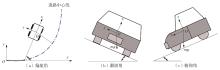
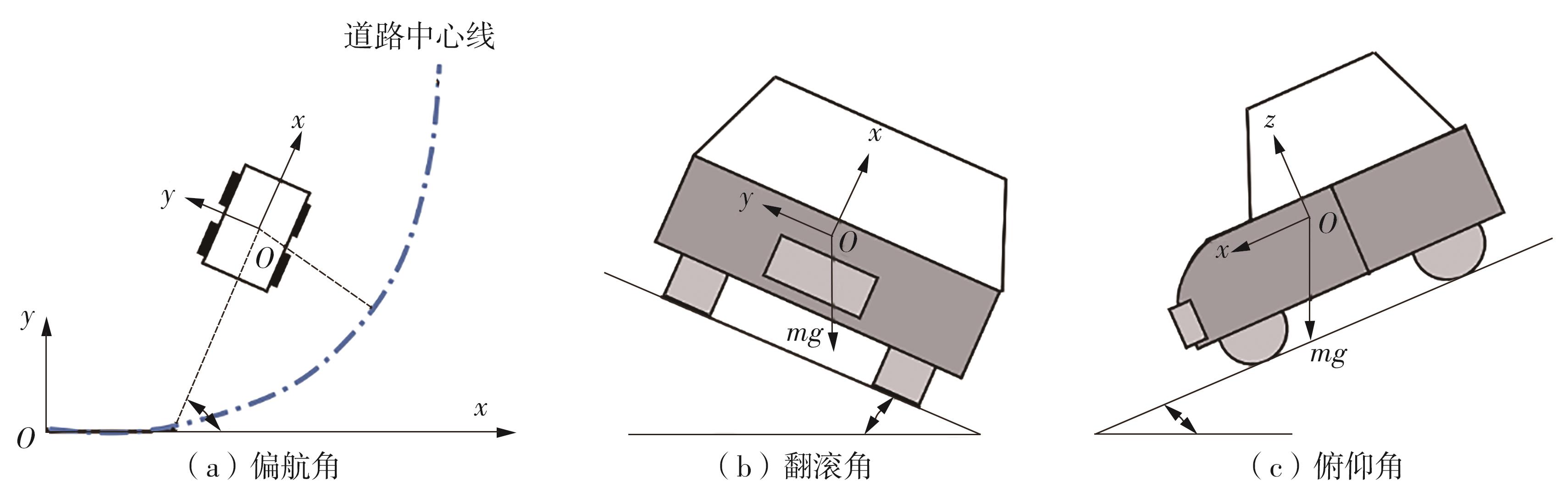
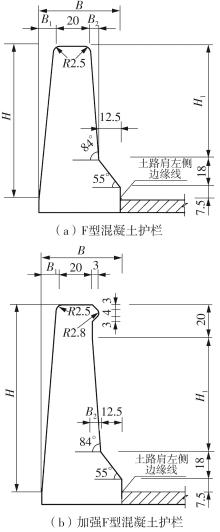
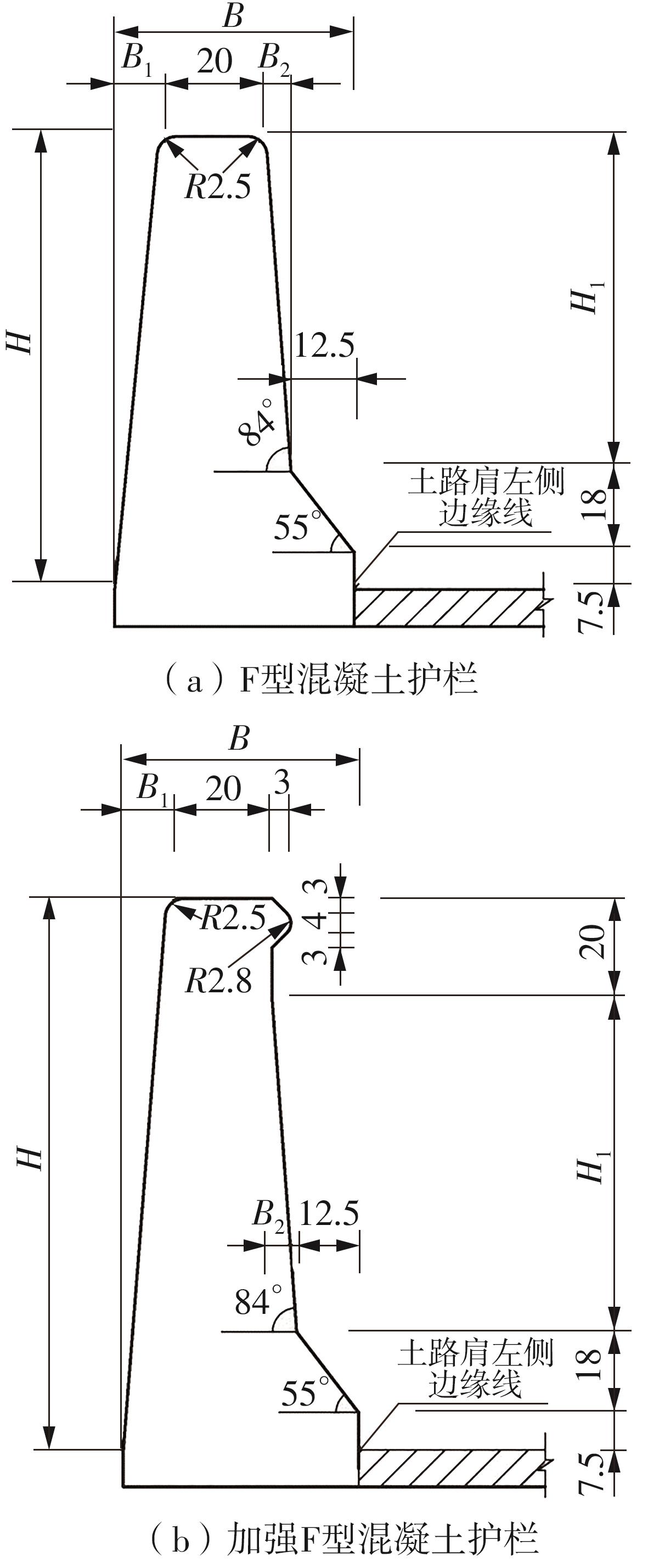
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 90-99.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220789
• Traffic & Transportation Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of Alignment Indexes of Highway Turning Section on Safety Performance of Concrete Guardrail
YANG Yonghong1 TANG Zude1 WANG Chun1,2 ZHU Guanru1,3
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Tunnel Safety and Emergency Support Technology and Equipment,Guangzhou 510545,Guangdong,China
3.Key Laboratory of Highway Engineering of the Ministry of Education,Changsha University of Science & Technology,Changsha 410114,Hunan,China
-
Received:2022-11-30Online:2024-01-25Published:2023-07-14 -
About author:杨永红(1977-),女,博士,副教授,主要从事道路设计和安全研究。E-mail:yangyh@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Key Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province(2022B0101070001);the Guangdong Provincial Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund(2021A1515011788)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Yonghong, TANG Zude, WANG Chun, et al.. Influence of Alignment Indexes of Highway Turning Section on Safety Performance of Concrete Guardrail[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 90-99.
share this article
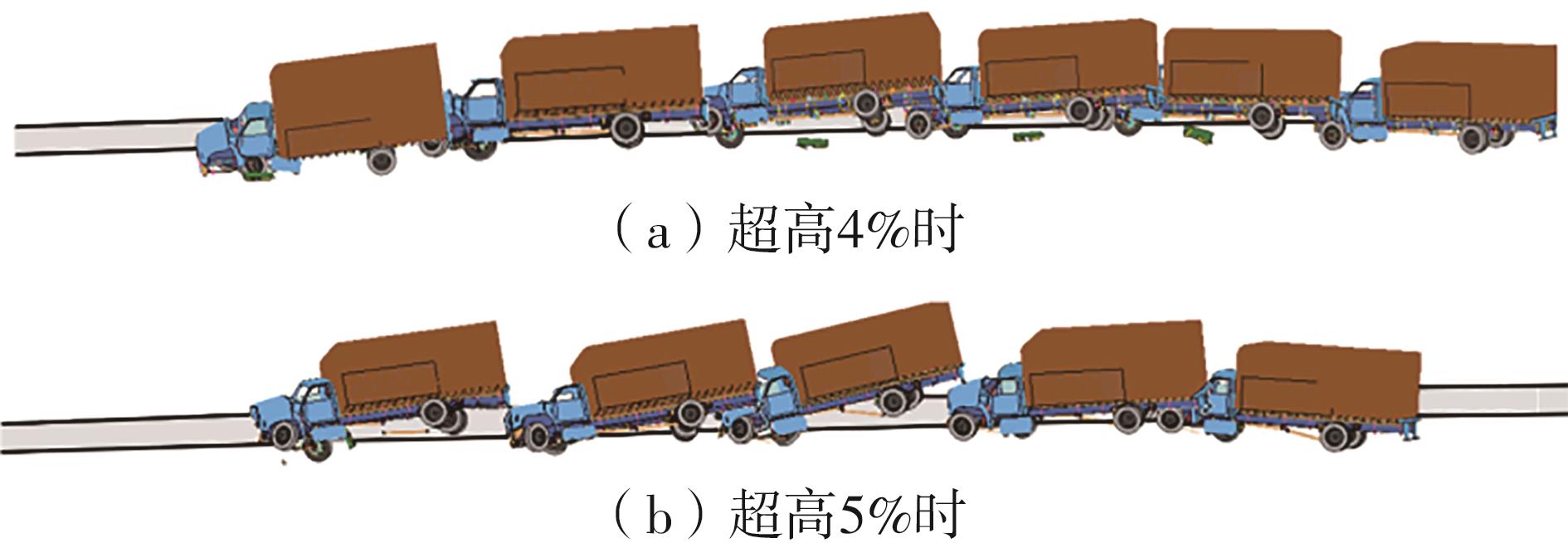
Table 6
Test results of guardrail safety performance at different superelevation values"
| 超高/% | 功能 | 是否满足功能 | 指标 | 指标值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 阻挡功能 | 满足 | 最大翻滚角/(°) | 23.18 |
| 最大俯仰角/(°) | 20.63 | |||
| 缓冲功能 | 满足 | 乘员碰撞速度纵向分量/(m·s-1) | 6.14 | |
| 乘员碰撞速度横向分量/(m·s-1) | 4.06 | |||
| 导向功能 | 满足 | 乘员碰撞加速度纵向分量/(m·s-2) | 169.7 | |
| 乘员碰撞加速度横向分量/(m·s-2) | 117.0 | |||
| 5 | 阻挡功能 | 满足 | 最大翻滚角/(°) | 26.92 |
| 最大俯仰角/(°) | 23.38 | |||
| 缓冲功能 | 满足 | 乘员碰撞速度纵向分量/(m·s-1) | 5.69 | |
| 乘员碰撞速度横向分量/(m·s-1) | 3.99 | |||
| 导向功能 | 满足 | 乘员碰撞加速度纵向分量/(m·s-2) | 166.9 | |
| 乘员碰撞加速度横向分量/(m·s-2) | 113.1 | |||
| 6 | 阻挡功能 | 满足 | 最大翻滚角/(°) | 39.48 |
| 最大俯仰角/(°) | 24.30 | |||
| 缓冲功能 | 满足 | 乘员碰撞速度纵向分量/(m·s-1) | 5.88 | |
| 乘员碰撞速度横向分量/(m·s-1) | 3.78 | |||
| 导向功能 | 满足 | 乘员碰撞加速度纵向分量/(m·s-2) | 161.4 | |
| 乘员碰撞加速度横向分量/(m·s-2) | 116.8 | |||
| 7 | 阻挡功能 | 不满足 | 最大翻滚角/(°) | 90.00 |
| 最大俯仰角/(°) | 20.48 | |||
| 缓冲功能 | 满足 | 乘员碰撞速度纵向分量/(m·s-1) | 5.97 | |
| 乘员碰撞速度横向分量/(m·s-1) | 3.12 | |||
| 导向功能 | 不满足 | 乘员碰撞加速度纵向分量/(m·s-2) | 165.2 | |
| 乘员碰撞加速度横向分量/(m·s-2) | 112.5 | |||
| 8 | 阻挡功能 | 不满足 | 最大翻滚角/(°) | 90.00 |
| 最大俯仰角/(°) | 30.82 | |||
| 缓冲功能 | 满足 | 乘员碰撞速度纵向分量/(m·s-1) | 5.54 | |
| 乘员碰撞速度横向分量/(m·s-1) | 3.65 | |||
| 导向功能 | 不满足 | 乘员碰撞加速度纵向分量/(m·s-2) | 162.8 | |
| 乘员碰撞加速度横向分量/(m·s-2) | 114.3 |
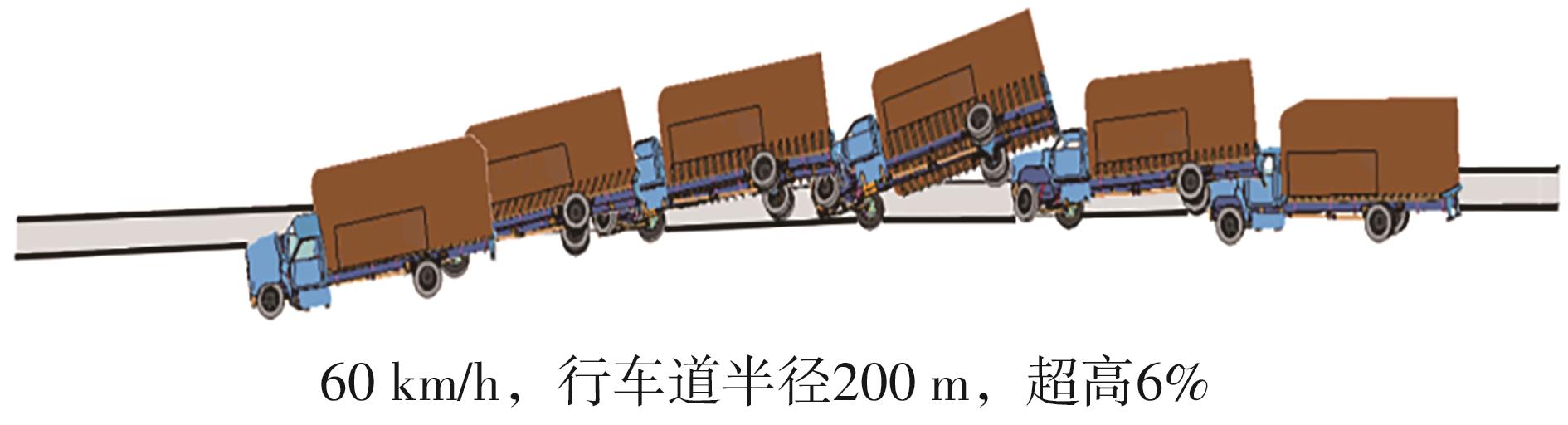
Table 8
Test results of guardrail safety performance at different shoulder widths with a speed of 60 km/h"
| 道路半径/m | 最大翻滚角/(°) | 碰撞速度纵向分量/(m·s-1) | 碰撞速度横向分量/(m·s-1) | 碰撞后最大加速度纵向分量/(m·s-2) | 碰撞后最大加速度横向分量/(m·s-2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.00 m路肩 | 0.75 m路肩 | 3.00 m路肩 | 0.75 m路肩 | 3.00 m路肩 | 0.75 m路肩 | 3.00 m路肩 | 0.75 m路肩 | 3.00 m路肩 | 0.75 m路肩 | |
| 125 | 39.18 | 90.00 | 5.86 | 6.03 | 3.48 | 3.74 | 162.5 | 178.3 | 108.2 | 125.7 |
| 200 | 35.06 | 34.26 | 5.52 | 5.71 | 3.65 | 3.55 | 165.9 | 162.5 | 106.9 | 114.2 |
| 400 | 34.54 | 33.41 | 5.19 | 5.01 | 3.15 | 3.53 | 161.2 | 154.0 | 100.4 | 107.8 |
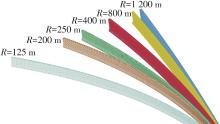
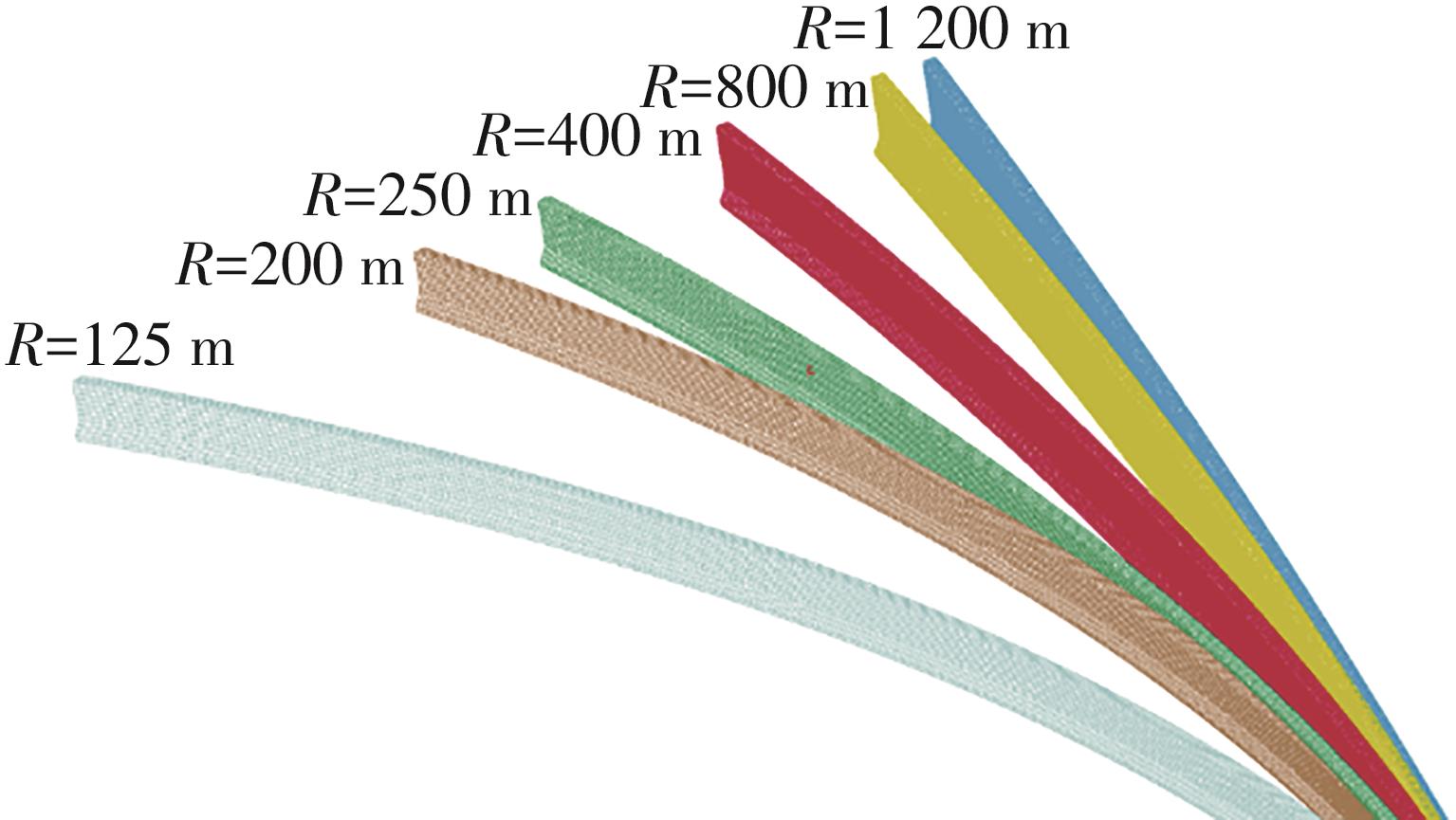
Table 10
Impact test results of concrete guardrail in highway turn section"
| 超高/% | 60 km/h车速下不同半径的试验结果 | 80 km/h车速下不同半径的试验结果 | 100 km/h车速下不同半径的试验结果 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 m | 200 m | 300 m | 400 m | 250 m | 400 m | 800 m | 400 m | 800 m | 1 200 m | |
| 4 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 |
| 5 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 |
| 6 | 不通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 不通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 不通过 | 不通过 | 通过 |
| 7 | 不通过 | 不通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 不通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 不通过 | 不通过 | 通过 |
| 8 | 通过 | 不通过 | 通过 | 通过 | 不通过 | 不通过 | 通过 | 不通过 | 不通过 | 不通过 |
| 1 | OFFICIALS T .Manual for assessing safety hardware,2009[M].[S.l.]:AASHTO,2009. |
| 2 | STOUT D, HUGHES W, MCGEE H T .Traffic barriers on curves,curbs,and slopes[R].[S.l.]:Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center,1993. |
| 3 | MOLAN M A, KSAIBATI K .Factors impacting injury severity of crashes involving traffic barrier end treatments[J].International Journal of Crashworthiness,2021,26(2):202-210. |
| 4 | RUSSO B J, SAVOLAINEN P T .A comparison of freeway median crash frequency,severity,and barrier strike outcomes by median barrier type[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2018,117:216-224. |
| 5 | MOLAN M A, REZAPOUR M, KSAIBATI K .Modeling the impact of various variables on severity of crashes involving traffic barriers[J].Journal of Transportation Safety & Security,2020,12(6):800-817. |
| 6 | MARZOUGUI D, KAN C S, DOLCI S,et al .Modeling and simulation of vehicle crashes on curved,superelevated road sections[C]∥Proceedings of the First International Roadside Safety Conference.San Francisco:Transportation Research Board,2017. |
| 7 | 张晶,白书锋,石红星,等 .车辆与弯道混凝土护栏碰撞的动态数值模拟及试验[J].中国公路学报,2007,20(1):102-106. |
| ZHANG Jing, BAI Shu-feng, SHI Hong-xing,et al .Dynamic numerical simulation and experiment for vehicle and curved concrete barriers crush[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport.2007,20(1):102-106. | |
| 8 | 雷正保,彭作,刘兰,等 .弯道混凝土护栏碰撞特性的优化设计[J].振动与冲击,2009,28(5):6-9. |
| LEI Zhengbao, PENG Zuo, LIU Lan,et al .The optimal design of collision characteristic of curve-road concrete barrier[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2009,28(5):6-9. | |
| 9 | 韩海峰,杨轸,郑挺 .高速公路路侧护栏碰撞能量需求研究[J].公路交通科技,2016,33(12):118-124. |
| HAN Hai-feng, YANG Zhen, ZHENG Ting .Study on collision energy requirement for expressway roadside guardrail[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2016,33(12):118-124. | |
| 10 | National Highway Traffic Safety Administration .Crash report sampling system (CRSS)[R].[S.l.]:National Highway Traffic Safety Administration,2021. |
| 11 | National Highway Traffic Safety Administration .Fatality analysis reporting system (FARS)[R].[S. l.]:Na-tional Highway Traffic Safety Administration,2021. |
| 12 | 崔鹏飞 .货车专用匝道超高取值仿真评价[J].路基工程,2022(1):139-145. |
| CUI Pengfei .Simulation evaluation of ultra-high value of special ramp for trucks[J].Subgrade Engineering,2022(1):139-145. | |
| 13 | 甘新众,甘有为,刘群艳,等 .半挂车撞击公路护栏时的等效模型[J].中外公路,2020,40(1):258-262. |
| GAN Xinzhong, GAN Youwei, LIU Qunyan,et al .Equivalent model when semi-trailer hitting highway guardrail[J].Journal of China & Foreign Highway,2020,40(1):258-262. | |
| 14 | 方乐,曾玉烨,陈林 .针对轻型与中型卡车撞击桥墩的通用车辆力学模型[J].自然灾害学报,2021,30(4):92-101. |
| FANG Le, ZENG Yuye, CHEN Lin .General vehicle mechanical model for light and medium trucks crashing into bridge piers[J].Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(4):92-101. | |
| 15 | CHEN L, WU H, LIU T .Shear performance evaluation of reinforced concrete piers subjected to vehicle collision[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2020,146(4):4020026. |
| 16 | 公路护栏安全性能评价标准: [S]. |
| 17 | 公路交通安全设施设计规范: [S]. |
| 18 | POLIVKA K A, FALLER R K, SICKING D L,et al .Performance evaluation of the permanent New Jersey safety shape barrier-update to NCHRP 350 Test No. 4-12 (2214NJ-2)[R].Lincoln:Mid-America Transportation Center,2006. |
| 19 | RAY M H, MONGIARDINI M, ANGHILERI M .Development of the roadside safety verification and validation program[EB/OL].[2022-08-13].. |
| 20 | 公路路线设计规范: [S]. |
| 21 | 公路交通安全设施设计细则: [S]. |
| [1] | ZANG Mengyan, WANG Lichen, ZHOU Tao, et al. Finite Element Simulation Analysis and Evaluation of Radial Tire's Transient Dynamic Characteristics [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(8): 124-129. |
| [2] | ZHANG Chi ZHANG Hong QI Chen BAI Haochen GAO Jianrong HOU Yudi. Study of the Horizontal and Vertical Combination of the Split-end of the Exit Ramp [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 99-108. |
| [3] |
ZHOU Xiaoyu MA Rujin CHEN Airong .
Safety Performance of a Bridge Deck Under Impact of a Massive Falling Cargo from Passing Truck
|
| [4] | Yang Hui-xian Huang Yan-sheng Li Jing. Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Cement-Based Composites [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(7): 50-56. |
| [5] | Wei Hong-yun Zhou Wei-feng Li Yuan-yuan. Performance Comparison of Cement Macadam Based on Different Molding Methods [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(8): 84-90. |
| [6] | Fu Xin-sha Long Li-dun Li Hai-feng Ge Ting. Method and System Architecture of True Three-Dimensional Highway Alignment Design Based on Motion Sensing Interaction [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(8): 91-96. |
| [7] | Fu Zhen Wang Xuan- cang Lu Kai- quan. Influence of Pipe- Burying Mode on Hydrothermal Snow Melting of Bridge Decks [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(5): 90-96. |
| [8] | Liu Wei-ming Deng Ru-feng Zhang Yang Zhuang Yan-hao. Setting Model of Safe Distance of Advance Guide Signs at Highway Exits [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(2): 37-43. |
| [9] | Zheng Yi Jia Jin-qing Shen Xiao-jun Xiong Wei-shi Gao Fei Zhang Yan-nian. Safety Evaluation Method for Laminated Rubber Bearings of Bridge Based on Extension Theory [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(9): 160-164. |
| [10] | Wang Hai-nian Hao Pei-wen Pang Li-guo Di Jian-hong. Investigation into Grading Characteristic of Coarse Aggregate via Digital Image Processing Technique [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 35(11): 54-58,62. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||