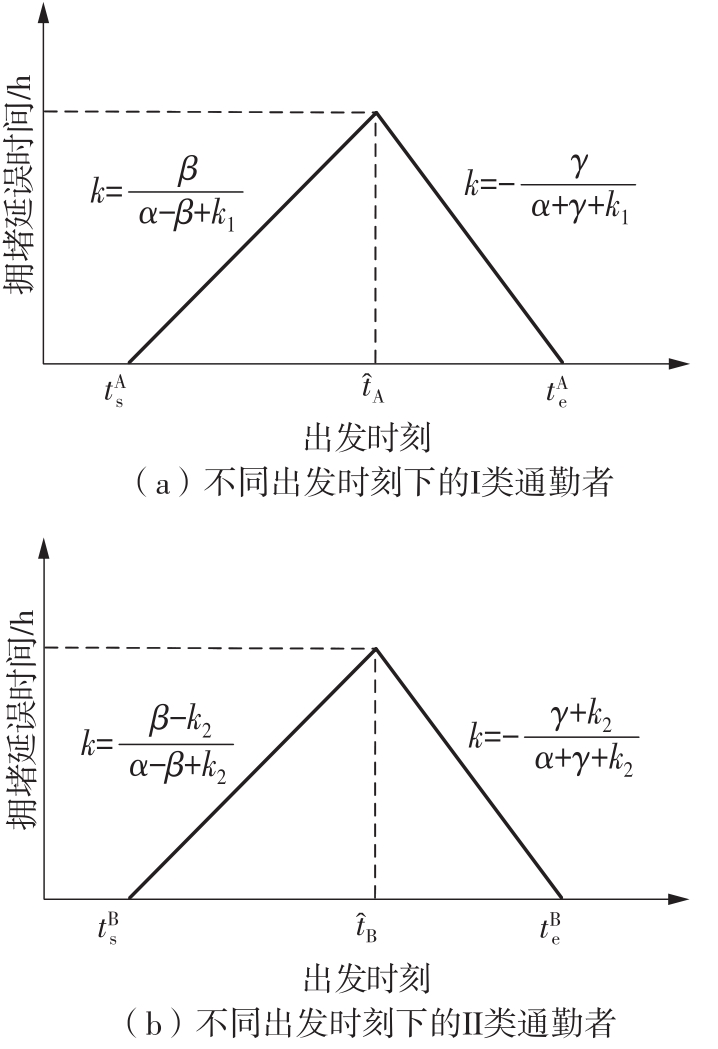
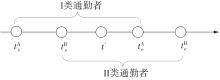
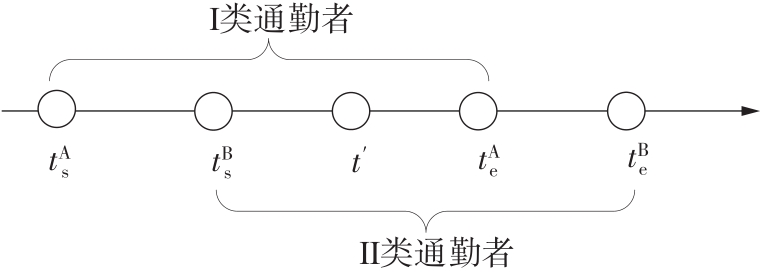
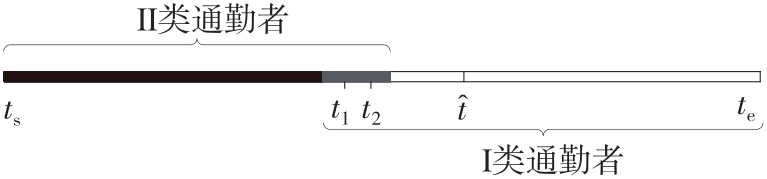
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (11): 14-24.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220004
Special Issue: 2022年交通运输工程
• Traffic & Transportation Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
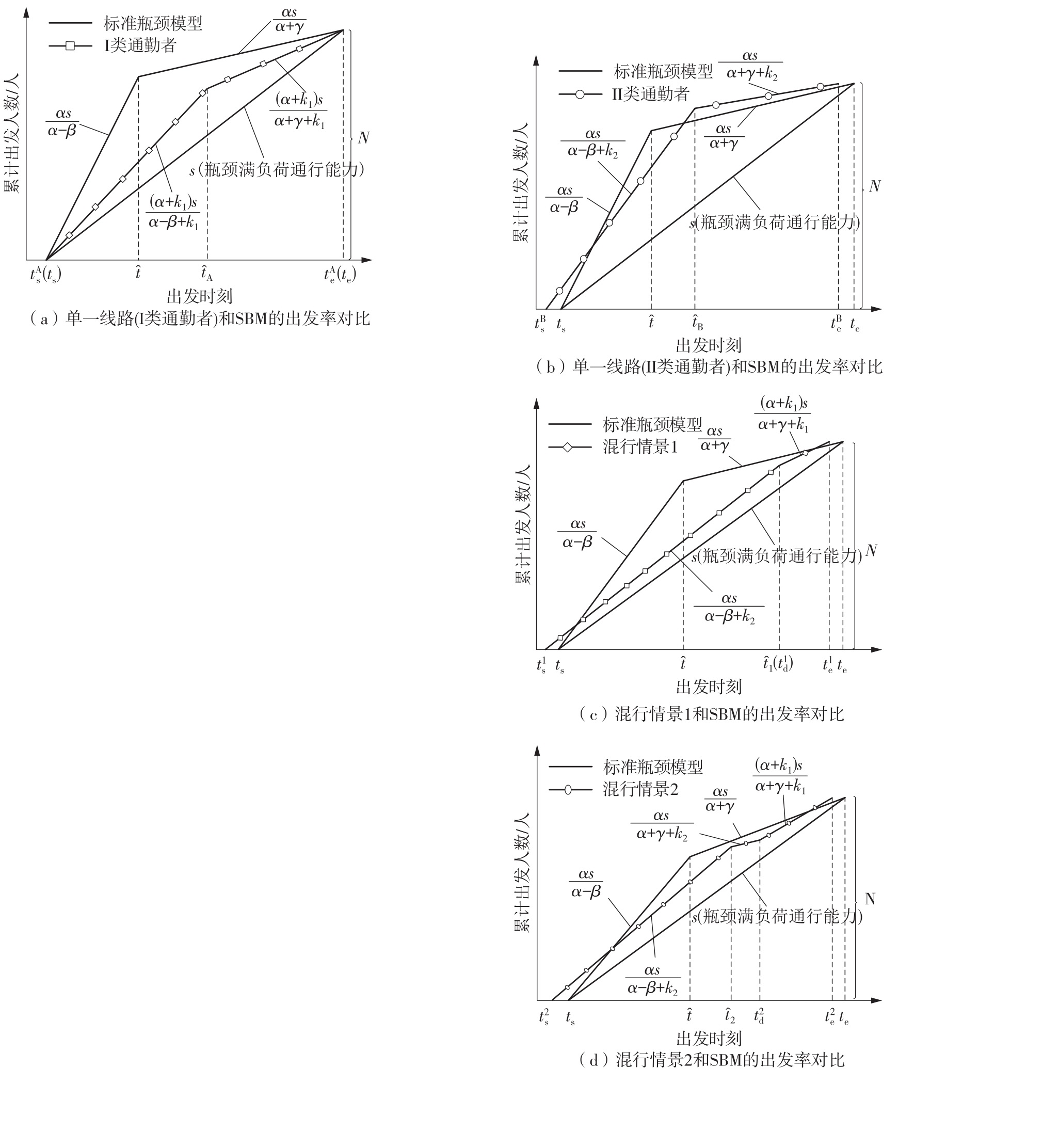
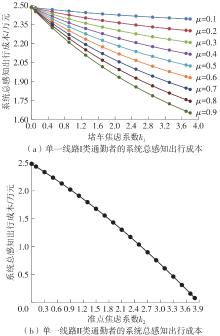
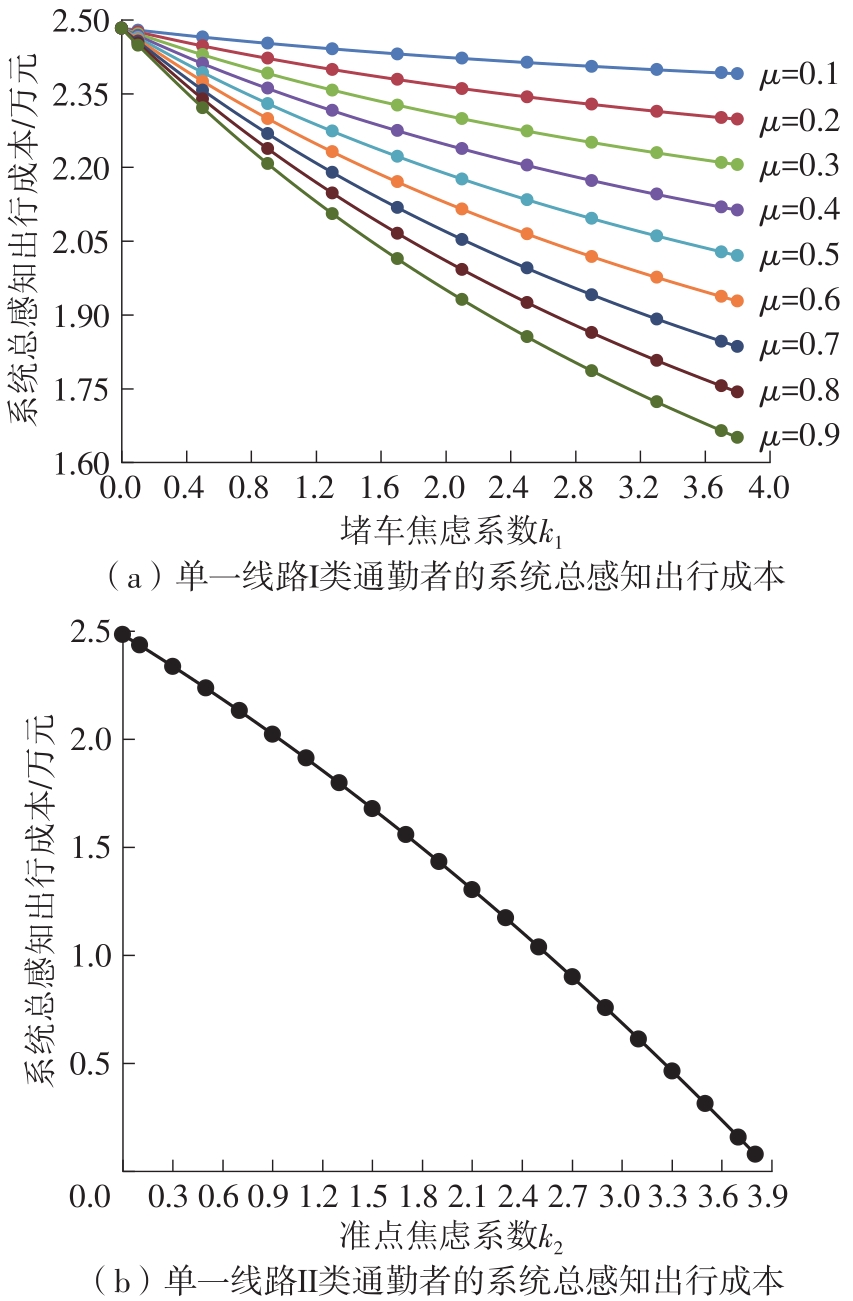
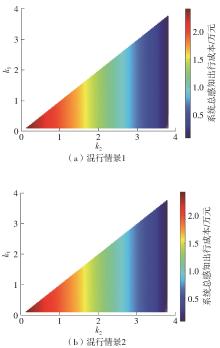
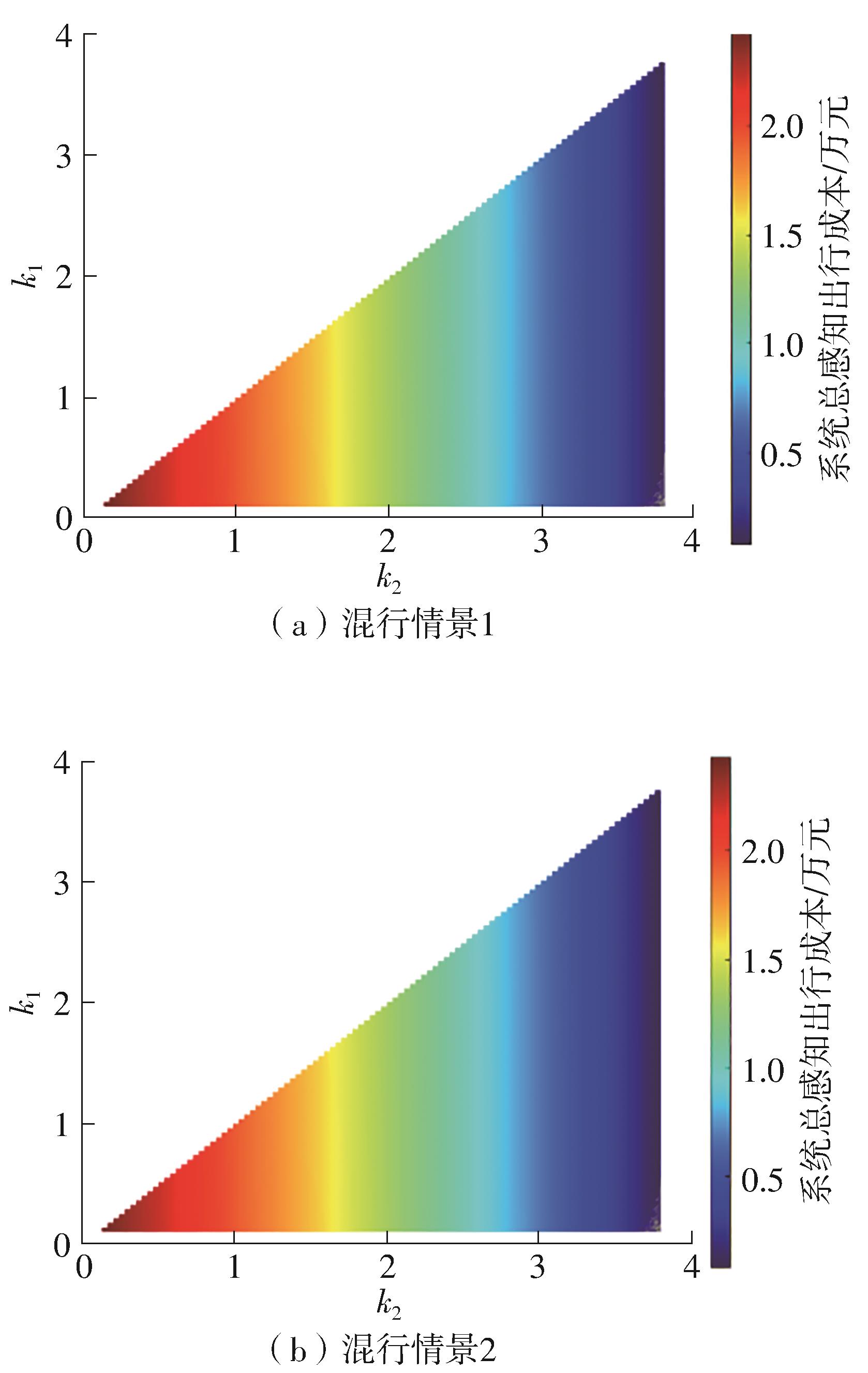
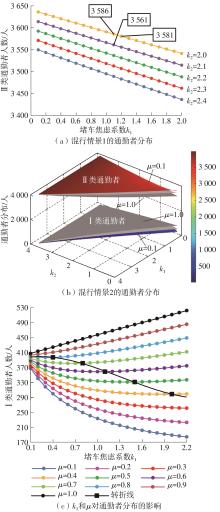
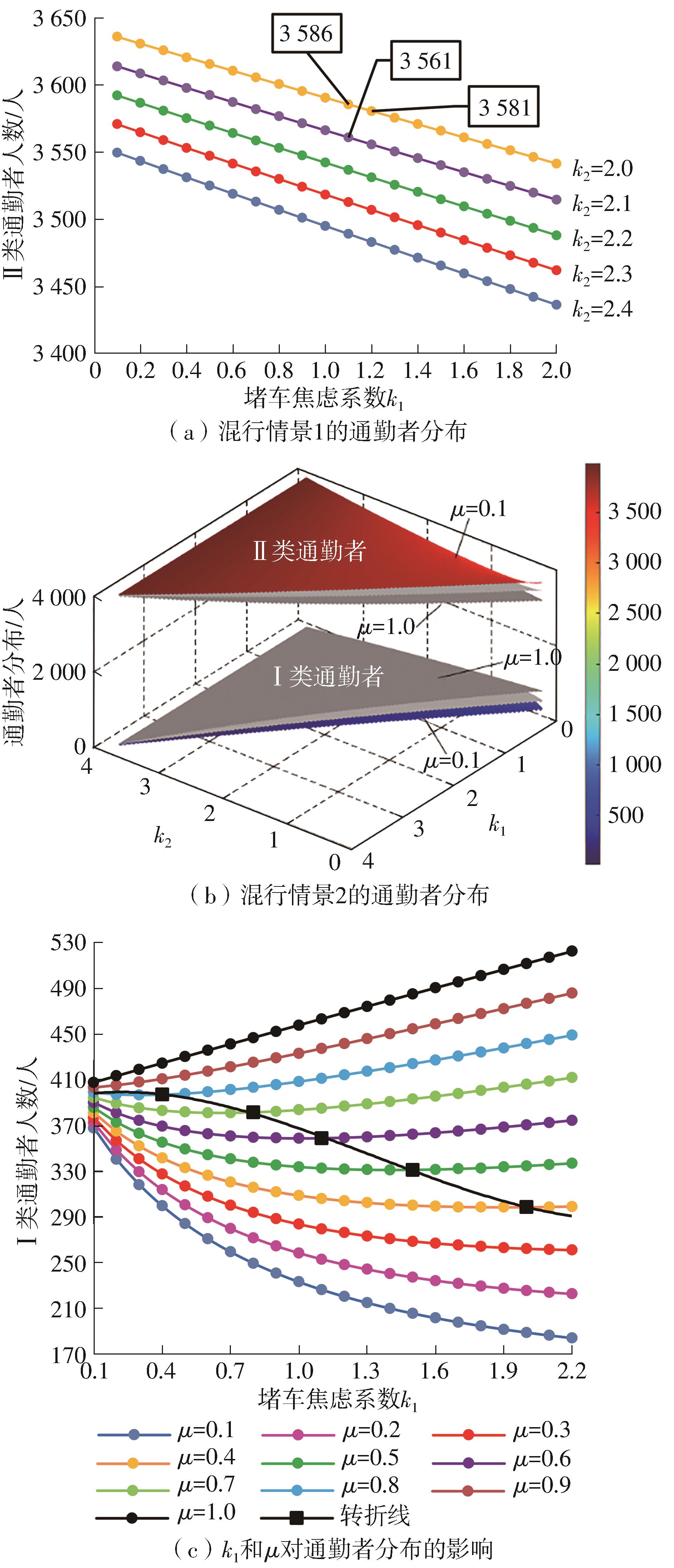
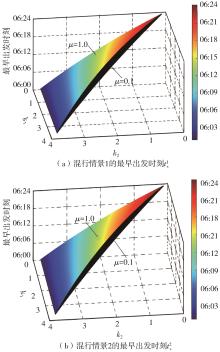
Study on the Choice of Morning Peak Departure Time of Heterogeneous Car Commuters Considering Travel Anxiety
HU Yucong1,2 LUO Mingming1,2 PAN Lei3 LING Meining4 LU Xiaoshan5
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Collaborative Innovation Center of Modern Urban Traffic Technologies,Nanjing 211189,Jiangsu,China
3.Guangzhou Transports Research Institute,Guangzhou 510627,Guangdong,China
4.Guangzhou Urban Planning and Design Survey Research Institute,Guangzhou 510060,Guangdong,China
5.School of Automobile and Transportation Engineering,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei 230009,Anhui,China