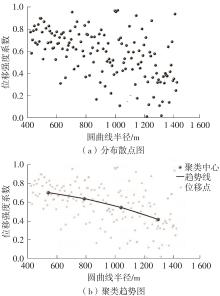
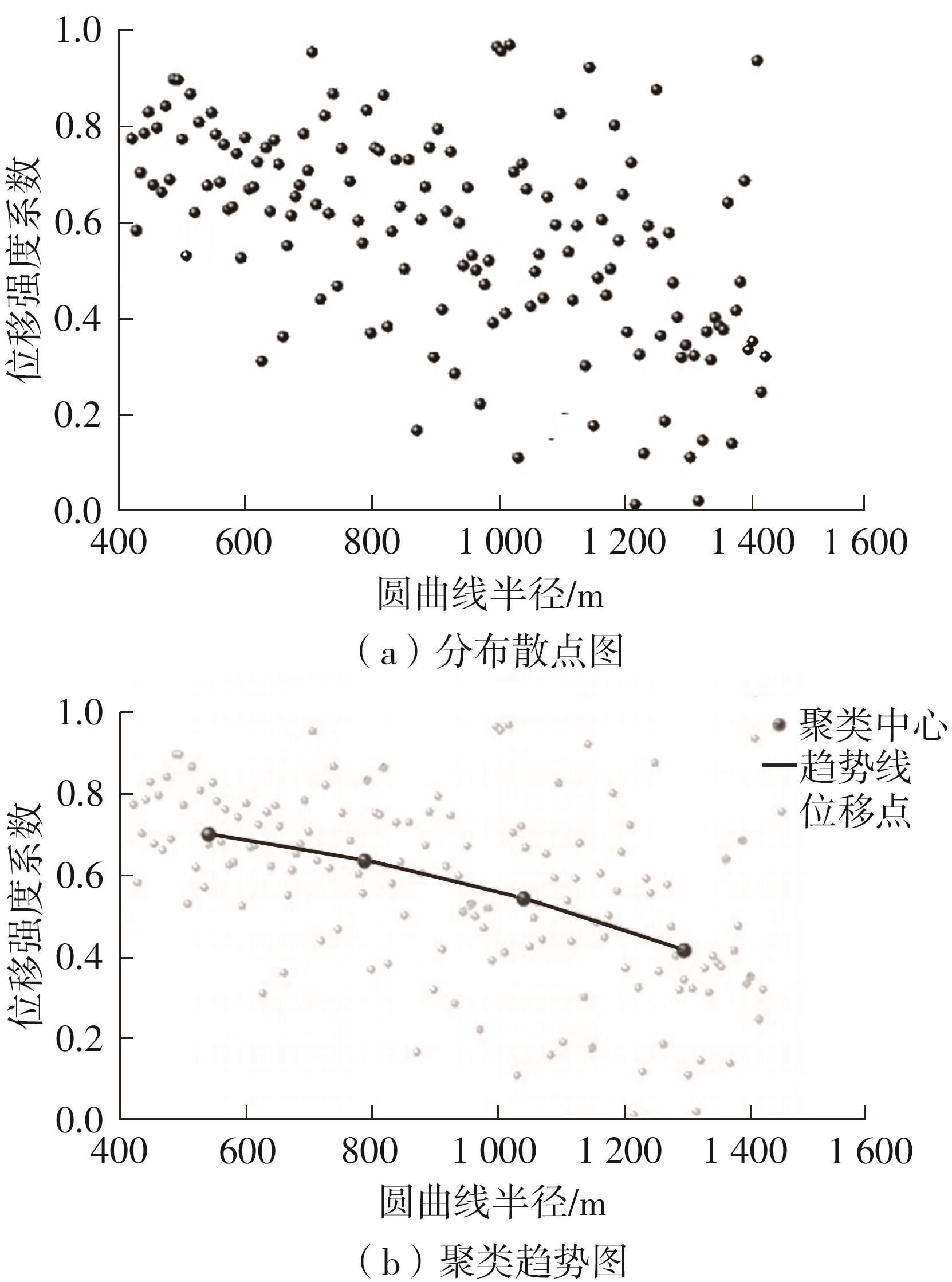
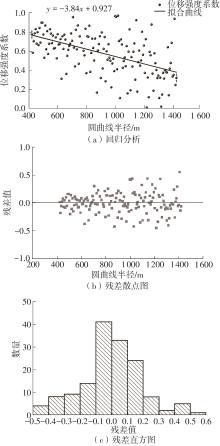
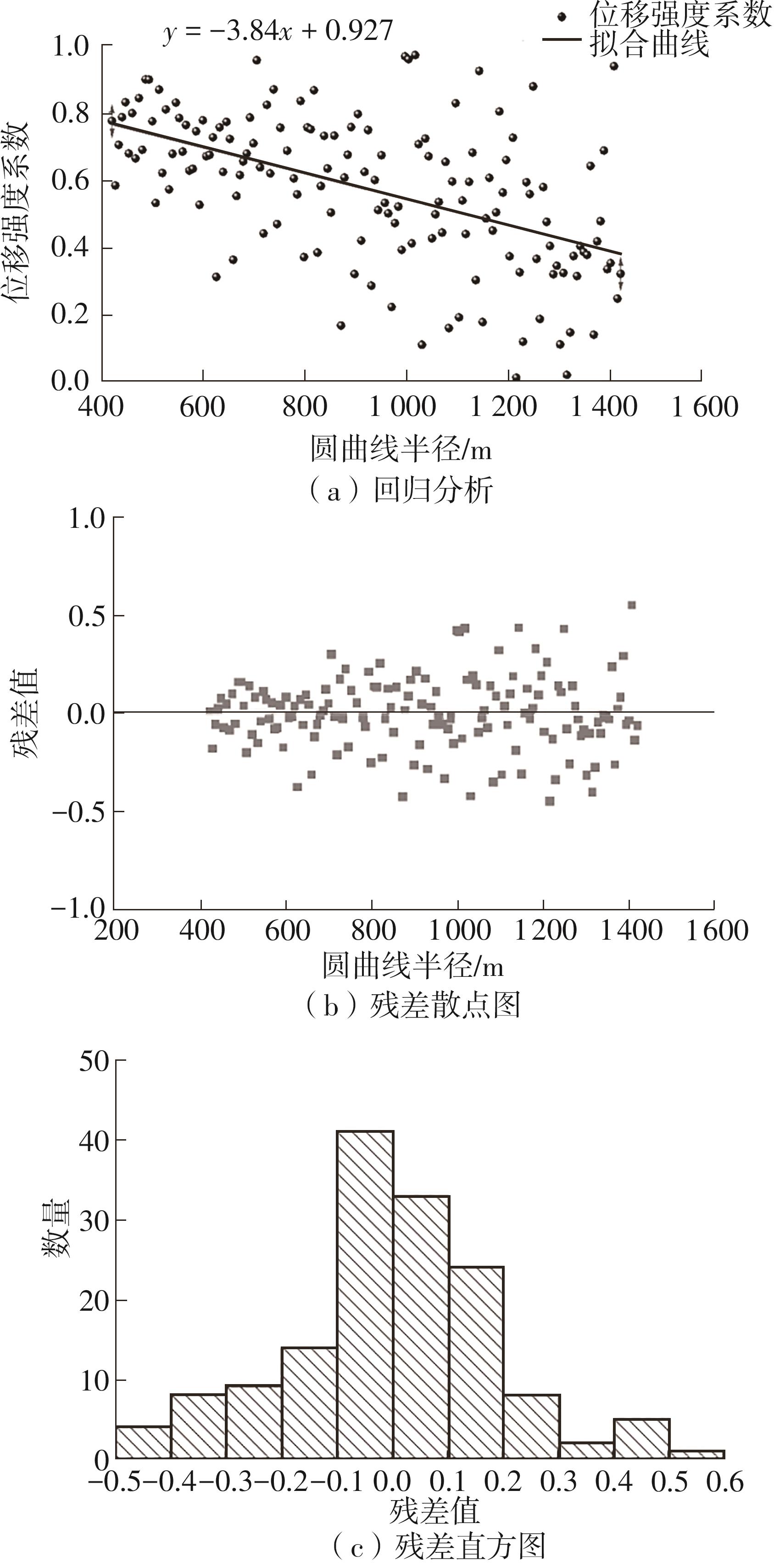
| 1 |
史培龙,刘瑞,余强,等 .重型货车坡道运行安全监控系统[J].科技导报,2015,33(4):104-110.
|
|
SHI Peilong, LIU Rui, YU Qiang,et al .Safety monitoring system for heavy duty vehicles running on rampway [J].Science & Technology Review,2015,33(4):104-110.
|
| 2 |
公路路线设计规范: [S].
|
| 3 |
MACADAM C .Understanding and modeling the human driver[J].Vehicle System Dynamics,2003,40(1):101-158.
|
| 4 |
DELAIGUE P, ESKANDARIAN A .A comprehensive vehicle braking model for predictions of stopping distances[J].Journal of Automobile Engineering,2004,218(12):1409-1417.
|
| 5 |
王雪松,朱美新,陈铭 .驾驶员前向避撞行为特征的降维及多元方差分析[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(12):1858-1866.
|
|
WANG Xuesong, ZHU Meixin, CHEN Ming .Dimension reduction and multivariate analysis of variance for drivers’ forward collision avoidance behavior characteristics [J].Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science),2016,44(12):1858-1866.
|
| 6 |
吴斌,朱西产,沈剑平 .基于自然驾驶数据的驾驶员紧急制动行为特征[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(11):1514-1519,1535.
|
|
WU Bin, ZHU Xichan, SHEN Jianping .Driver emergency braking behavior based on naturalistic driving data [J].Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science),2018,46(11):1514-1519,1535.
|
| 7 |
李霖,贺锦鹏,刘卫国,等 .基于驾驶员紧急制动行为特征的危险估计算法[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2014,42(1):109-114.
|
|
LI Lin, HE Jinpeng, LIU Weiguo,et al .Threat assessment algorithm based on characteristics of driver emergency braking behavior[J].Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science),2014,42(1):109-114.
|
| 8 |
刘瑞,贺经纬,朱西产,等 .基于自然驾驶数据的跟车场景潜在危险估计模型[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版),2019,49(4):788-795.
|
|
LIU Rui, HE Jingwei, ZHU Xichan,et al .Potential risk assessment model in car following based on naturalistic driving data[J].Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition),2019,49(4):788-795.
|
| 9 |
张驰,孟良,汪双杰,等 .高速公路曲线路段小客车制动行为侧滑风险仿真分析[J].中国公路学报,2015,28(12):134-142.
|
|
ZHANG Chi, MENG Liang, WANG Shuangjie,et al .Sideslip risk simulation analysis of passenger car braking behavior on expressway curved sections[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2015,28(12):134-142.
|
| 10 |
徐进,汪旭,王灿,等 .山区公路纵坡段驾驶人脚操纵特征及驾驶负荷[J].中国公路学报,2018,31(1):91-100.
|
|
XU Jin, WANG Xu, WANG Can,et al .Foot manoeuvres and workload of driver on mountainous roads with longitudinal slopes[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2018,31(1):91-100.
|
| 11 |
BLOOK H .The flash temperature concept[J].Wear,1963,6(6):483-494.
|
| 12 |
苏波,方守恩,王俊骅 .基于大货车制动性能的山区高速公路坡度坡长限制研究[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2009,28(2):287-289,297.
|
|
SU Bo, FANG Shouen, WANG Junhua .Research on longitudinal slope and slope length limit of mountain-expressway based on heavy vehicles’ braking ability [J].Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Science Edition),2009,28(2):287-289,297.
|
| 13 |
OLESIAK Z, PYRYEV Y, YEVTUSHENKO A .Determination of temperature and wear during braking[J].Wear,1997,210(1/2):120-126.
|
| 14 |
MOOMEN M, KSAIBATI K .Updating the grade severity rating system(GSRS)for wyoming mountain passes:a description of tests and results[J].SAE International Journal of Commercial Vehicles,2020,13(1):71-85.
|
| 15 |
杜博英,方守恩,迟爽,等 .货车制动在公路长大下坡安全研究中的应用[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报,2010,42(4):656-659.
|
|
DU Bo-ying, FANG Shou-en, CHI Shuang,et al .U-sing of truck braking in security research of long and steep downgrade on highway[J].Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2010,42(4):656-659.
|
| 16 |
贾伟 .制动器温升与山区道路参数及车辆工况关系研究[D].重庆:重庆交通大学,2012.
|
| 17 |
张驰,侯宇迪,秦际涵,等 .基于制动毂温升的连续下坡安全设计方法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(10):139-150.
|
|
ZHANG Chi, HOU Yudi, QIN Jihan,et al .Safety design method of long slope downhill slope based on temperature increase of brake[J].Journal of south China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2019,47(10):139-150.
|
| 18 |
潘兵宏,牛肖,白浩晨,等 .高速公路连续下坡路段货车制动毂温升模型修正研究[J].公路交通科技,2021,38(9):85-91.
|
|
PAN Binhong, NIU Xiao, BAI Haochen,et al .Study on temperature rise model of truck brake hubs on continuous downhill section of expressway[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Deve-lopment,2021,38(9):85-91.
|
| 19 |
BEN-AKIVA M, HIRSH M, PRASHKER J .Probabilistic and economic factors in highway geometric design[J].Transportation Science,1985,19(1):38-57.
|
| 20 |
杨晨,程建川 .基于可靠度的道路不设缓和曲线最小半径的计算[J].公路交通科技,2013,30(7):7-11.
|
|
YANG Chen, CHENG Jianchuan. Calculation of minimum circular radius of road without transition curve based on reliability[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2013,30(7):7-11.
|
| 21 |
秦玉秀 .基于可靠性的道路行车视距分析和线形设计研究[D].南京:东南大学,2015.
|
| 22 |
张航,涂智佳,田晟,等 .山区高速公路爬坡车道长度可靠性设计[J].武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版),2022,46(3):495-500.
|
|
ZHANG Hang, TU Zhijia, TIAN Sheng,et al .Reliability design of climbing lane length of expressway in mountainous area[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Enginee-ring),2022,46(3):495-500.
|
| 23 |
王路,程建川 .基于可靠度的高速公路准临界坡长[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(1):181-187.
|
|
WANG Lu, CHENG Jianchuan .Pre-critical grade length of expressway based on reliability[J].Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition),2018,48(1):181-187.
|
| 24 |
刘斌,李刚,黄春富,等 .基于可靠度的地下互通立交匝道坡度指标研究[J].公路,2022,67(10):9-17.
|
|
LIU Bin, LI Gang, HUANG Chunfu,et al .Research on the slope index of underground interchange ramp based on reliability[J].Highway,2022,67(10):9-17.
|
| 25 |
工程结构可靠性设计统一标准: [S].
|