华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 51-58.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230368
基于速度控制的机器人轨迹摩擦补偿控制算法
叶伯生 李思澳 谭帅 李晓昆 金雄程 邵柏岩
- 华中科技大学 机械科学与工程学院,湖北 武汉 430074
Trajectory Friction Compensation Algorithm for Robots Based on Velocity Control
YE Bosheng LI Siao TAN Shuai LI Xiaokun JIN Xiongcheng SHAO Baiyan
- School of Mechanical Science and Engineering,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430074,Hubei,China
摘要:
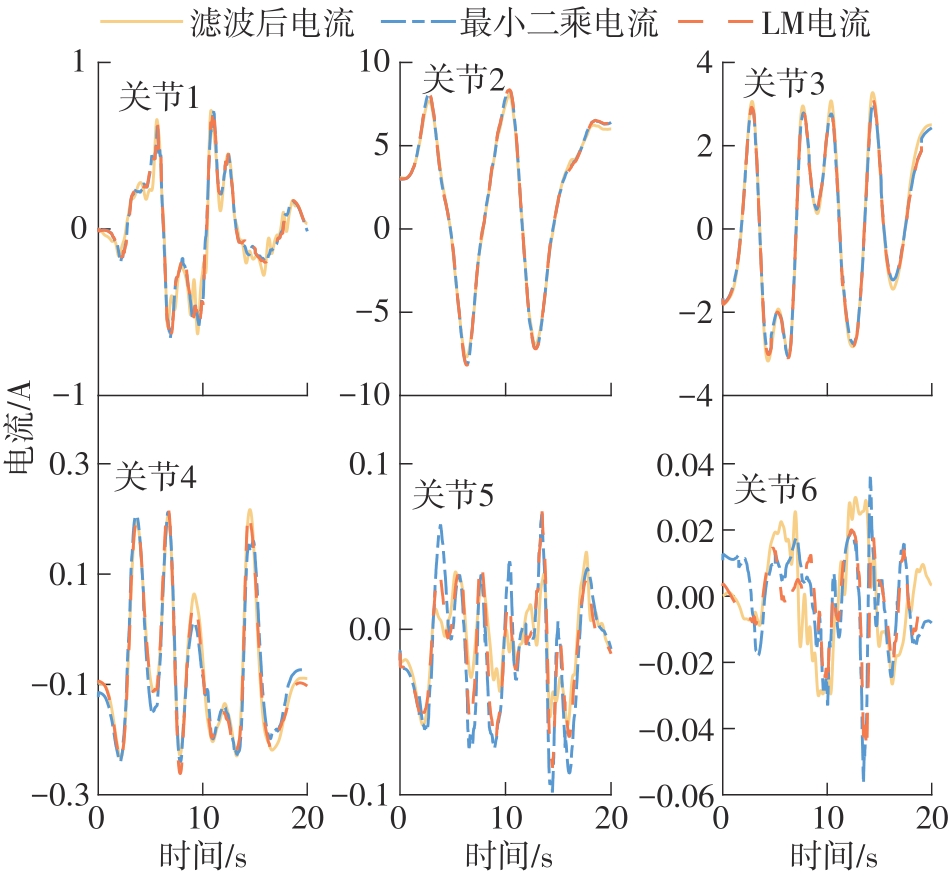
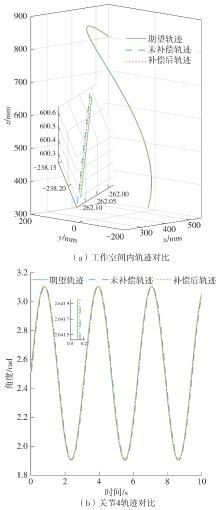
目前机器人已在工业生产制造中得到广泛的应用,但由于机器人系统中关节摩擦等因素的影响,机器人的轨迹跟踪精度难以满足高精度生产的需求。为减少机械结构中非线性摩擦因素和系统中未建模干扰等因素对机器人运行稳定性和加工精度的影响,文中提出了一种速度模式下的摩擦补偿控制算法。首先,基于傅里叶级数和5次多项式混合的方式设计最优激励轨迹,通过最小二乘法完成动力学参数的预辨识,并利用Levenberg-Marquardt法对预辨识结果进行迭代寻优,从而建立更为精确的机器人动力学模型;然后,基于李雅普诺夫方法设计机器人轨迹跟踪控制算法,将最速离散跟踪微分器中采集的关节角度输入所设计的轨迹跟踪控制算法中,得到实时的关节速度补偿值,将补偿值实时输入机器人中实现摩擦补偿控制;最后,以六自由度串联机器人为实验对象,对所设计的摩擦补偿控制算法进行实验验证。结果表明,相对于摩擦补偿前,机器人的末端轨迹跟踪精度提升约35%,从而验证了文中所提算法在机器人摩擦补偿领域的有效性。
中图分类号: