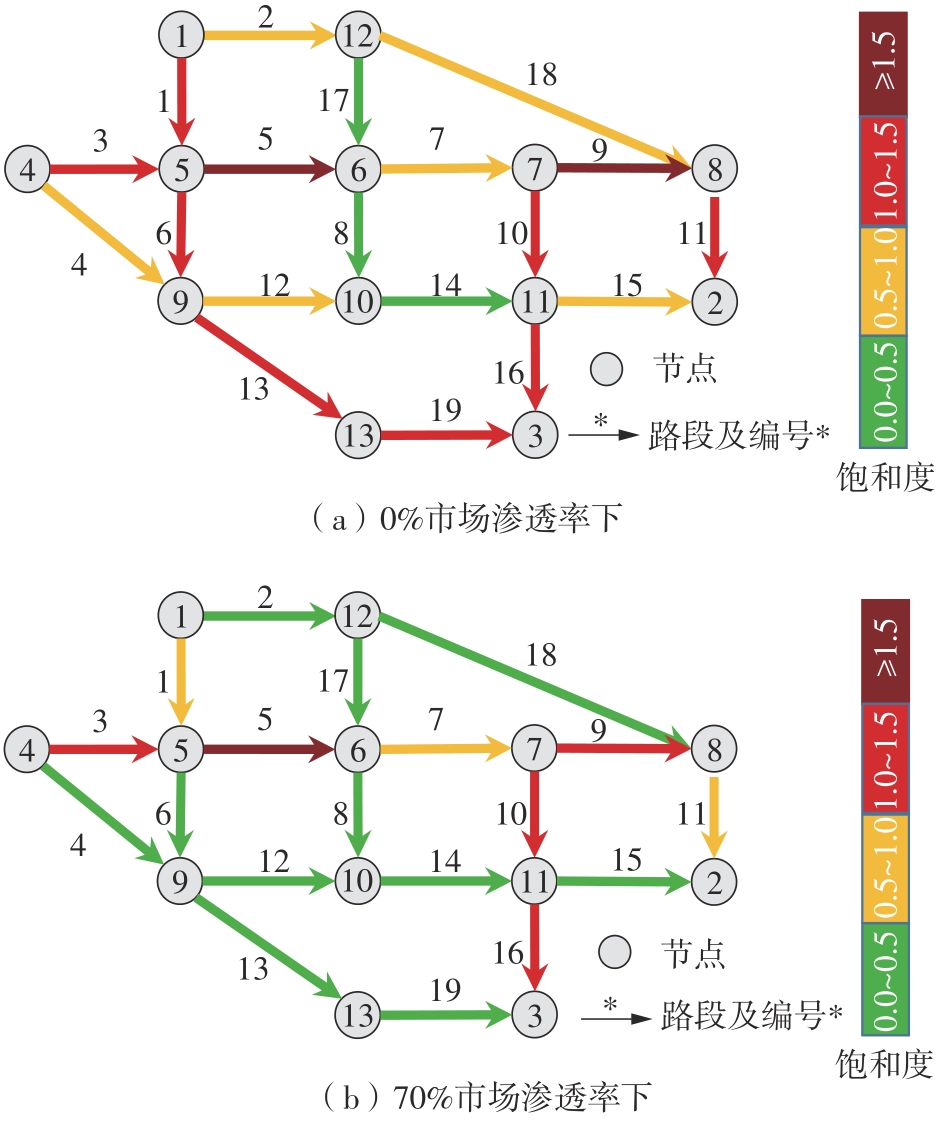
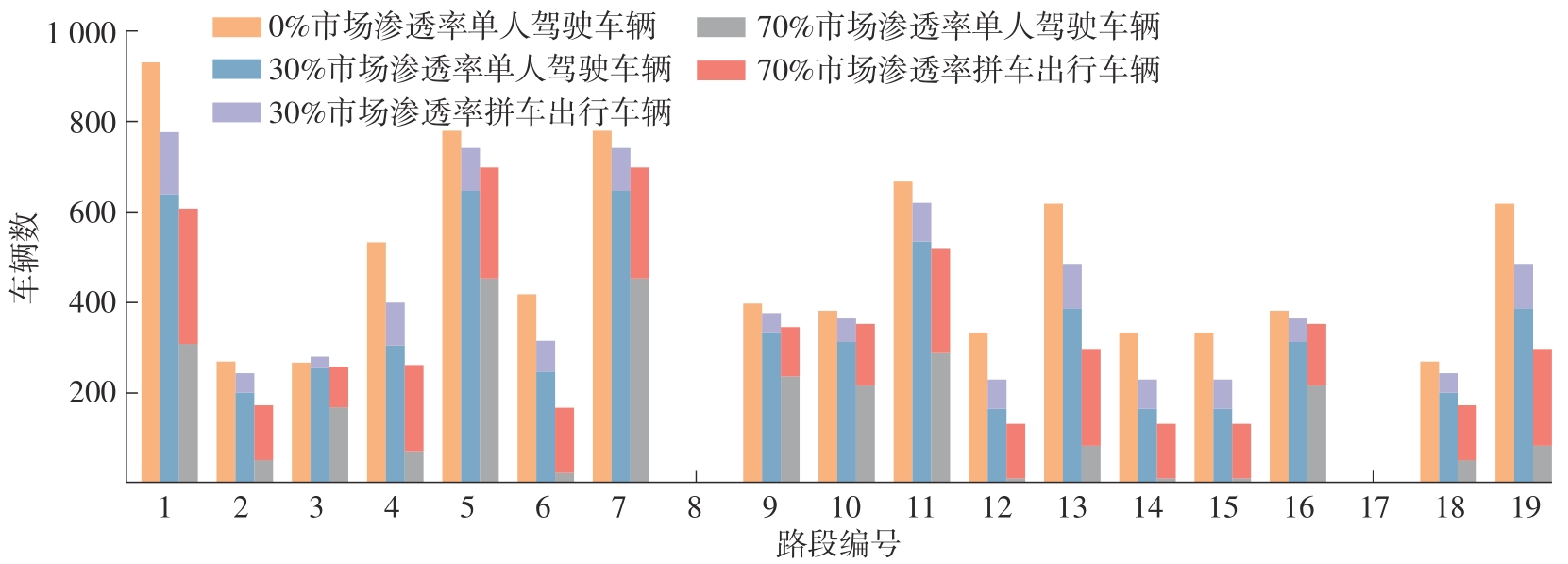
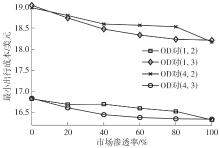
| 1 |
SIDDIQUE A, IFFAT S .Effects of traffic demand management in reduction of congestion in Dhaka city[C]∥Proceedings of the 4th Annual Paper Meet and 1st Civil Engineering Congress.Dhaka:Institution of Engineers,2011:139-144.
|
| 2 |
HU X, CHIU Y C, ZHU L .Behavior insights for an incentive-based active demand management platform[J].International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology,2015,4(2):119-133.
|
| 3 |
LI H, HAO Y, XIE C,et al .Emerging technologies and policies for carbon-neutral transportation[J].International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology,2023,12(1):329-334.
|
| 4 |
YU B, MA Y, XUE M,et al .Environmental benefits from ridesharing:a case of Beijing[J].Applied Energy,2017,191:141-152.
|
| 5 |
缪欣君 .滴滴:打造出行领域航空母舰[R].武汉:天风证券,2021.
|
| 6 |
WANG J P, BAN X J, HUANG H J .Dynamic ridesharing with variable-ratio charging-compensation scheme for morning commute[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2019,122:390-415.
|
| 7 |
佚名 .中国互联网车服务研究报告之拼车[R].上海:艾瑞市场咨询,2015.
|
| 8 |
HUANG K, LIU Z, KIM I,et al .Analysis of the influencing factors of carpooling schemes[J].IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine,2019,11(3):200-208.
|
| 9 |
XIAO L L, LIU T L, HUANG H J .On the morning commute problem with carpooling behavior under parking space constraint[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2016,91:383-407.
|
| 10 |
ZHONG L, ZHANG K, NIE Y M,et al .Dynamic carpool in morning commute:role of high-occupancy-vehicle (HOV) and high-occupancy-toll (HOT) lanes[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2020,135:98-119.
|
| 11 |
LIU Y, LI Y .Pricing scheme design of ridesharing program in morning commute problem[J].Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies,2017,79:156-177.
|
| 12 |
MA R, ZHANG H M .The morning commute problem with ridesharing and dynamic parking charges[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2017,106:345-374.
|
| 13 |
XU H, PANG J, ORDÓÑEZ F,et al .Complementarity models for traffic equilibrium with ridesharing[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2015,81:161-182.
|
| 14 |
YAN C, HU M, JIANG R,et al .Stochastic ridesharing user equilibrium in transport networks[J].Networks and Spatial Economics,2019,19:1007-1030.
|
| 15 |
DI X, MA R, LIU H X,et al .A link-node reformulation of ridesharing user equilibrium with network design[J].Transportation Research Part B: Methodological,2018,112:230-255.
|
| 16 |
LI M, DI X, LIU H X,et al .A restricted path-based ridesharing user equilibrium[J].Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems,2020,24(4):383-403.
|
| 17 |
MA J, XU M, MENG Q,et al .Ridesharing user equilibrium problem under OD-based surge pricing strategy[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2020,134:1-24.
|
| 18 |
孙静,刘文超,张凡 .北京MaaS平台提升绿色出行吸引力:参与用户破百万 累计碳减排量近10万吨[N].中国交通报,2022-03-30(7).
|
| 19 |
SUN J, WU J, XIAO F,et al .managing bottleneck congestion with incentives[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2020,134:143-166.
|
| 20 |
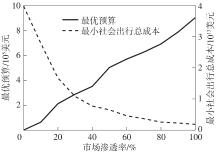
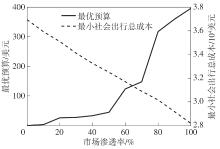
XIAO L, WU J, TIAN Y,et al .Optimizing budget allocation for incentive-based active travel demand management solutions[J].Transportation Research Record,2021,2675(11):1245-1257.
|
| 21 |
韩维正 .共享单车:曾经浮沉起落坚信路在前方[N].人民日报海外版,2019-07-12(10).
|
| 22 |
CHEN T Y, JOU R C, CHIU Y C .Using the multilevel random effect model to analyze the behavior of carpool users in different cities[J].Sustainability,2021,13(2):1-13.
|
| 23 |
BLIEMER M, DICKE-OGENIA M, ETTEMA D .Rewarding for avoiding the peak period:a synthesis of three studies in the Netherlands[C]∥Proceedings of European Transport Conference 2009.Noordwijkerhout:Association for European Transport,2009:1-15.
|
| 24 |
BAHAT O, BEKHOR S .Incorporating ridesharing in the static traffic assignment model[J].Networks and Spatial Economics,2016,16:1125-1149.
|
| 25 |
WANG X, WANG J, GUO L,et al .A convex programming approach for ridesharing user equilibrium under fixed driver/rider demand[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2021,149:33-51.
|
| 26 |
KELLEY K L .Casual carpooling—enhanced[J].Journal of Public Transportation,2007,10(4):119-130.
|
| 27 |
CAULFIELD B .Estimating the environmental benefits of ride-sharing: a case study of Dublin[J].Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment,2009,14(7):527-531.
|
| 28 |
SUWANSIRIKUL C, FRIESZ T L, TOBIN R L .Equilibrium decomposed optimization:a heuristic for the continuous equilibrium network design problem[J].Transportation Science,1987,21(4):254-263.
|
| 29 |
LITMAN T .Transportation cost and benefit analysis[J].Victoria Transport Policy Institute,2009,31:1-19.
|
| 30 |
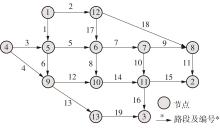
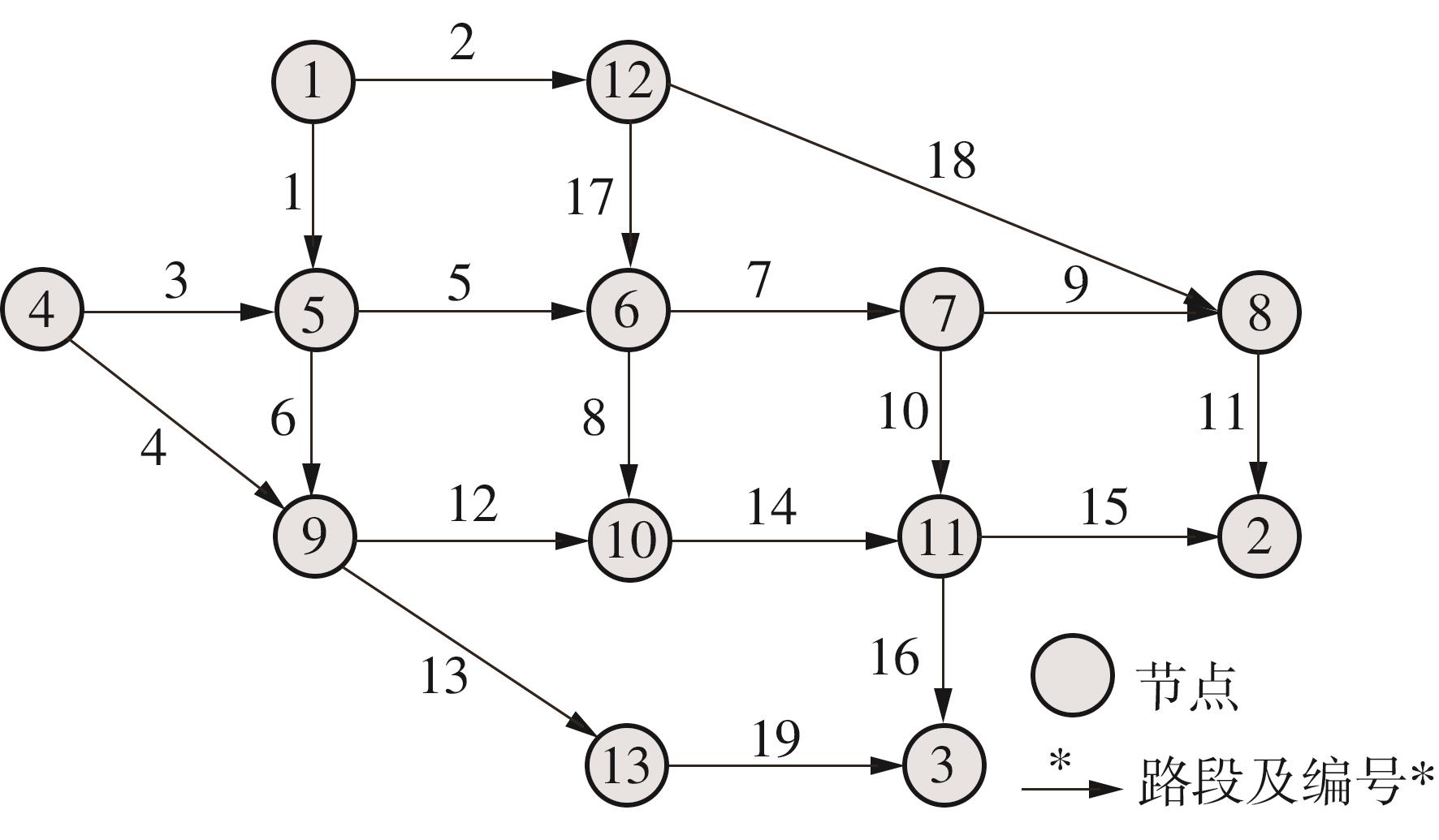
ZHENG Y, GUO W, ZHANG Y,et al .A generalized comfort function of subway systems based on a nested logit model[J].Tsinghua Science and Technology,2014,19(3):300-306.
|
| 31 |
NGUYEN S, DUPUIS C .An efficient method for computing traffic equilibria in networks with asymmetric transportation costs[J].Transportation Science,1984,18(2):185-202.
|
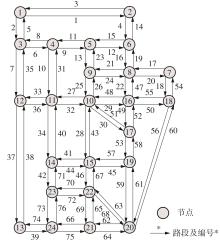
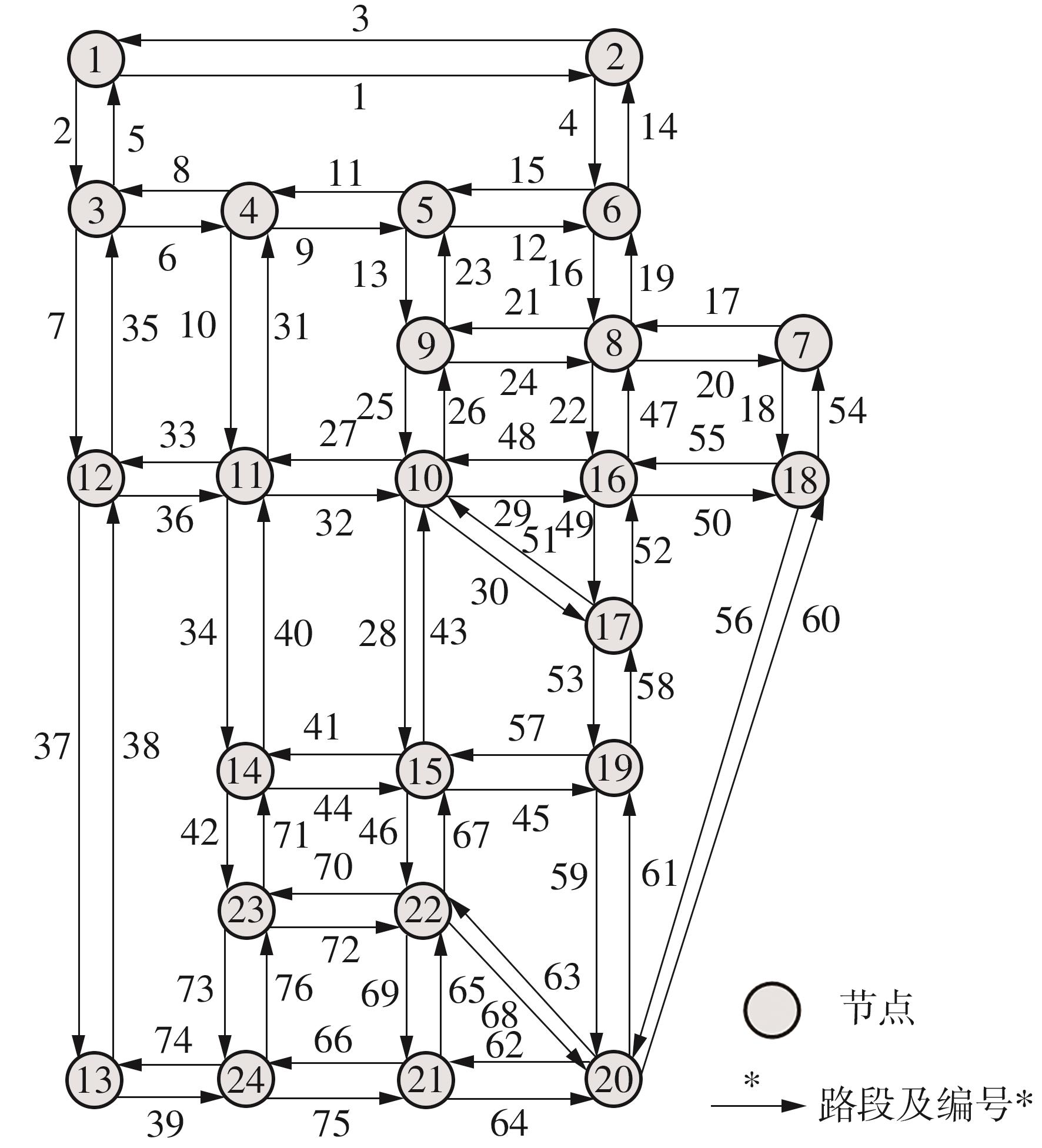
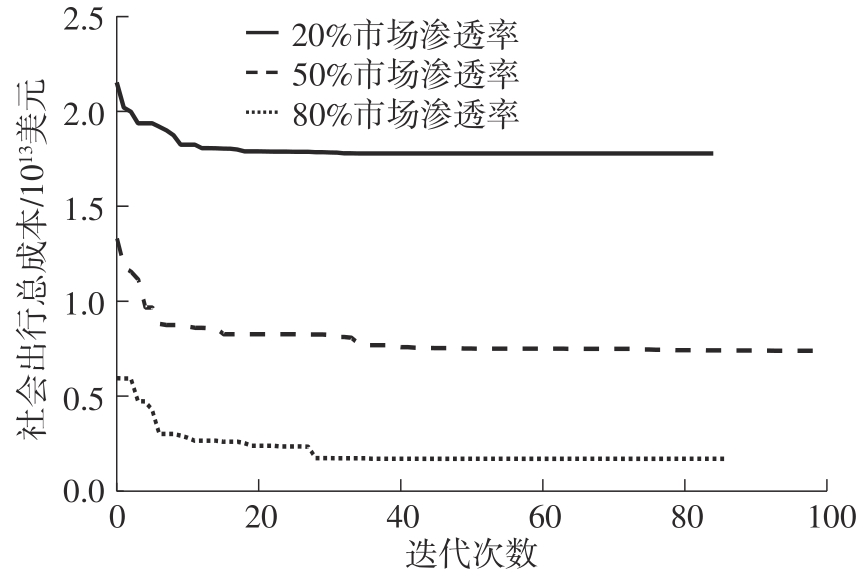
 ), WU Jiyan, LI Zheng, TIAN Ye
), WU Jiyan, LI Zheng, TIAN Ye