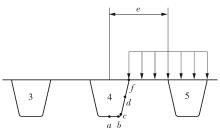
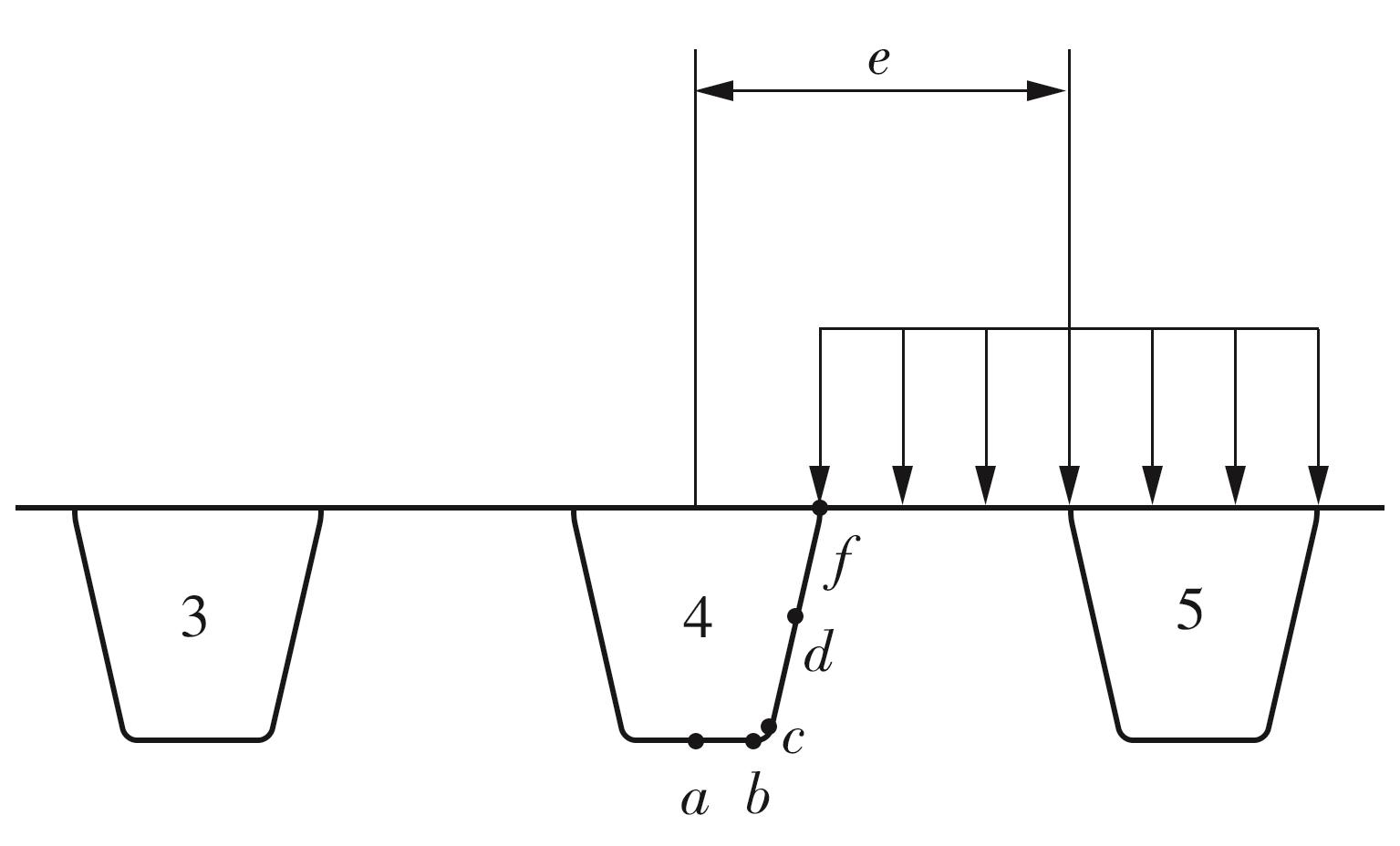
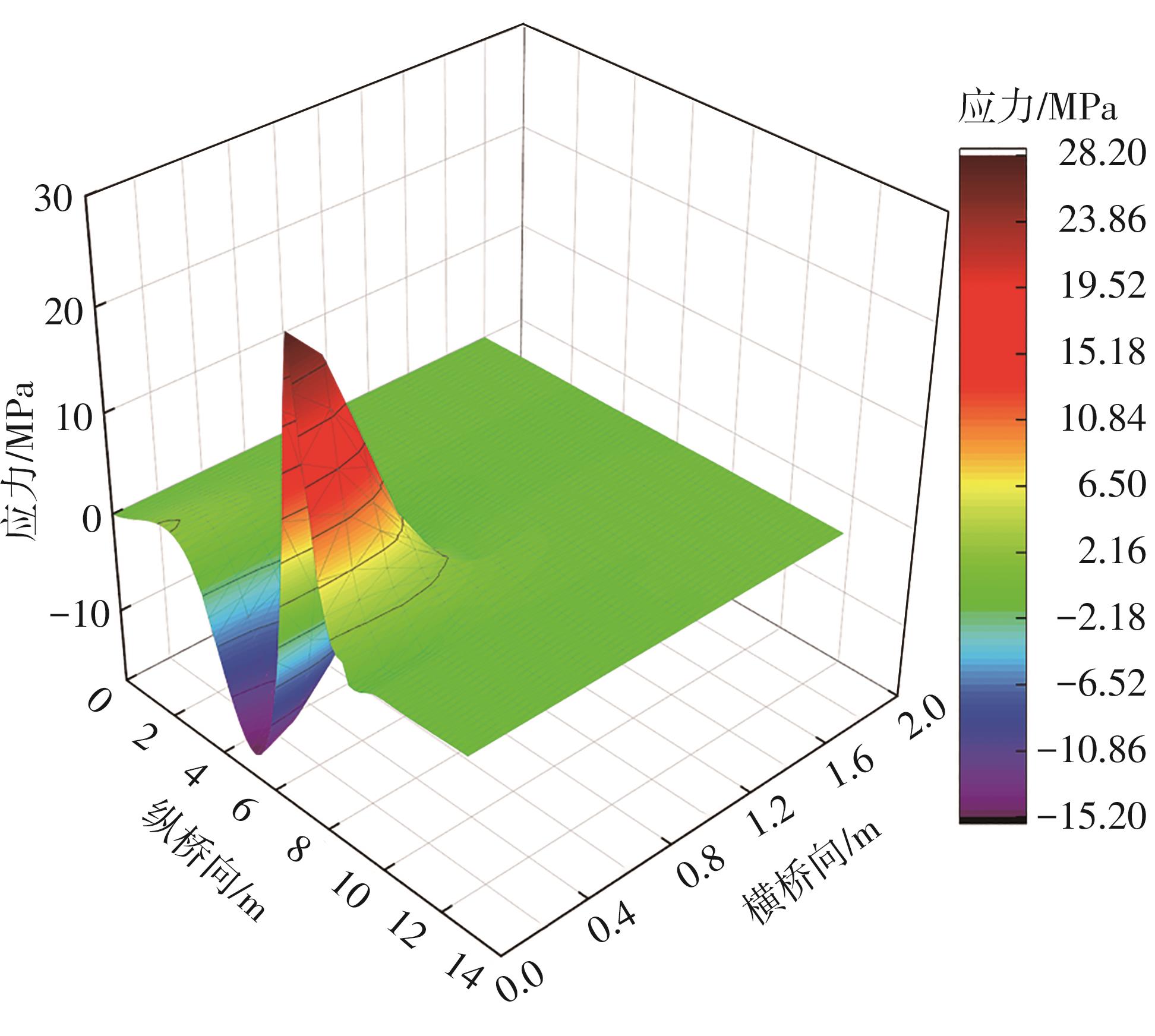
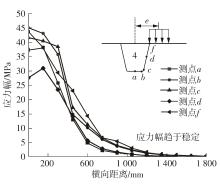
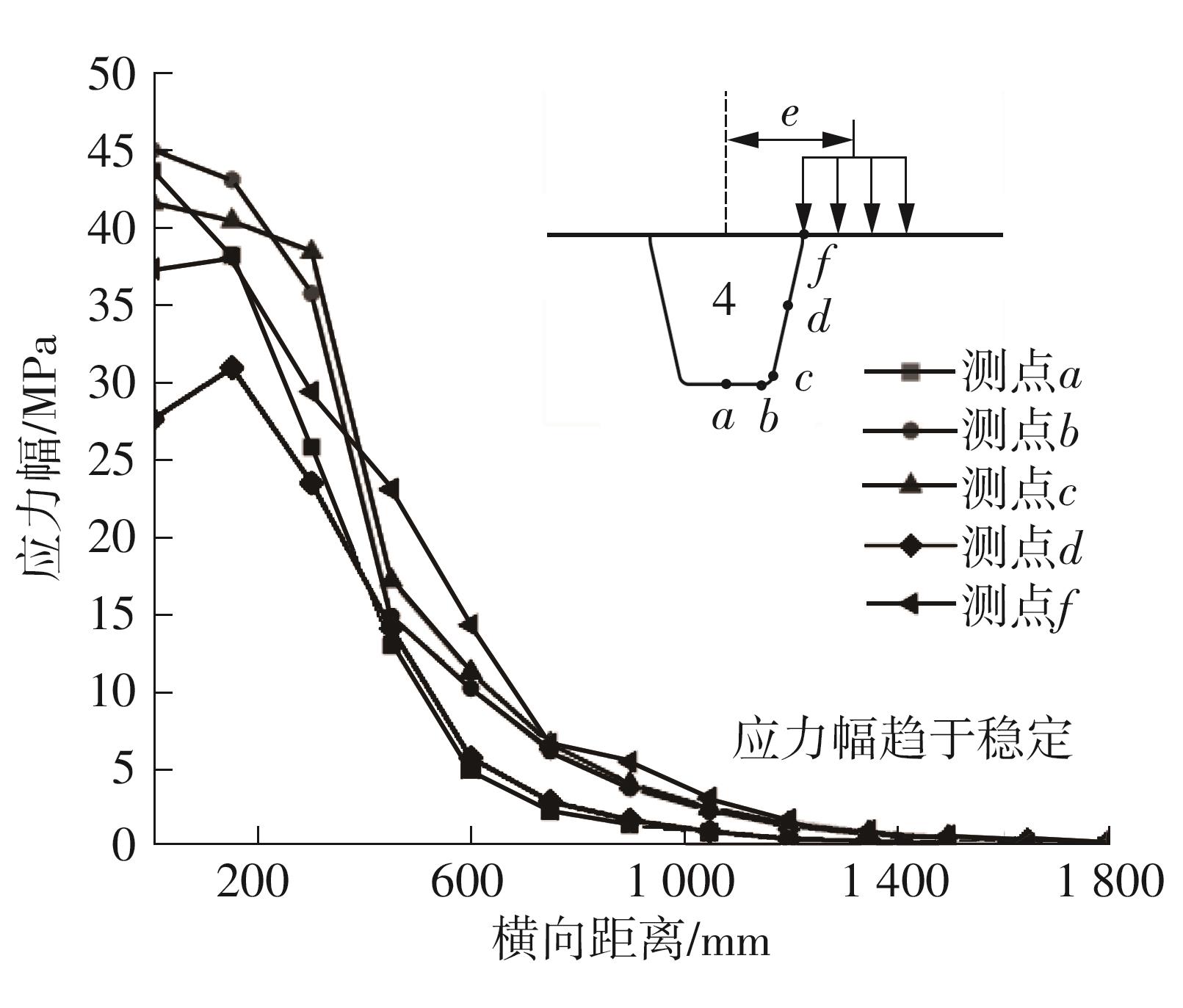
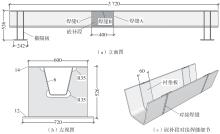
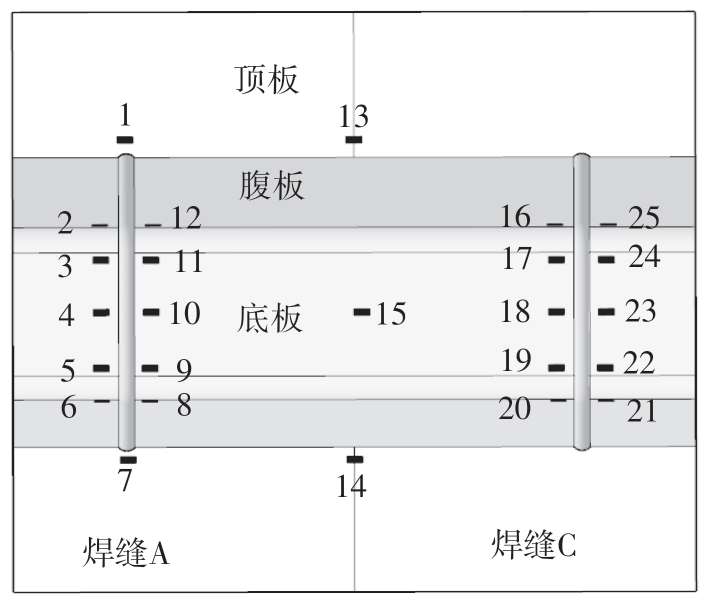
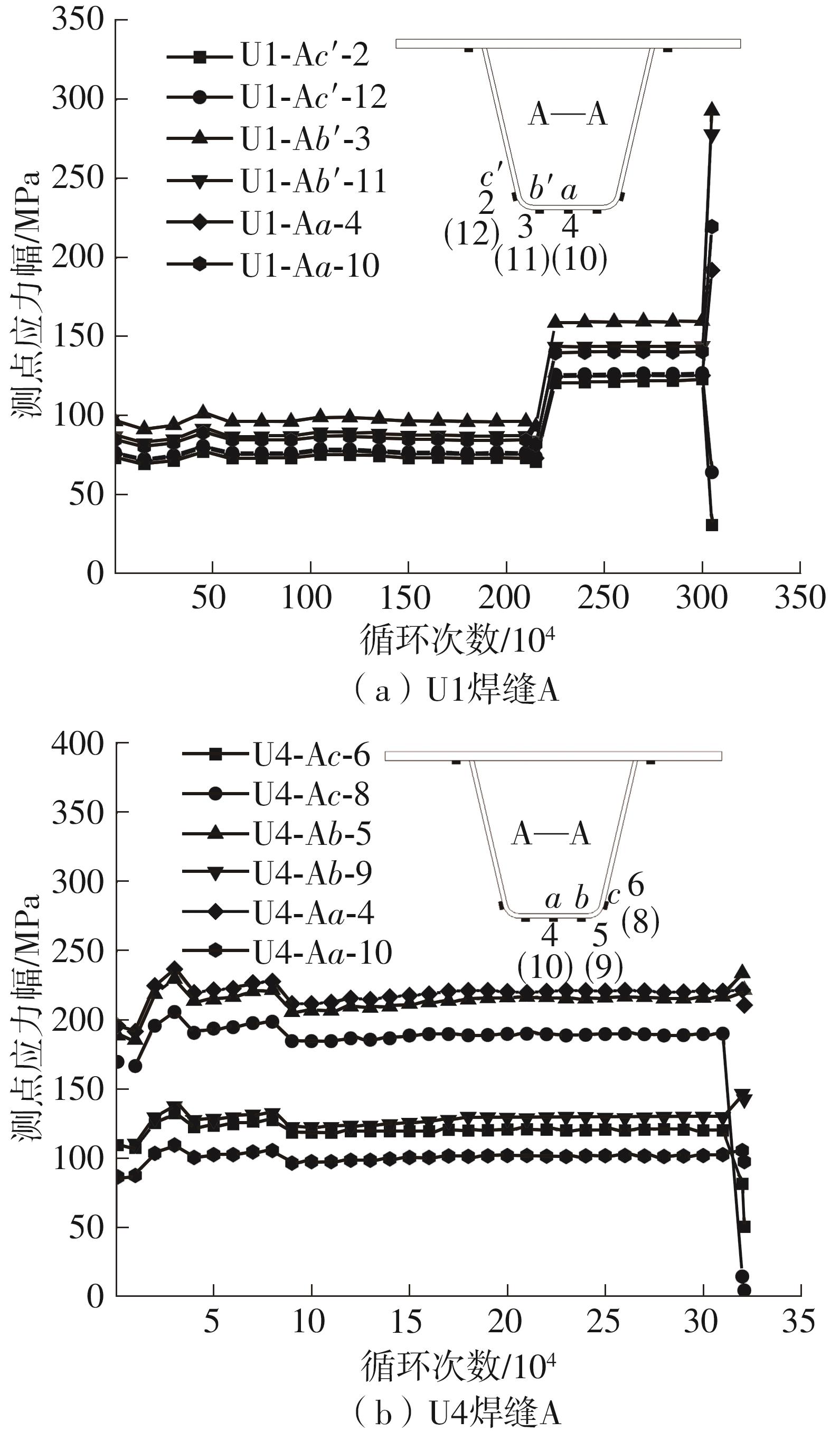
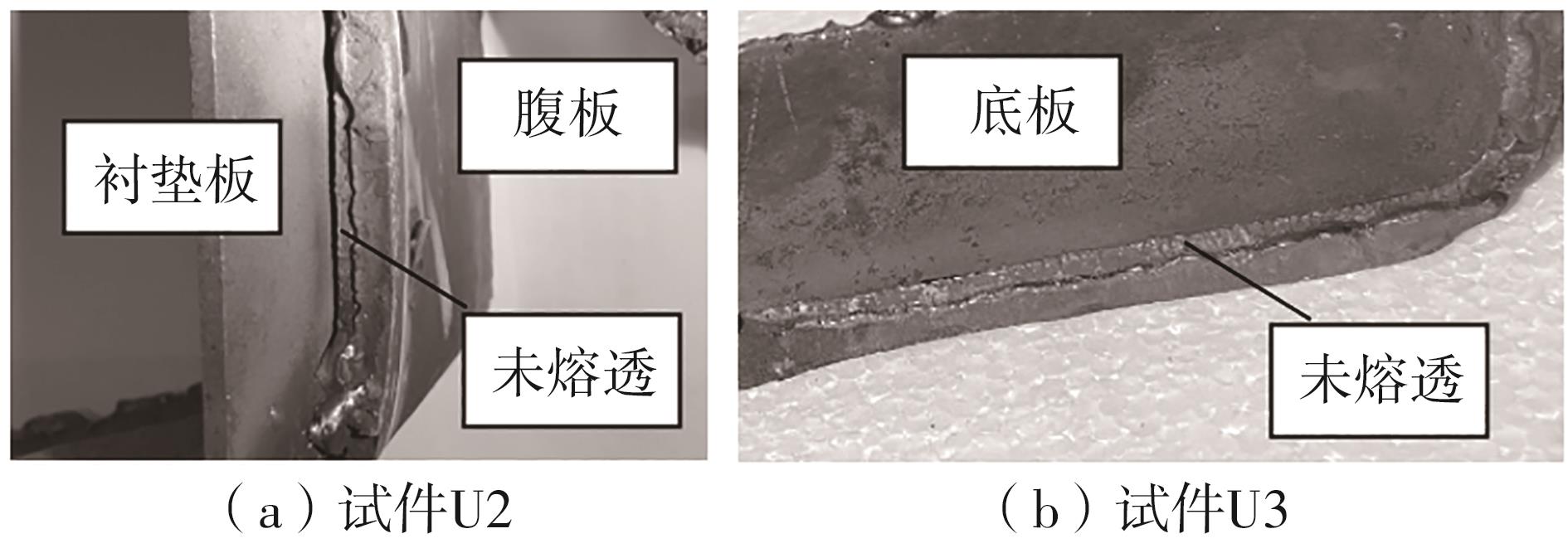
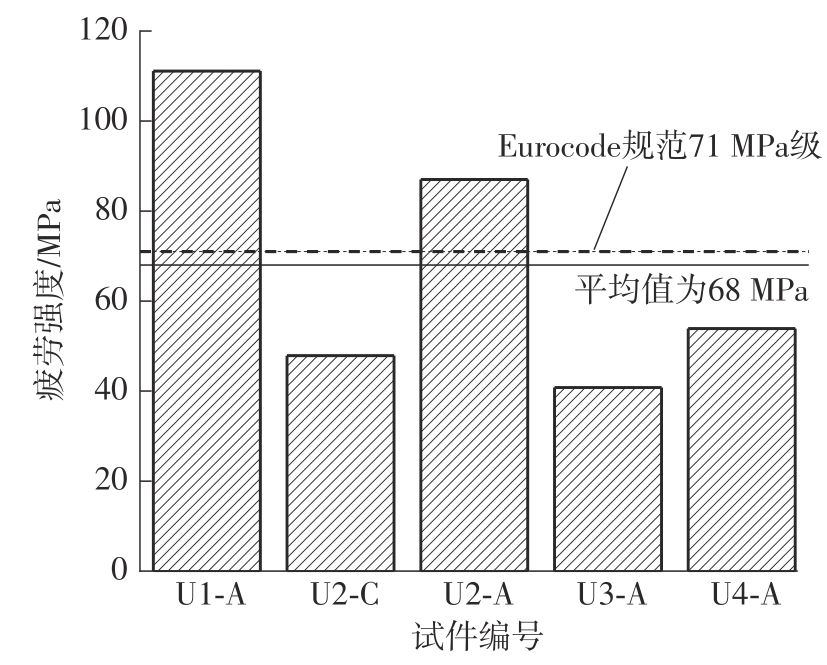
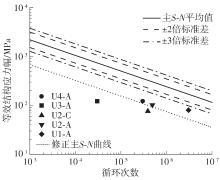
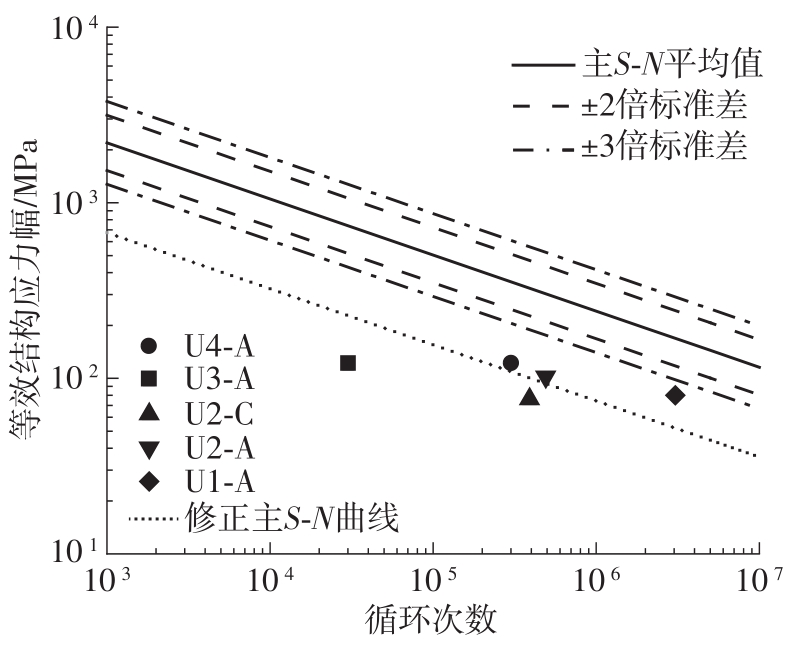
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 92-100.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230071
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fatigue Cracking Characteristics of Butt Welds in U-Rib Embedded Section of Steel Bridge Decks
JIANG Xu( ), LÜ Zhilin, QIANG Xuhong(
), LÜ Zhilin, QIANG Xuhong( ), FAN Mingxin
), FAN Mingxin
- College of Civil Engineering,Tongji University,Shanghai 200092,China
-
Received:2023-02-27Online:2024-05-25Published:2023-11-03 -
Contact:强旭红(1984-),女,博士,副教授,博士生导师,主要从事钢桥疲劳加固研究。 E-mail:qiangxuhong@tongji.edu.cn -
About author:姜旭(1982-),男,博士,副教授,博士生导师,主要从事钢桥面板疲劳性能研究。E-mail: jiangxu@tongji.edu.cn -
Supported by:the the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52278207);the Shanghai Science and Technology Planning Project(21ZR1466100)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIANG Xu, LÜ Zhilin, QIANG Xuhong, et al. Fatigue Cracking Characteristics of Butt Welds in U-Rib Embedded Section of Steel Bridge Decks[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 92-100.
share this article
| 1 | HUANG W, PEI M, LIU X,et al .Design and construction of super-long span bridges in China:review and future perspectives[J].Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering,2020,14(4):803-838. |
| 2 | 吴冲,袁远,姜旭 .正交异性钢桥面板闭口加劲肋对接焊缝疲劳性能评价[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(4):436-443. |
| WU Chong, YUAN Yuan, JIANG Xu .Fatigue assessment method of the close ribs butt weld of the orthotropic steel deck[J].Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2018,46(4):436-443. | |
| 3 | 张清华,张登科,崔闯,等 .基于超声导波的钢桥面板纵肋对接焊缝疲劳裂纹检测方法[J].中国公路学报,2022,35(6):101-112. |
| ZHANG Qing-hua, ZHANG Deng-ke, CUI Chuang,et al .Fatigue crack detection method based on ultrasonic-guided waves for the longitudinal rib butt weld of steel decks[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2022,35(6):101-112. | |
| 4 | KUHLMANN U, BOVE S, HUBMANN M .Instandsetzung und verstärkung von stahlbrücken mit kategorie-2-schäden[J].Stahlbau,2017,86(7):574-586. |
| 5 | 王春生,翟慕赛, HOUANKPO T O N .正交异性钢桥面板典型细节疲劳强度研究[J].工程力学,2020,37(8):102-111. |
| WANG Chun-sheng, ZHAI Mu-sai, HOUANKPO T O N .Fatigue strength of typical details in orthotropic steel bridge deck[J].Engineering Mechanics,2020,37(8):102-111. | |
| 6 | 陈欣,傅中秋,姚悦,等 .钢桥面板U肋对接焊缝位置对疲劳受力性能的影响分析[J].湖南科技大学学报(自然科学版),2021,36(3):43-49. |
| CHEN Xin, FU Zhong-qiu, YAO Yue,et al .Analysis of the influence of U-rib butt weld position on fatigue stress characteristics of steel bridge deck[J].Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,36(3):43-49. | |
| 7 | SAIFALDIEN S, ALEMDAR F .Experimental study of fatigue crack behavior of rib-to-rib butt welded connections in orthotropic steel decks[J].Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures,2018,15(10):1-19. |
| 8 | YANG M, KAINUMA S, JONG Y S .Structural behavior of orthotropic steel decks with artificial cracks in longitudinal ribs[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2018,141:132-144. |
| 9 | 张中平,郑舟军 .钢箱梁U肋嵌补段疲劳开裂机理与养护措施研究[J].世界桥梁,2020,48(1):53-58. |
| ZHANG Zhong-ping, ZHENG Zhou-jun .Study of fatigue cracking mechanism for location of steel box girder where U ribs are embedded and added as well as maintenance measures[J].World Bridges,2020,48(1):53-58. | |
| 10 | 吉伯海,朱伟,傅中秋,等 .正交异性钢桥面板U肋对接焊缝疲劳寿命评估[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2015,34(1):16-21. |
| JI Bohai, ZHU Wei, FU Zhongqiu,et al .Fatigue life evaluation of U-rib butt weld of the orthotropic steel bridge[J].Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science),2015,34(1):16-21. | |
| 11 | 陈世鸣,马家欢,程栋柱 .正交异性钢桥面板纵肋对接焊缝疲劳性能研究[J].桥梁建设,2018,48(1):48-53. |
| CHEN Shi-ming, MA Jia-huan, CHENG Dong-zhu .Study of fatigue performance of butt weld joints for longitudinal ribs of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J].Bridge Construction,2018,48(1):48-53. | |
| 12 | CHEN S, HUANG Y, ZHOU C,et al .Experimental and numerical study on fatigue performance of U-rib connections[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2019,163:105796/1-11. |
| 13 | HUANG Z, LEI J, GUO S,et al .Fatigue performance of U-rib butt welds in orthotropic steel decks[J].Engineering Structures,2020,211:110485/1-15. |
| 14 | 黄云,张清华,卜一之,等 .港珠澳大桥正交异性钢桥面板纵肋现场接头疲劳特性[J].中国公路学报,2016,29(12):34-43,59. |
| HUANG Yun, ZHANG Qing-hua, BU Yi-zhi,et al .Fatigue properties on field splice joints of longitudinal ribs in orthotropic steel bridge decks of Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2016,29(12):34-43,59. | |
| 15 | 曹蕾蕾,王留涛,王严,等 .基于等效结构应力法的挖掘机工作装置疲劳寿命评估[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(8):62-70. |
| CAO Leilei, WANG Liutao, WANG Yan,et al .Fatigue life evaluation of excavator working device based on equivalent structural stress method[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(8):62-70. | |
| 16 | ZENG Y, QU Y, TAN Y,et al .Analysis of fatigue cracking of orthotropic steel decks using XFEM[J].Engineering Failure Analysis,2022,140:106536/1-12. |
| 17 | van DEN BERG N, XIN H, VELJKOVIC M .Effects of residual stresses on fatigue crack propagation of an orthotropic steel bridge deck[J].Materials & Design,2021,198:109294/1-19. |
| 18 | 公路钢结构桥梁设计规范: [S]. |
| 19 | DI J, RUAN X, ZHOU X,et al .Fatigue assessment of orthotropic steel bridge decks based on strain monitoring data[J].Engineering Structures,2021,228:111437/1-12. |
| 20 | Eurocode 3:Design of Steel Structures Part 1-9:Fatigue [S]. |
| 21 | YANG H, WANG P, QIAN H .Fatigue behavior of typical details of orthotropic steel bridges in multiaxial stress states using traction structural stress[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2020,141:105862/1-13. |
| 22 | WEI Z, PEI X, JIN H,et al .Evaluation of welded cast steel joint fatigue data using structural stress methods[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2021,186:106895/1-15. |
| 23 | YANG H, WANG P, QIAN H,et al .Analysis of fatigue test conditions for reproducing weld toe cracking into U-rib wall in orthotropic bridge decks[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2022,162:106976/1-12. |
| 24 | JIANG X, SUN K, QIANG X,et al .XFEM-based fatigue crack propagation analysis on key welded connections of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J].International Journal of Steel Structures,2022,23:404-416. |
| 25 | SIMULIA D S .Abaqus 2021 help documentation[Z].Boston:Dassault Systems Simulia Corp,2021. |
| 26 | 何龙龙,刘志芳,顾俊杰,等 .基于XFEM的疲劳裂纹扩展路径和寿命预测[J].西北工业大学学报,2019,37(4):737-743. |
| HE Longlong, LIU Zhifang, GU Junjie,et al .Fatigue crack propagation path and life prediction based on XFEM[J].Journal of Northwesten Polytechnical University,2019,37(4):737-743. | |
| 27 | Guide on methods for assessing the acceptability of flaws in metallic structures: [S]. |
| [1] | CAO Leilei, WANG Liutao, WANG Yan, et al. Fatigue Life Evaluation of Excavator Working Device Based on Equivalent Structural Stress Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(8): 62-70. |
| [2] | Jiang Zheng- wen Shen Kong- jian Wan Shui. Fracture Mechanics Analysis of FGM Plates Based on Layered Linear Discrete Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(4): 77-84,90. |
| [3] | Meng Yong-jun Zhang Xiao-ning. Fatigue Performances of Modified Asphalts Based on Cumulative Dissipated Energy Ratio [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(2): 99-103. |
| [4] | Ma Niu-jing Wang Rong-hui. Combined Plate-Beam Element Method for Local Vibration Computation of Orthotropic Steel Bridge Deck [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(9): 34-40. |
| [5] | Wan Cheng Zhang Xiao-ning Yu Jiang-miao. Evaluation of Fatigue Performance of Asphalt Mixture Using Cooper NU-14 Test System [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(7): 52-56. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||