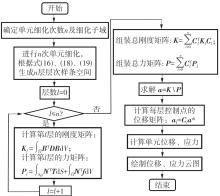
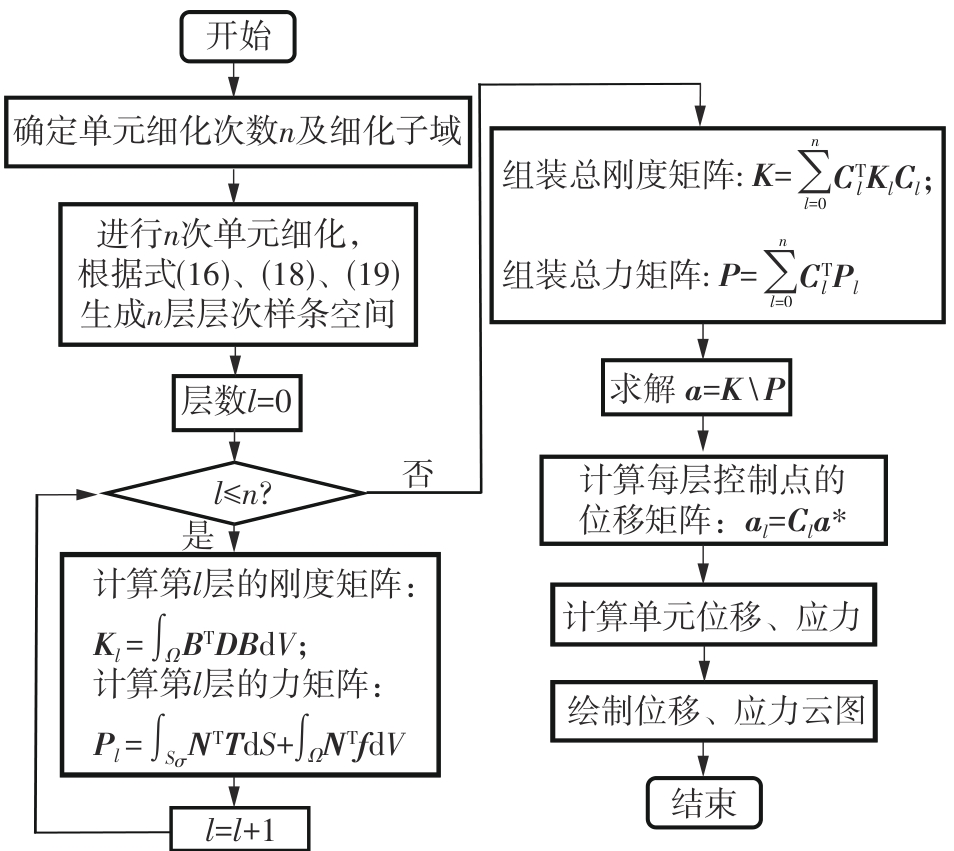
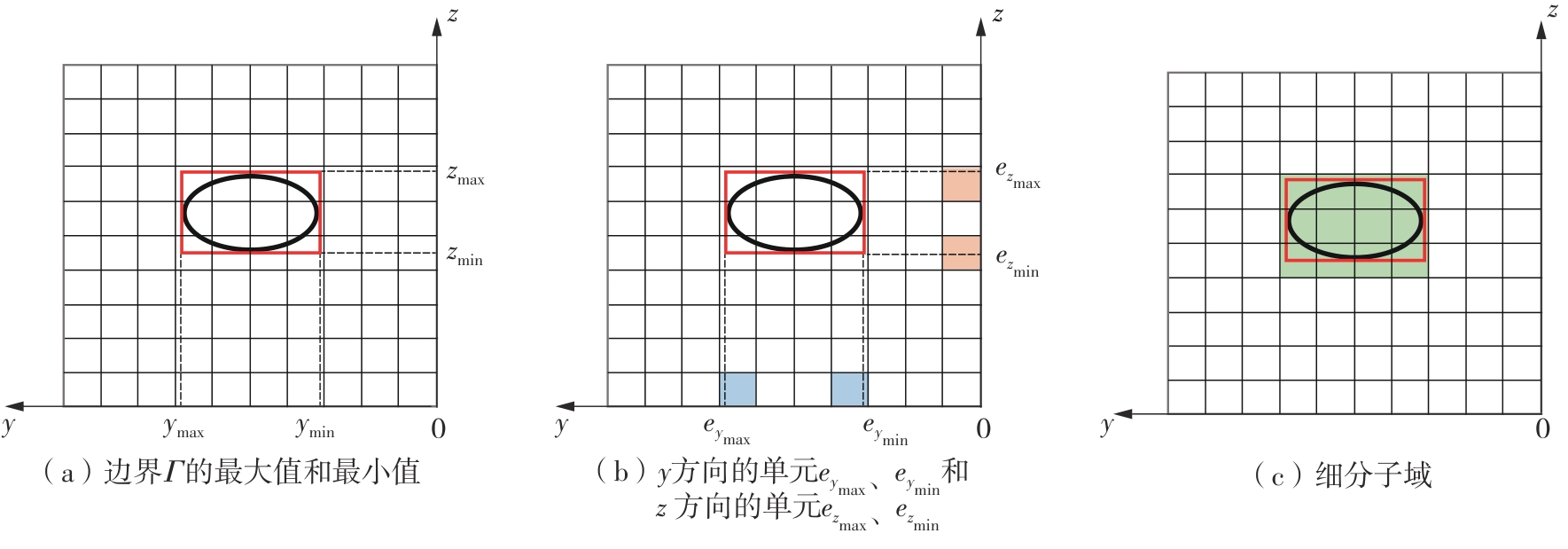
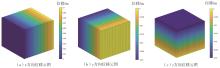
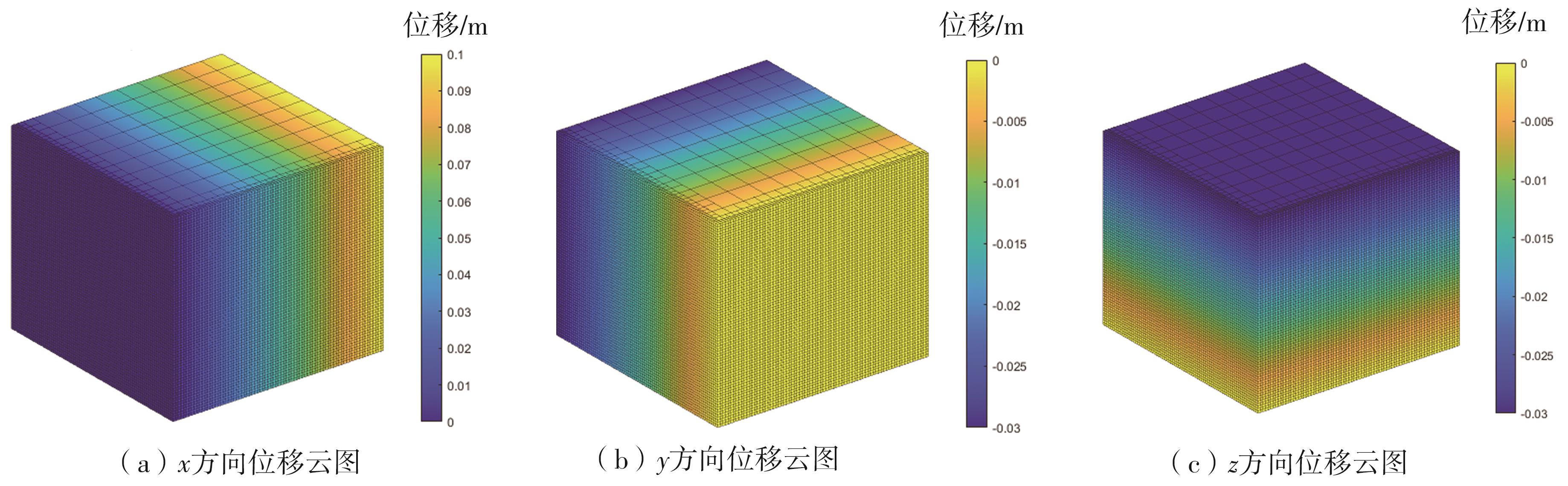
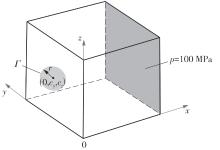
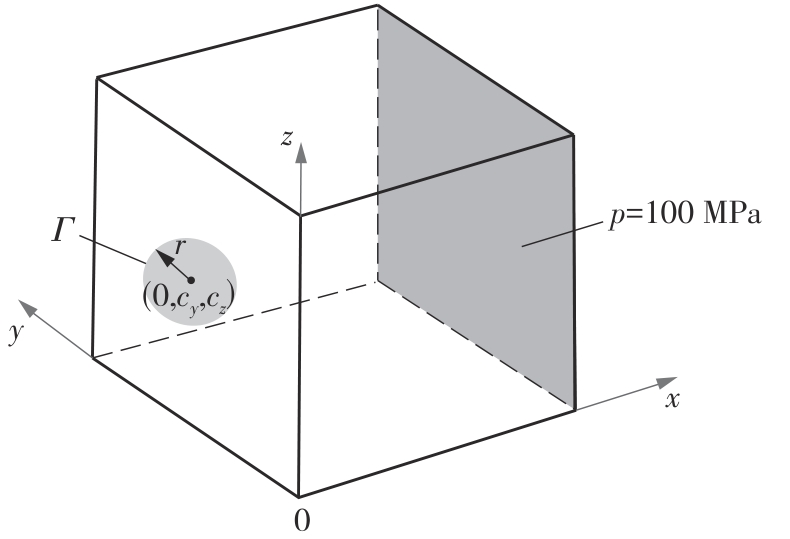
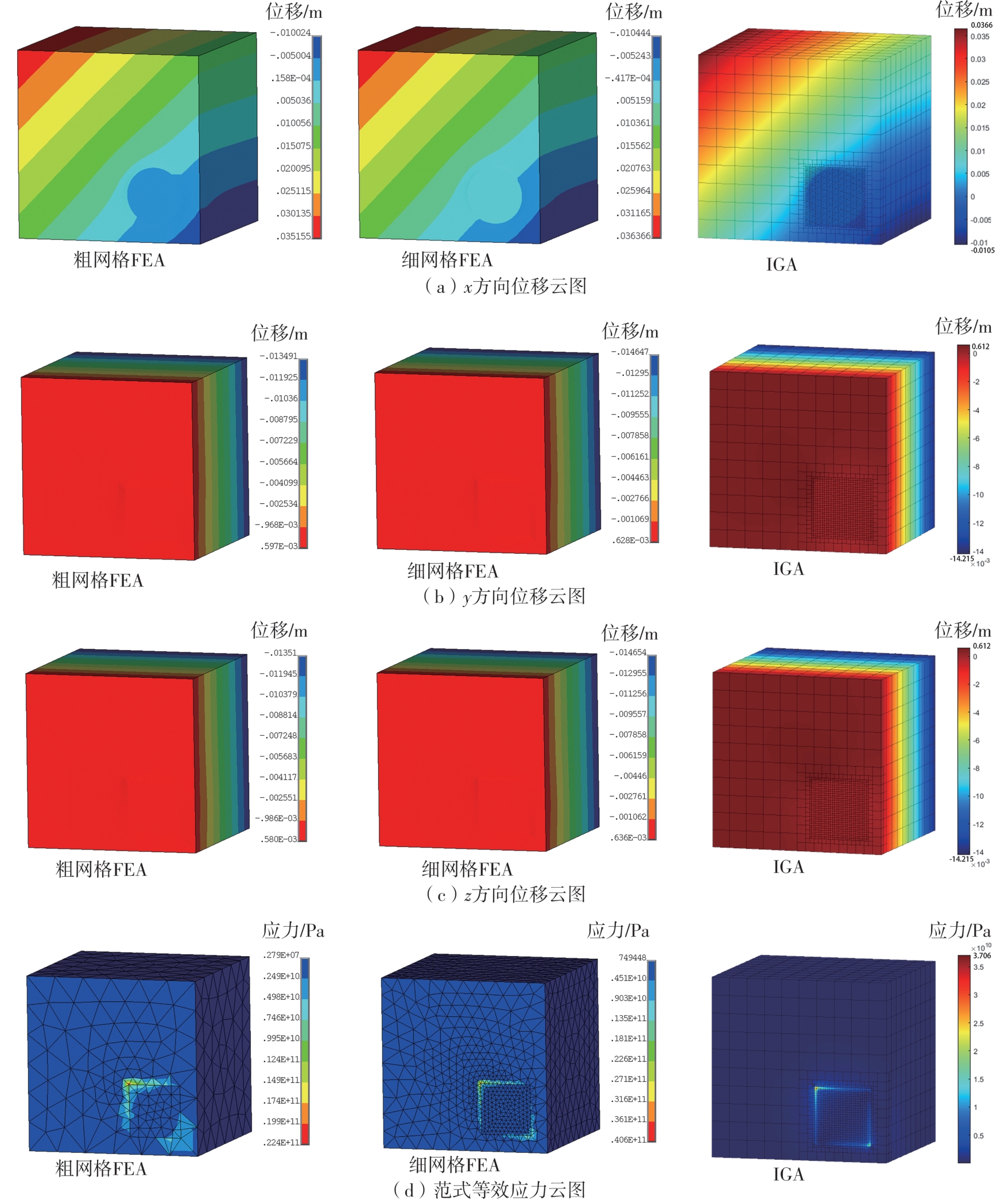
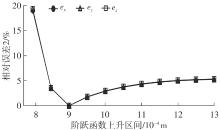
| 1 |
乔发杰 .基于等几何分析的大变形梁结构仿真分析算法[D].大连:大连理工大学,2022.
|
| 2 |
郭玉杰,吴晗浪,李薇,等 .基于等几何分析的参数化曲梁结构非线性动力学降阶模型研究[J].工程力学,2022,39(8):31-48.
|
|
GUO Yujie, WU Hanlang, LI Wei,et al .Model order reduction for nonlinear dynamic analysis of parameterized curved beam structures based on isogeometric analysis[J].Engineering Mechanics,2022,39(8):31-48.
|
| 3 |
金灵智,王禹,郝鹏,等 .加筋路径驱动的板壳自适应等几何屈曲分析[J].力学学报,2023,55(5):1151-1164.
|
|
JIN Lingzhi, WANG Yu, HAO Peng,et al .Adaptive isogeometric buckling analysis of stiffened panels driven by stiffener paths[J].Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2023,55(5):1151-1164.
|
| 4 |
费建国,罗会信,左兵权,等 .雷诺方程的数值计算方法概述[J].润滑与密封,2020,45(4):130-140.
|
|
FEI Jianguo, LUO Huixin, ZUO Bingquan,et al .An overview of numerical methods for Reynolds equation[J].Lubrication Engineering,2020,45(4):130-140.
|
| 5 |
于嘉瑞,岳宝增,李晓玉 .燃料大幅晃动等几何分析仿真及航天器耦合动力学研究[J].力学学报,2023,55(2):476-486.
|
|
YU Jiarui, YUE Baozeng, LI Xiaoyu .Study on isogeometric analysis for large-amplitude propellant sloshing and spacecraft coupled dynamics[J].Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2023,55(2):476-486.
|
| 6 |
PEROTTO S, BELLINI G, BALLARIN F,et al .Isogeometric hierarchical model reduction for advection-diffusion process simulation in microchannels[M]∥CHINESTA F,CUETO E,PAYAN Y,et al eds.Reduced Order Models for the Biomechanics of Living Organs.Pittsburgh:Academic Press,2023:197-211.
|
| 7 |
张洪海,莫蓉,万能 .应用等几何配点法求解电磁涡流场问题[J].计算机辅助设计与图形学学报,2019,31(3):496-503.
|
|
ZHANG Honghai, MO Rong, WAN Neng .Solving eddy current fields with isoeometric collocation method[J].Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics,2019,31(3):496-503.
|
| 8 |
ASHOUR M, VALIZADEH N, RABCZUK T .Isogeometric analysis for a phase-field constrained optimization problem of morphological evolution of vesicles in electrical fields[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,2021,377:113669/1-27.
|
| 9 |
刘涛,张顺琦,刘庆运 .热环境下压电功能梯度板的非线性等几何建模与主动控制研究[J].振动与冲击,2023,42(8):38-50.
|
|
LIU Tao, ZHANG Shunqi, LIU Qingyun .Nonlinear isogeometric modeling and active control of piezoelectric functionally graded plates in thermal environment[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2023,42(8):38-50.
|
| 10 |
高建伟,陈龙 .基于等几何分析的股骨模型静力学分析[J].计算机仿真,2015,32(5):340-343.
|
|
GAO Jianwei, CHEN Long .Construction and static analysis of femur based on IGA[J].Computer Simulation,2015,32(5):340-343.
|
| 11 |
产启平,陈龙 .基于等几何分析的非均质股骨近端模型的受力分析[J].电子科技,2018,31(2):15-19.
|
|
CHAN Qiping, CHEN Long .Stress analysis of heterogeneous femoral proximal model by using isogeometric analysis[J].Electronic Science and Technology,2018,31(2):15-19.
|
| 12 |
马书豪 .心脏瓣膜流固耦合问题的等几何分析快速仿真方法[D].杭州:杭州电子科技大学,2022.
|
| 13 |
COSTANTINI P, MANNI C, PELOSI F,et al .Quasi-interpolation in isogeometric analysis based on generalized B-splines[J].Computer Aided Geometric Design,2010,27(8):656-668.
|
| 14 |
陈涛,莫蓉,万能 .等几何分析中Dirichlet边界条件的配点施加方法[J].机械工程学报,2012,48(5):157-164.
|
|
CHEN Tao, MO Rong, WAN Neng .Imposing Dirichlet boundary conditions with point collocation method in isogeometric analysis[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2012,48(5):157-164.
|
| 15 |
陈涛,莫蓉,万能,等 .等几何分析中采用Nitsche法施加位移边界条件[J].力学学报,2012,44(2):371-381.
|
|
CHEN Tao, MO Rong, WAN Neng,et al .Imposing displacement boundary conditions with Nitsche’s method in isogeometric analysis[J].Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2012,44(2):371-381.
|
| 16 |
HÖLLIG K, REIF U, WIPPER J .Weighted extended B-spline approximation of Dirichlet problems[J].SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis,2001,39(2):442-462.
|
| 17 |
SHAPIRO V .Theory of R-functions and applications[R].Ithaca:Cornell University,1988.
|
| 18 |
SHAPIRO V, TSUKANOV I .Meshfree simulation of deforming domains[J].Computer-Aided Design,1999,31(7):459-471.
|
| 19 |
TSUKANOV I, SHAPIRO V, ZHANG S .A meshfree method for incompressible fluid dynamics problems[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,2003,58(1):127-158.
|
| 20 |
SHAPIRO V, TSUKANOV I .The architecture of SAGE - a meshfree system based on RFM[J].Engineering with Computers,2002,18:295-311.
|
| 21 |
ZHANG W, ZHAO L, CAI S .Shape optimization of Dirichlet boundaries based on weighted B-spline finite cell method and level-set function[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,2015,294:359-383.
|
| 22 |
VERSCHAEVE J C G .A weighted extended B-spline solver for bending and buckling of stiffened plates[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2016,107:580-596.
|
| 23 |
BURLA R K, KUMAR A V .Implicit boundary method for analysis using uniform B‐spline basis and structured grid[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,2008,76(13):1993-2028.
|
| 24 |
KUMAR A V, PADMANABHAN S, BURLA R .Implicit boundary method for finite element analysis using non‐conforming mesh or grid[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,2008,74(9):1421-1447.
|
| 25 |
COTTRELL J A, HUGHES T J R, REALI A .Studies of refinement and continuity in isogeometric structural analysis[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,2007,196(41-44):4160-4183.
|
| 26 |
SEDERBERG T W, ZHENG J, BAKENOV A,et al .T-splines and T-NURCCs[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics(TOG),2003,22(3):477-484.
|
| 27 |
SEDERBERG T W, CARDON D L, FINNIGAN G T,et al .T-spline simplification and local refinement[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics(TOG),2004,23(3):276-283.
|
| 28 |
BUFFA A, CHO D, SANGALLI G .Linear independence of the T-spline blending functions associated with some particular T-meshes[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,2010,199(23/24):1437-1445.
|
| 29 |
FORSEY D R, BARTELS R H .Hierarchical B-spline refinement[C]∥Proceedings of the 15th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques.New York:Association for Computing Machinery,1988:205-212.
|
| 30 |
FORSEY D R, BARTELS R H .Surface fitting with hie-rarchical splines[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG),1995,14(2):134-161.
|
| 31 |
LI X, CHEN F, KANG H,et al .A survey on the local refinable splines[J].Science China Mathematics,2016,59(4):617-644.
|
| 32 |
GARAU E M, VÁZQUEZ R .Algorithms for the implementation of adaptive isogeometric methods using hierarchical B-splines[J].Applied Numerical Mathe-matics,2018,123:58-87.
|
| 33 |
KURU G, VERHOOSEL C V, VAN DER ZEE K G,et al .Goal-adaptive isogeometric analysis with hierarchical splines[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,2014,270:270-292.
|
| 34 |
SCHMIDT M, NOËL L, DOBLE K,et al .Extended isogeometric analysis of multi-material and multi-physics problems using hierarchical B-splines[J].Computational Mechanics,2023,71(6):1179-1203.
|
| 35 |
KHOEI A R .Extended finite element method:theory and applications[M].Hoboken:John Wiley & Sons,2014.
|