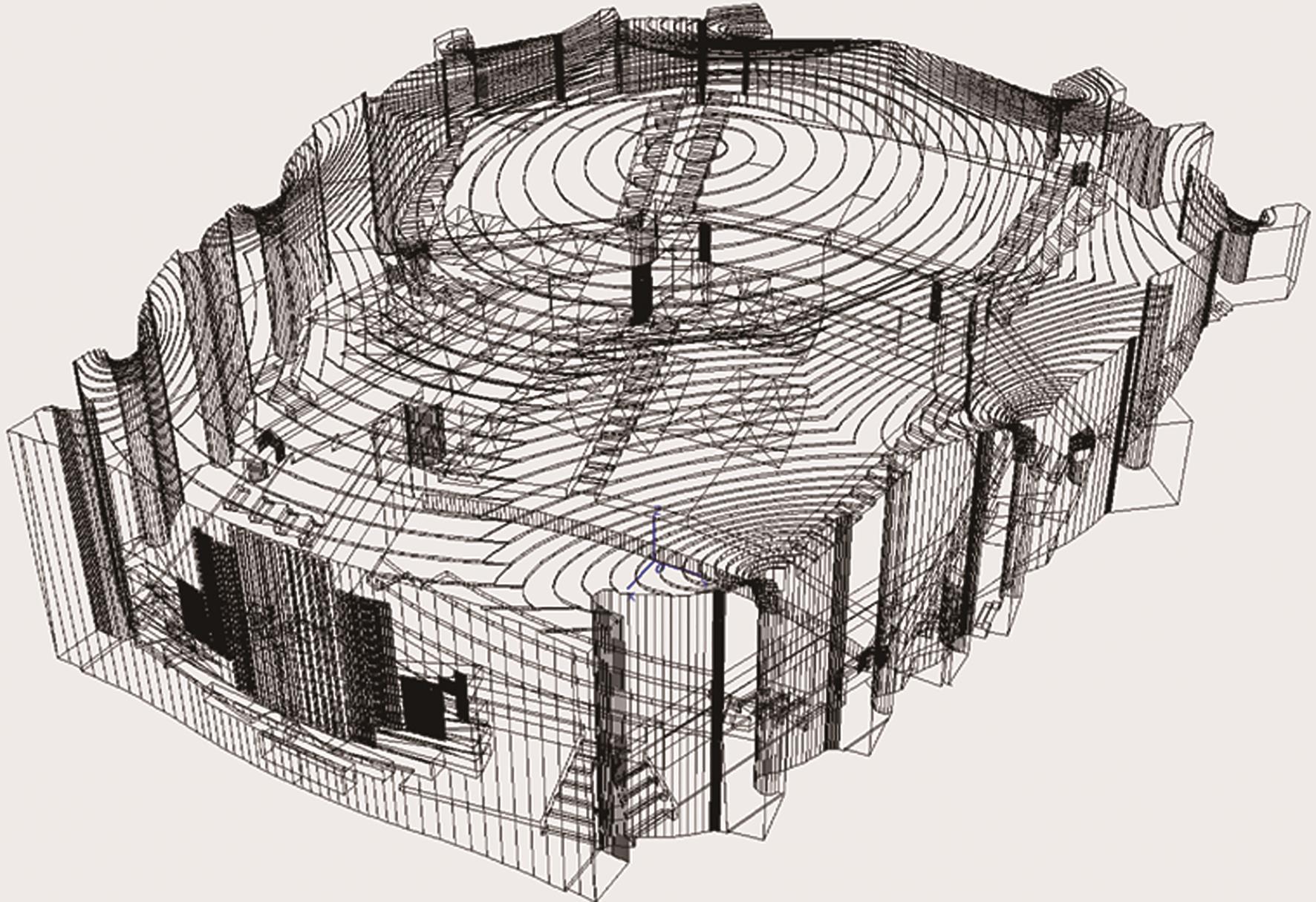
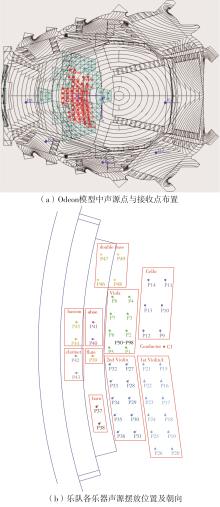
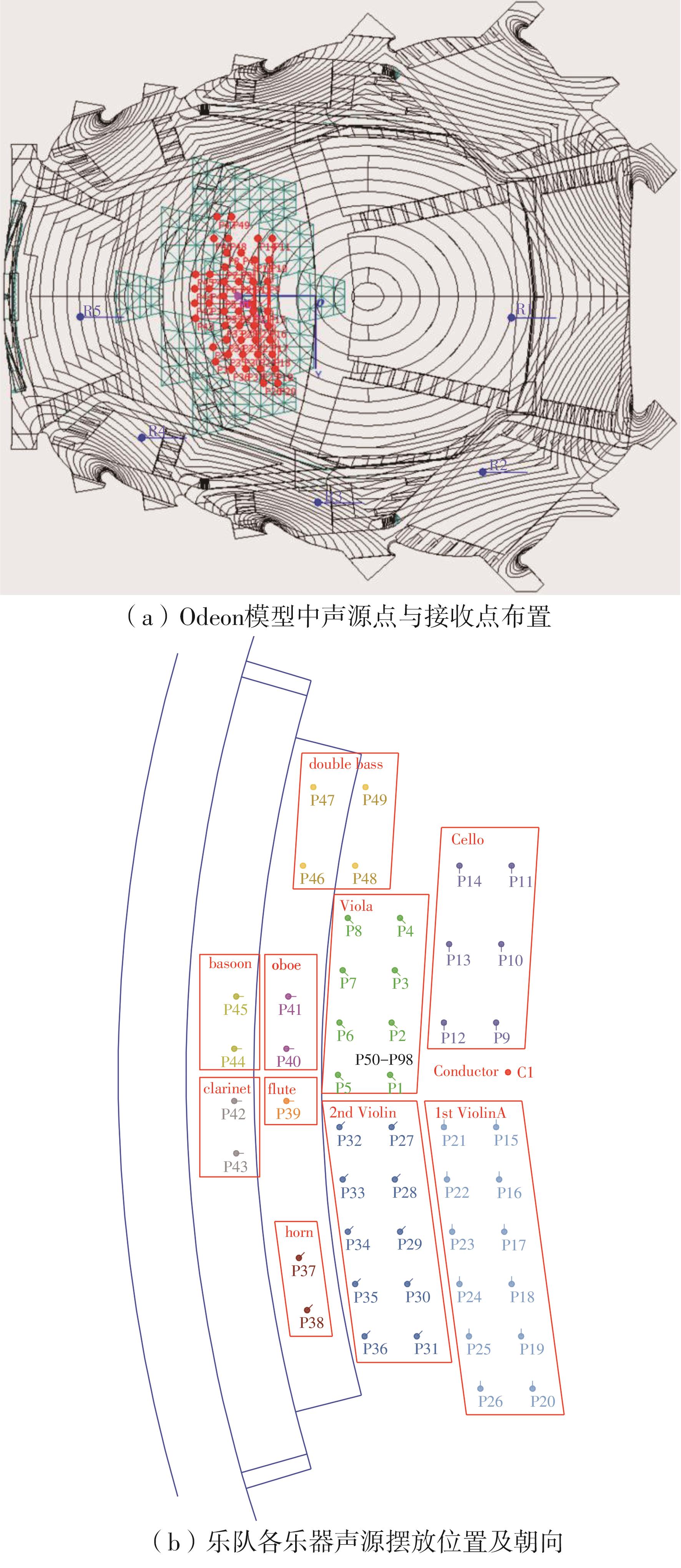
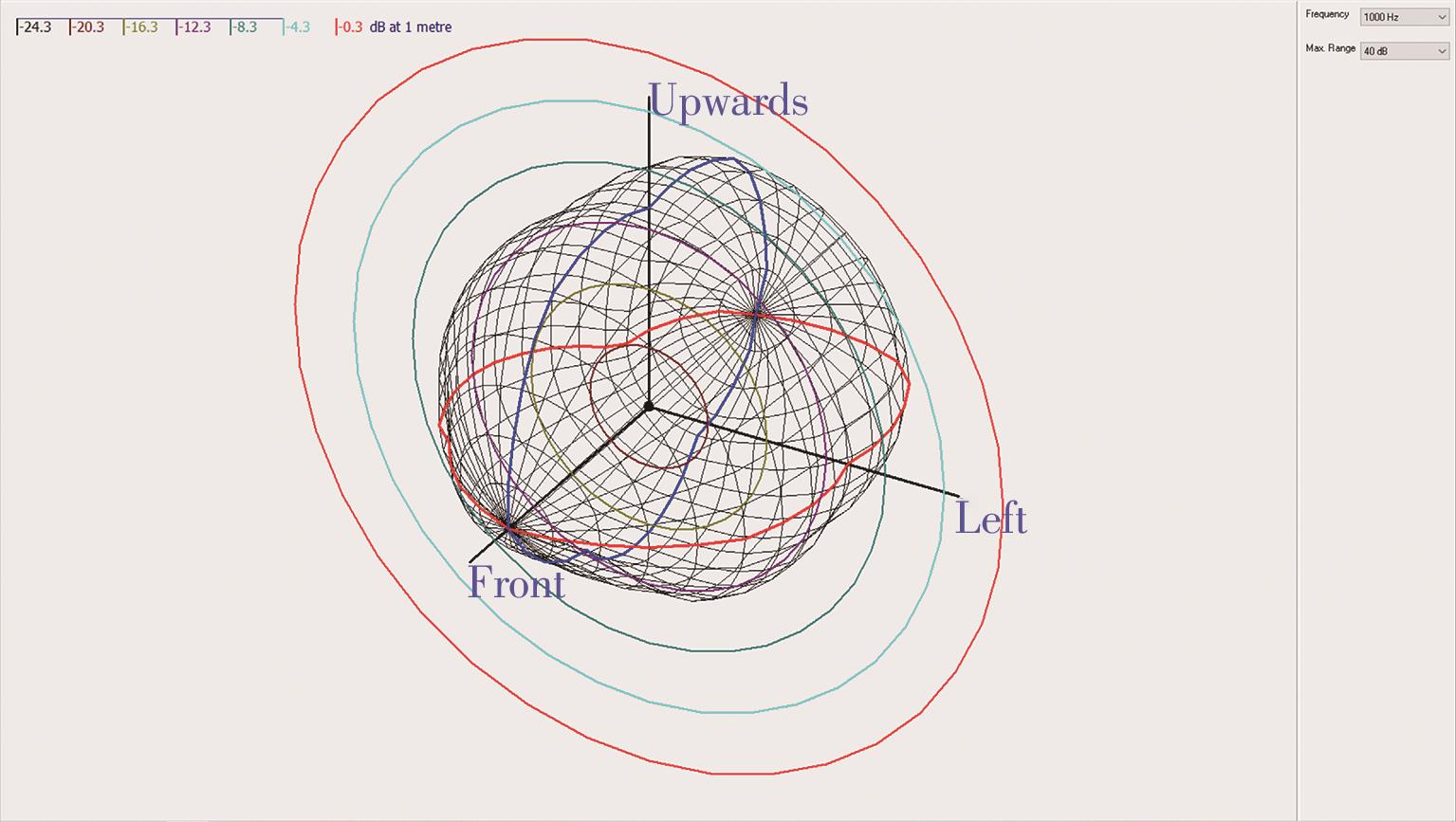
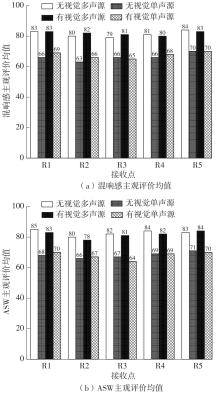
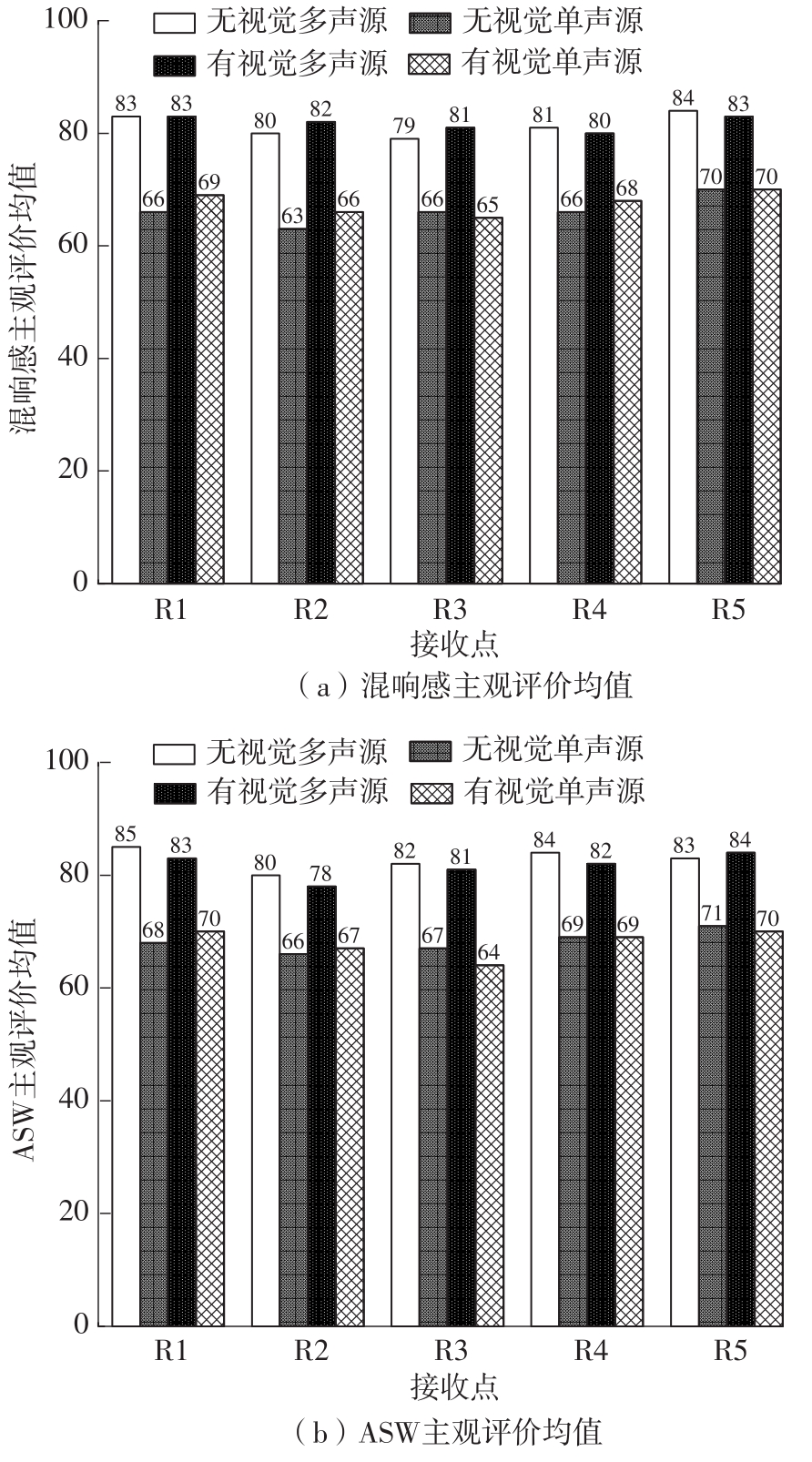
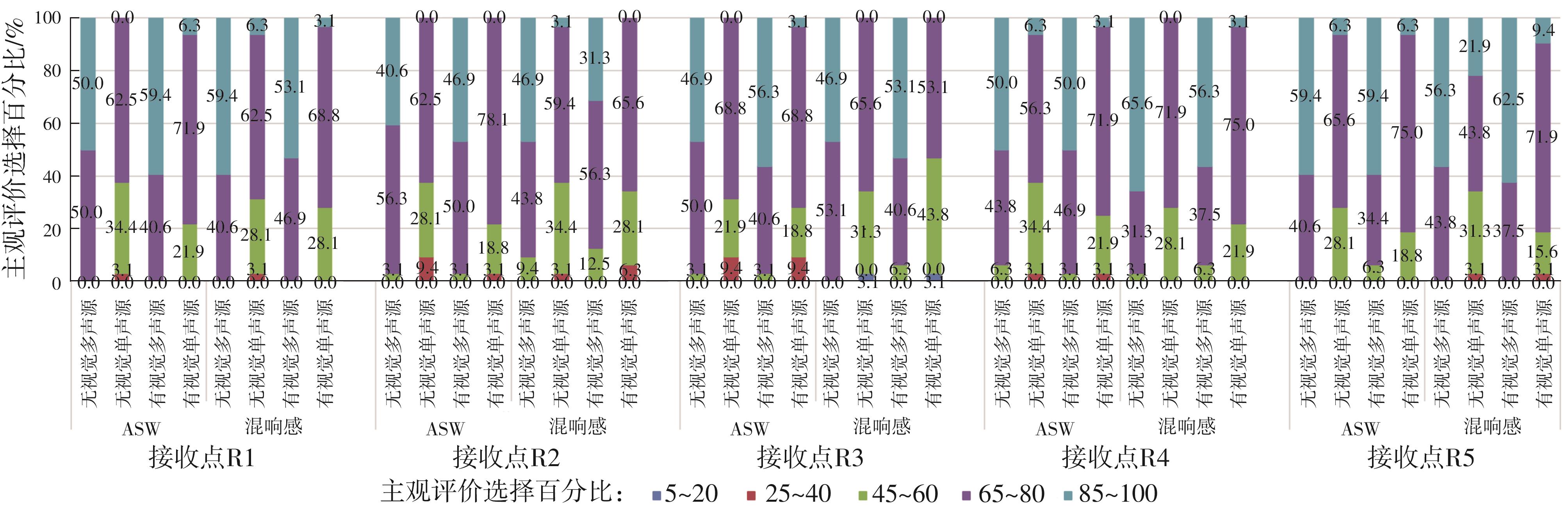
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 71-79.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220209
Special Issue: 2023年土木建筑工程
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
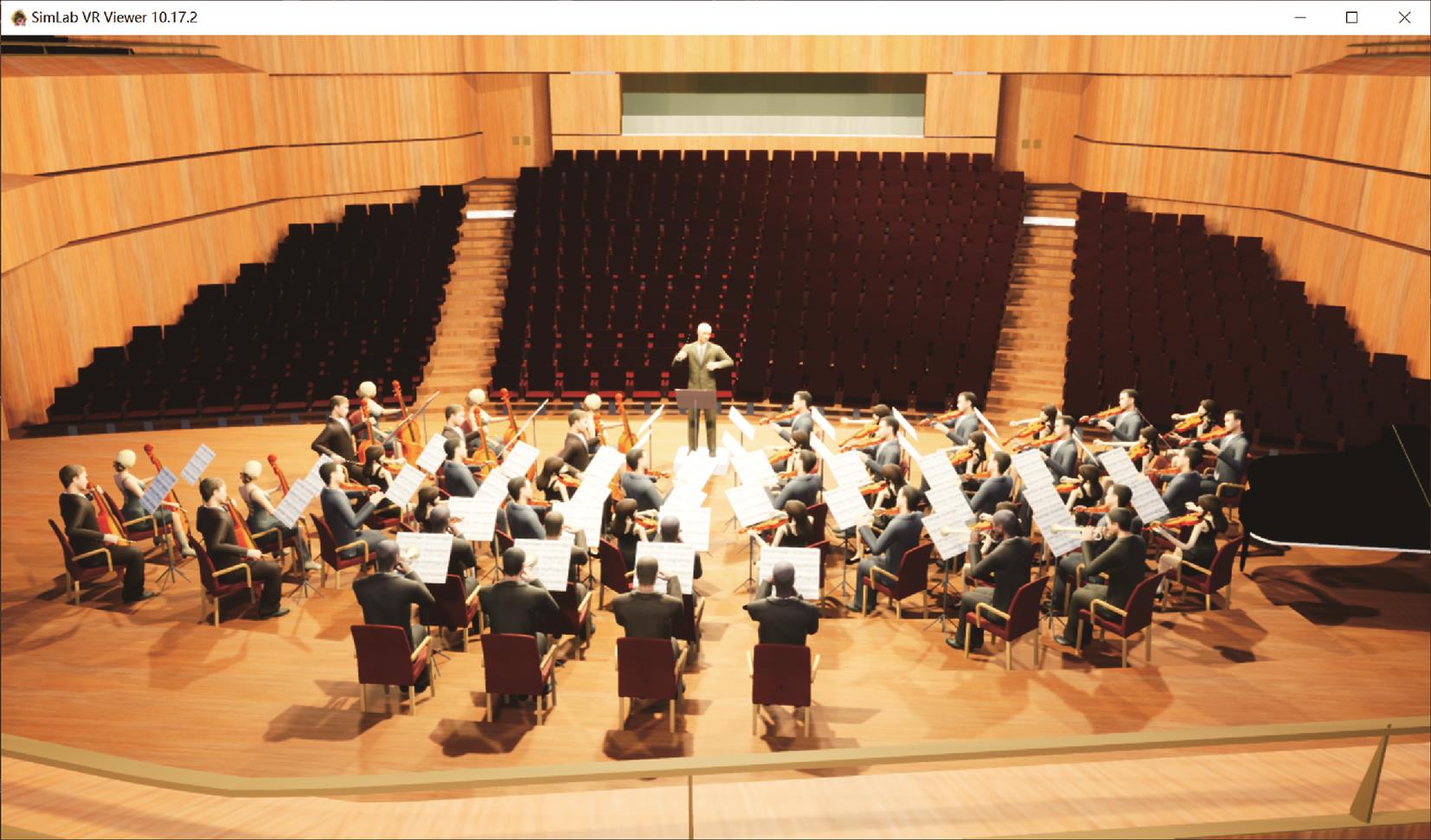
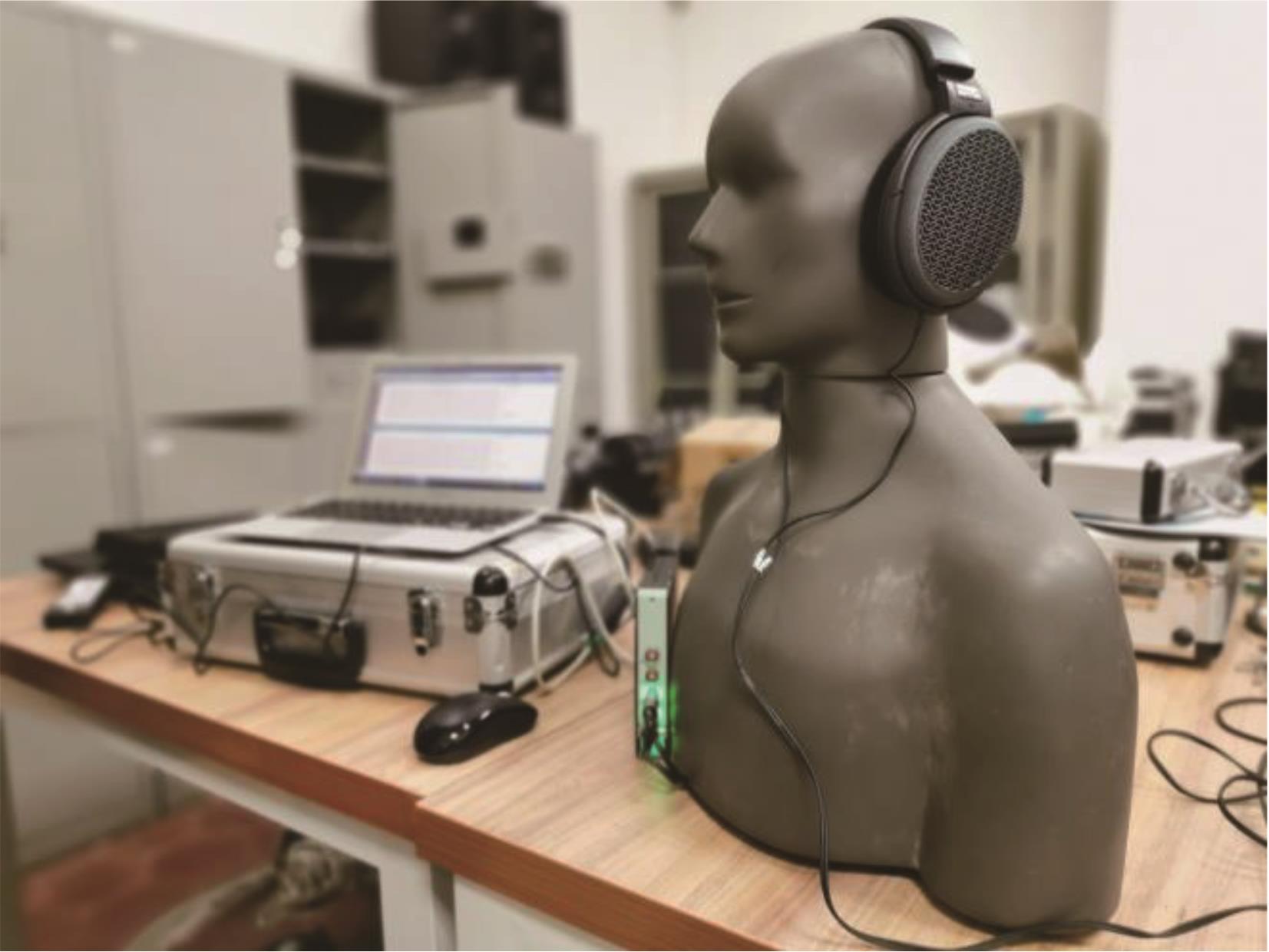
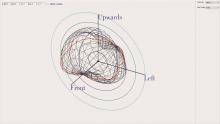
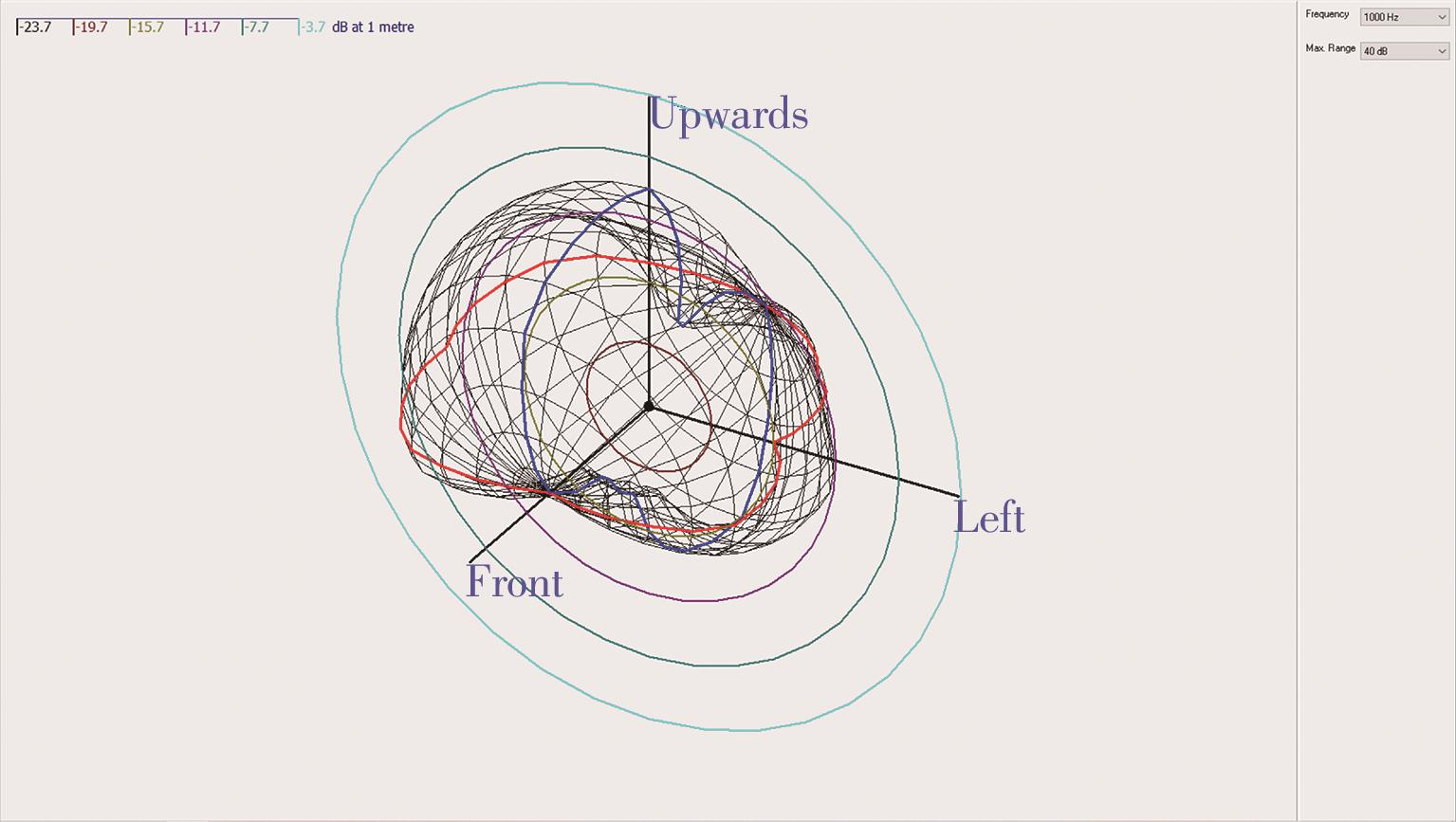
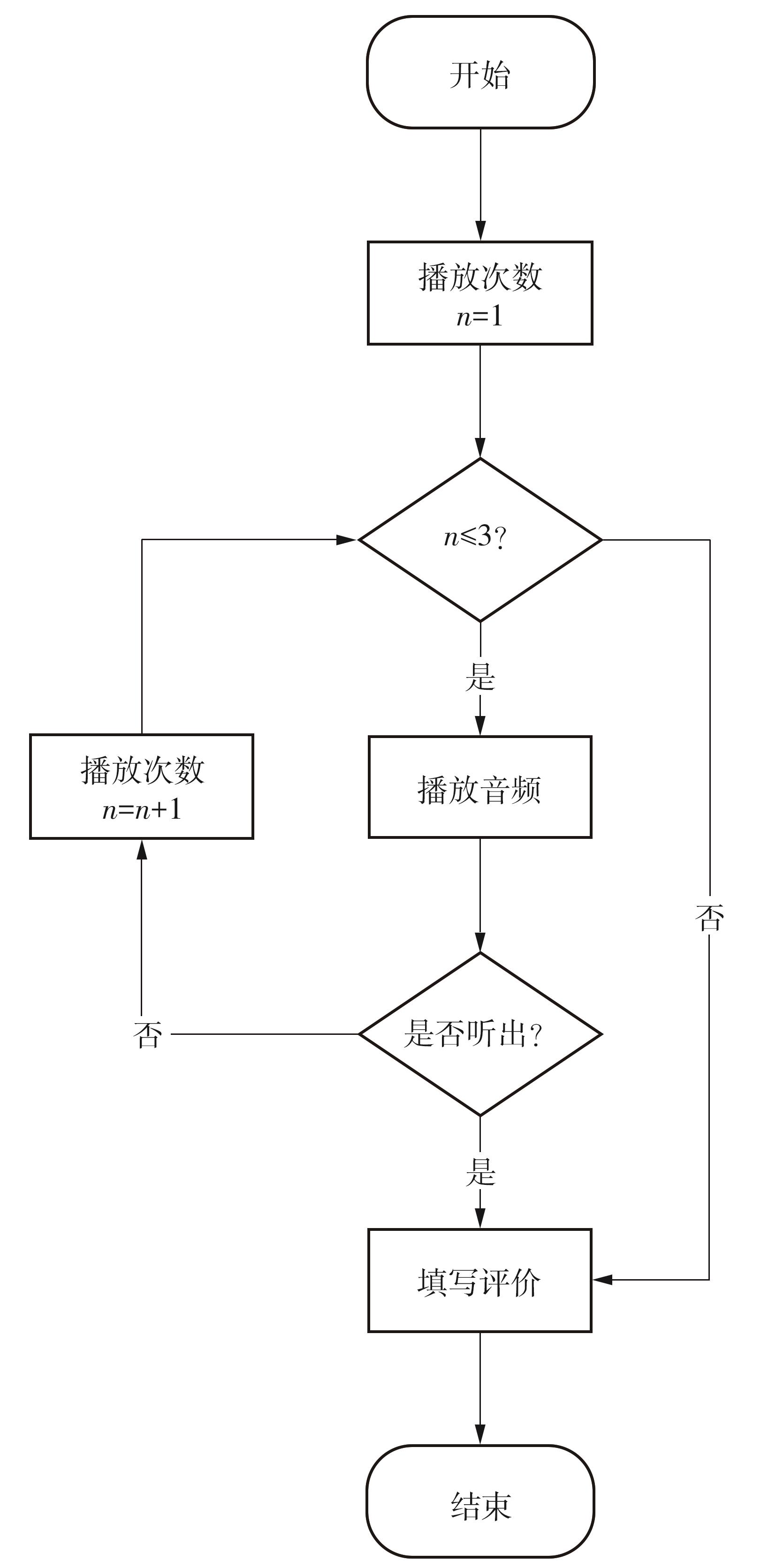
Research on Audio-Visual Integration Based on Architectural Acoustic Simulation
SUN Haitao YANG Yu
- State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building Science/School of Architecture,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China