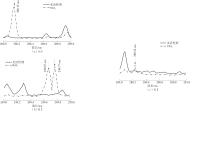
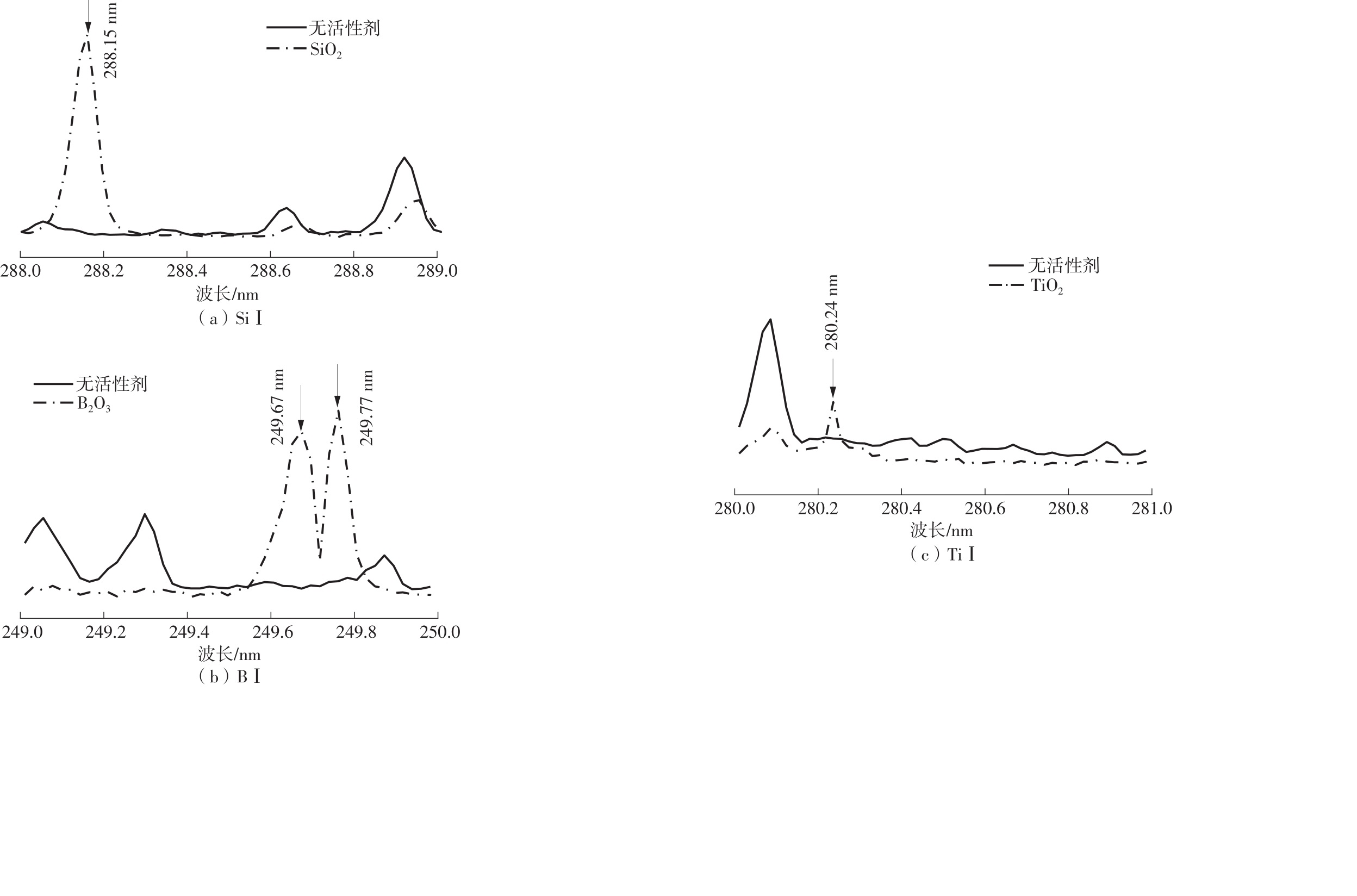
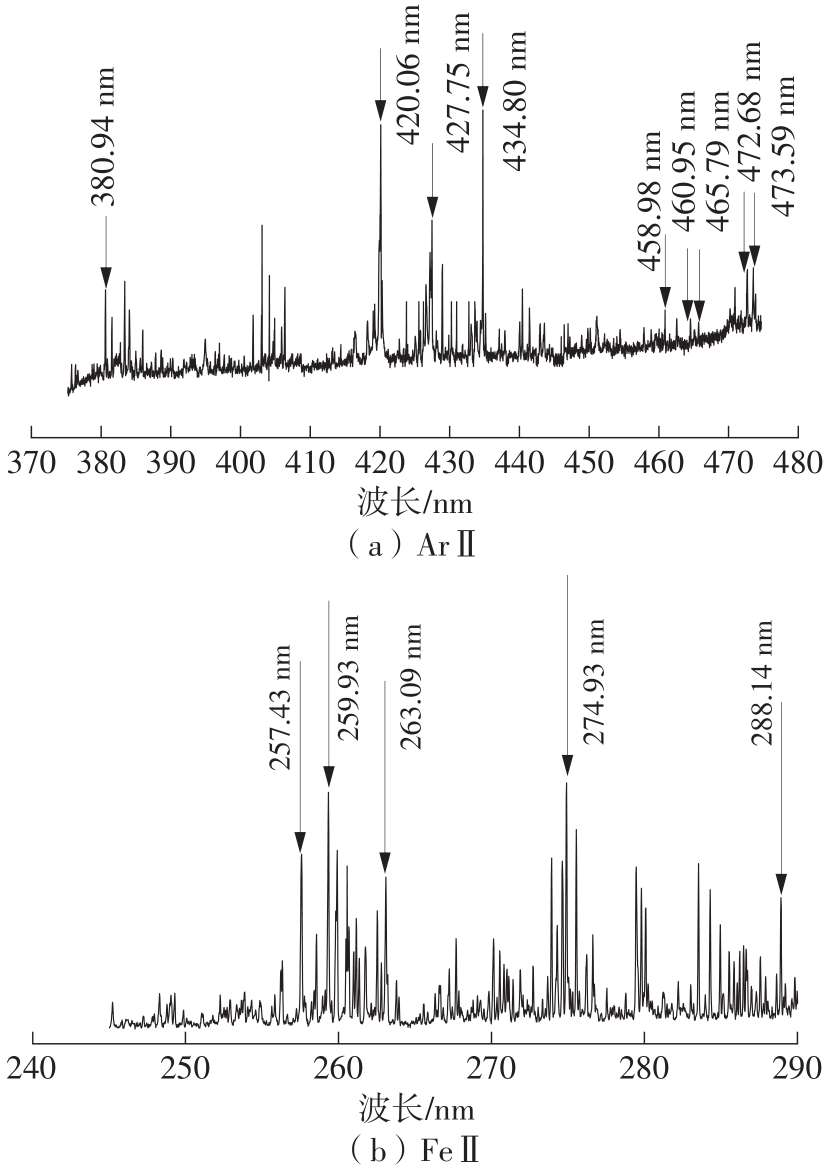
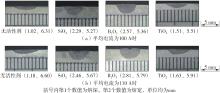
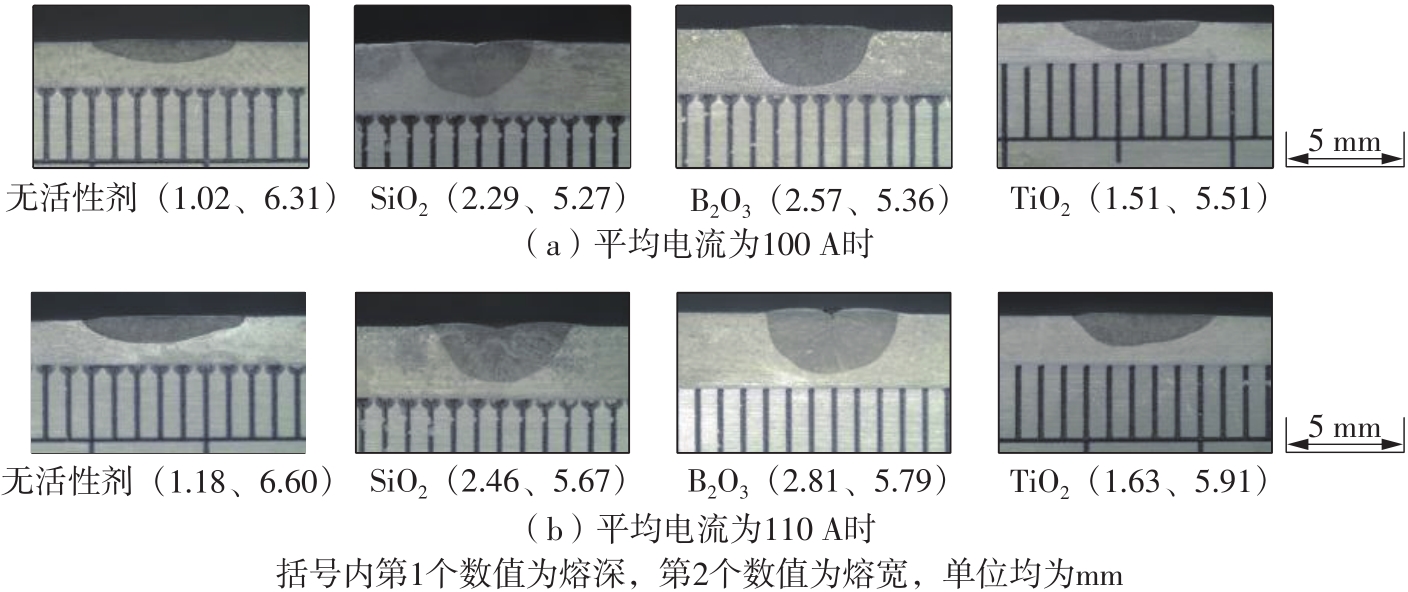
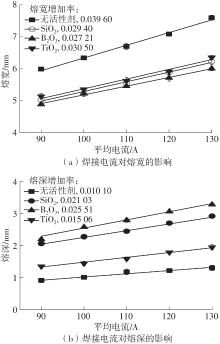
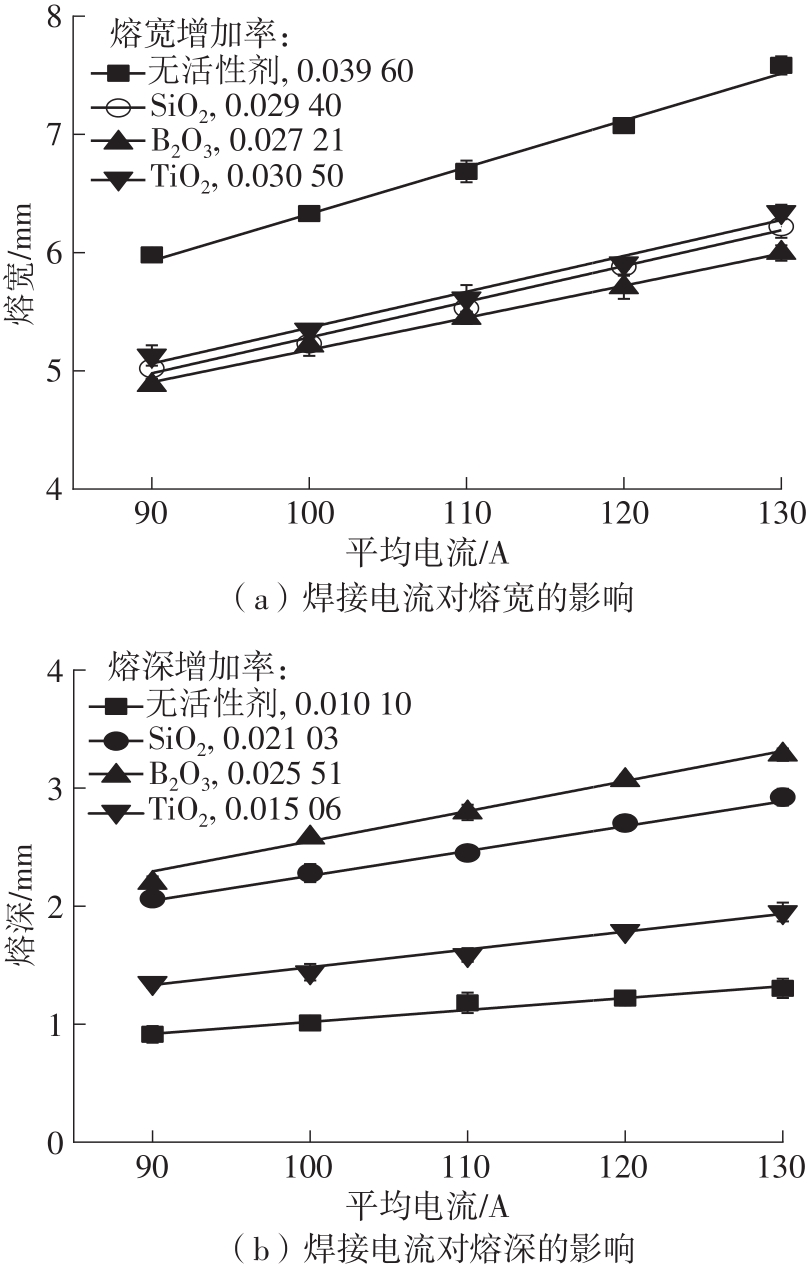
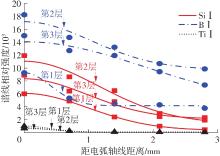
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (8): 128-135.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210699
Special Issue: 2022年材料科学与技术
• Materials Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
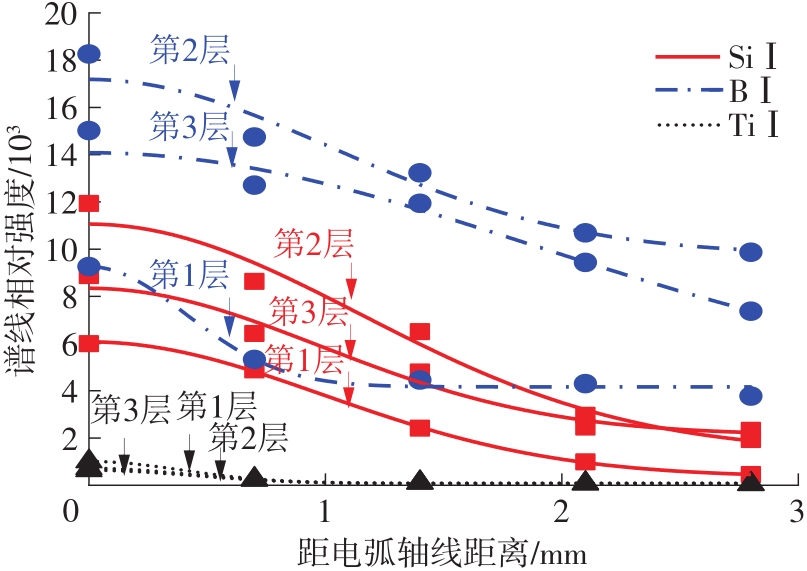
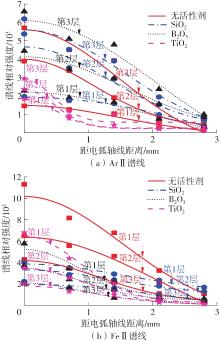
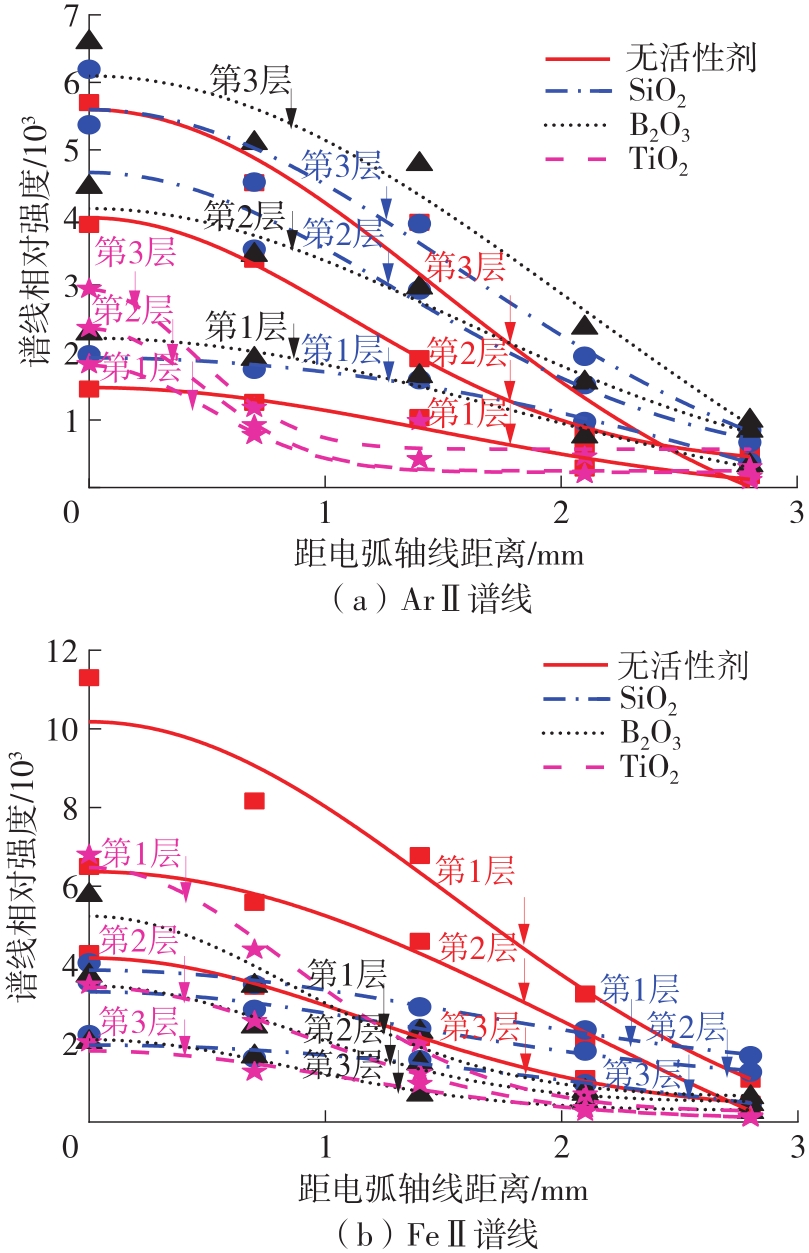
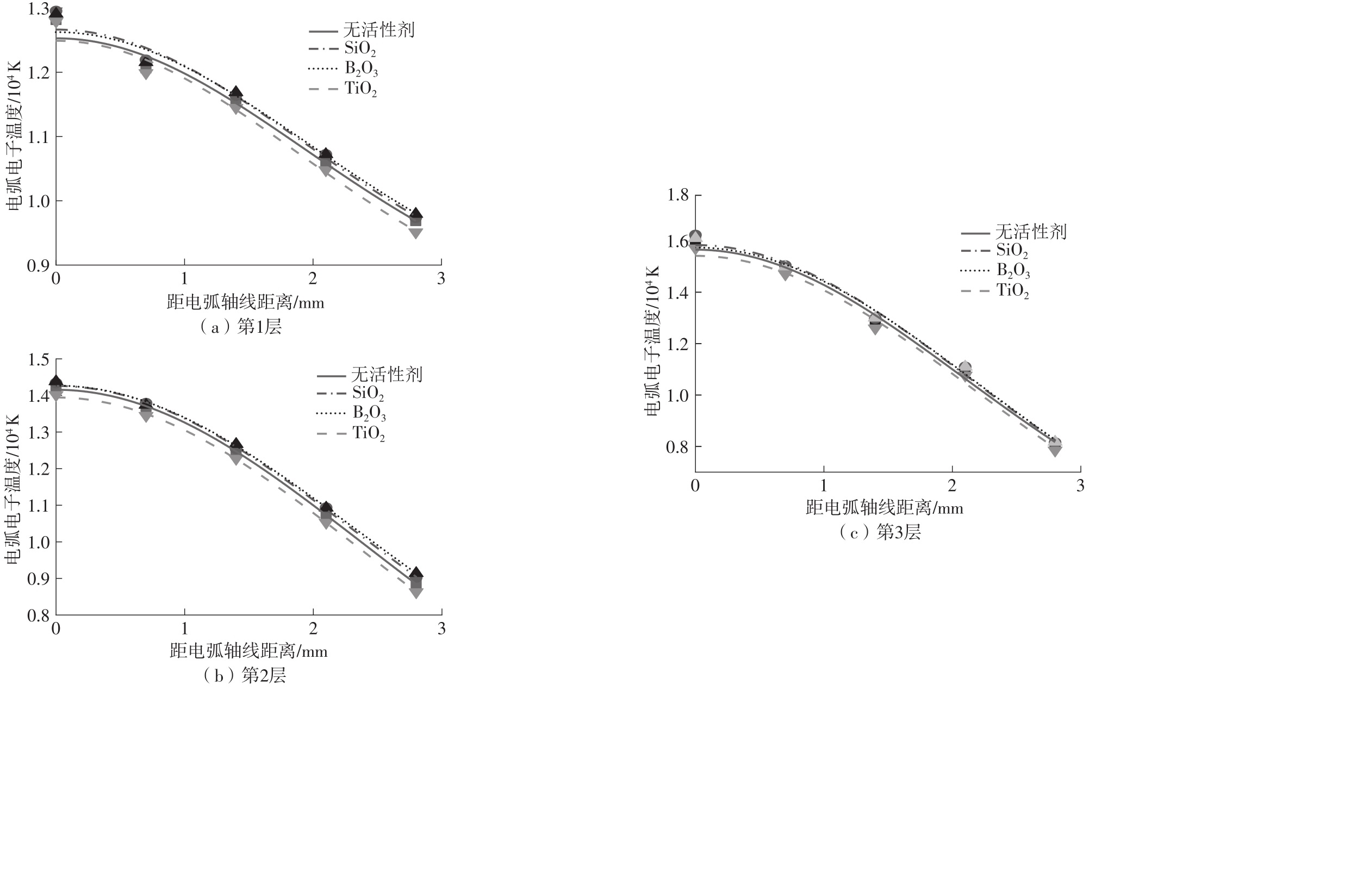
Analysis of Arc Characteristics in Oxide Active TIG Welding Based on Spectroscopy Diagnosis
LI Chunkai1,2,3 DING Bin1,2 SHI Yu1 GU Yufen1 DAI Yue1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Advanced Processing and Reuse of Nonferrous Metals,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,Gansu,China
2.Wenzhou Engineering Institute of Pump & Valve,Lanzhou University of Technology,Wenzhou 325100,Zhejiang,China
3.School of Mechanical Engineering,Beijing Institute of Petrochemical Technology,Beijing 102617,China