

Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science) >
Segmentation Method of Barefoot Footprint Based on Multi-Granularity Feature and Region Relationship
Received date: 2024-06-06
Online published: 2024-08-23
Supported by
the Key R & D Program of Anhui Province(2022k07020006);the University Natural Science Research Major Program of Anhui Province(KJ2021ZD0004);the University Collaborative Innovation Program of Anhui Pro-vince(GXXT-2022-038)
When using semantic segmentation methods to automatically segment barefoot footprint images, although manual intervention can be reduced, the issue of blurred toe regions in barefoot footprint image segmentation requires the neural network model to pay more attention to feature extraction from these areas. For barefoot footprint images with uneven lighting, the model can establish contextual relationships between the global and local regions of the footprint, using the feature information from the global region to enhance the feature expression of the uneven lighting areas, thereby improving the accuracy and robustness of image segmentation. To address this, this paper proposed a barefoot footprint segmentation method based on multi-granularity feature-region relationships. By using local region labels, the method enhances feature representation in the toe area, extracts multi-granularity features of footprints, and integrates them with global footprint features to improve segmentation performance in blurred areas. Meanwhile, spatial transformations were applied to both the original image and the footprint feature map, and a matrix multiplication approach was used to establish a barefoot region relationship matrix between them. This relationship matrix was then utilized to spatially modulate the global barefoot features, achieving feature enhancement. Furthermore, this paper constructed an in-the-wild barefoot footprint dataset consisting of 1 100 barefoot footprint images from 25 individuals and conducted experiments on four types of barefoot footprint images: blurred, unevenly illuminated, both blurred and unevenly illuminated, and normal. The results show that the intersection over union (IoU) for the barefoot class reaches 93.50% on normal barefoot footprint images. For blurred, uneven lighting, and blurry-uneven lighting images, the IoU are 92.90%, 93.06%, and 91.66%, respectively. Notably, the IoU for blurry-uneven lighting images is improved by 1.15 percentage points compared to U-Net.
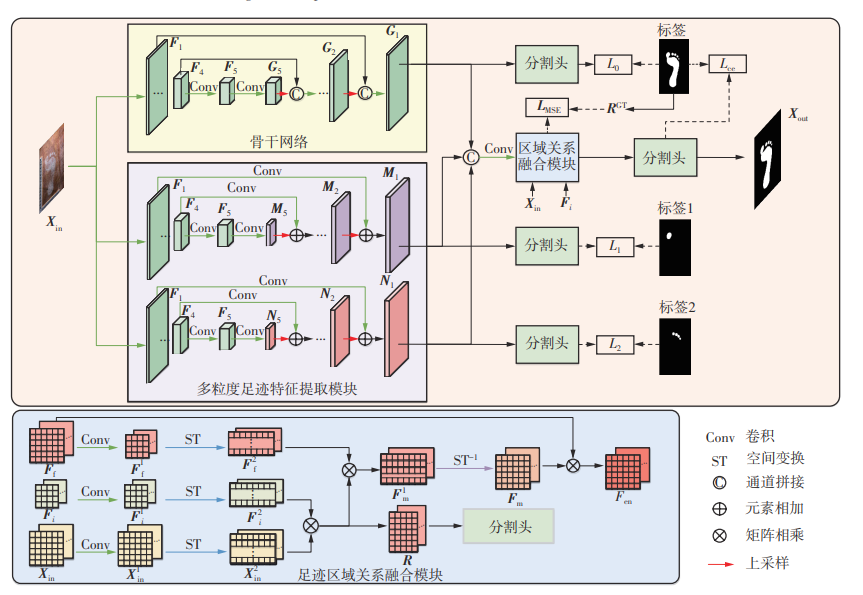
ZHANG Yan , YAN Yi , WU Hongying , WANG Sitong , WU Yefeng , WANG Nian . Segmentation Method of Barefoot Footprint Based on Multi-Granularity Feature and Region Relationship[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2025 , 53(3) : 57 -67 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240290
| 1 | 吴一全,朱丽,吴诗婳 .基于二维Arimoto灰度熵的图像阈值分割快速迭代算法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(5):48-57. |
| WU Yi-quan, ZHU Li, WU Shi-hua .Fast iterative algorithm for image threshold segmentation based on two-dimensional Arimoto gray entropy [J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,44(5):48-57. | |
| 2 | TREMEAU A, BOREL N .A region growing and mer-ging algorithm to color segmentation[J].Pattern Recognition,1997,30(7):1191-1203. |
| 3 | 王卫星,吴林春 .基于分数阶积分谷底边界检测的路面裂缝提取[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2014,42(1):117-122. |
| WANG Wei-xing, WU Lin-chun .Extraction of pavement cracks based on valley edge detection of fractional integral[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2014,42(1):117-122. | |
| 4 | 徐曼 .基于改进快速分水岭算法的图像分割技术研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2010. |
| 5 | LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T .Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017,39(4):640-651. |
| 6 | BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R .SegNet:a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(12):2481-2495. |
| 7 | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T .U-Net:convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Munich:Springer,2015:234-241. |
| 8 | CHAURASIA A, CULURCIELLO E .LinkNet:exploi-ting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing.St.Petersburg:IEEE,2017:1-4. |
| 9 | XIA X, KULIS B .W-Net:a deep model for fully unsuper-vised image segmentation[EB/OL].(2017-11-22) [2024-04-25].. |
| 10 | YUAN Y, CHEN X, WANG J .Object-contextual re-presentations for semantic segmentation[C]∥ Procee-dings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:173-190. |
| 11 | ZHAO H, SHI J, QI X,et al .Pyramid scene parsing network[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:6230-6239. |
| 12 | CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I,et al .DeepLab:semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets,atrous convolution,and fully connected CRFs[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,40(4):834-848. |
| 13 | CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F,et al .Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. (2017-06-17)[2024-04-25].. |
| 14 | LI H, XIONG P, AN J, et al .Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation [EB/OL].(2018-05-25)[2024-04-25].. |
| 15 | PUNN N S, AGARWAL S .Modality specific U-Net variants for biomedical image segmentation:a survey [J].Artificial Intelligence Review,2022,55(7):5845-5889. |
| 16 | 杨晋生,陈洪鹏,关欣,等 .一种多尺度轻量级脑胶质瘤图像分割网络[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(12):132-141. |
| YANG Jinsheng, CHEN Hongpeng, GUAN Xin,et al .A multi-scale lightweight brain glioma image segmentation network[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(12):132-141. | |
| 17 | XU J, XIONG Z, BHATTACHARYYA S P .PIDNet:a real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by PID controllers[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Vancouver:IEEE,2023:19529-19539. |
| 18 | CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G,et al .End-to-end object detection with transformers[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:213-229. |
| 19 | DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A,et al .An image is worth 16×16 words:transformers for image recognition at scale[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Learning Representations.[S.l.]: OpenReview.net,2021:1-21. |
| 20 | ZHENG S, LU J, ZHAO H,et al .Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Nashville:IEEE,2021:6877-6886. |
| 21 | STRUDEL R, GARCIA R, LAPTEV I,et al .Segmenter:transformer for semantic segmentation[C] ∥Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Confe-rence on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:7242-7252. |
| 22 | XIE E, WANG W, YU Z,et al .SegFormer:simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers [C] ∥ Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34:35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.San Diego:Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation,Inc.,2021:12077-12090. |
| 23 | RANFTL R, BOCHKOVSKIY A, KOLTUN V .Vision transformers for dense prediction[C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2021:12159-12168. |
| 24 | CHEN Y, DAI X, CHEN D,et al .Mobile-Former:bridging MobileNet and transformer[C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:5260-5269. |
| 25 | MEHTA S, RASTEGARI M .MobileVit:light-weight,general-purpose,and mobile-friendly vision transformer[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Tenth International Confe-rence on Learning Representations.[S.l.]:OpenReview.net,2022:1-26. |
| 26 | ZHANG W, HUANG Z, LUO G,et al .TopFormer:token pyramid transformer for mobile semantic segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Confe-rence on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:12073-12083. |
| 27 | LI Y, YUAN G, WEN Y,et al .EfficientFormer: vision transformers at MobileNet speed[C] ∥ Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35:36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.San Diego:Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation,Inc.,2022:1-16. |
| 28 | WAN Q, HUANG Z, LU J,et al .SeaFormer: squeeze-enhanced axial transformer for mobile semantic segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.[S.l.]:OpenReview.net,2023:1-19.. |
| 29 | LIN T Y, DOLLáR P, GIRSHICK R,et al .Feature pyramid networks for object detection [C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:936-944. |
| 30 | GU J, KWON H, WANG D,et al .Multi-scale high- resolution vision transformer for semantic segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:12084-12093. |
| 31 | HUANG H, LIN L, TONG R,et al .UNet 3+:a full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Confe-rence on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing.Barcelona:IEEE,2020:1055-1059. |
| 32 | CHEN L C, ZHU Y, PAPANDREOU G,et al . Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision.Munich:Springer,2018:833-851. |
| 33 | YUAN Y, HUANG L, GUO J,et al .OCNet:object context for semantic segmentation[J].International Journal of Computer Vision,2021,129:2375-2398. |
| 34 | FU J, LIU J, TIAN H,et al .Dual attention network for scene segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:3141-3149. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |