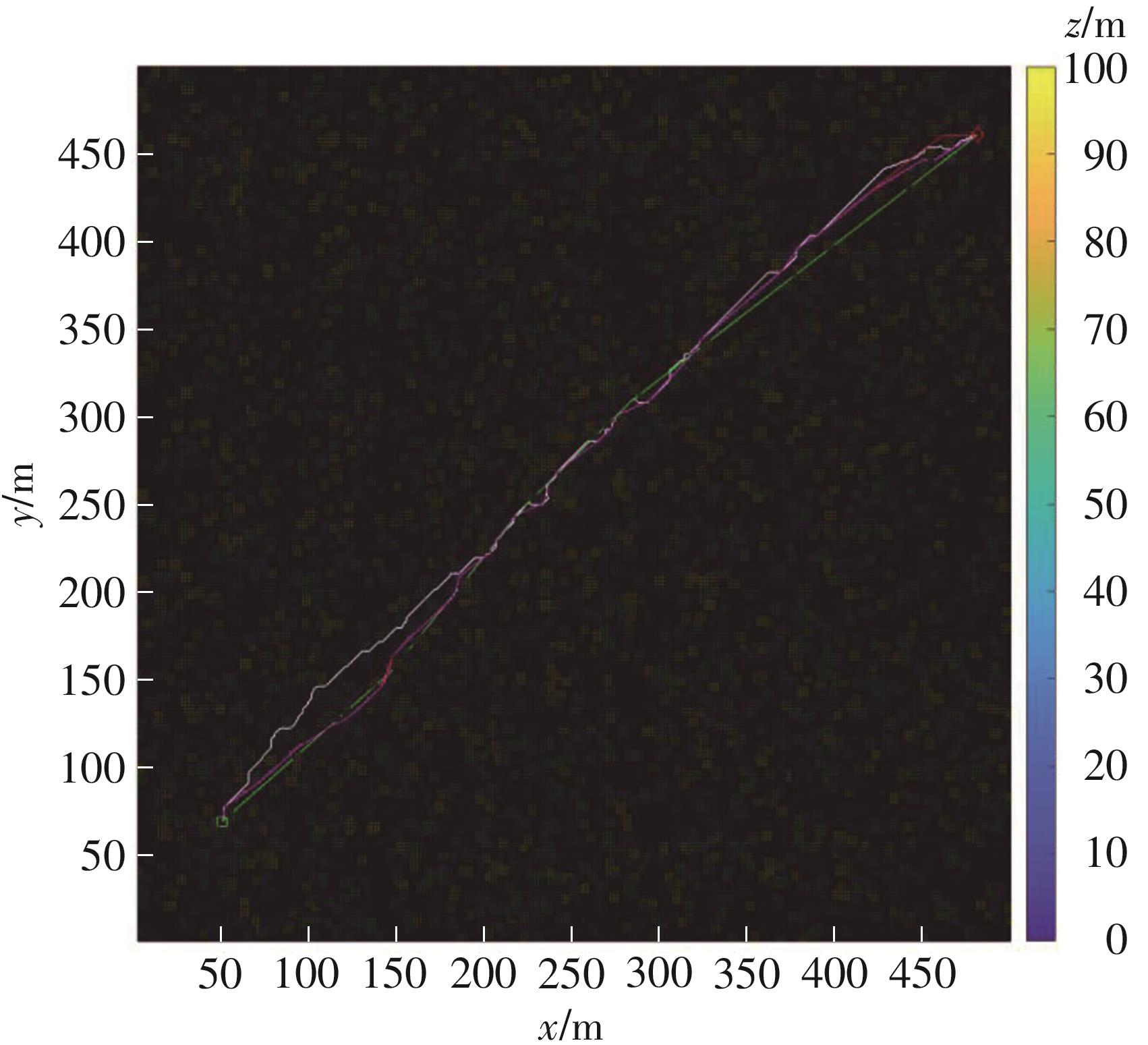
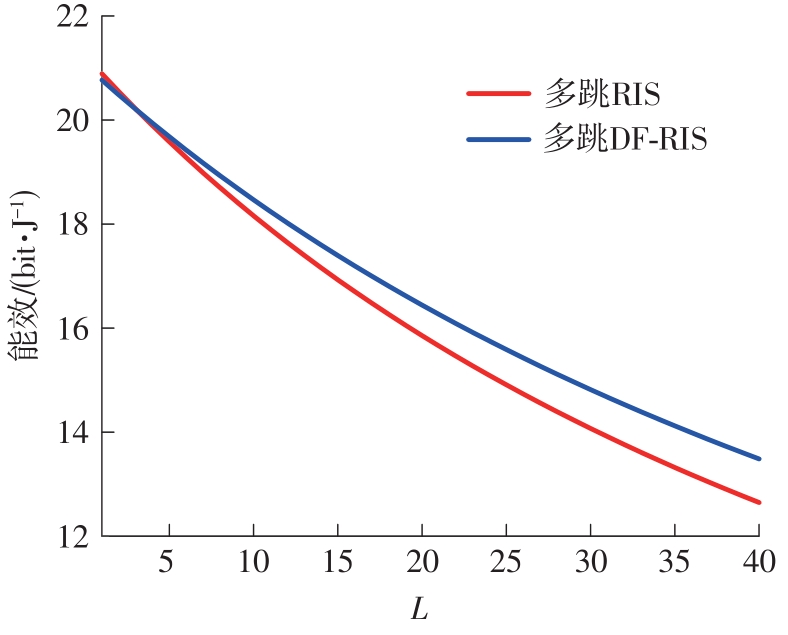
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 112-118.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230016
• Electronics, Communication & Automation Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
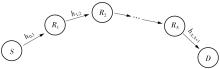
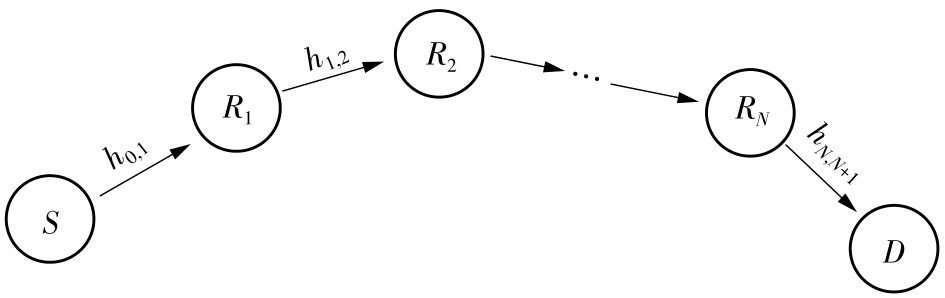
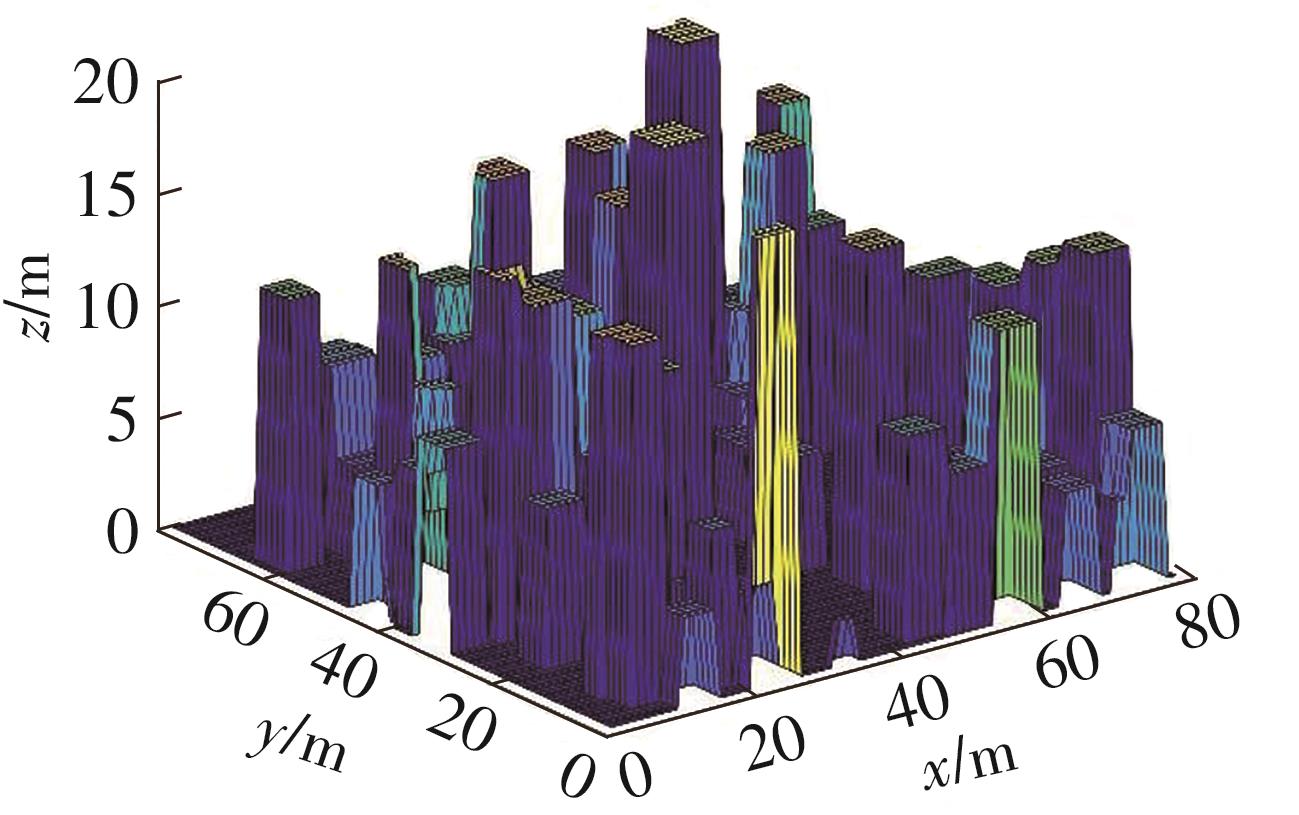
Research on Transmission Scheme Based on Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface in Dense Urban Agglomeration
ZHUANG Ling LIU Yuhang
- School of Communication and Information Engineering /Key Laboratory of Mobile Communication Technology,Ministry of Industry and Information,Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Chongqing 400065,China