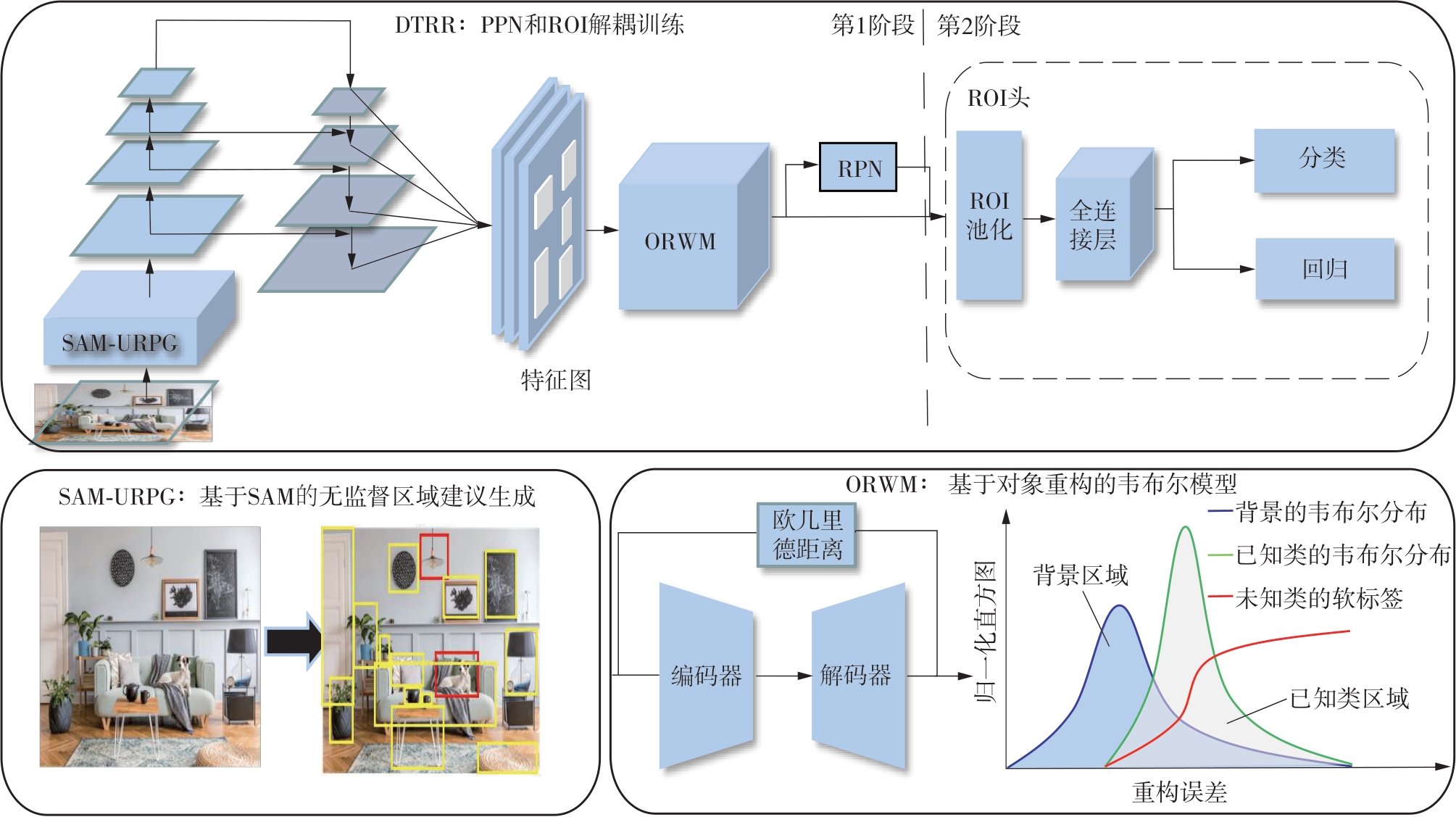
| 1 |
REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R,et al . Faster R-CNN:towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks [J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(6):1137-1149.
|
| 2 |
REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R,et al .You only look once:unified,real-time object detection [C]∥ Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas:IEEE,2016:779-788.
|
| 3 |
LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R,et al .Focal loss for dense object detection [J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2020,42(2):318-327.
|
| 4 |
ZHU X, SU W, LU L,et al . Deformable DETR:deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection [C]∥ Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations.Vienna:OpenReview.net,2021:1-16.
|
| 5 |
DHAMIJA A, GÜNTHER M, VENTURA J,et al .The overlooked elephant of object detection:open set [C]∥ Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision.Snowmass:IEEE,2020:1010-1019.
|
| 6 |
JOSEPH K J, KHAN S, KHAN F S,et al .Towards open world object detection [C]∥ Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Nashville:IEEE,2021:5826-5836.
|
| 7 |
GUPTA A, NARAYAN S, JOSEPH K J,et al .OW-DETR:open-world detection transformer[C]∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:9225-9234.
|
| 8 |
ZOHAR O, WANG K C, YEUNG S .PROB:probabilistic objectness for open world object detection [C]∥ Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Vancouver:IEEE,2023:11444-11453.
|
| 9 |
MA S, WANG Y, WEI Y,et al .CAT:localization and identification cascade detection transformer for open-world object detection [C]∥ Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Vancouver:IEEE,2023:19681-19690.
|
| 10 |
DONG N, ZHANG Y, DING M,et al .Open world DETR:transformer based open world object detection [EB/OL].(2022-12-06)[2024-03-05]..
|
| 11 |
WANG X, YU Z, DE MELLO S,et al .FreeSOLO:learning to segment objects without annotations [C]∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans:IEEE,2022:4156-4166.
|
| 12 |
BAR A, WANG X, KANTOROV V,et al .DETReg:unsupervised pretraining with region priors for object detection [C]∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:14585-14595.
|
| 13 |
KIRILLOV A, MINTUN E, RAVI N,et al .Segment anything [C]∥ Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Paris:IEEE,2023:3992-4003.
|
| 14 |
ZHOU Y .Rethinking reconstruction autoencoder-based out-of-distribution detection [C]∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:7369-7377.
|
| 15 |
JIANG W, GE Y, CHENG H,et al . READ:aggregating reconstruction error into out-of-distribution detection [C]∥ Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Washington D C:AAAI,2023:14910-14918.
|
| 16 |
OSADA G, TAKAHASHI T, AHSAN B,et al .Out-of-distribution detection with reconstruction error and typicality-based penalty [C]∥ Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision.Waikoloa:IEEE,2023:5540-5552.
|
| 17 |
FANG R H, PANG G S, ZHOU L,et al .Unsupervised recognition of unknown objects for open-world object detection [EB/OL]. (2023-08-31)[2024-03-05]..
|
| 18 |
SHMELKOV K, SCHMID C, ALAHARI K .Incremental learning of object detectors without catastrophic forgetting[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:3420-3429.
|
| 19 |
HAO Y, FU Y, JIANG Y,et al .An end-to-end architecture for class-incremental object detection with knowledge distillation [C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo.Shanghai:IEEE,2019:1-6.
|
| 20 |
YANG B, DENG X, SHI H,et al .Continual object detection via prototypical task correlation guided gating mechanism[C]∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:9245-9254.
|
| 21 |
HE K, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P,et al .Mask R-CNN [C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:2980-2988.
|
| 22 |
WEI F, GAO Y, WU Z,et al .Aligning pretraining for detection via object-level contrastive learning[C]∥ Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.Red Hook:Curran Associates Inc., 2021:22682-22694.
|
| 23 |
LI Z, HOIEM D .Learning without forgetting[C]∥Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision.Amsterdam:Springer,2016:614-629.
|
| 24 |
DHAR P, SINGH R V, PENG K C,et al .Learning without memorizing[C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Visionand Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:5133-5141.
|
| 25 |
HE K, ZHANG X, REN S,et al .Deep residual learning for image recognition [C]∥ Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas:IEEE,2016:770-778.
|
| 26 |
UIJLINGS J R, GEVERS T, SMEULDERS W A .Selective search for object recognition[J].International Journal of Computer Vision,2013,104(2):154-171.
|
 ), XU Yong, XI Xing, LUO Ronghua(
), XU Yong, XI Xing, LUO Ronghua( )
)