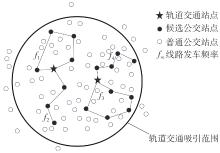
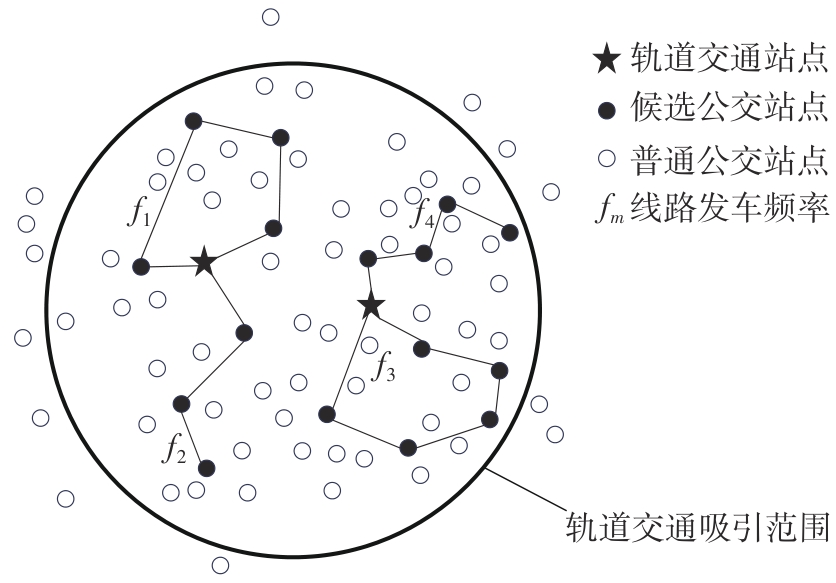
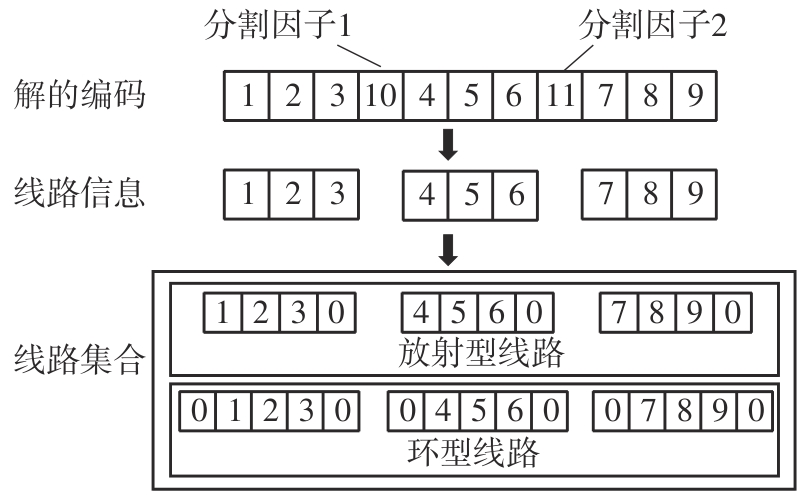
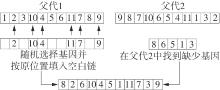
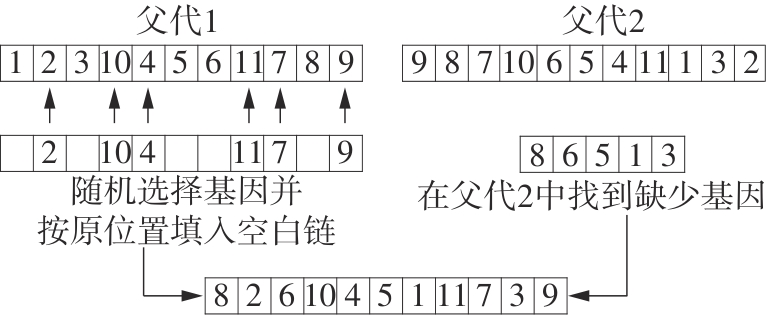
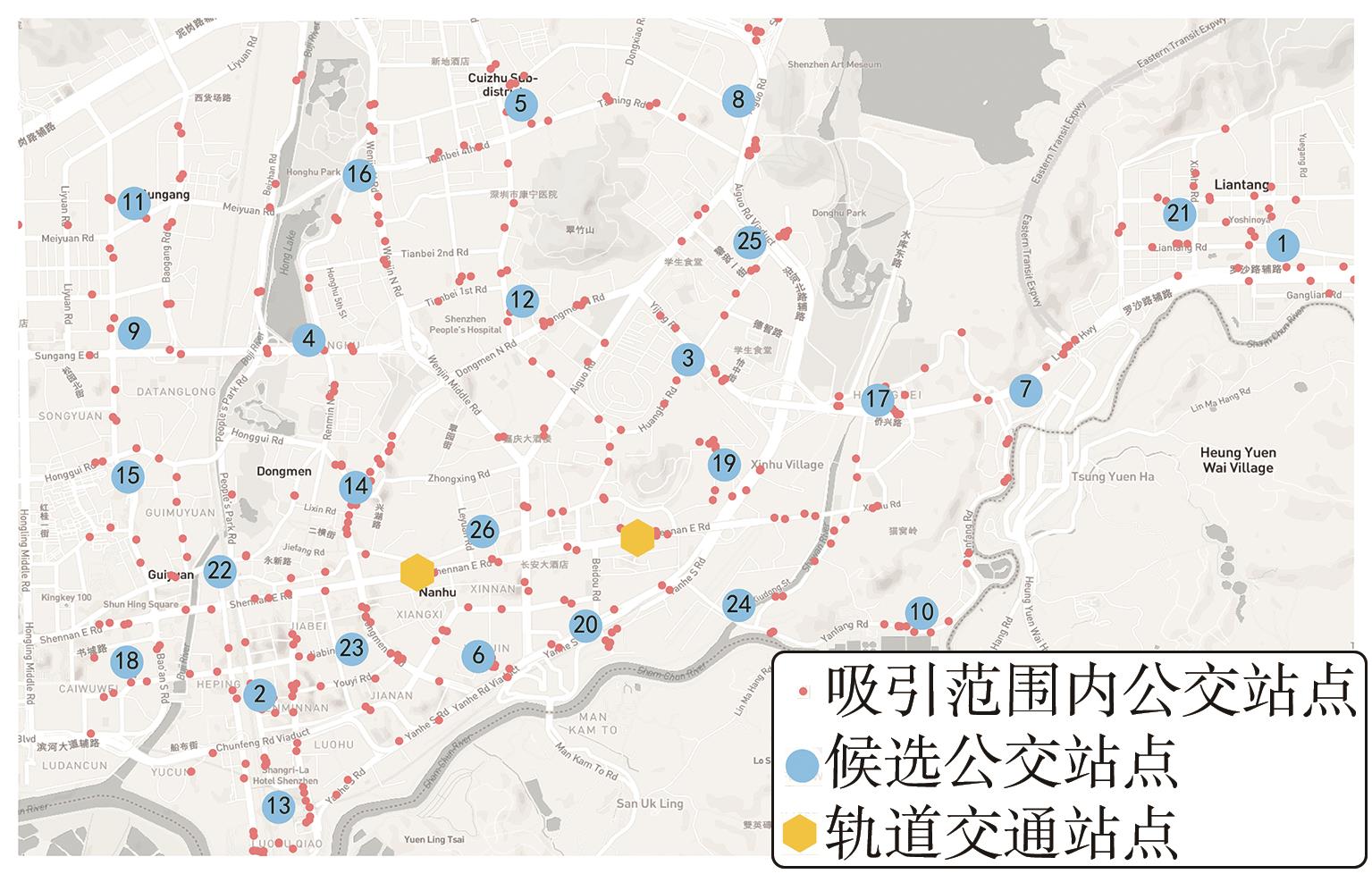
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 95-105.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230595
Special Issue: 2024年智慧交通系统
• Intelligent Transportation System • Previous Articles Next Articles
Optimization of Metro Feeder Bus Routes Based on Surrogate-Assisted NSGA-Ⅱ Algorithm
TANG Jinjun( ), REN Maoxin, LI Zhitao, GAO Yifan
), REN Maoxin, LI Zhitao, GAO Yifan
- School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,Central South University,Changsha 410075,Hunan,China
-
Received:2023-09-22Online:2024-11-25Published:2024-05-10 -
About author:唐进君(1983—),男,博士,教授,主要从事智能交通系统研究。E-mail:jinjuntang@csu.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52172310);the Key R&D Program of Hunan Province(2023GK2014)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
TANG Jinjun, REN Maoxin, LI Zhitao, et al. Optimization of Metro Feeder Bus Routes Based on Surrogate-Assisted NSGA-Ⅱ Algorithm[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(11): 95-105.
share this article
Table 1
Variable and collection definition"
| 类别 | 符号 | 释义 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 集合 | 方案所含线路集合 | ||
| 公交站点集合 | |||
| 轨道站点集合 | |||
| 参数 | 研究的时间长度 | s | |
| 接驳公交平均车速 | km/h | ||
| 车辆i最大载客数 | 人次 | ||
| 车辆i最大座位数 | 人次 | ||
| 第k个站的乘客平均到站率与离站率 | 人次/h | ||
| 站点i与j之间的距离 | km | ||
| 接驳线路应满足的最小与最大发车频率 | s/车次 | ||
| 接驳线路应满足的最短与最长线路长度 | km | ||
| 乘客候车单位时间成本 | 元/s | ||
| 乘客车上单位时间成本 | 元/s | ||
| 无座乘客车上单位时间拥挤成本 | 元/s | ||
| 车辆公里燃料成本 | 元/km | ||
| 企业单位时间运营成本 | 元/s | ||
| 乘客单次乘坐公交票价 | 元 | ||
| 第 | s | ||
| 决策变量 | 0~1决策变量,站点 | ||
| 0~1决策变量,站点 | |||
| 0~1决策变量,站点 | |||
| 连续变量,接驳线路 | km | ||
| 连续变量,接驳公交线路 | s/车次 | ||
| 连续变量,接驳线路 | % |
Table 3
Information about the final selected route scheme"
| 线路序号 | 接驳线路 | 线路线型 | 发车频率/(s·车次-1) | 客流需求/(人·h-1) | 线路长度/m | 有效服务率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
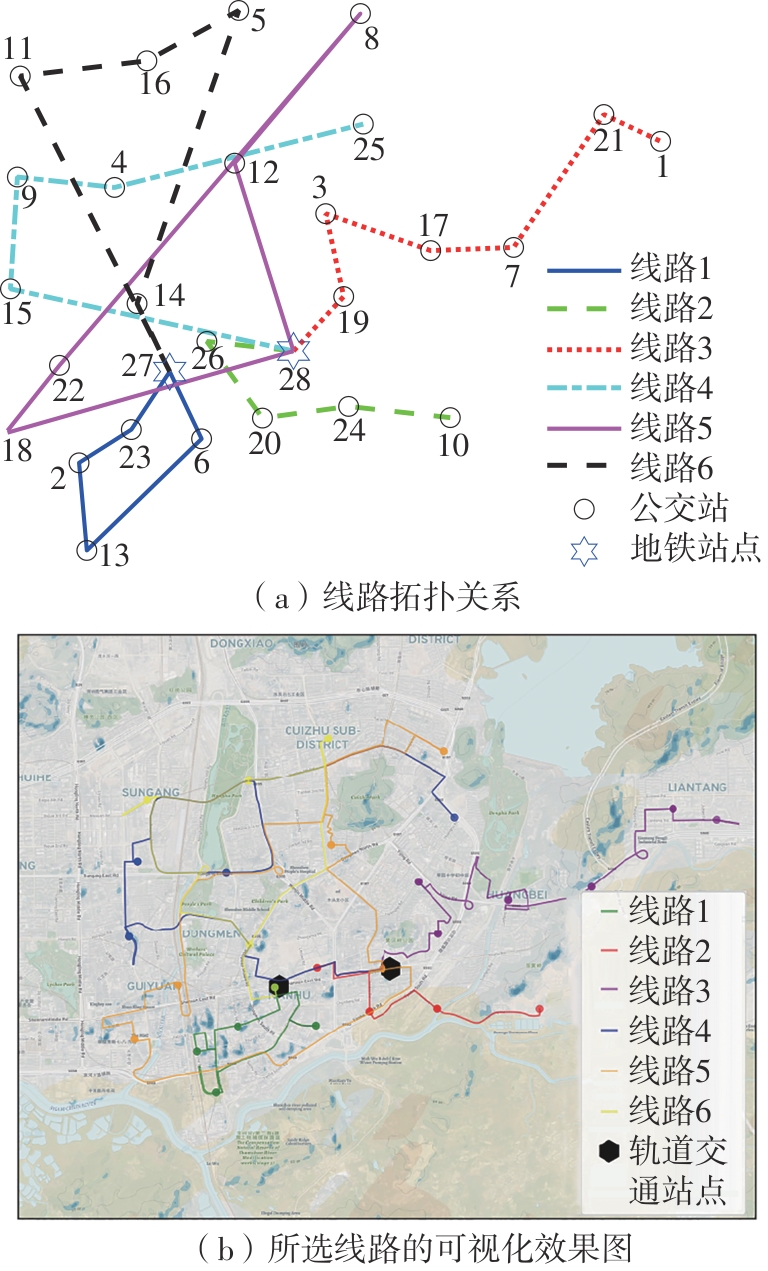
| 线路1 | 27-23-2-13-6-27 | 环型 | 720 | 30 | 3 222.261 | 100.00 |
| 线路2 | 28-26-20-24-10 | 放射型 | 780 | 40 | 3 491.666 | 97.96 |
| 线路3 | 28-19-3-17-7-21-1 | 放射型 | 360 | 97 | 5 097.731 | 91.21 |
| 线路4 | 28-15-9-4-25 | 放射型 | 840 | 51 | 7 096.012 | 100.00 |
| 线路5 | 28-18-22-8-12-28 | 环型 | 900 | 44 | 9 264.829 | 100.00 |
| 线路6 | 27-11-16-5-14-27 | 环型 | 840 | 42 | 7 924.427 | 98.43 |
| 1 | 陈廷照,陈艳艳,王子理,等 .“轨道交通微中心”理念下的慢行影响区范围确定方法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(7):56-65. |
| CHEN Tingzhao, CHEN Yanyan, WANG Zili,et al .Methods of determining the range of non-motorized travel influence area under the concept of “metro transit micro-center”[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(7):56-65. | |
| 2 | SAM E F, DANIELS S, BRIJS K,et al .Modelling public bus/minibus transport accident severity in Ghana[J].Accident Analysis and Prevention,2018,119:114-121. |
| 3 | DOU X, WANG H, MENG Q .Parallel shuttle bus service design for planned mass rapid transit shutdown:the Singapore experience[J].Transportation Research Part C,2019,108(C):340-356. |
| 4 | 陈嘉超,宋程 .基于聚类分析法的地铁与常规公交换乘客流分析[J].科技和产业,2018,18(5):100-104. |
| CHEN Jiachao, SONG Cheng .Analysis on the transfer passenger flow between bus and subway system based on cluster analysis[J].Science Technology and Industry,2018,18(5):100-104. | |
| 5 | 石兆,符卓 .配送选址-多车型运输路径优化问题及求解算法[J].计算机科学,2015,42(5):245-250. |
| SHI Zhao, FU Zhuo .Distribution location-routing problem of heterotypic vehicles and its algorithms[J].Computer Science,2015,42(5):245-250. | |
| 6 | LIANG J, WU J, GAO Z,et al .Bus transit network design with uncertainties on the basis of a metro network:a two-step model framework[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2019,126:115-138. |
| 7 | BORNDÖRFER R, GRÖTSCHEL M, PFETSCH M E .A column-generation approach to line planning in public transport[J].Transportation Science,2007,41(1):123-132. |
| 8 | IBARRA-ROJAS O J, DELGADO F, GIESEN R,et al .Planning,operation,and control of bus transport systems:a literature review[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2015,77:38-75. |
| 9 | SUMAN H K, BOLIA N B .Improvement in direct bus services through route planning[J].Transport Policy,2019,81:263-274. |
| 10 | ZHENG M N, ZHOU R X, LIU S S,et al .Route design model of multiple feeder bus service based on existing bus lines[J].Journal of Advanced Transportation,2020,2020(8):885387/1-12. |
| 11 | ALMASI M H, SADOLLAH A, KANG S,et al .Optimization of an improved intermodal transit model equipped with feeder bus and railway systems using metaheuristics approaches[J].Sustainability,2016,8(6):537/1-27. |
| 12 | PATTNAIK S B, MOHAN S, TOM V M .Urban bus transit route network design using genetic algorithm[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering,1998,124(4):368-375. |
| 13 | SHRIVASTAVA P, OMAHONY M .A model for development of optimized feeder routes and coordinated schedules—a genetic algorithms approach[J].Transport Policy,2006,13(5):413-425. |
| 14 | XIONG J, HE Z, GUAN W,et al .Optimal timetable development for community shuttle network with metro stations[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2015,60:540-565. |
| 15 | 邓连波,高伟,赖天珍,等 .基于换乘网络的城市轨道交通关联公交接驳线网优化[J].铁道科学与工程学报,2012,9(6):77-83. |
| DENG Lian-bo, GAO Wei, LAI Tian-zhen,et al .Optimal design of feeder-bus network related to urban rail transit based on transfer network[J].Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2012,9(6):77-83. | |
| 16 | JIANG S, GUAN W, YANG L,et al .Feeder bus accessibility modeling and evaluation[J].Sustainability,2020,12(21):8942/1-17. |
| 17 | CAO Y, JIANG D, WANG S .Optimization for feeder bus route model design with station transfer[J].Sustainability,2022,14(5):2780/1-15. |
| 18 | 韩月一,王登忠,王如杰,等 .城市地铁站点接驳公交多目标优化方法[J].交通运输工程与信息学报,2023,21(1):80-93. |
| HAN Yueyi, WANG Dengzhong, WANG Rujie,et al .Multi-objective optimization method for connecting buses in urban subway stations[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information,2023,21(1):80-93. | |
| 19 | BADIA H, JENELIUS E .Design and operation of feeder systems in the era of automated and electric buses[J].Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice,2021,152:146-172. |
| 20 | 赵传林,孙正一 .考虑乘客异质性的公交运行模型仿真研究[J].计算机仿真,2023,40(7):148-153. |
| ZHAO Chuan-lin, SUN Zheng-yi .Simulation study of bus operation model considering passenger heterogeneity[J].Computer Simulation,2023,40(7):148-153. | |
| 21 | SEBASTIANI M T, LÜDERS R, FONSECA K V O .Evaluating electric bus operation for a real-world BRT public transportation using simulation optimization[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2016,17(10):2777-2786. |
| 22 | 宋俪婧,白同舟,贺玉龙,等 .基于混合整数非线性规划的接驳公交优化模型[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2022,22(3):104-111. |
| SONG Li-jing, BAI Tong-zhou, HE Yulong,et al .Feeder bus routes and frequency optimization based on mixed integer nonlinear programming[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2022,22(3):104-111. | |
| 23 | HADAS Y, SHNAIDERMAN M .Public-transit frequency setting using minimum-cost approach with stochastic demand and travel time[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2012,46(8):1068-1084. |
| 24 | 张鑫 .考虑舒适度的公交线网优化设计[D].广州:华南理工大学,2018. |
| 25 | 谭佳慧 .接驳城市轨道的多模式公交线路优化研究[D].济南:山东建筑大学,2022. |
| 26 | DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S,et al .A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:NSGA-Ⅱ[J].IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation,2002,6(2):182-197. |
| 27 | SZETO W Y, WU Y Z, HO S C .An artificial bee colony algorithm for the capacitated vehicle routing problem[J].European Journal of Operational Research,2011,215(1):126-135. |
| 28 | 王伟仲 .基于代理模型的高代价问题优化算法[D].广州:广东工业大学,2021. |
| 29 | 任艳军 .城市地铁与常规公交的协同研究——以青岛市为例[D].西安:长安大学,2019. |
| 30 | 刘珊珊 .轨道接驳型社区公交线路优化方法研究[D].南京:东南大学,2020. |
| 31 | 宗芳,隽志才,张慧永,等 .出行时间价值计算及应用研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2009,9(3):114-119. |
| ZONG Fang, JUAN Zhi-cai, ZHANG Hui-yong,et al .Calculation and application of value of travel time[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2009,9(3):114-119. | |
| 32 | 陈维亚,李泽宇,张衡鹏,等 .智轨列车与常规公交共线组合发车间隔优化[J].铁道科学与工程学报,2022,19(10):2833-2841. |
| CHEN Weiya, LI Zeyu, ZHANG Hengpeng,et al .Optimization of the combined departure interval for joint operation of ART and conventional bus[J].Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2022,19(10):2833-2841. |
| [1] | XIE Kun, XING Xinyuan, DONG Honghui, et al. Workplace and Residence Identification and Travel Activity Classification Driven by Trajectory Data [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(6): 131-139. |
| [2] |
LONG Xueqin, ZHAI Manrong, WANG Yuanze, et al.
A Carpooling Matching Method Considering Passengers’ Time-Price Elasticity #br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(6): 119-130. |
| [3] | CHENG Haiying, LI Nanxi, MA Dengcheng, WU Wenxia. Optimized Design of Foamed Asphalt Spraying Device Considering Viscosity Change and State Change [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(4): 81-89. |
| [4] | WENG Jiancheng, WU Mingzhu, WEI Ruicong, et al. Speed Prediction for Road Around Large Scale Activities Venues Considering Multiple Factors Synergism [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 34-44. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yueming, LI Tianyu, JI Shuting. Influence of Cycloidal Pinwheel Reducer Parameters on Transmission Efficiency and Parameter Optimization [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(4): 77-87. |
| [6] | LIU Ning, HUA Tianbiao, WANG Gao, CHEN Faming. A Batch Scheduling Method of Flexible Job-Shop with Partially Out-of-Ordered Execute Operation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(10): 51-63. |
| [7] | WANG Xuewu, FANG Junyu, GAO Jin, et al. Multi-Objective Optimization Based on Improved Distribution of Solutions [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(8): 137-148. |
| [8] | LI Shuxun, HU Yinggang, LI Cheng, et al. Optimization of Body Profile Line of Axial Flow Control Valve Based on Surrogate Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(3): 41-52. |
| [9] | LIU Guoyong, ZHANG Wenpeng, ZHANG Tongxin, et al. Structural Optimization and Flow Field Characteristics of Large Format SLM Forming Bin [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(12): 53-63. |
| [10] | ZHAO Kegang, HE Kunyang, LI Jie, et al. Multi-objective Energy Management Strategy of HEV Based on Improved Dynamic Programming Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 138-148. |
| [11] | JIANG Tao, LU Zhou. Multi-objective Optimization of Flat Skylights in the Elevated Railway Station [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 13-24. |
| [12] | LIU Hanwu, LEI Yulong, FU Yao, et al. Adaptive Regenerative Braking Control Strategy of Range-Extended Electric Vehicle Based on Multi-Objective Optimization [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(7): 42-50,65. |
| [13] | JIN Xia, HU Juncong, WANG Wei, et al. Adjustment Strategy for Automobile Hood Matching in Virtual Environment [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(6): 87-96. |
| [14] |
WU Di LIU Li LI Xiaojun LIU Conghong.
Research on the Technologies of Passive Low Energy Buildings on the Basis of Multi-Objective Optimization Method———by Taking Cold Zone Residential Buildings for Example
|
| [15] | BAI Zhong-hao HE Cheng ZHU Feng. Analysis of Electromagnetic and Shock Wave Mitigation Capability of a Novel Sandwich Plate with Composites [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(9): 137-143. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||