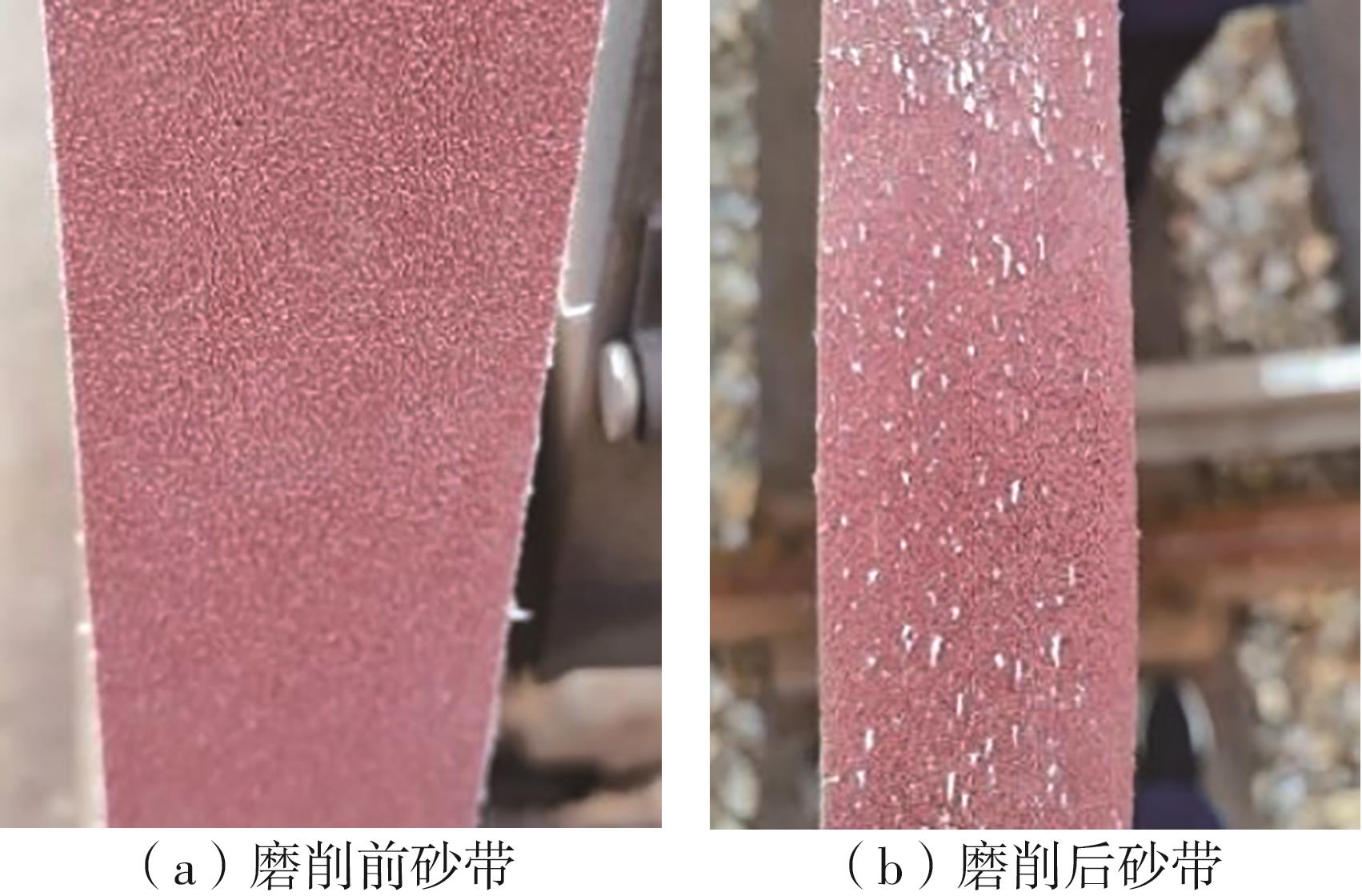
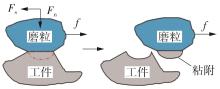
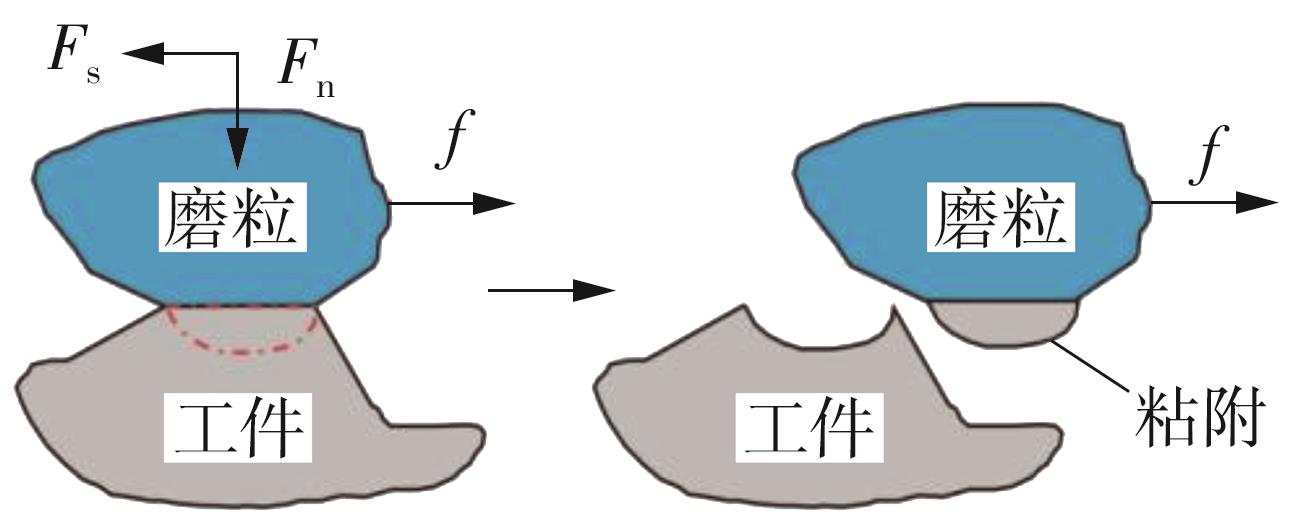
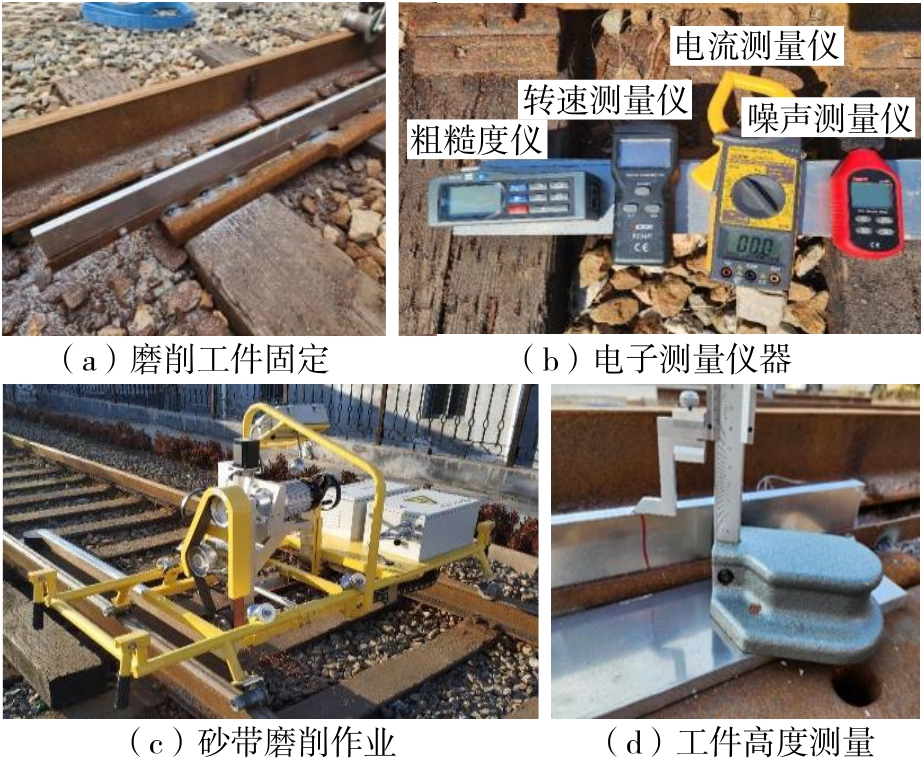
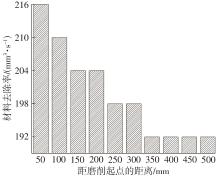
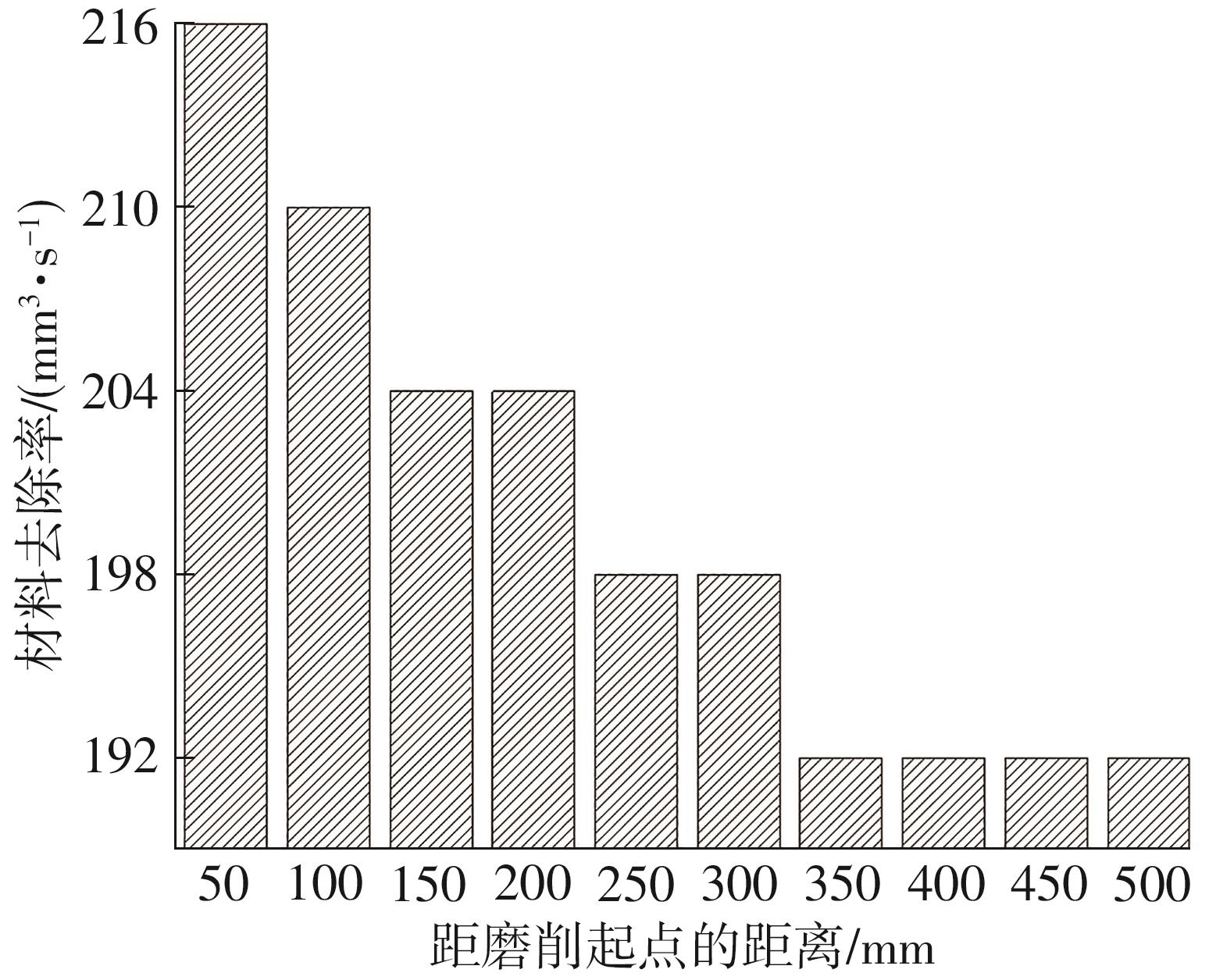
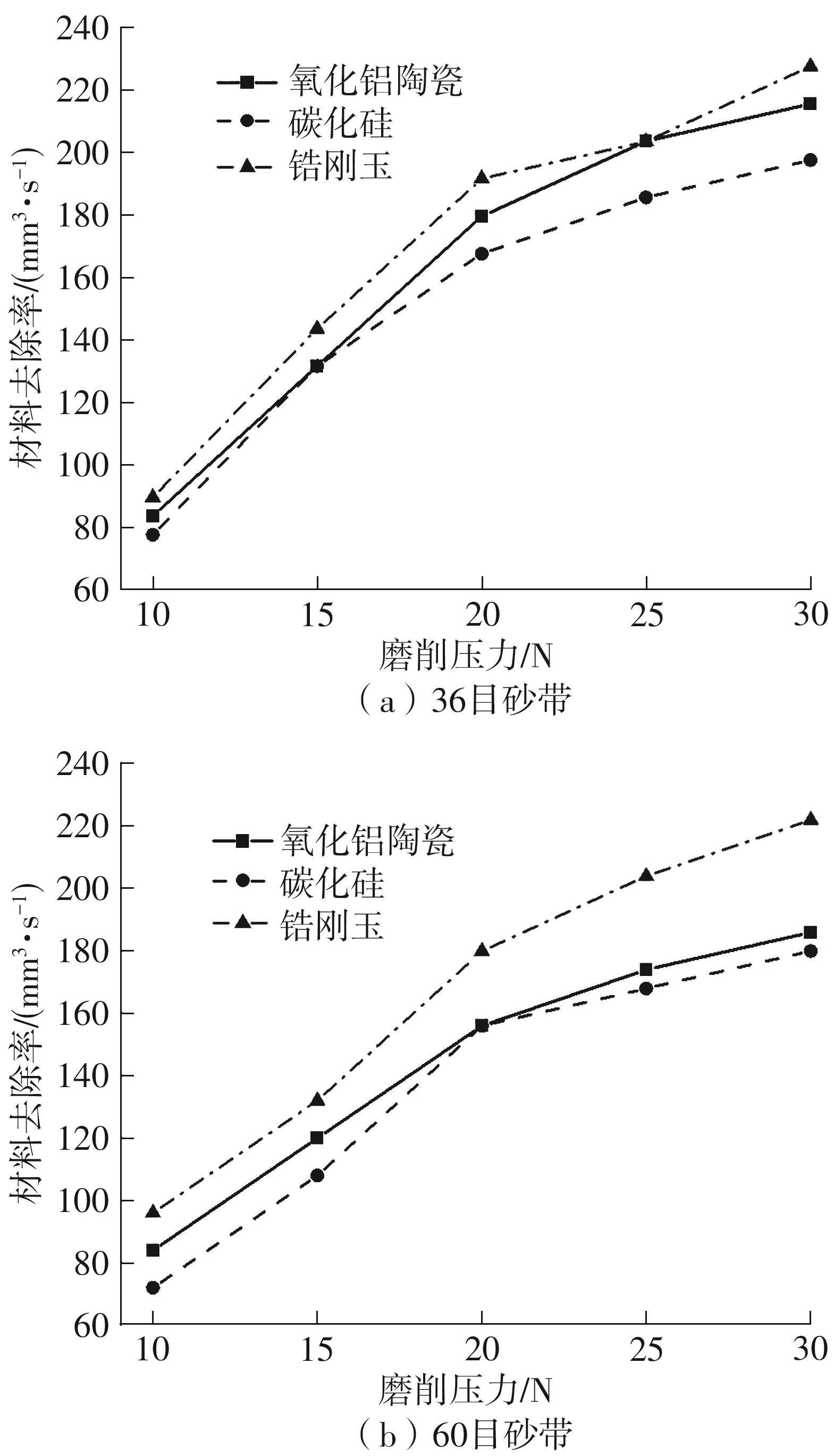
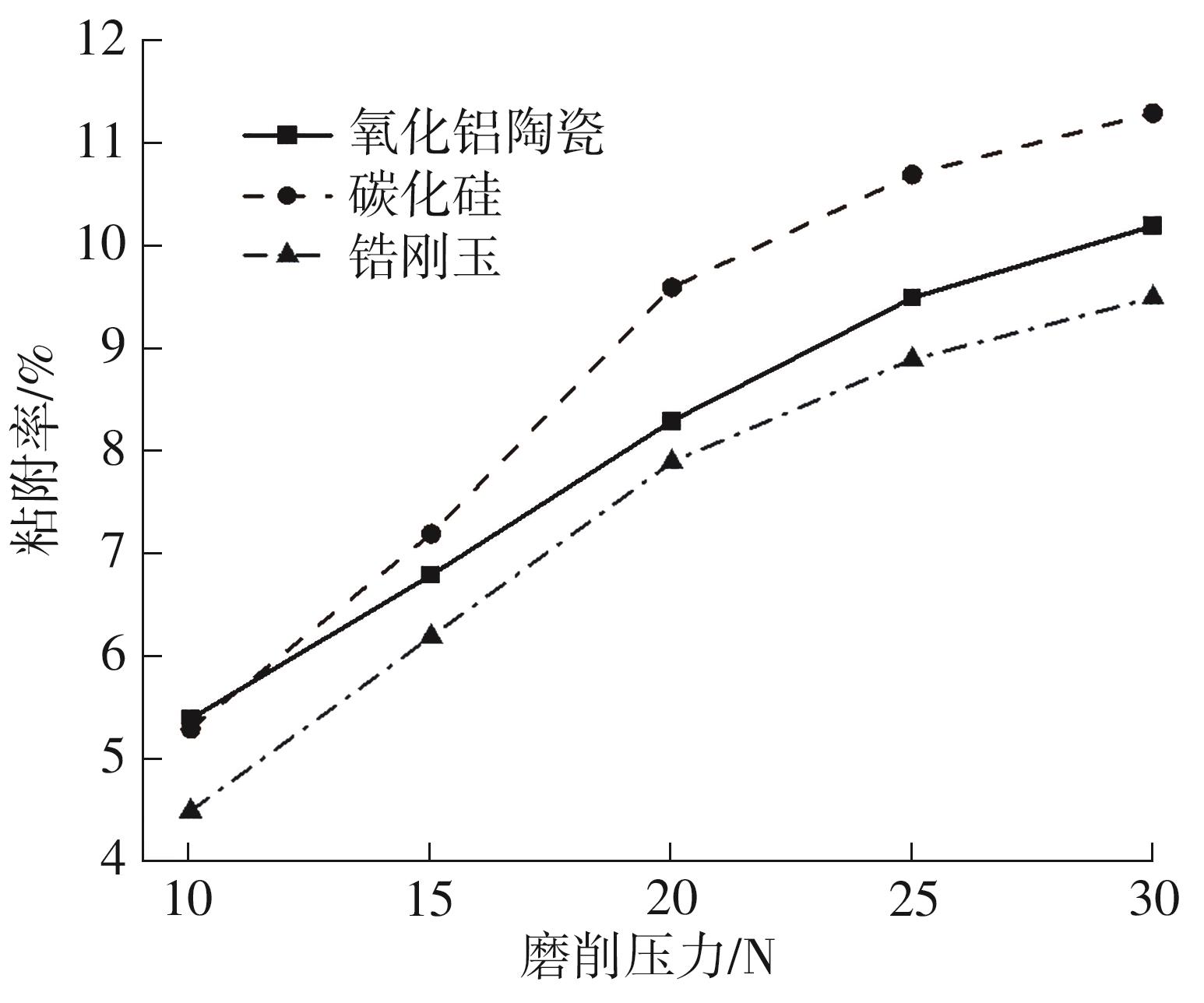
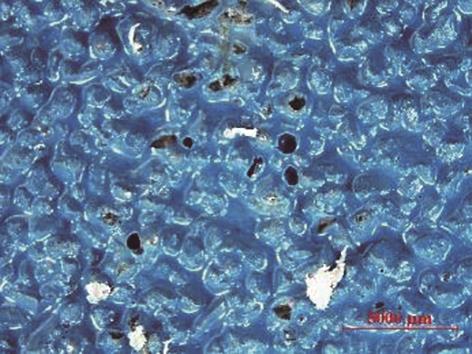
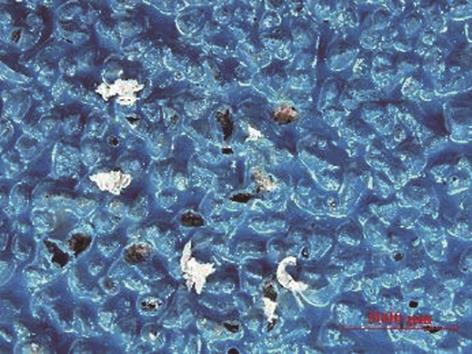
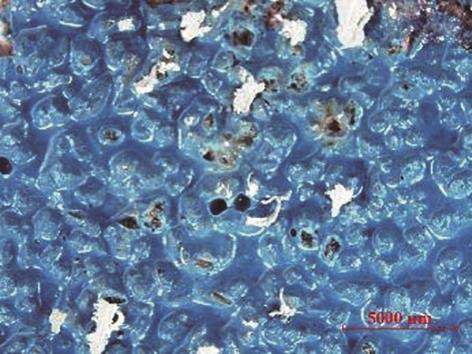
| 1 |
沈刚 .铝合金轨道客车焊缝磨抛机器人关键技术研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2016.
|
| 2 |
李晓彤,汤笑之,郭雅芳 .经验原子势下铝镁合金中溶质原子向位错芯迁移的最低能量路径[J].工程科学学报,2019,41(7):898-905.
|
|
LI Xiaotong, TANG Xiaozhi, GUO Yafang .Minimum energy path of a solute atom diffusing to an edge dislocation core in Al-Mg alloys based on empirical atomic potential[J].Chinese Journal of Engineering,2019,41(7):898-905.
|
| 3 |
李滨,刘思宇,袁文洋,等 .车铣复合加工方法在铝镁合金机匣中的应用[J].工具技术,2018,52(1):82-85.
|
|
LI Bin, LIU Siyu, YUAN Wenyang,et al .Application of turning-milling complex machining technology in aluminum-magnesium alloy casing[J].Tool Enginee-ring,2018,52(1):82-85.
|
| 4 |
KUMAR S .Evolution of nano-porous structure of aluminium-magnesium alloy during multi-axial tensile deformation:estimation of stress-strain response and dimension-less aspect ratio[J].Materials Chemistry and Physics,2018,220:50-57.
|
| 5 |
徐波,但楚臣,何兆坤,等 .镁/铝合金回填式搅拌摩擦点焊的组织与性能[J].焊接学报,2019,40(11):106-110,165-166.
|
|
XU Bo, DAN Chuchen, HE Zhaokun,et al .Microstructure and properties of magnesium/aluminum alloy backfill friction stir spot welding[J].Transactions of the China Welding Institution,2019,40(11):106-110,165-166.
|
| 6 |
卢耀辉,李振生,尹小春,等 .动车组铝合金车体焊缝质量等级评价的应力因数计算方法[J].交通运输工程学报,2022,22(1):133-140.
|
|
LU Yaohui, LI Zhensheng, YIN Xiaochun,et al .Calculation methods of stress factor in welding seam quality grade of emus aluminum alloy car body[J].Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2022,22(1):133-140.
|
| 7 |
何柏林,封亚明,李力 .超声冲击及焊缝余高对6082铝合金焊接接头疲劳性能的影响[J].中国有色金属学报,2019,29(7):1377-1383.
|
|
HE Bolin, FENG Yaming, LI Li .Effect of ultrasonic impact and weld residual height on fatigue properties of 6082 aluminum alloy welded joint[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2019,29(7):1377-1383.
|
| 8 |
史爱强 .铝镁合金力学性能及微观变形行为研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2023.
|
| 9 |
尤芳怡,钟明杰,刘建春,等 .铝合金磨削加工的研究综述[J].航空制造技术,2022,65(23/24):133-141.
|
|
YOU Fangyi, ZHONG Mingjie, LIU Jianchun,et al .Review of research on grinding of aluminum alloy[J].Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2022,65(23/24):133-141.
|
| 10 |
张研,任延华 .难加工材料磨削中的砂轮粘附及其抑制措施[J].航空制造技术,2001,6(14):52-54.
|
|
ZHANG Yan, REN Yanhua .Wheel adhesion and its restraint measures during grinding diffcult-to-machining materials[J].Eronautical Manufacturing Technology,2001,6(14):52-54.
|
| 11 |
卢守相,郭塞,张建秋,等 .高性能难加工材料可磨削性研究进展[J].表面技术,2022,51(3):12-42.
|
|
LU Shouxiang, GUO Sai, ZHANG Jianqiu,et al .Grindability of high performance difficult-to-machine materials[J].Surface Technology,2022,51(3):12-42.
|
| 12 |
HUANG G Q, YU K F, ZHANG M Q,et al .Grinding characteristics of aluminium alloy 4032 with a brazed diamond wheel[J].The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2018,95(9):4573-4581.
|
| 13 |
FAN W G, WU C X, WU Z W,et al .Static contact mechanism between serrated contact wheel and rail in rail grinding with abrasive belt[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2022,84:1229-1245.
|
| 14 |
吴志伟,樊文刚,王谦,等 .钢轨砂带打磨与砂轮打磨综合性能对比实验研究[J].中国机械工程, 2022,33(17):2125-2132.
|
|
WU Zhiwei, FAN Wengang, WANG Qian,et al .Experimental investigation on comprehensive performance comparison for rail grinding using abrasive belt and abrasive wheel[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2022,33(17):2125-2132.
|
| 15 |
蒋靖宇,赖松柏,路丽英,等 .5XXX系铝镁合金的研究进展[J].载人航天,2019,25(3):411-418.
|
|
JIANG Jingyu, LAI Songbai, LU Liying,et al .Research progress of 5xxx series Al-Mg alloy[J].Manned Spaceflight,2019,25(3):411-418.
|
| 16 |
徐喆,连峰,张会臣 .基于激光加工和自组装技术改性处理铝镁合金的表面润湿性[J].中国有色金属学报,2012,22(7):1855-1862.
|
|
XU Zhe, LIAN Feng, ZHANG Huichen .Wettability of Al-Mg alloy based on laser modification and self-assembled monolayers[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012,22(7):1855-1862.
|
| 17 |
毕波 .铝合金材料砂带磨削机理的试验研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2009.
|
| 18 |
王福明,黄云 .基于砂带磨削的铝合金磨削力和表面粗糙度的研究[J].机床与液压,2008(1):43-45.
|
|
WANG Fuming, HUANG Yun .Research of grinding force and surface roughness of aluminum alloy based on the abrasive belt grinding[J].Machine Tool & Hydraulics,2008(1):43-45.
|
| 19 |
HUANG Z, HUANG Y, WU Y Y .Finishing advanced surface of magnesium alloy tube based on abrasive belt grinding technology[J].Materials Science Forum,2009,610(1):975-978.
|
| 20 |
AHN J H, LEE M C, JEONG H D,et al .Intelligently automated polishing for high quality surface formation of sculpture die[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2002(130):339-344.
|
| 21 |
张晓芳 .超声辅助砂带磨削铝合金仿真与实验研究[D].泉州:华侨大学,2016.
|
| 22 |
高宾华,保文成,陈超群,等 .延塑性航空合金磨削砂轮粘附及粘附抑制技术的研究现状与展望[J].航空制造技术,2021,64(7):53-71.
|
|
GAO Binhua, BAO Wencheng, CHEN Chaoqun,et al .Research status and future development of wheel loading and suppressed in grinding of ductility aeronautical alloys[J].Aeronautical Manufacturing Techno-logy,2021,64(7):53-71.
|
| 23 |
何喆 .面向钢轨打磨的砂带磨损机理与规律研究[D].北京:北京交通大学,2021.
|
| 24 |
巩亚东,赵显力,张伟健,等 .机器人砂带磨削单磨粒材料去除影响因素[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版),2023,44(9):1285-1291.
|
|
GONG Yadong, ZHAO Xianli, ZHANG Weijian,et al .Factors influencing single abrasive material removal for robotic abrasive belt grinding[J].Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2023,44(9):1285-1291.
|
 ), FAN Wengang(
), FAN Wengang( ), WU Zhiwei, LI Jiang, JIANG Yuhao
), WU Zhiwei, LI Jiang, JIANG Yuhao