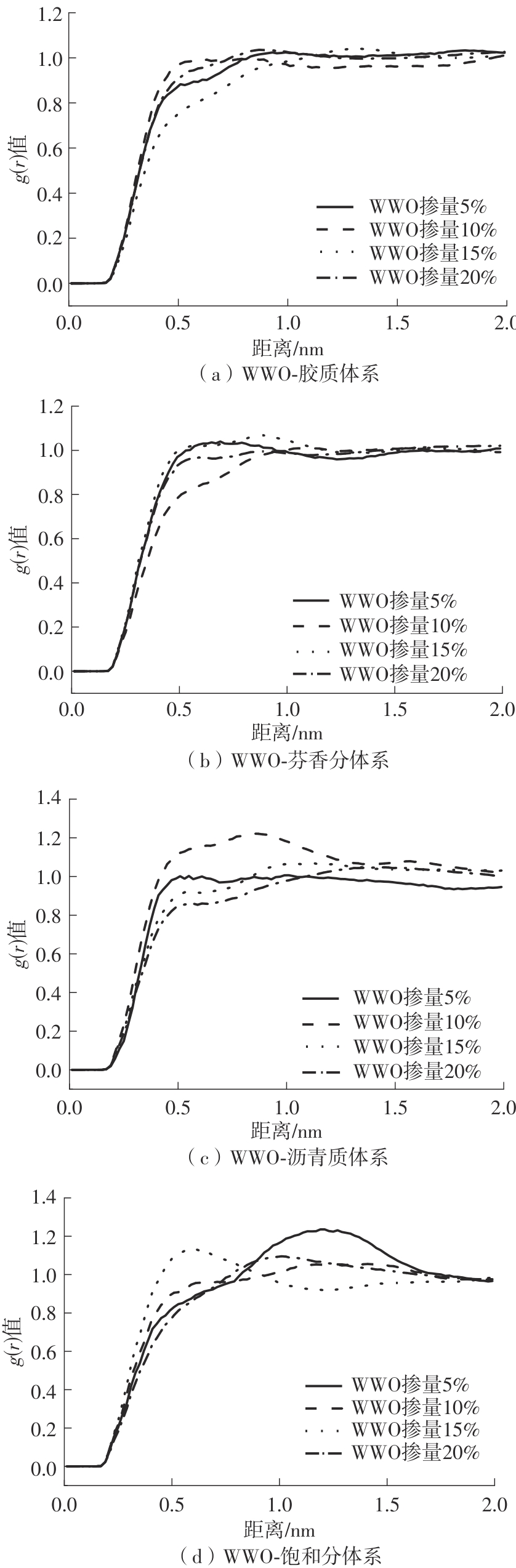
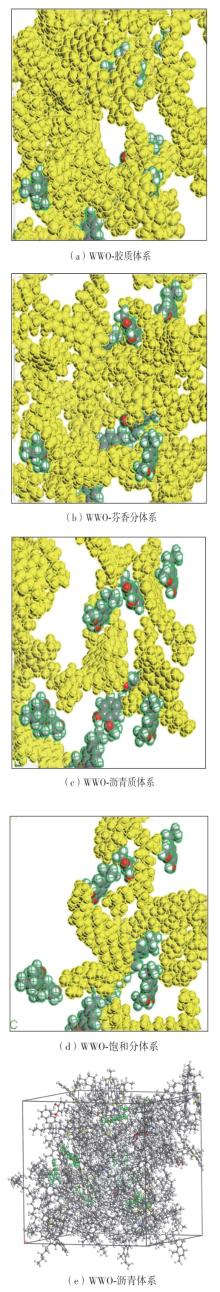
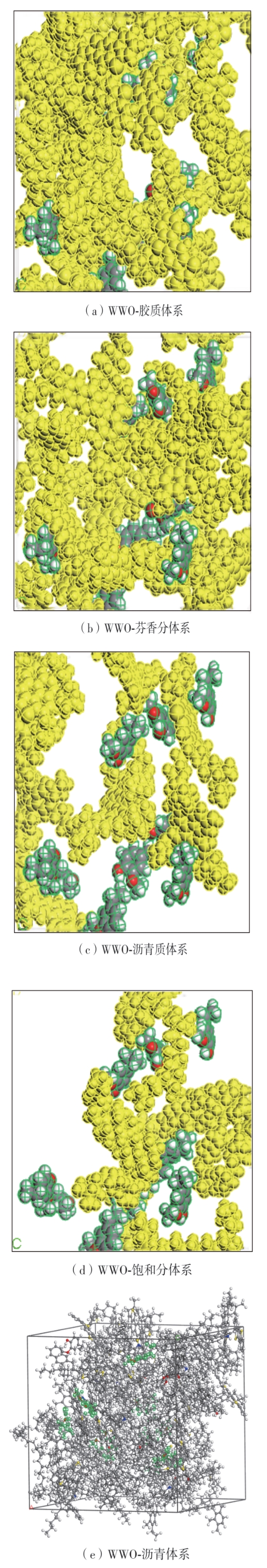
为从分子尺度阐明废木屑基生物沥青中沥青组分与废木油(WWO)之间的相互作用机理,采用分子动力学(MD)方法,基于四组分(SARA)理论建立了包括基质沥青与4种生物沥青在内的5个沥青分子模型,并利用模型的原子径向分布函数(RDF)、能量、密度与溶解度参数等对模型进行了有效性验证,通过分析WWO与沥青四组分之间的相互作用能、RDF、稳定构型的MD快照,探究其相互作用行为。研究结果显示:不同生物沥青体系中,WWO与沥青四组分之间的相互作用能均为负值,表明分子之间相互吸引;WWO与沥青各组分的相互作用能按WWO-胶质>WWO-芳香分>WWO-沥青质>WWO-饱和分排序,说明WWO与胶质分子间的相互作用力最大,与饱和分之间的相互作用力最小;WWO与沥青四组分之间的分子间RDF曲线随着其距离的增大而趋于稳定,最终区域密度与全局密度的比值趋近于1.0,表明体系内的分子在远程呈无序分布;WWO与胶质、芳香分、沥青质的分子间RDF曲线较为平坦,均未出现显著峰值,而与饱和分的分子间RDF曲线在0.5~1.5 nm的距离范围内出现了明显的波动峰,但最大峰值仅为1.24,表明WWO与饱和分在部分区域存在分子聚集。此外,通过分析稳定构型的MD快照,也发现了与相互作用能和RDF分析结果类似的结论。该文研究结果从分子层面证明了WWO与沥青四组分整体上是相容的。
中图分类号: