华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 80-88.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220250
所属专题: 2023年能源、动力与电气工程
系泊形式对浮式风力机动力响应的影响
张若瑜 李耀隆 李焱 李昊然 黎国彦 唐友刚
- 天津大学 天津市港口与海洋工程重点实验室/水利工程仿真与安全国家重点实验室/建筑工程学院,天津 300350
Study on the Effect of Mooring Form on the Dynamic Response of Floating Offshore Wind Turbine
ZHANG Ruoyu LI Yaolong LI Yan LI Haoran LI Guoyan TANG Yougang
- Tianjin Key Laboratory of Port and Ocean Engineering/State Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Engineering Simulation and Safety/School of Civil Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300350,China
摘要:
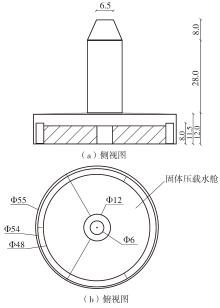
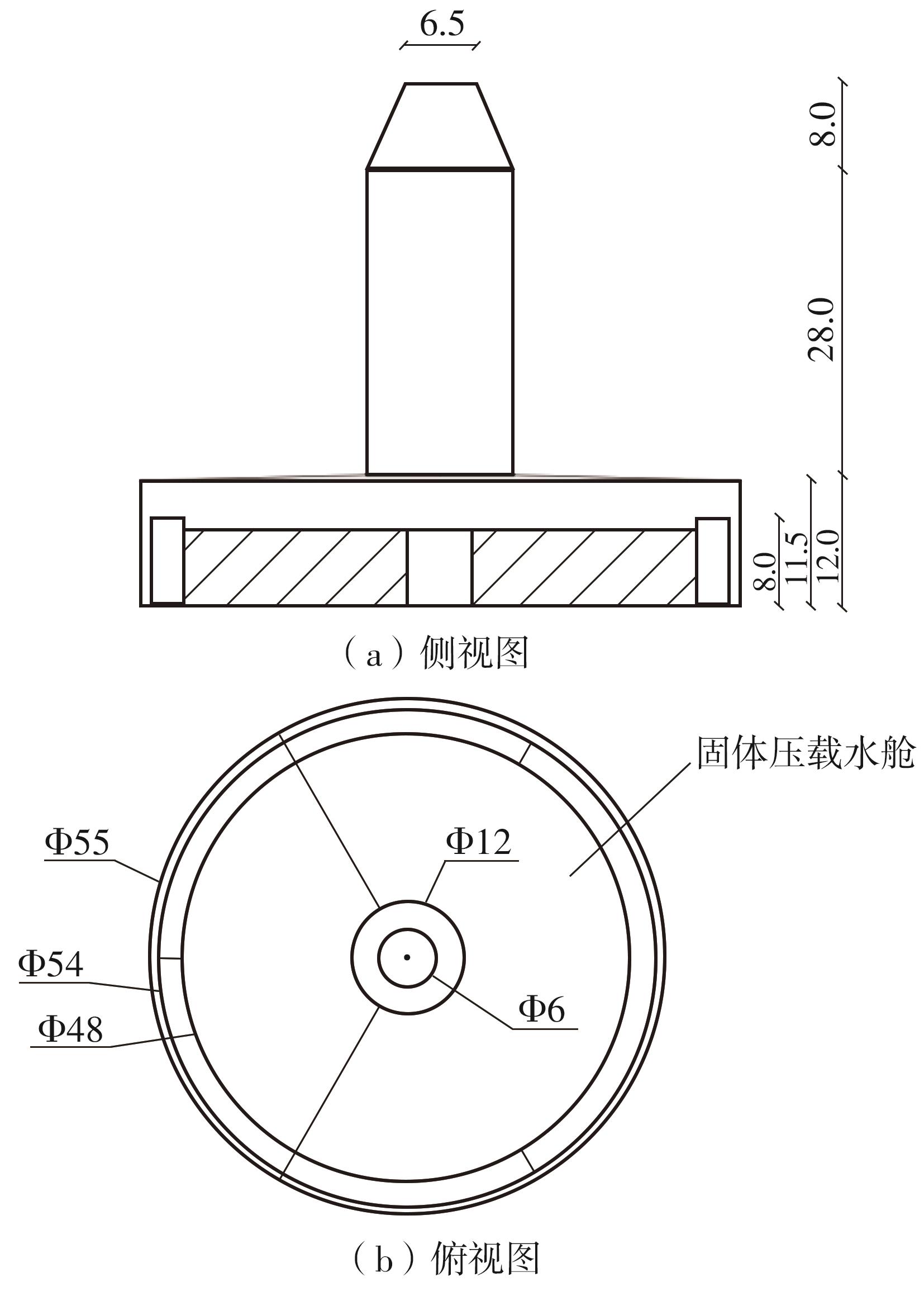
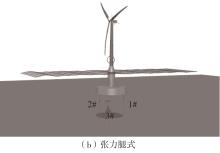
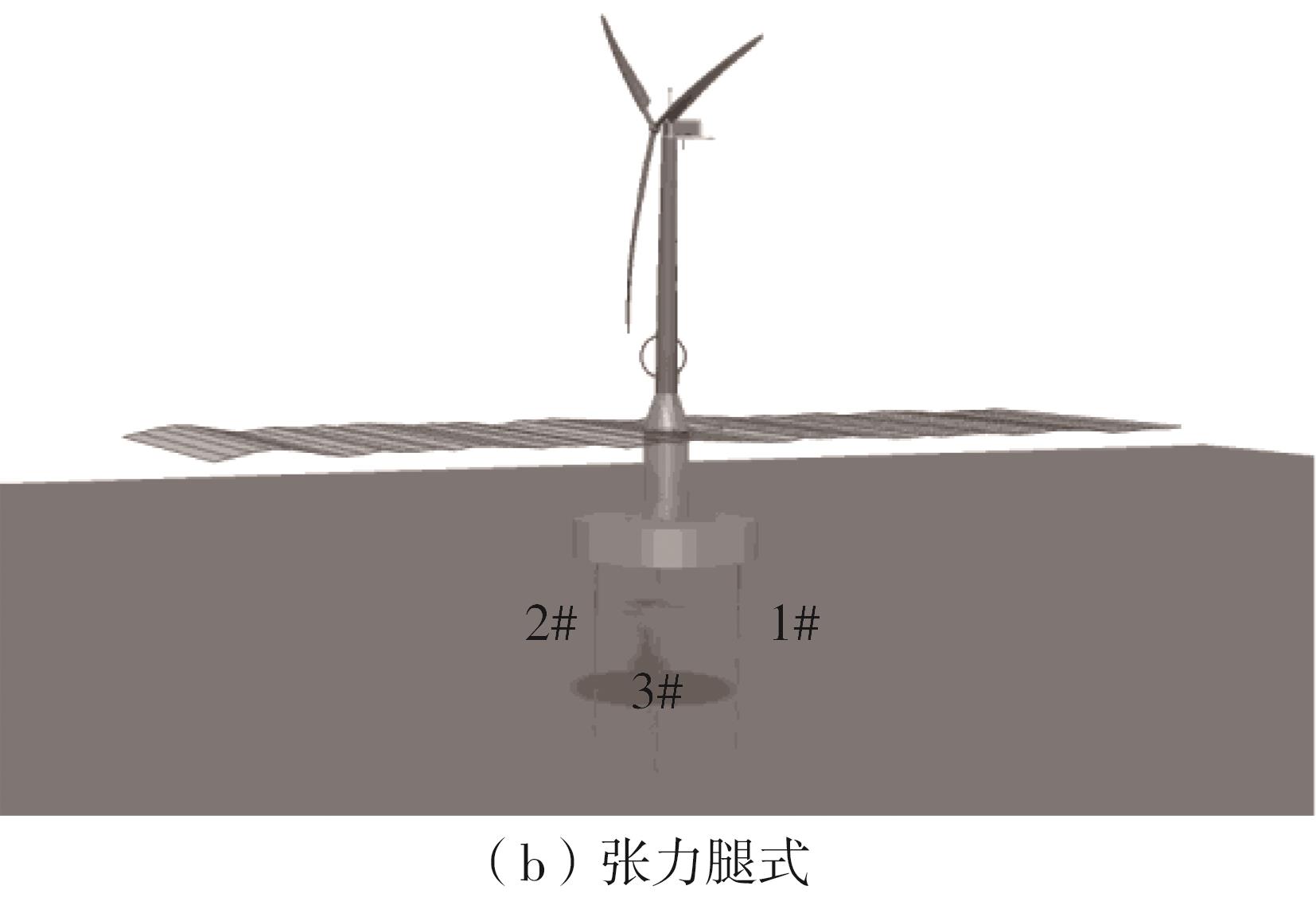
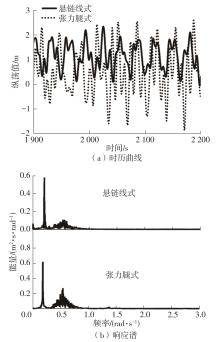
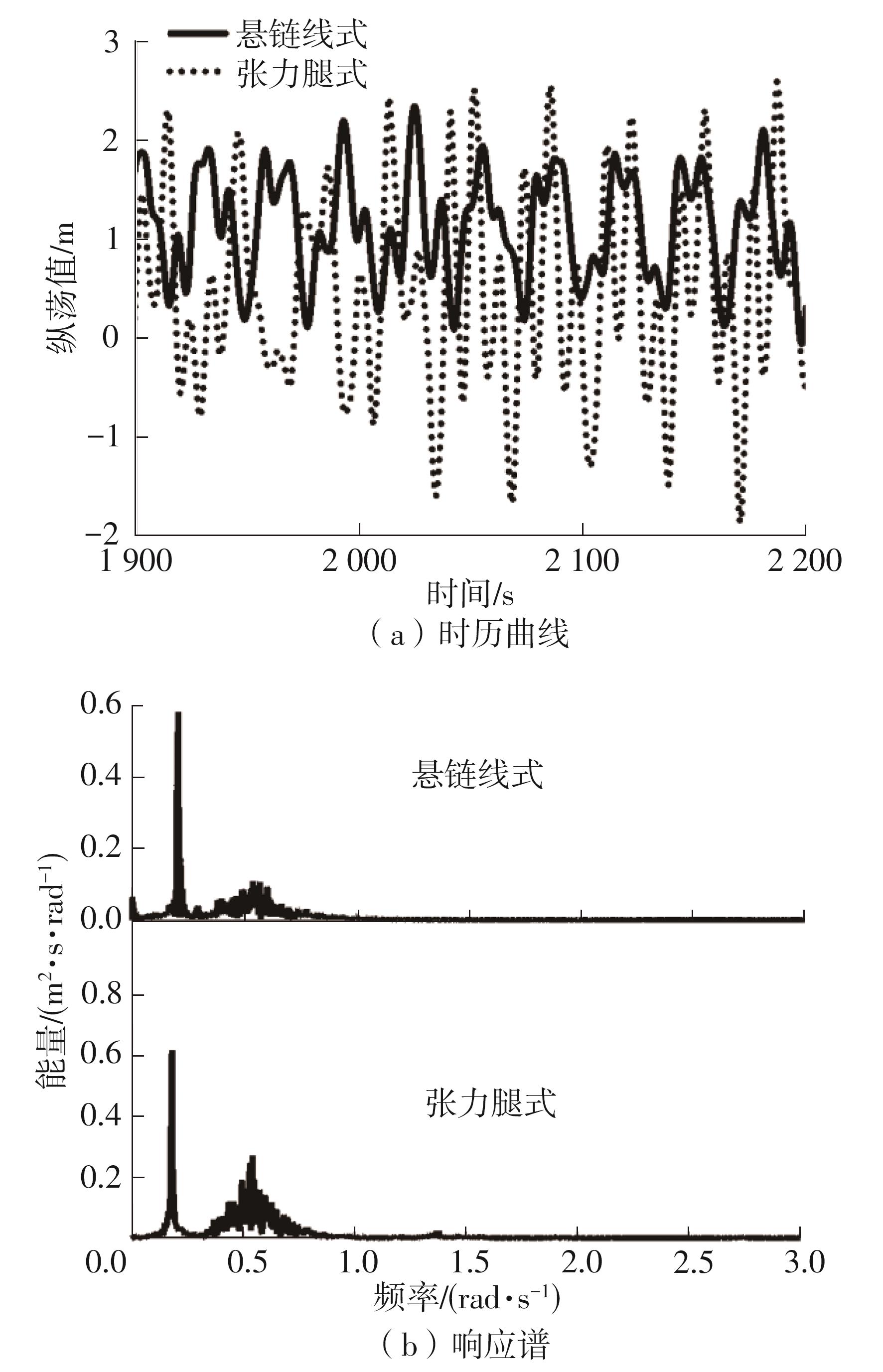
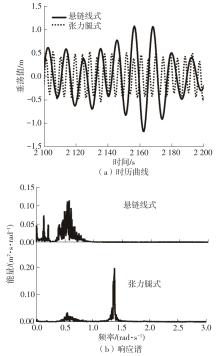
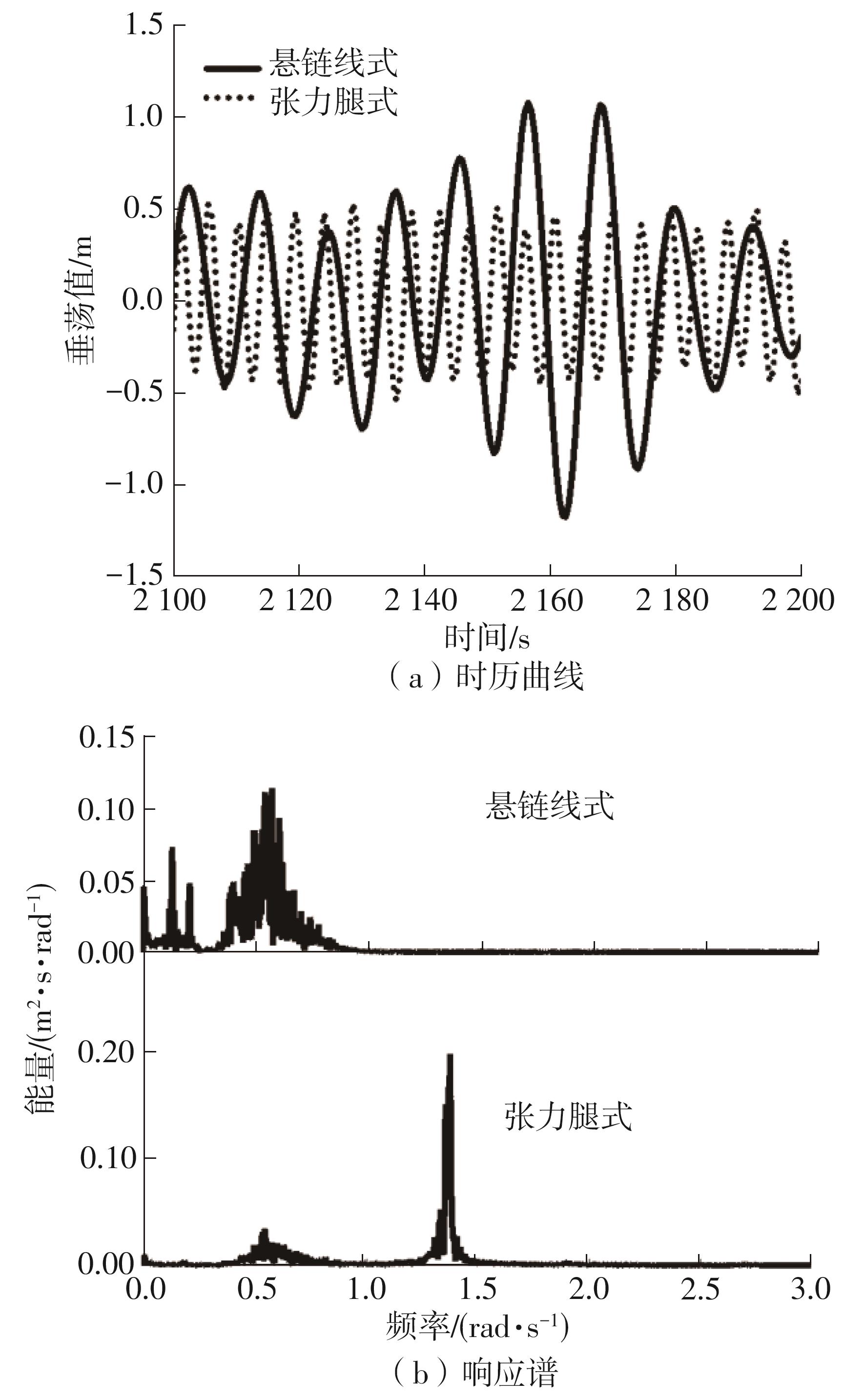
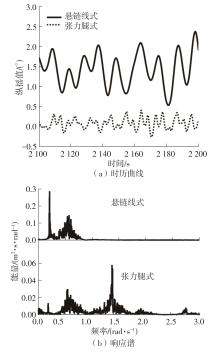
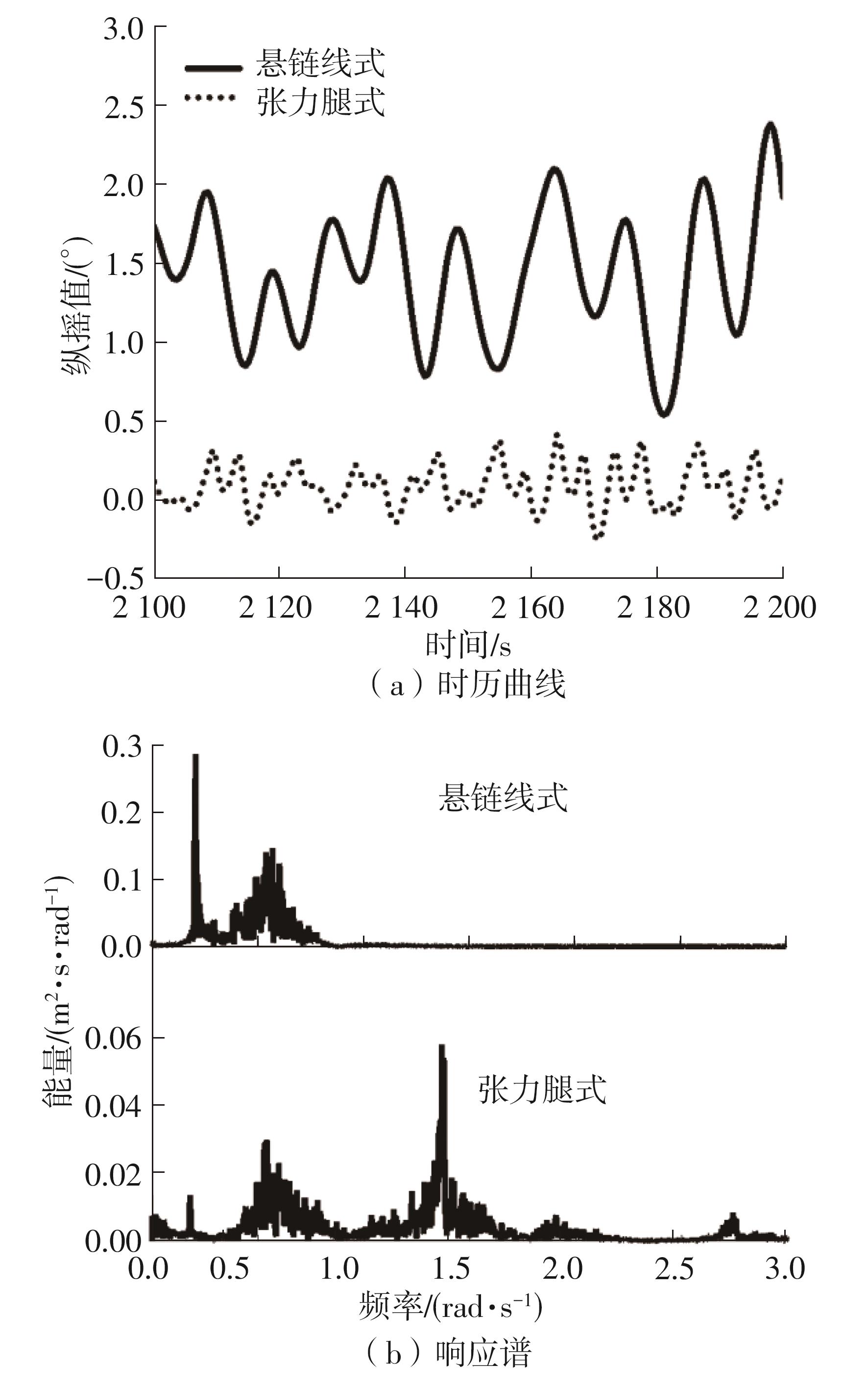
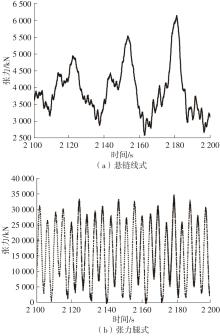
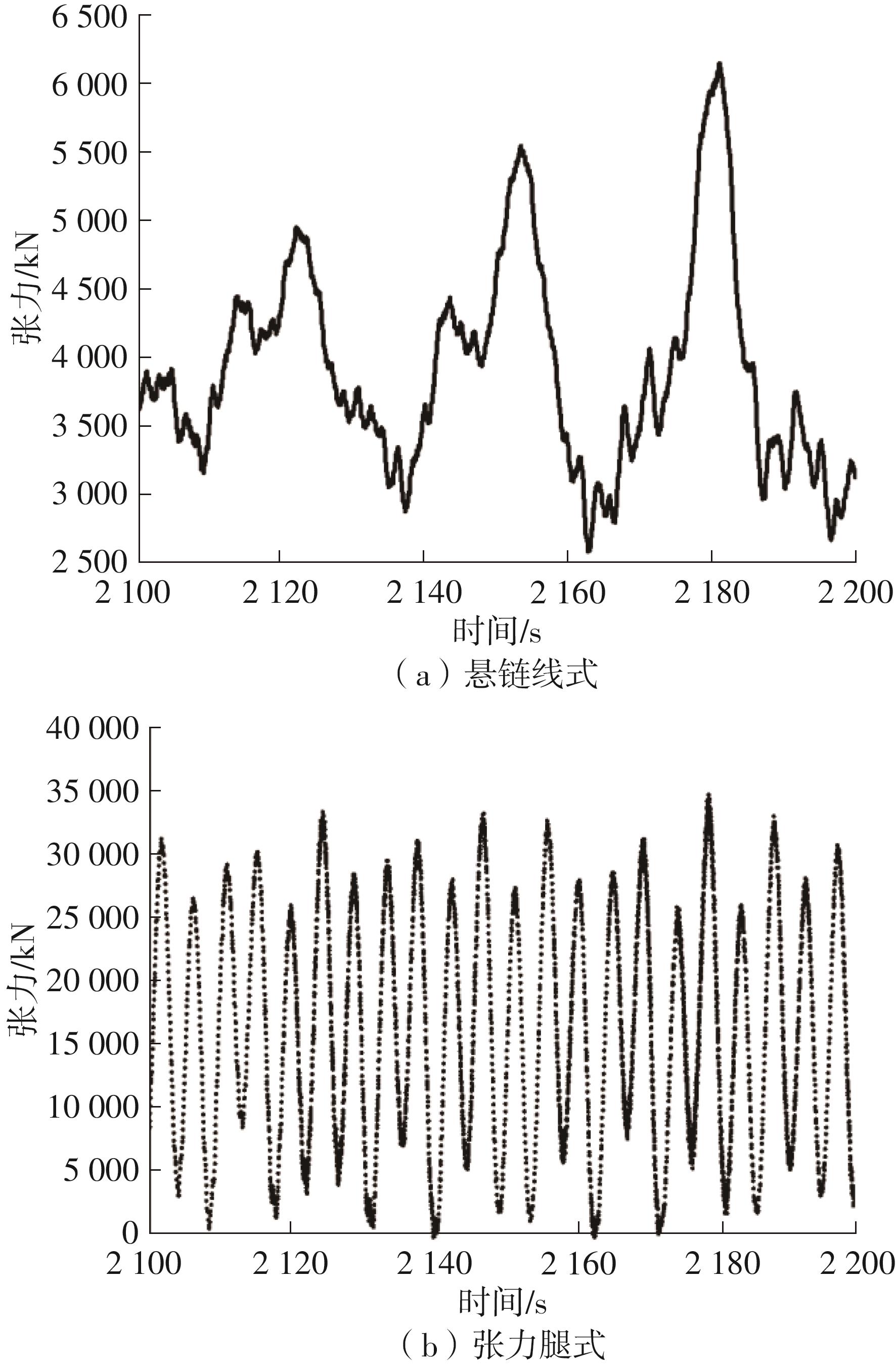
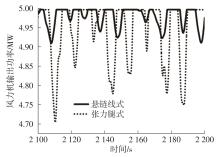
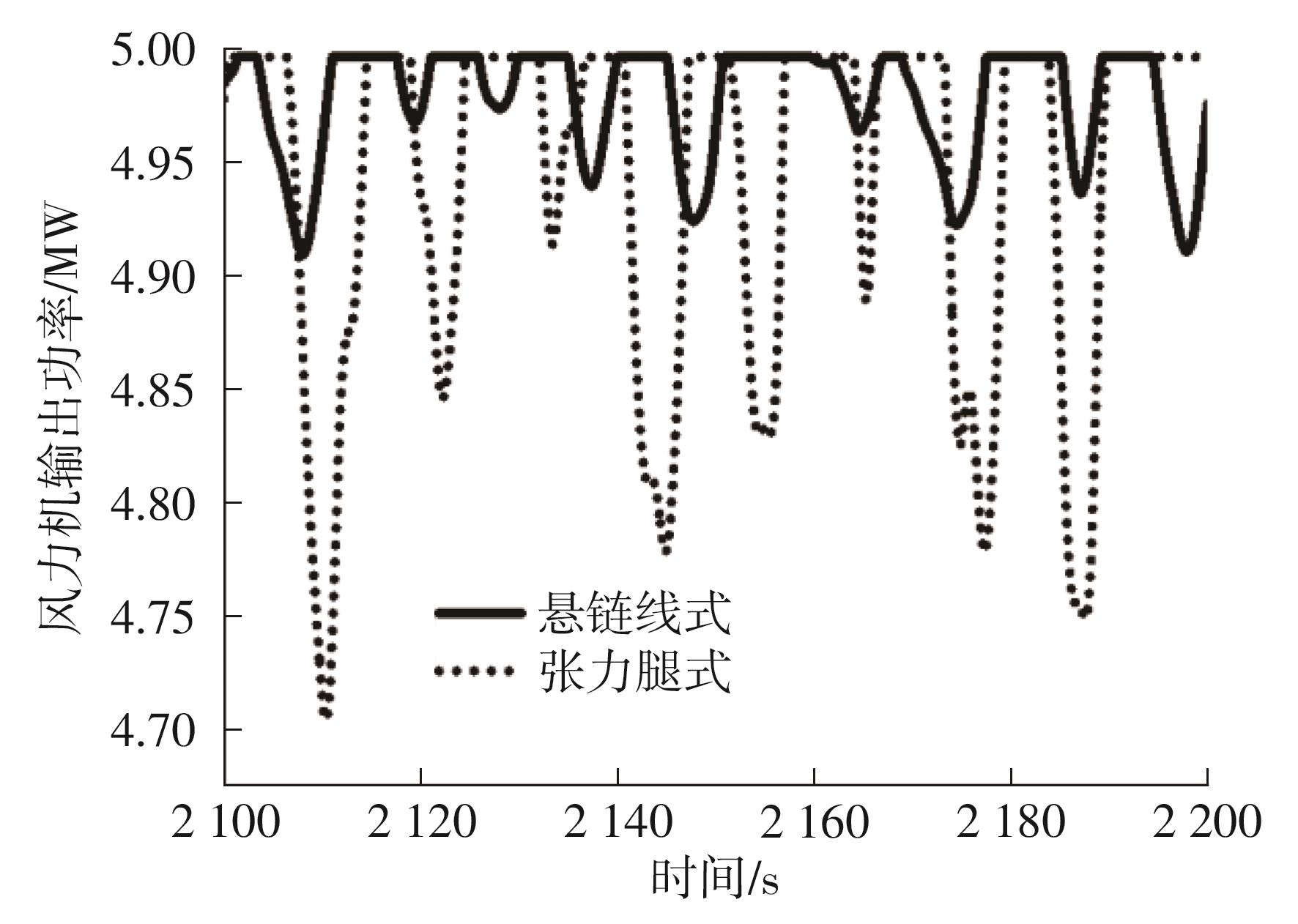
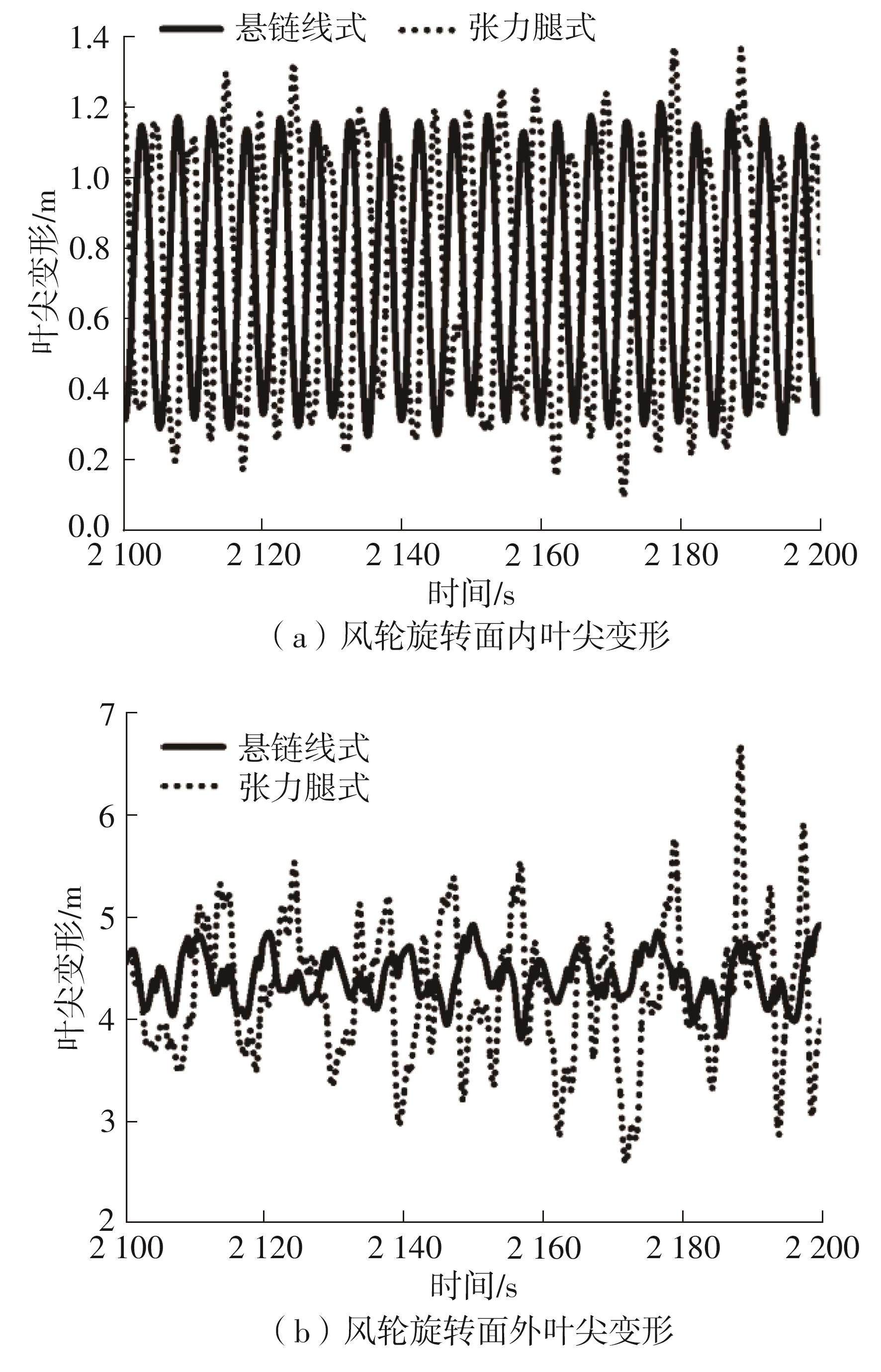
系泊系统是影响浮式风力机动力响应的关键因素,关系到风力机系统的安全与效率。为研究不同系泊系统对浮式风力机动力响应的影响,以一种新型浅吃水型浮式基础为研究对象,基于该基础储备浮力大的特点,分别采用悬链线式与张力腿式两种不同系泊系统,用于海上5 MW漂浮式风力机定位。建立风力机-基础-系泊系统耦合动力学数值模型,基于叶素-动量理论计算气动载荷,运用势流理论计算水动力载荷,采用三维有限元动力分析模型分别计算两种系泊缆张力。基于该耦合数值模型,对两种漂浮式风力机在作业状态下的动力响应特性进行时域计算,计算结果表明:在额定作业海况下,对比悬链线式系泊系统,采用张力腿式系泊的浮式风力机的纵荡运动均值减少0.7 m,垂荡运动幅值减少39%,同时纵摇运动均值和幅值显著降低,采用张力腿式系泊系统的浮式风力机具有更好的基础运动性能,但其系泊缆内张力均值与幅值更大,同时风机输出功率与风轮叶尖变形的变化幅值也更显著。因此,对于文中提出的新型浮式基础,采用张力腿式的系泊方式具有更好的运动性能,但其系泊安全性与发电效率不如采用悬链线式的系泊方式。
中图分类号: