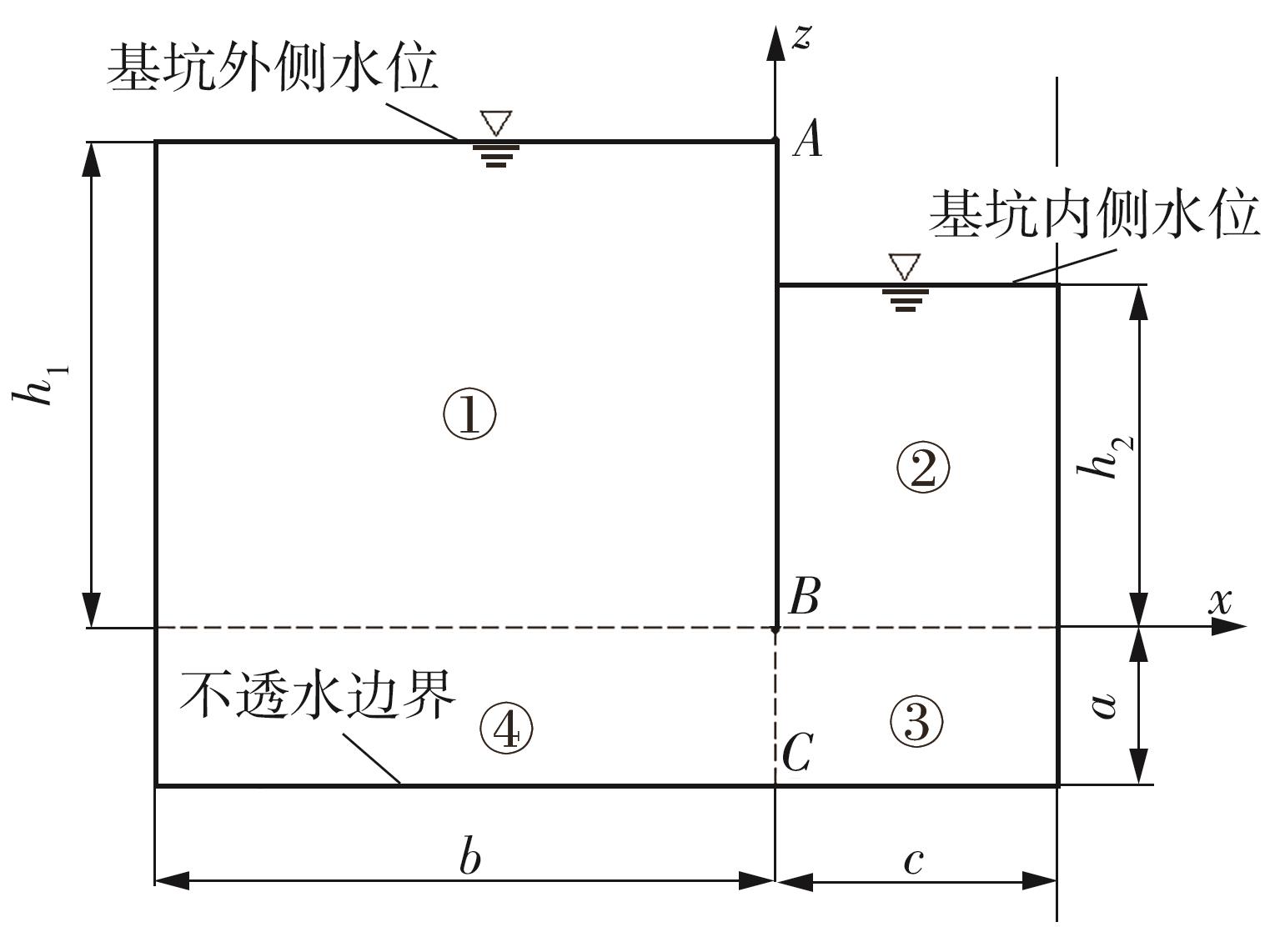
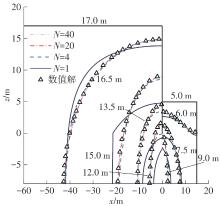
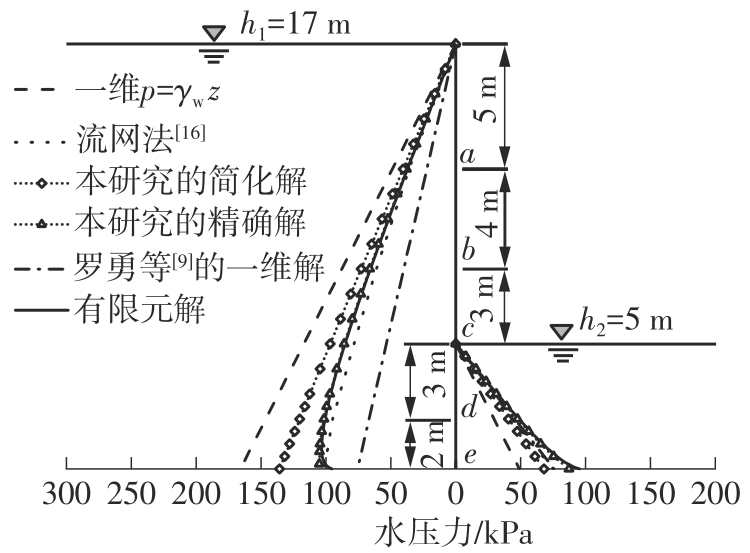
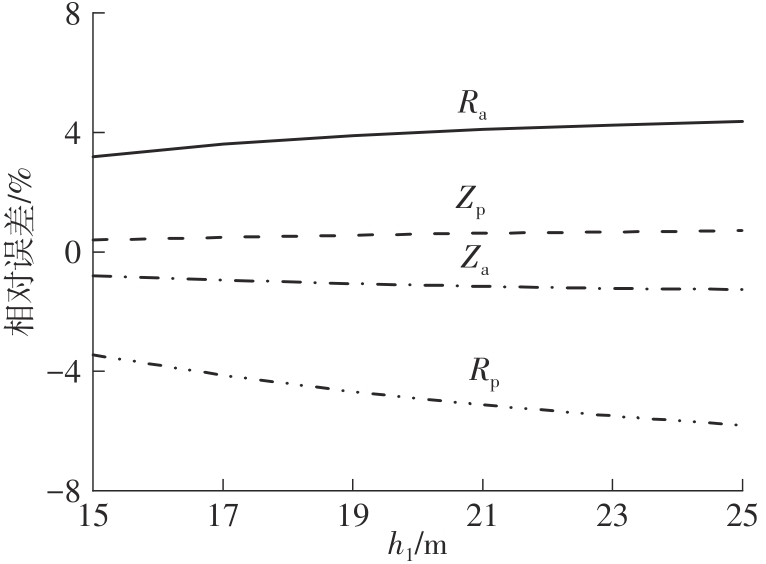
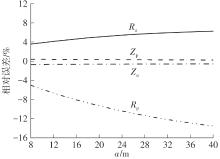
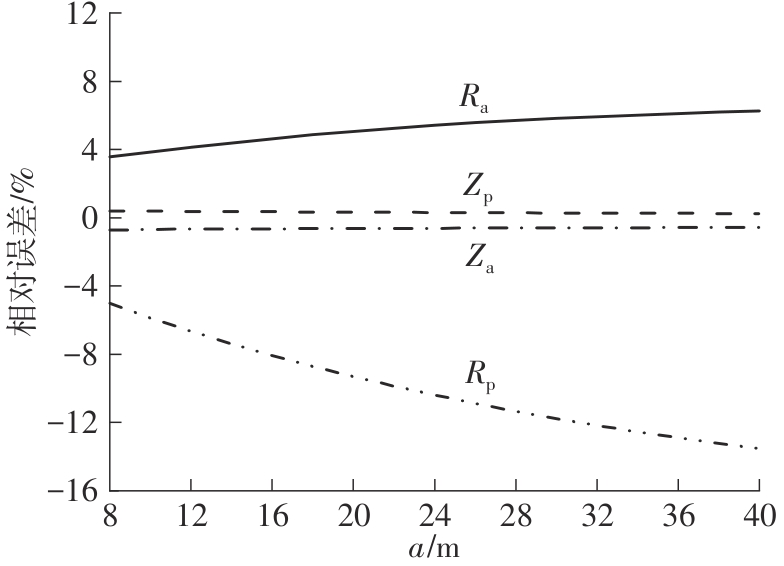
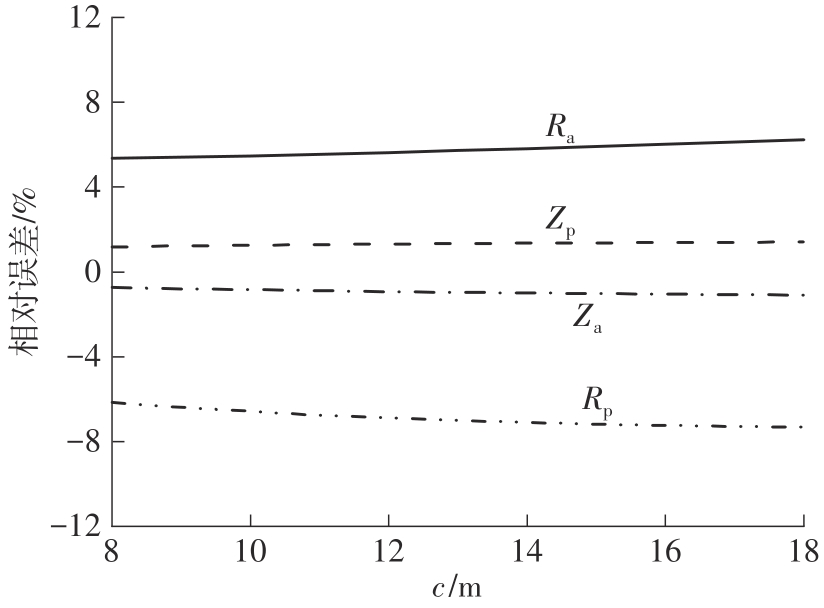
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 84-91.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230075
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analytical Solution and Simplified Solution of Two-Dimensional Steady Seepage Field in Foundation Pit
YU Jun( ), ZHENG Jingfan, ZHANG Zhizhong, LI Dongkai
), ZHENG Jingfan, ZHANG Zhizhong, LI Dongkai
- School of Civil Engineering,Central South University,Changsha 410075,Hunan,China
-
Received:2023-03-01Online:2024-05-25Published:2023-07-12 -
About author:余俊(1978- ),男,博士,副教授,主要从事隧道与地下工程研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52078496)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YU Jun, ZHENG Jingfan, ZHANG Zhizhong, et al. Analytical Solution and Simplified Solution of Two-Dimensional Steady Seepage Field in Foundation Pit[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 84-91.
share this article
Table 2
Error comparison of different calculation methods of water pressure at each point on the retaining wall outside the pit"
| 计算点号 | 深度zi /m | 精确解误差/% | 流网法误差/% | 简化解误差/% | 一维考虑渗流误差/% | 一维静水误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合力 | 1.35 | -5.76 | 17.58 | -37.40 | 37.72 | |
| a | 5 | 1.06 | -2.47 | 10.02 | -39.64 | 32.76 |
| b | 9 | 1.17 | -4.74 | 15.40 | -38.50 | 35.30 |
| c | 12 | 0.40 | -8.00 | 17.34 | -37.36 | 37.82 |
| d | 15 | 0.91 | -5.86 | 23.87 | -33.72 | 45.82 |
| e | 17 | 4.09 | -1.73 | 37.04 | -26.53 | 61.62 |
| 1 | 汤连生,黄国怡,杜赢中,等 .考虑地下水渗流的基坑水土压力计算新图式[J].岩土力学,2004,25(4):565-569. |
| TANG Lian-sheng, HUANG Guo-yi, DU Ying-zhong,et al .A new calculation chart of water-earth pressure on foundation pit considering groundwater seepage[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2004,25(4):565-569. | |
| 2 | ZHANG M, YAO D X, LU H F,et al .Solution of seepage field in different soil layers of concrete dam foundation by flow net method[J].IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2020,546(5),052053/1-7. |
| 3 | 张邦芾 .基坑工程地下水渗流场特性研究[D].北京:中国建筑科学研究院,2014. |
| 4 | 薛丽影,杨斌,刘丰敏,等 .基坑工程地下水渗流模型试验系统研究[J].岩土工程学报,2017,39(S1):126-130,11. |
| XUE Li-ying, YANG Bin, LIU Feng-min,et al .Model test system for groundwater seepage in foundation pit engineering[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(S1):126-130,11. | |
| 5 | SHI C H, SUN X H, LIU S L,et al .Analysis of seepage characteristics of a foundation pit with horizontal waterproof curtain in highly permeable strata[J].Water,2021,13(9):1303/1-26. |
| 6 | LI Y F, CHAI J R, XU Z G .Analysis of influence of seepage on stability of foundation pit[J].IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering,2017,207(1):012093/1-6. |
| 7 | SHI J J, WU B, LIU Y,et al .Analysis of the influence of groundwater seepage on the deformation of deepfoundation pit with suspended impervious curtain[J].Advances in Mechanical Engineering,2022,14(3):1-10. |
| 8 | CAO Cheng-yong, SHI Cheng-hua .Analytical procedure for massive water-sealing barriers used in deep excavations considering seepage effect and its application[J].Journal of Central South University,2022,29(6):2033-2048. |
| 9 | 罗勇,龚晓南,吴瑞潜 .考虑渗流效应下基坑水土压力计算的新方法[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2007,41(1):157-160. |
| LUO Yong, GONG Xiao-nan, WU Rui-qian .New method for calculation of water-earth pressure on foundation pit considering groundwater seepage[J].Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science),2007,41(1):157-160. | |
| 10 | FOX E N, MCNAMEE J .The two-dimensional potential problem of seepage into a cofferdam[J].Philosophical Magazine Series 7,1948,39(290):165-203. |
| 11 | BERESLAVSKII E N .The flow of ground waters around a Zhukovskii sheet pile[J].Journal of Applied Mathematics & Mechanics,2011,75(2):210-217. |
| 12 | 黄大中,谢康和,应宏伟 .渗透各向异性土层中基坑二维稳定渗流半解析解[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2014,48(10):1802-1808. |
| HUANG Da-zhong, XIE Kang-he, YING Hong-wei .Semi-analytical solution for two-dimensional steady seepage around foundation pit in soil layer with anisotropic permeability[J].Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science),2014,48(10):1802-1808. | |
| 13 | YU J, YANG X X, DENG P B,et al .Analytical solution for a steady seepage field of a foundation pit in layered soil[J].International Journal of Geomechanics,2022,22(10):04022160/1-10. |
| 14 | THUSHARA A M, NAGARATNAM S .Simple solutions for square and rectangular cofferdam seepage problems[J].Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2018,56(5):730-745. |
| 15 | 张承宗 .数学物理方法与复数特殊函数[M].北京:中国宇航出版社,2014. |
| 16 | 王钊,邹维列,李广信 .挡土结构上的土压力和水压力[J].岩土力学,2003,24(2):146-150. |
| WANG Zhao, ZOU Wei-lie, LI Guang-xin .Earth pressure and water pressure on retaining structure[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2003,24(2):146-150. | |
| 17 | 余俊,李东凯,胡钟伟,等 .考虑挡墙厚度基坑稳态渗流场的解析解[J].岩土工程学报,2023,45(7):1402-1411. |
| YU Jun, LI Dongkai, HU Zhongwei,et al .Analytical solution of steady seepage field of foundation pit considering thickness of retaining wall[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2023,45(7):1402-1411. |
| [1] | HAO Tianzhi, LI Chunhua, YANG Tao, et al. Mechanism and Mechanical Characteristics of Cable-Catenary Arch Combined Structure [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 89-102. |
| [2] | CHEN Yanfeng, CHEN Sheng, ZHANG Bo, et al. Analysis of Transient and Steady-State Characteristics of Fractional-Order Cuk Converter [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(3): 1-12. |
| [3] | LU Aizhong LI Zhiyu. Analytical Solution of Steady-State Temperature Field in the Plane Double Connected Domain [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(9): 9-17. |
| [4] | SHI Chenghua LIU Jianwen WANG Zuxian PENG Limin YANG Gaoshang . Improved Method of Calculating the Influence of Foundation Pit Excavation on Adjacent Single Pile#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(10): 105-113. |
| [5] | SHEN Aiqin SONG Pan GUO Yinchuan LI Peng. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Transient Hydrodynamic Pressure on the Road Surface Based on COMSOL Multiphysics [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(11): 92-101. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yong-qiang. Theoretical Analysis and Numerical Simulation of Large-Diameter and Thin-Wall Pipelines During Ultra-Deep J-Lay Installation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(8): 126-131. |
| [7] | Han Qiang Wang Zhi-gang Zhang Yong-qiang Tao Xu. Singular Perturbation Analysis of Large-Diameter and Thin-Wall Pipeline During Ultra-Deep S-lay Installation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(6): 116-121. |
| [8] | Zhang Ai-jun Mo Hai-hong Zhu Zhen-de. Analytical Method of Elasto-Plastic Subgrade Reaction for Single Pile Subjected to Lateral Soil Movement [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(9): 153-159. |
| [9] | Liu Xin Hong Bao-ning Han Shang-yu Chen Xing-zhuan. Calculation of Construction Period Value-at-Risk of Foundation Pit Engineering for Subway Station [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(6): 139-144. |
| [10] | Wu Jia-ming Cui Yin Gong Guo-wei Zhu Liang-sheng. Hydrodynamic Analysis Considering Dynamic Boundary Under Slamming by Flat-Bottom Structure [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(10): 111-117. |
| [11] | Yang Yi Liu Ji-ke. Precision Analysis of Classical Bending Deflection Formulae of Simply-Supported Beams [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(6): 30-34. |
| [12] | Wang Chao Zhang Yao Xia Cheng-jun Liu Yong-qiang . Determination of Attraction Region of High-Dimension System Based on Analytical Solution to Unstable Limit Cycle [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(6): 133-137. |
| [13] | Pan Jian Chen Hong-bing . Application of Self-Learning Method for Engineering Simulation to Excavation of Foundation Pit [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(3): 108-113. |
| [14] | He Zhi-yong Zheng Wei. Deformation Prediction of Deep Foundation Pit Based on BP Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(10): 92-96. |
| [15] | Wu Jia-ming Gong Guo-wei Zhu Liang-sheng . Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Restricted Water Under Slamming by Flat-Bottom Structure [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(10): 97-101,107. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||