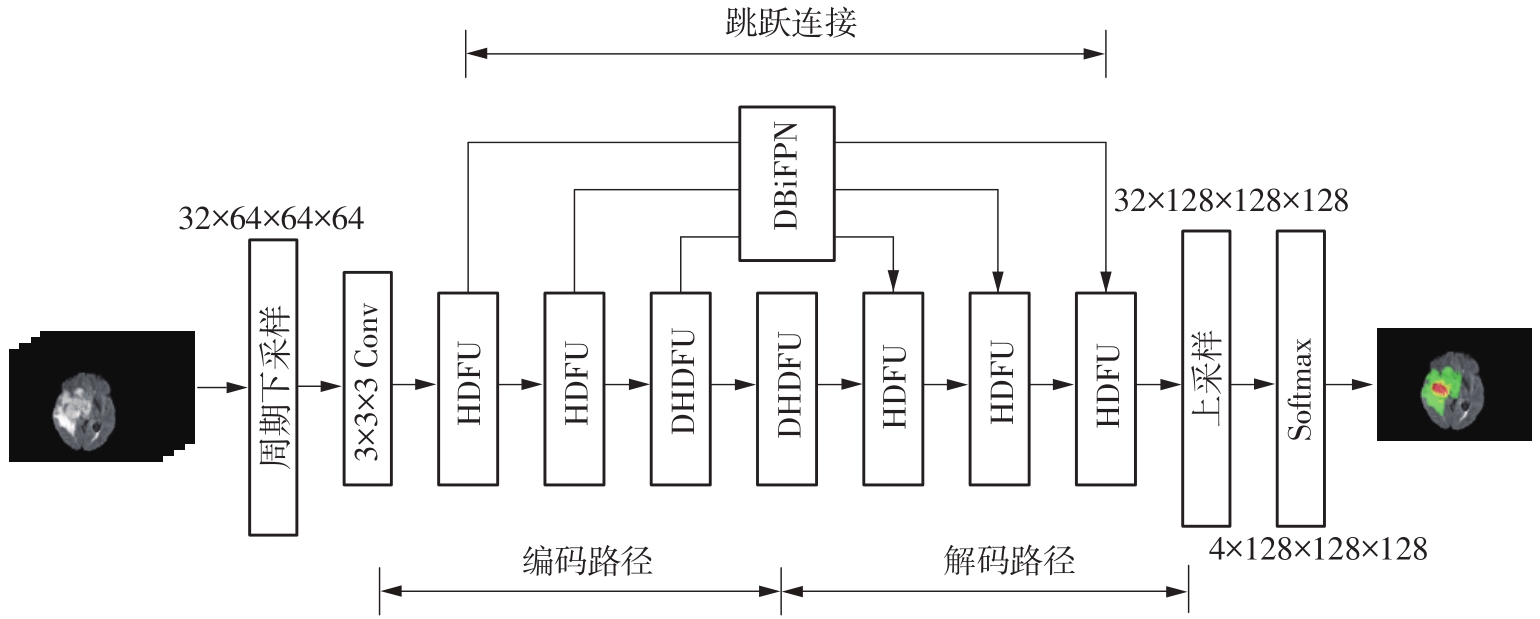
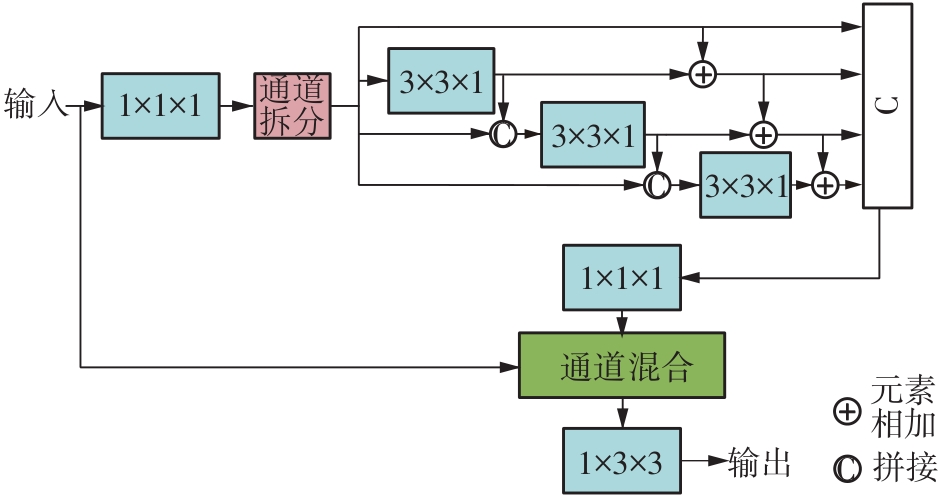
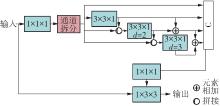
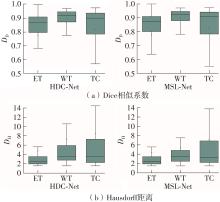
| 1 |
TABATABAI G, STUPP R, van den BENT M J,et al .Molecular diagnostics of gliomas:the clinical perspective[J].Acta Neuropathologica,2010,120(5):585-592.
|
| 2 |
WADHWA A, BHARDWAJ A, VERMA V S .A review on brain tumor segmentation of MRI images[J].Magnetic Resonance Imaging,2019,61:247-259.
|
| 3 |
CUI S, MAO L, JIANG J,et al .Automatic semantic segmentation of brain gliomas from MRI images using a deep cascaded neural network[J].Journal of Healthcare Engineering,2018,2018:4940593/1-15.
|
| 4 |
PINTO A, PEREIRA S, RASTEIRO D,et al .Hierarchical brain tumor segmentation using extremely rando-mized trees[J].Pattern Recognition,2018,82:105-117.
|
| 5 |
DEEPAK S, AMEER P M .Brain tumor classification using deep CNN features via transfer learning[J].Computers in Biology and Medicine,2019,111:103345/1-7.
|
| 6 |
TIWARI A, SRIVASTAVA S, PANT M .Brain tumor segmentation and classification from magnetic resonance images:review of selected methods from 2014 to 2019[J].Pattern Recognition Letters,2020,131:244-260.
|
| 7 |
HAVAEI M, DAVY A, WARDE-FARLEY D,et al .Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks[J].Medical Image Analysis,2017,35:18-31.
|
| 8 |
ZHAO X, WU Y, SONG G,et al .A deep learning model integrating FCNNs and CRFs for brain tumor segmentation[J].Medical Image Analysis,2018,43:98-111.
|
| 9 |
LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T .Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]∥ Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Boston:IEEE,2015:3431-3440.
|
| 10 |
RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T .U-Net:convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥ Proceedings of the 18th International Confe-rence on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Munich:Springer,2015:234-241.
|
| 11 |
ÇICEK Ö, ABDULKADIR A, LIENKAMP S S,et al .3D U-Net:learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation[C]∥ Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Athens:Springer,2016:424-432.
|
| 12 |
HUANG C, HAN H, YAO Q,et al .3D U2-Net:a 3D universal U-Net for multi-domain medical image segmentation[C]∥ Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Shenzhen:Springer,2019:291-299.
|
| 13 |
CHEN C, LIU X, DING M,et al .3D dilated multi-fiber network for real-time brain tumor segmentation in MRI[C]∥ Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Shenzhen:Springer,2019:184-192.
|
| 14 |
DING Y, GONG L, ZHANG M,et al .A multi-path adaptive fusion network for multimodal brain tumor segmentation[J].Neurocomputing,2020,412:19-30.
|
| 15 |
HUANG G, LIU Z, van der MAATEN L,et al .Densely connected convolutional networks[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:4700-4708.
|
| 16 |
LUO Z, JIA Z, YUAN Z,et al .HDC-Net:hierarchical decoupled convolution network for brain tumor segmentation[J].IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics,2020,25(3):737-745.
|
| 17 |
OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, FOLGOC L L,et al .Attention U-Net:learning where to look for the pancreas[EB/OL]. (2018-05-20)[2021-12-30]..
|
| 18 |
IBTEHAZ N, RAHMAN M S .MultiResUNet:rethin-king the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation[J].Neural Networks,2020,121:74-87.
|
| 19 |
WANG Y L, ZHAO Z J, HU S Y,et al .CLCU-Net:cross-level connected U-shaped network with selective feature aggregation attention module for brain tumor segmentation[J].Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine,2021,207:106154/1-9.
|
| 20 |
LI X, LUO G, WANG K .Multi-step cascaded networks for brain tumor segmentation[C]∥ Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Brainlesion:Glioma,Multiple Sclerosis,Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries.Shenzhen:Springer,2019:163-173.
|
| 21 |
VALANARASU J M J, SINDAGI V A,HACIHALILOG- LU I,et al .KiU-Net:overcomplete convolutional architectures for biomedical image and volumetric segmentation[EB/OL]. (2021-10-14)[2021-12-30]..
|
| 22 |
SUDRE C H, LI W, VERCAUTEREN T,et al .Gene-ralised dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations[M]∥ Deep learning in medical image analysis and multimodal learning for clinical decision support.Berlin:Springer,2017:240-248.
|
| 23 |
LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R,et al .Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:2980-2988.
|
| 24 |
YU F, KOLTUN V, FUNKHOUSER T .Dilated residual networks[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:472-480.
|
| 25 |
MEHTA S, RASTEGARI M, CASPI A,et al .ESPNet:efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation[C]∥ Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision.Munich:Springer,2018:552-568.
|
| 26 |
ZHANG X, ZHOU X, LIN M,et al .ShuffleNet:an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]∥ Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Salt Lake City:IEEE,2018:6848-6856.
|
| 27 |
TAN M, PANG R, LE Q V .EfficientDet:scalable and efficient object detection[C]∥ Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Seattle:IEEE,2020:10781-10790.
|