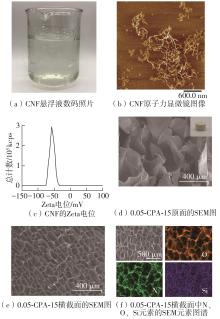
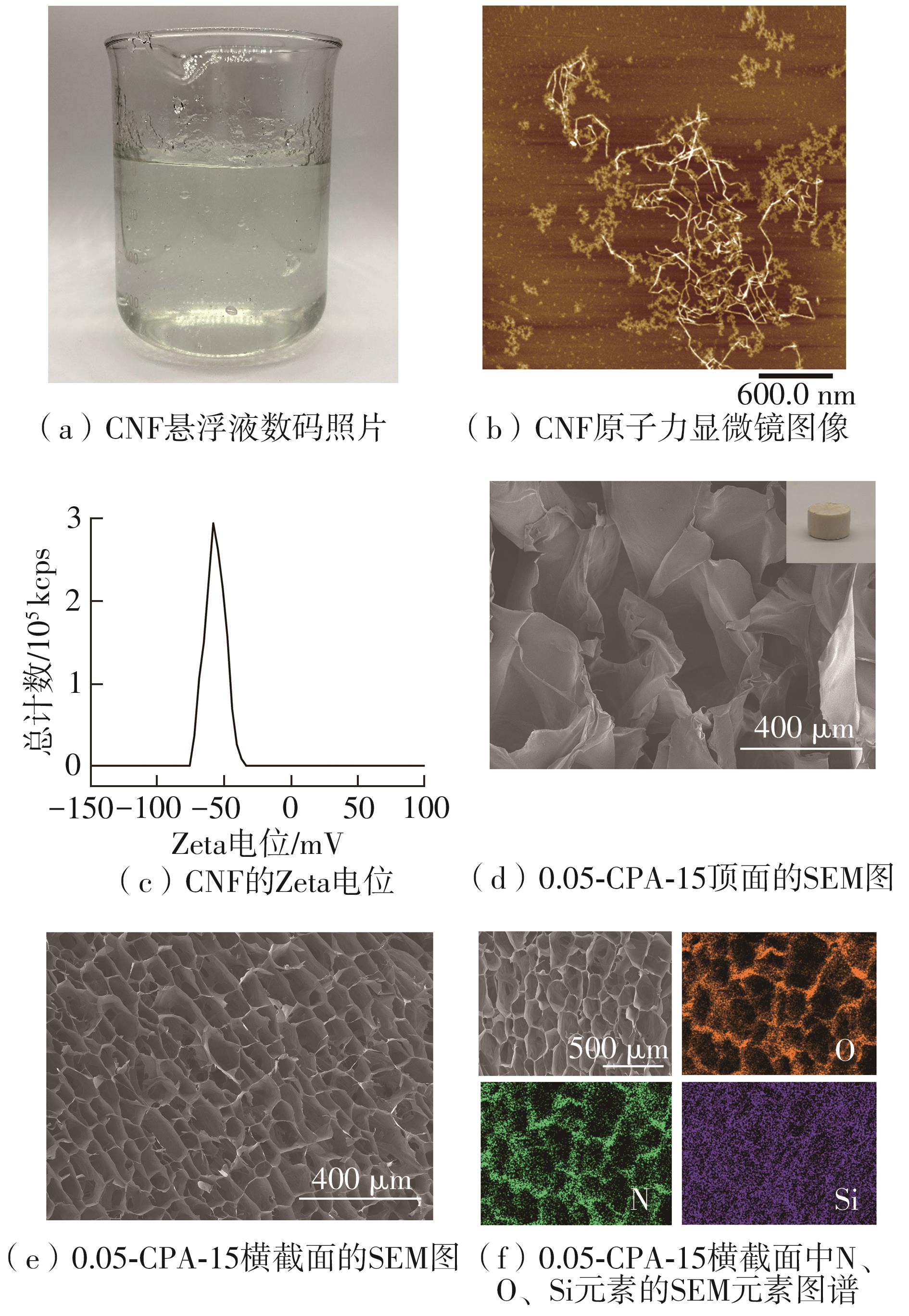
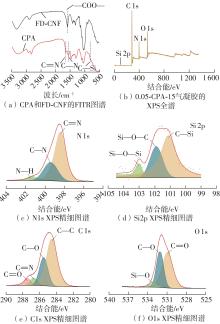
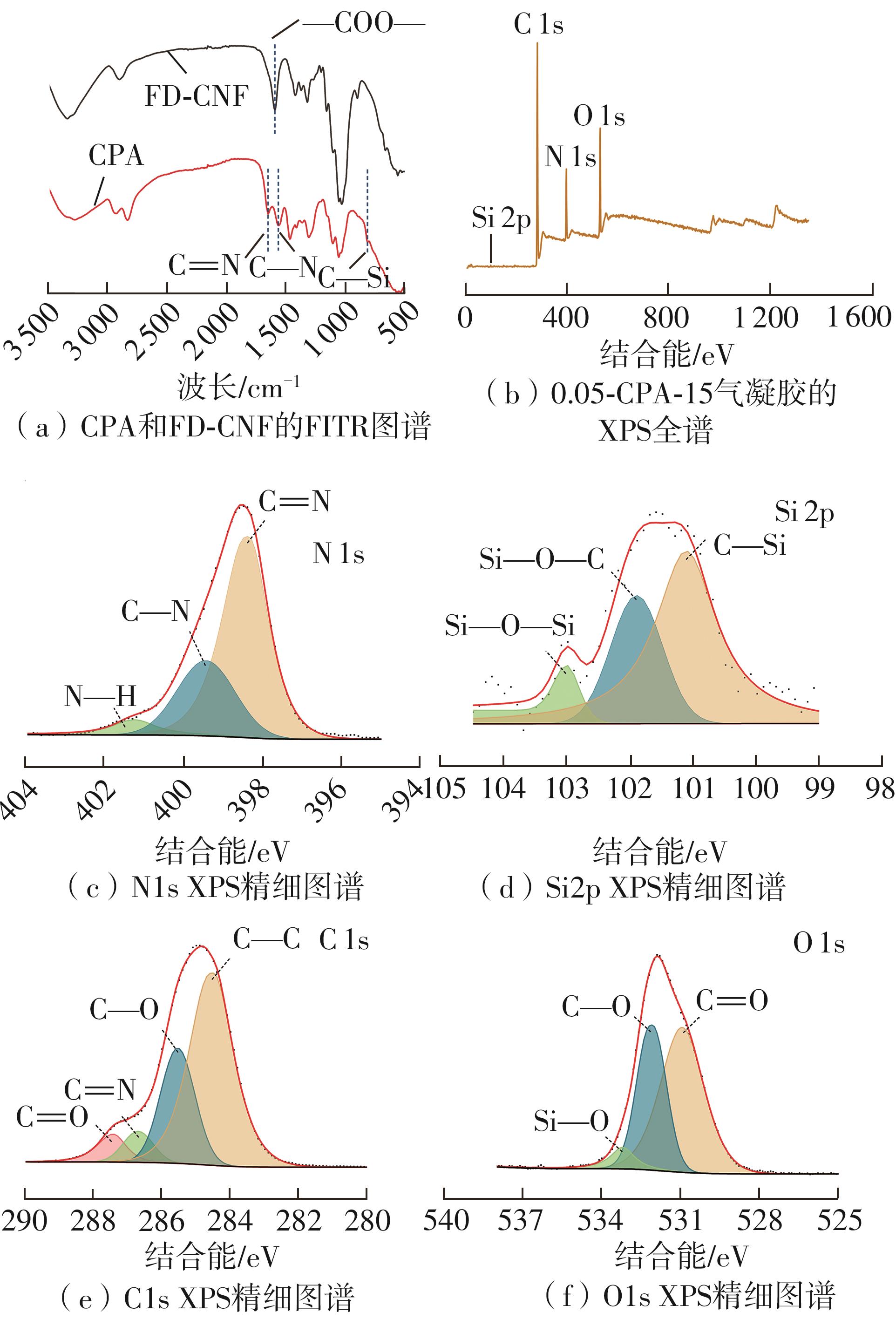
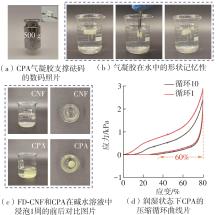
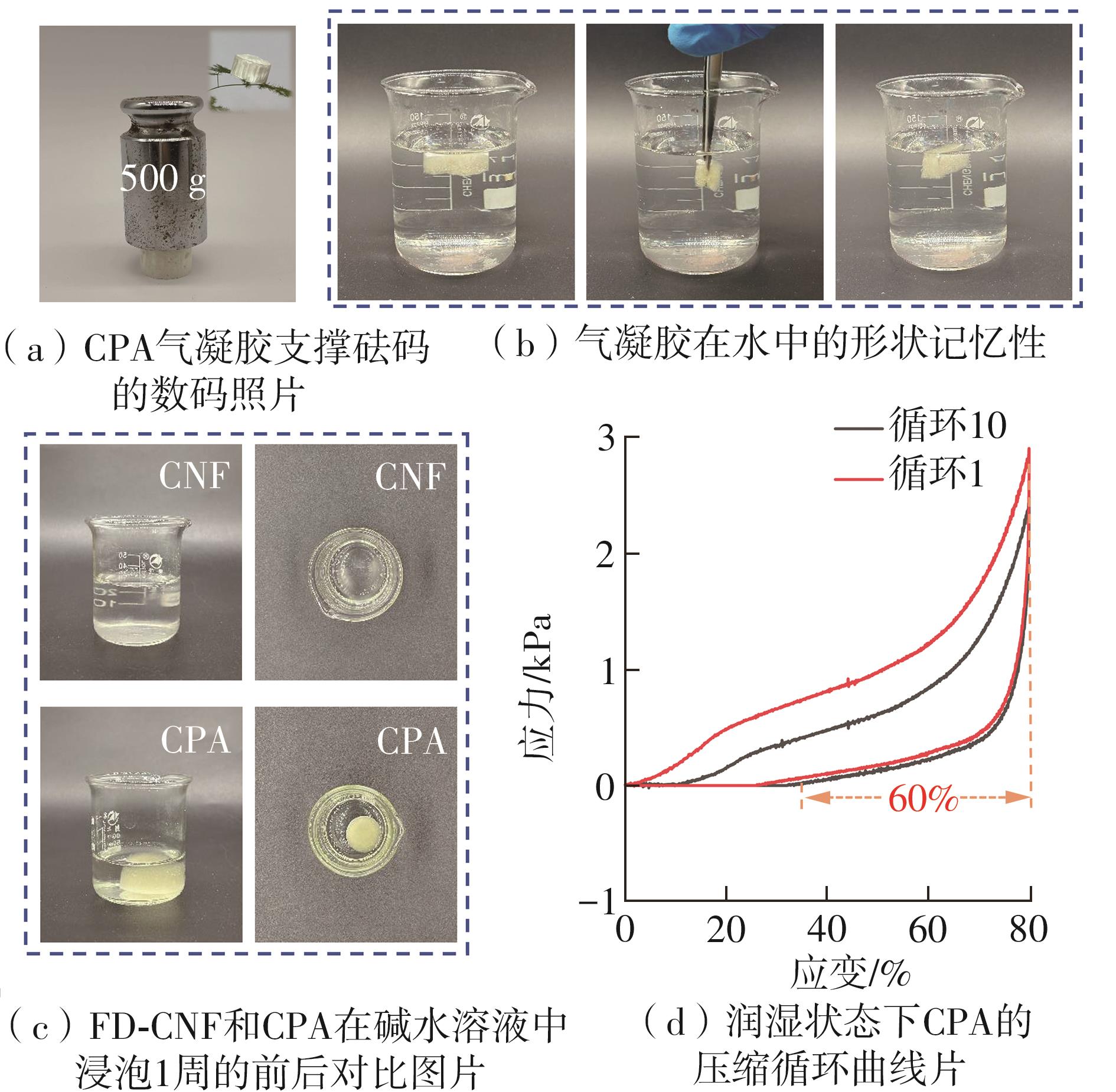
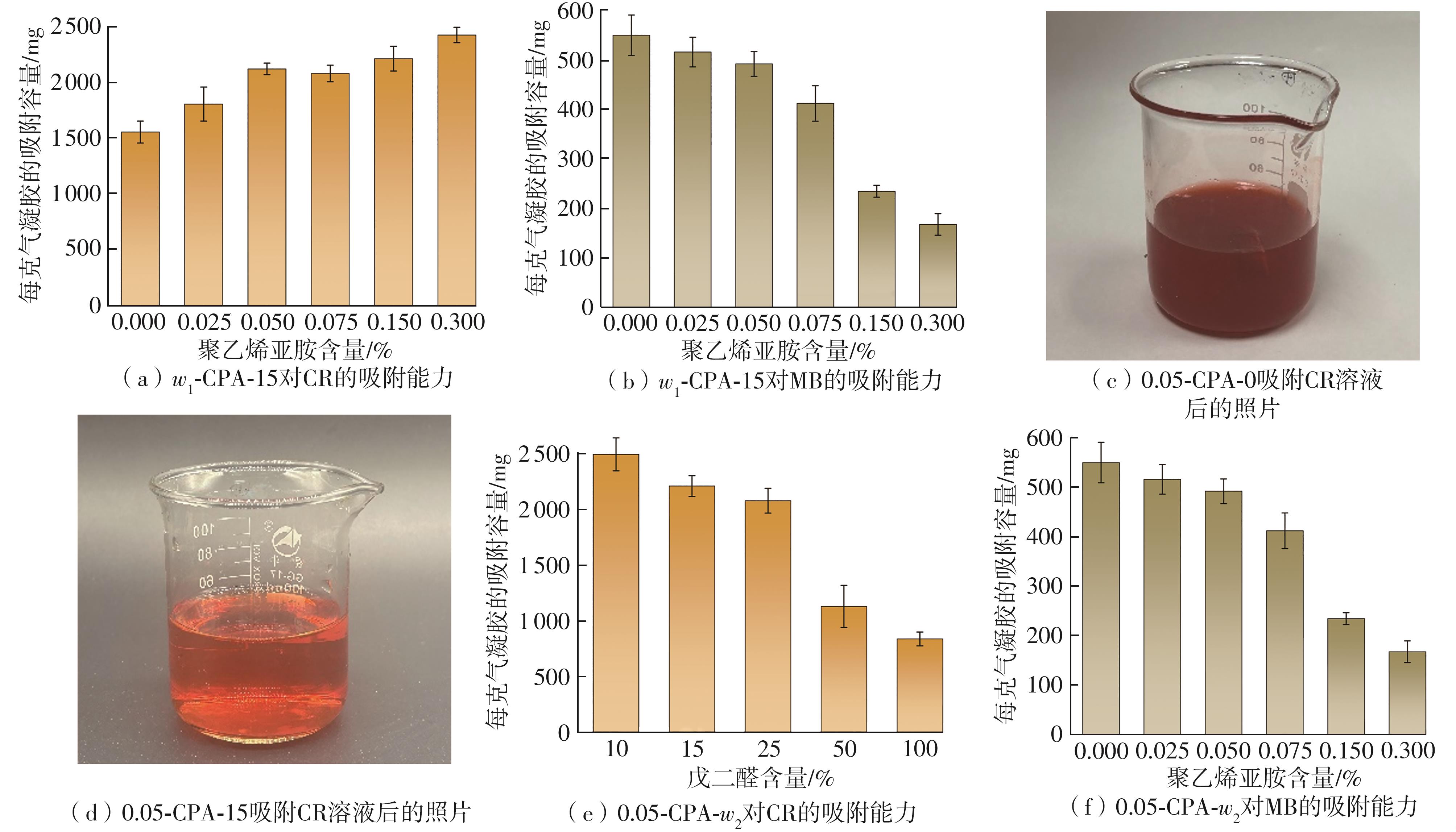
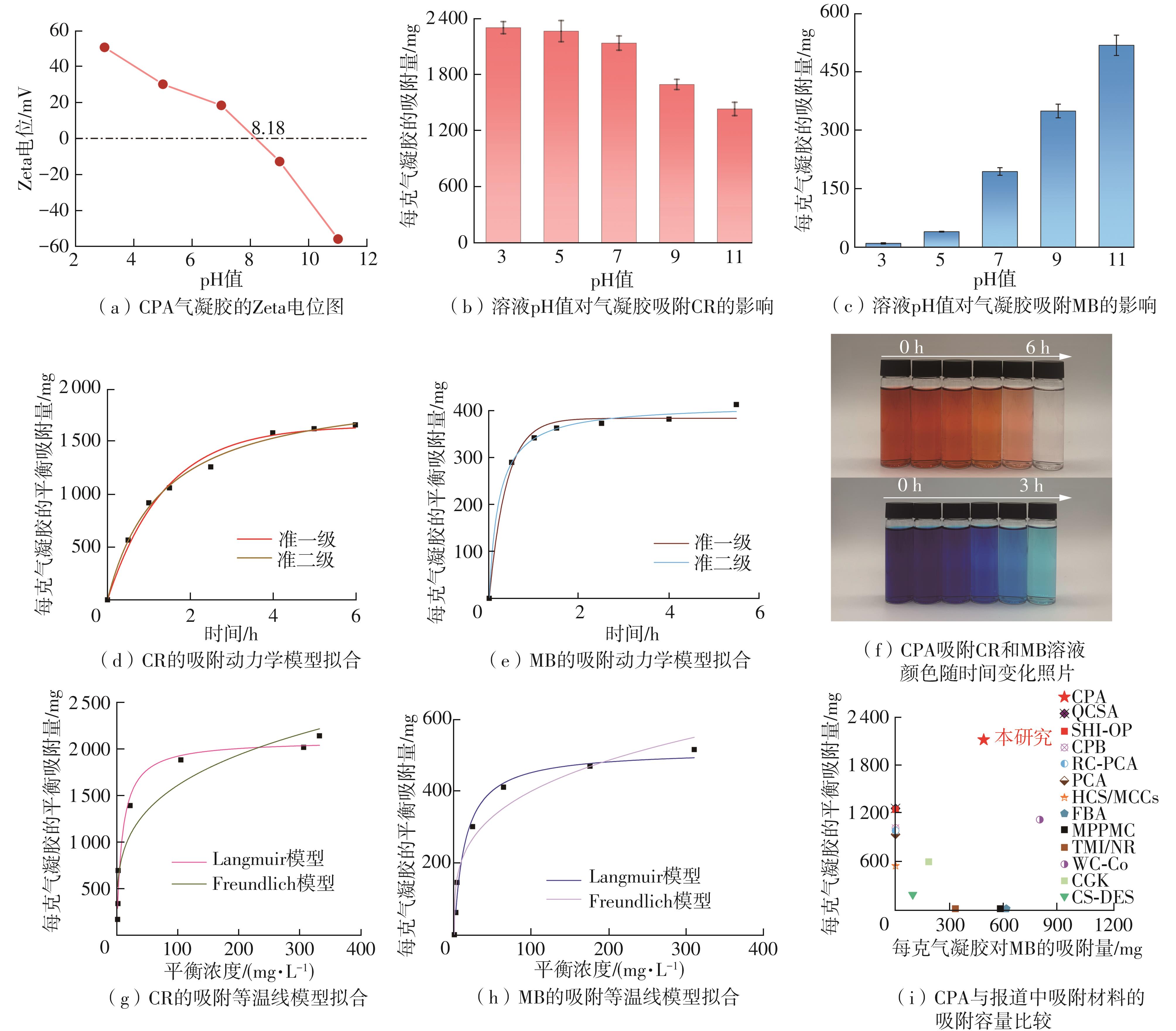
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 149-157.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240587
• Materials Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study of Dye Adsorption Properties of Cellulose-Based Nanocellulose Aerogels
CHEN Gang, AO Jie, HE Yingying, WANG Chunyu, ZHANG Cheng
- State Key Laboratory of Pulp and Paper Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2025-03-21Online:2025-08-25Published:2025-03-21 -
About author:陈港(1967—),男,博士,教授,主要从事造纸技术与特种纸研究。E-mail: papercg@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund of Guangdong Provinc(2021A1515010538)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Gang, AO Jie, HE Yingying, WANG Chunyu, ZHANG Cheng. Study of Dye Adsorption Properties of Cellulose-Based Nanocellulose Aerogels[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(8): 149-157.
share this article
| [1] | LIU Y, KE Y, SHANG Q,et al .Fabrication of multifunctional biomass-based aerogel with 3D hierarchical porous structure from waste reed for the synergetic adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,451(3):138934/1-15. |
| [2] | CHENG S, ZHAO S, XING B,et al .Preparation of magnetic adsorbent-photocatalyst composites for dye removal by synergistic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,348:131301/1-11. |
| [3] | QIAO A, CUI M, HUANG R,et al .Advances in nanocellulose-based materials as adsorbents of heavy metals and dyes[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,272:11847/1-15. |
| [4] | GAO X, REN P, WANG J,et al .Fabrication of visible-light responsive Tio 2 @c photocatalyst with an ultra-thin carbon layer to efficiently degrade organic pollutants[J].Applied Surface Science,2020,532:147482/1-10. |
| [5] | WANG K, LIU X, TAN Y,et al .Two-dimensional membrane and three-dimensional bulk aerogel materials via top-down wood nanotechnology for multibehavioral and reusable oil/water separation[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,371:769-780. |
| [6] | NASROLLAHZADEH M, SAJJADI M, IRAVANI S,et al .Green-synthesized nanocatalysts and nanomate-rials for water treatment:current challenges and future perspectives[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,401:123401/1-24. |
| [7] | 刚恺悦,张宝浩,马宁,等 .基于静电作用选择性吸附染料的超分子凝胶剂[J].精细化工,2022,39(11):2328-2336. |
| GANG Kaiyue, ZHANG Baojie, MA Ning,et al .Supramolecular gels for selective adsorption of dyes based on electrostatic interaction[J].Fine Chemicals,2022,39(11):2328-2336. | |
| [8] | GUO J, ZHOU S, MA X,et al .Regenerated cellulose/polyethyleneimine composite aerogel for efficient and selective adsorption of anionic dyes[J].Separation and Purification Technology,2024,330:125480/1-14. |
| [9] | YU J, TIAN S, YAO A,et al .Compressible polydopamine modified pomelo peel powder/poly(ethyleneimine)/k-carrageenan aerogel with pH-tunable charge for selective removal of anionic and cationic dyes[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2024,323:121377/1-17. |
| [10] | MA X, ZHAO S, TIAN Z,et al .MOFs meet wood:reusable ragnetic hydrophilic composites toward efficient water treatment with super-high dye adsorption capacity at high dye concentration[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,446(1):136851/1-9. |
| [11] | QIN W, LI M X, ZHANG Y,et al .High capacity and selective adsorption of congo red by cellulose-based aerogel with mesoporous structure:adsorption properties and statistical data simulation[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2024,259(1):129137/1-15. |
| [12] | PARALE V G, KIM T, CHOI H,et al .Mechanically strengthened aerogels through multiscale,multicompositional,and multidimensional approaches:a review[J].Advanced Materials,2024,36(18):2307772/1-47. |
| [13] | 庄杰,徐朝阳 .纤维素基气凝胶吸附性能的研究进展[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2022,38(3):144-150. |
| ZHUANG Jie, XU Chaoyang .Advances in the adsorption properties of cellulose-based aerogels[J].Polymeric Materials Science and Engineering,2022,38(3):144-150. | |
| [14] | DAS R, LINDSTROM T, SHARMA P R,et al .Nanocellulose for sustainable water purification[J].Chemical Reviews,2022,122(9):8936-9031. |
| [15] | 欧阳志宇 .戊二醛-聚乙烯亚胺/羧甲基壳聚糖荷电纳滤膜的制备及性能研究[D].南京:南京理工大学,2019. |
| [16] | XU H, ZHANG Z, JIANG W,et al .Multifunctional amphibious superhydrophilic-oleophobic cellulose nanofiber aerogels for oil and water purification[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2024,330:121774/1-12. |
| [17] | WANG Z, HE Y, WANG C,et al .A moisture-absorbing cellulose nanofibril-based foam via ambient drying for high-performance dehumidification[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2024,486:150063/1-9. |
| [18] | WU N, YANG Y, WANG C,et al .Ultrathin cellulose nanofiber assisted ambient-pressure-dried,ultralight,mechanically robust,multifunctional Mxene aerogels[J].Advanced Materials,2023,35(1):2207969/1-12. |
| [19] | HU X, ZHANG S, YANG B,et al .Preparation of ambient-dried multifunctional cellulose aerogel by freeze-linking technique[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,477:147044/1-10. |
| [20] | 李方,雷春发,陈港 .基于抄纸法制备羧甲基改性高强纤维素膜及性能研究[J].造纸科学与技术,2021,40(1):23-28. |
| LI Fang, LEI Chunfa, CHEN Gang .Preparat-ion of carboxymethyl-modified high-strength cellulose membranes based on paper copying method and study of their properties[J].Paper Science and Technology,2021,40(1):23-28. | |
| [21] | ZHU P, YU Z, SUN H,et al .3D printed cellulose nanofiber aerogel scaffold with hierarchical porous structures for fast solar-driven atmospheric water harvesting[J].Advanced Materials,2024,36(1):2306653/1-9. |
| [22] | QIU C, LI Y, LIU H,et al .A novel crosslinking strategy on functional cellulose-based aerogel for effective and selective removal of dye[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,463:142404/1-10. |
| [23] | LI D, SUN L, YANG L,et al .Adsorption behavior and mechanism of modified pinus massoniana pollen microcarriers for extremely efficient and rapid adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye[J].Journal of Hazar-dous Materials,2024,465:133308/1-15. |
| [24] | LOREVICE M V, CLARO P I C, ALEIXO N A,et al .Designing 3D fractal morphology of eco-friendly nanocellulose-based composite aerogels for water remediation[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,462:142166/1-14. |
| [25] | LI B, ZHAO Y .Facile synthesis and ultrastrong adsorption of a novel polyacrylamide-modified diatomite/cerium alginate hybrid aerogel for anionic dyes from aqueous environment[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,253(5):127114/1-14. |
| [26] | DU N, HUANG L, XIONG Y,et al .Micro-mechanism insights into the adsorption of anionic dyes using quaternary ammonium-functionalised chitosan aerogels[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2023,313:120855/1-17. |
| [27] | ZENG X, ZHU J, ZHANG G,et al .Molecular-level understanding on complexation-adsorption-degradation during the simultaneous removal of aqueous binary po-llutants by magnetic composite aerogels[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,468:143536/1-16. |
| [28] | LEE J, MATHUR S, SHEN S,et al .MoSe2 nanoflowers for highly efficient industrial wastewater treatment with zero discharge[J].Advanced Science,2021,8(23):2102857/1-8. |
| [29] | VARAMESH A, ABRAHAM B D, WANG H,et al .Multifunctional fully biobased aerogels for water remediation:applications for dye and heavy metal adsorption and oil / water separation[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2023,457:131824/1-18. |
| [30] | XIA N N, WU Q, BI S L .Ultra efficient removal of heavy-metal ions and dyes using a novel cellulose-based three-dimensional network[J].Cellulose,2024,31(6):3747-3761. |
| [1] | XIE Pingbo, SHI Ruixue. Study on the Compatibility Between Surface Modifiers of TiO2 Nanoparticles and Orginic Solvents [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(6): 129-135. |
| [2] | ZHU Penghui CHEN Gang OU Huajie JIANG Chenying CHE Mingyang . Preparation and Humidity Sensitive Performance of Nanocellulose/Carbon Nanotube Composite Films [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(8): 129-135. |
| [3] |
YANG Yongmin QIAO Ruilong XIE Xiaogeng ZHANG Tongsheng LIU Xiaofei.
Modification of Ceramsite by FeCl3 and the Corresponding Enhancement of Heavy Metals Adsorption
|
| [4] | QIAO Liying YAO Yan WANG Yong LAI Ning WANG Weilang. Preparation and Characterization of Polydopamine Films on Pure Magnesium Surface [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(7): 16-23. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zhijie CHENG Congmi GAN Wei Lü Hang WEI Ronghui ZHANG Qiuhua. Effect of Composite Thermal Insulation System on High Temperature Insulation Performance of Cement-Based Coatings [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(7): 1-6. |
| [6] | CHEN Gang LIN Dong-han FANG Zhi-qiang. Preparation and Properties of Composite Paper-Based Supercapacitors with Nanocellulose [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(9): 118-127. |
| [7] | GU Ju LIANG Xiao-rong HUANG Fei WANG Juan HUANG Shi-wen. Research Progress in Nanocellulose as a Rubber Reinforcing Filler [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(2): 124-132. |
| [8] | Yang Wei Chen Sheng-zhou Xue Jian-jun Hu Xin-fa Xia Xin-de Lin Wei-ming. Effects of Different Carbon Aerogel Conductive Agents on Performance of Li-MnO2 Battery [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(6): 37-41. |
| [9] | Su Jin- zhan He Zhao- xia. High- Precision Modification of Tooth Surface for Spiral Bevel Gears [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(4): 91-96,104. |
| [10] | Li Zhong Zhang Hong Xia Qi-bin Zhang Wei Yu Mo-xin. Adsorption of Dibenzothiophene in Acetonitrile on Fe3+ / Cu2+ / Ag+ -Modified Activated Carbons with High Specific Surface Area [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(1): 100-104,111. |
| [11] | Ye Dai-yong Zhou Liu-jia. Nanocellulose Whiskers as Thickening Rheological Agent for Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersion [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(9): 63-67,74. |
| [12] | Fu Shi-yu Li Hui Liu Hao Li Xue-yun Zhan Huai-yu. Hydrophobic Modification of Pulp Fiber Surface via Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly of Lignosulfonates [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(4): 1-5. |
| [13] | Li Bin Li You-ming Yang Wen-liang. Synthesis and Application of Zircoaluminate Coupling Agent as Surface Modifier of Nano-Sized Titanium Dioxide [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(6): 7-12. |
| [14] | Li Zhong Fu Kan Xia Qi-bin. Modification of Natural Zeolite and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen by Modified Natural Zeolite [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 35(4): 6-10. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||