华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 141-150.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230167
• 电子、通信与自动控制 • 上一篇
单绳缠绕式矿井提升机制动瞬态冲击抑制策略
解辉1 沈刚2 刘东3 汤裕1 朱真才1
- 1.中国矿业大学 机电工程学院, 江苏 徐州 221000
2.安徽理工大学 机电工程学院, 安徽 淮南 232000
3.中国船舶集团有限公司 第七一三研究所, 河南 郑州 450015
Braking Transient Impact Suppression Strategy for Single Rope Winding Mine Hoist
XIE Hui1 SHEN Gang2 LIU Dong3 TANG Yu1 ZHU Zhencai1
- 1.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou 221000,Jiangsu,China
2.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Anhui University of Technology,Huainan 232000,Anhui,China
3.713th Research Institute of China Shipbuilding Industry Group Co. ,Ltd,Zhengzhou 450015,Henan,China
摘要:
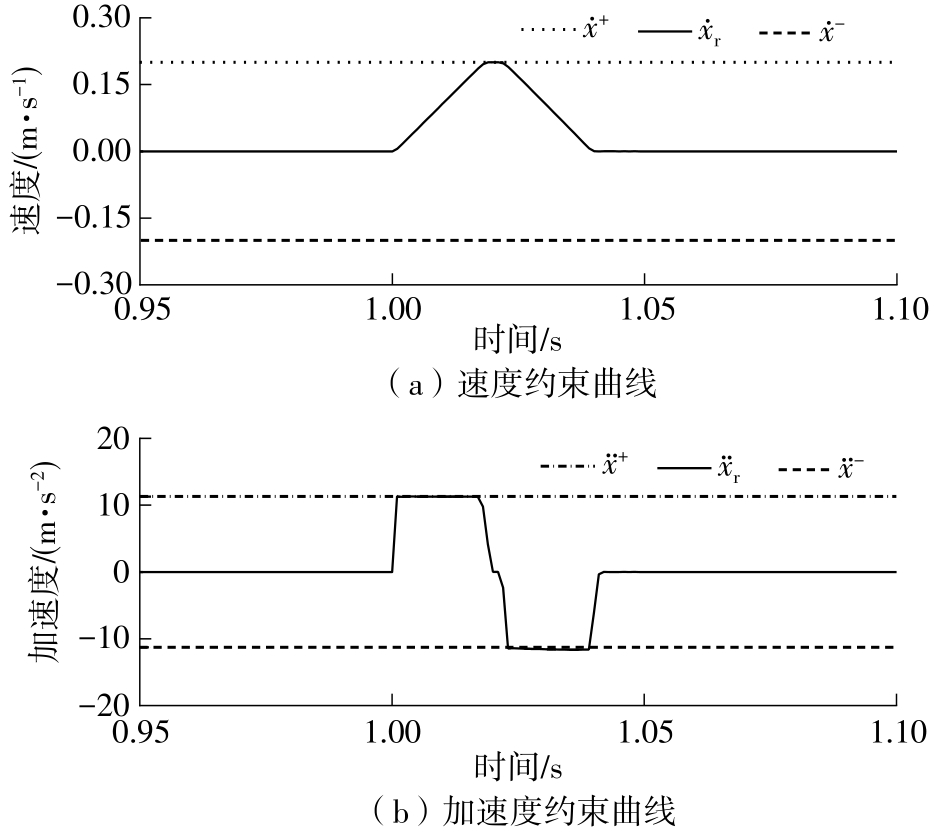
在矿井提升机的制动控制中,制动瞬态冲击是影响矿井提升机安全可靠运行的关键问题。由于受到技术和经济成本的制约,目前包含贴闸/压紧的制动过程全程采用力闭环控制,这不可避免地导致闸瓦与闸盘刚性接触时的制动力瞬态冲击问题。针对矿井提升机制动瞬态冲击问题,文中提出了一种基于滞回切换原理的混合贴闸/压紧制动控制策略。首先,分别利用非奇异快速终端滑模控制和反步控制设计了贴闸和压紧控制器;其次,为达到快速贴闸的目的,设计了一种基于离散积分器的在线贴闸轨迹再规划方法,有效地减小了制动器贴闸时间;然后,为实现由贴闸控制到压紧控制的安全切换,利用滞回切换原理,制定了混合贴闸/压紧控制稳态切换策略,大大减小了制动力瞬态冲击;最后,为验证提出方法的有效性,选择传统全程力闭环控制策略C1与混合贴闸/压紧直接切换策略C2作为对比方法,在单绳缠绕式提升试验台进行了对比实验,从贴闸时间、制动力最大跟踪误差和提升钢丝绳最大张力3个方面对实验结果进行了分析。实验结果表明:相较于C1控制策略,提出制动控制策略的贴闸时间缩短了64.5%,钢丝绳张力峰值减小了41 N;相较于C2控制策略,提出制动控制策略的制动力冲击减小了90.3%,钢丝绳张力峰值减小了88 N。上述结果表明本文提出的方法能有效改善制动瞬态冲击,减小制动空动时间,提高制动系统安全性,同时本研究也为一类需要混合力/位置控制的电液伺服系统提供了一种有效的解决方法。
中图分类号: