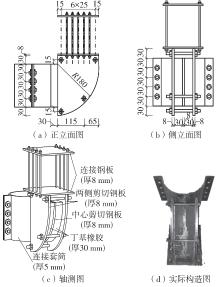
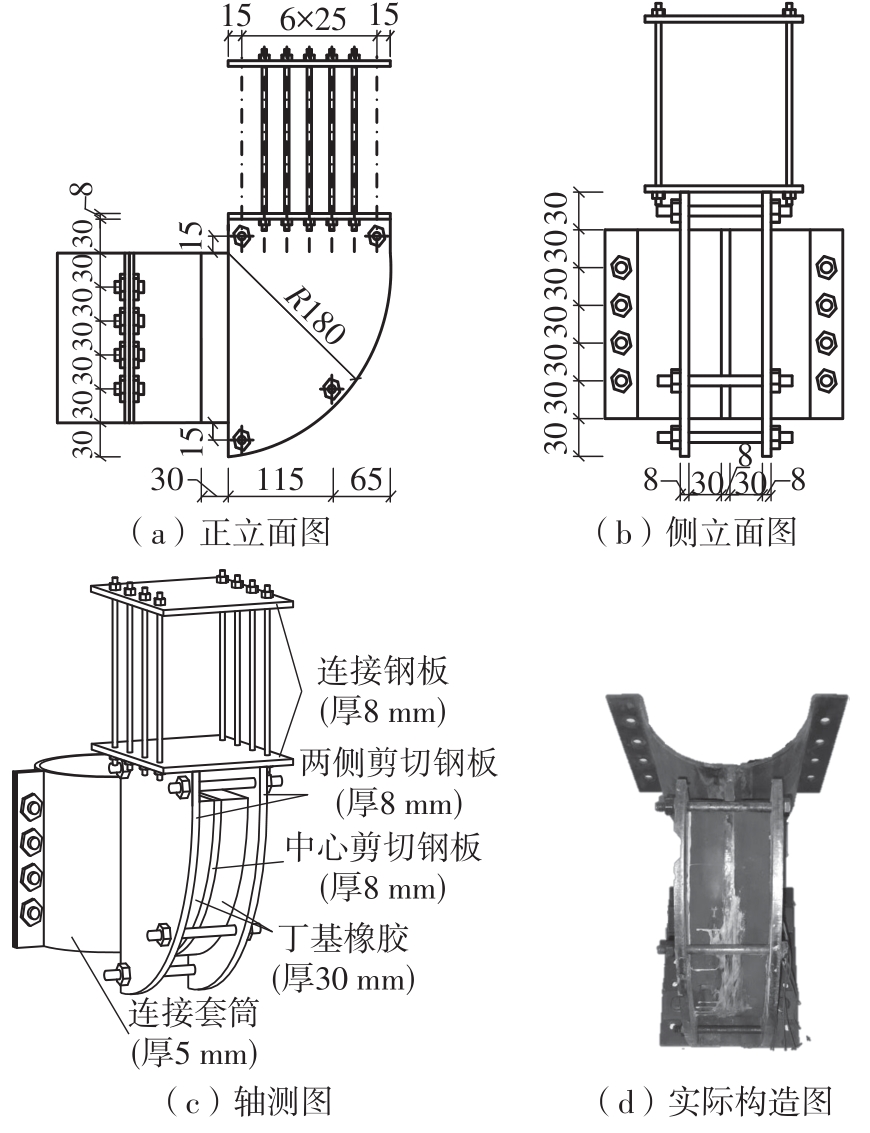
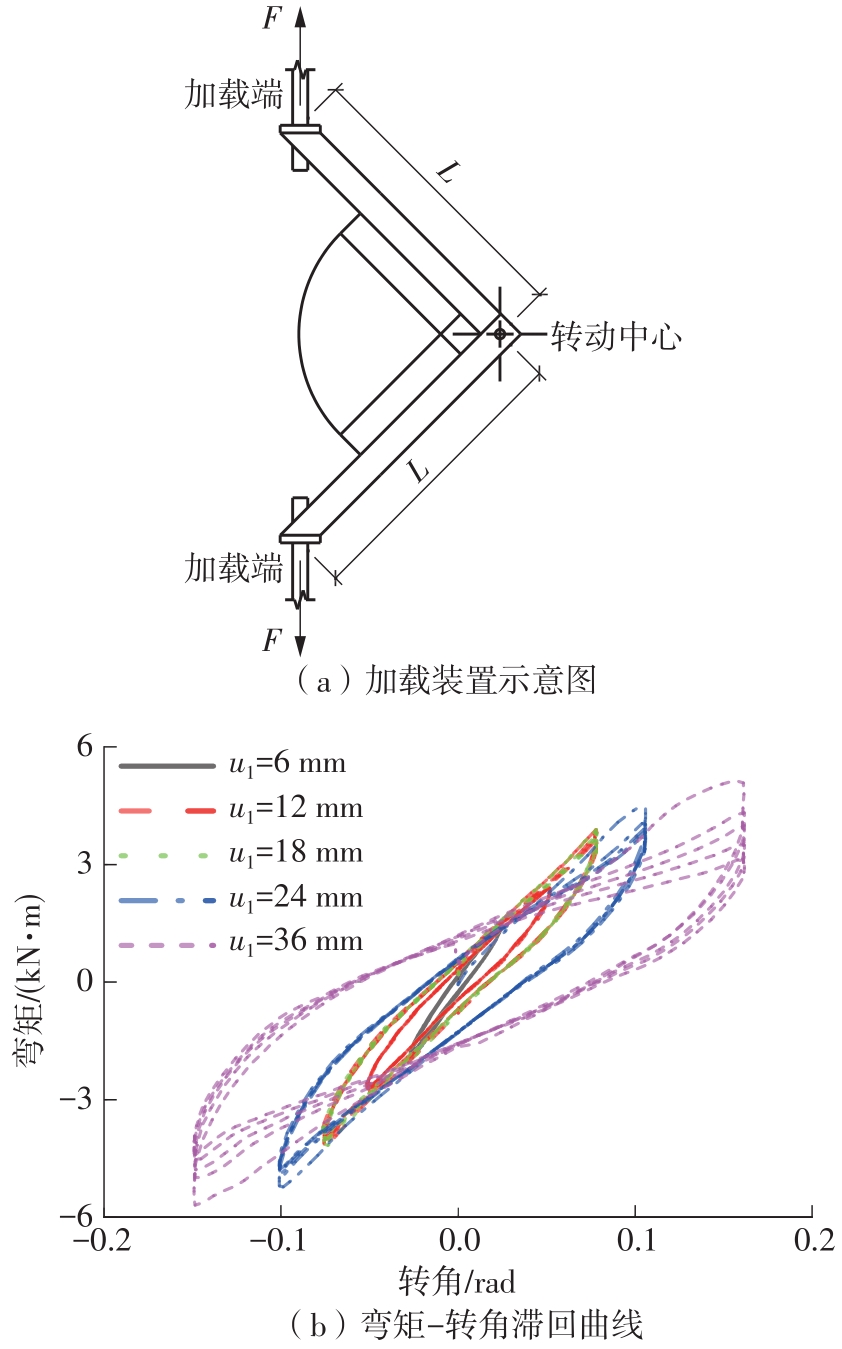
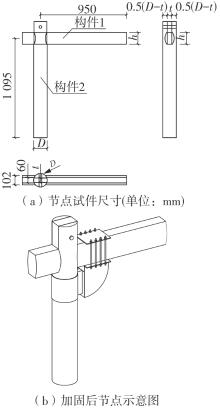
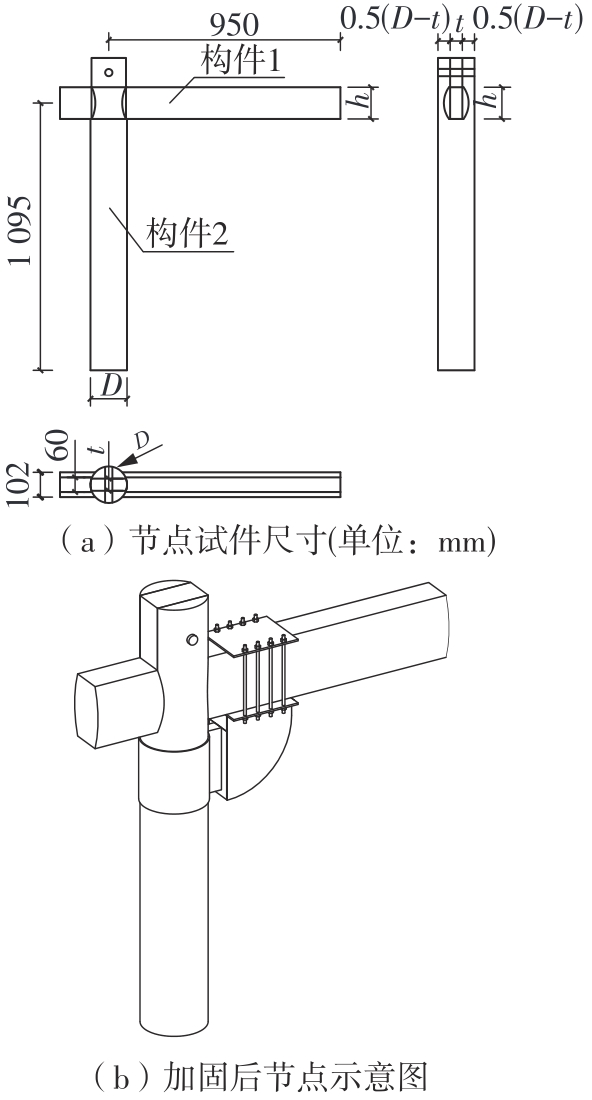
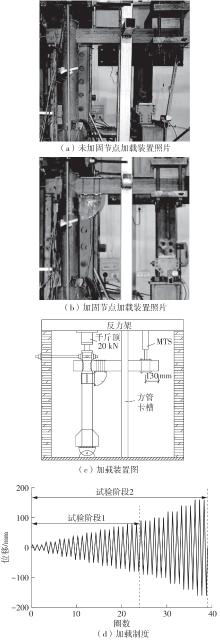
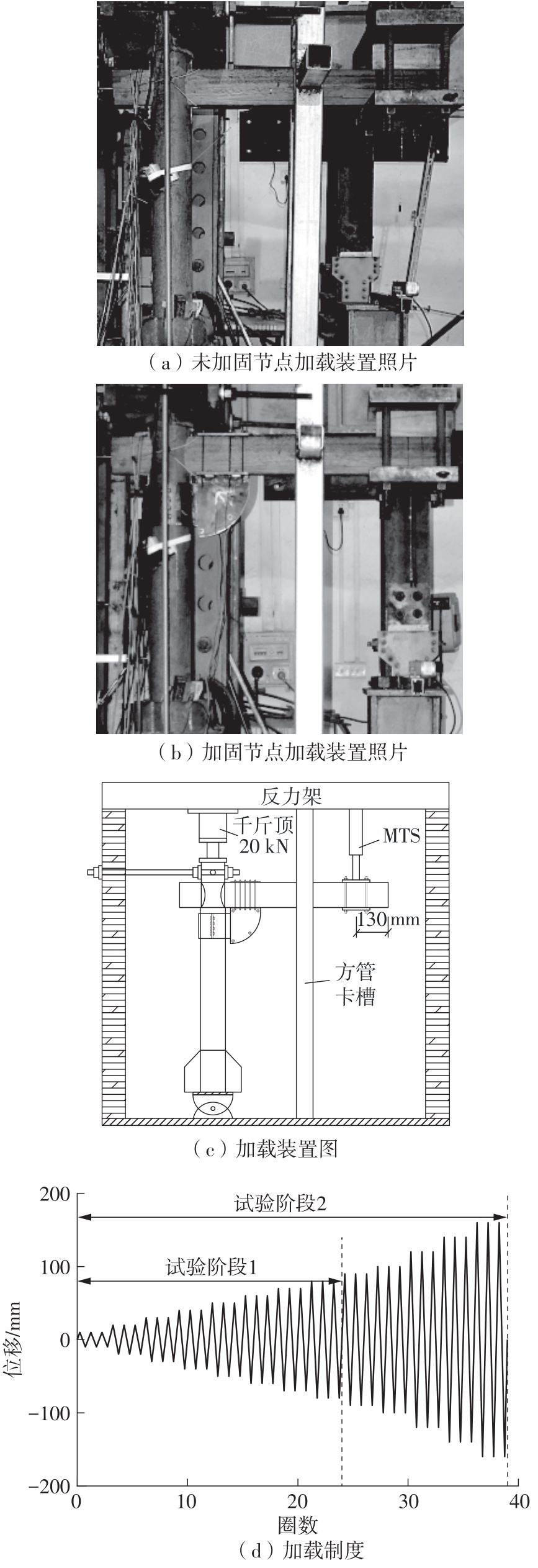
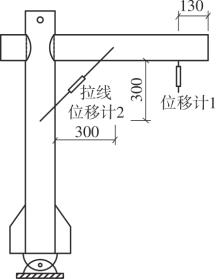
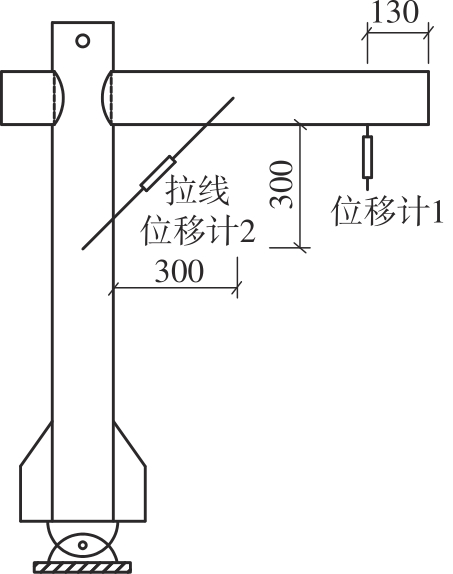
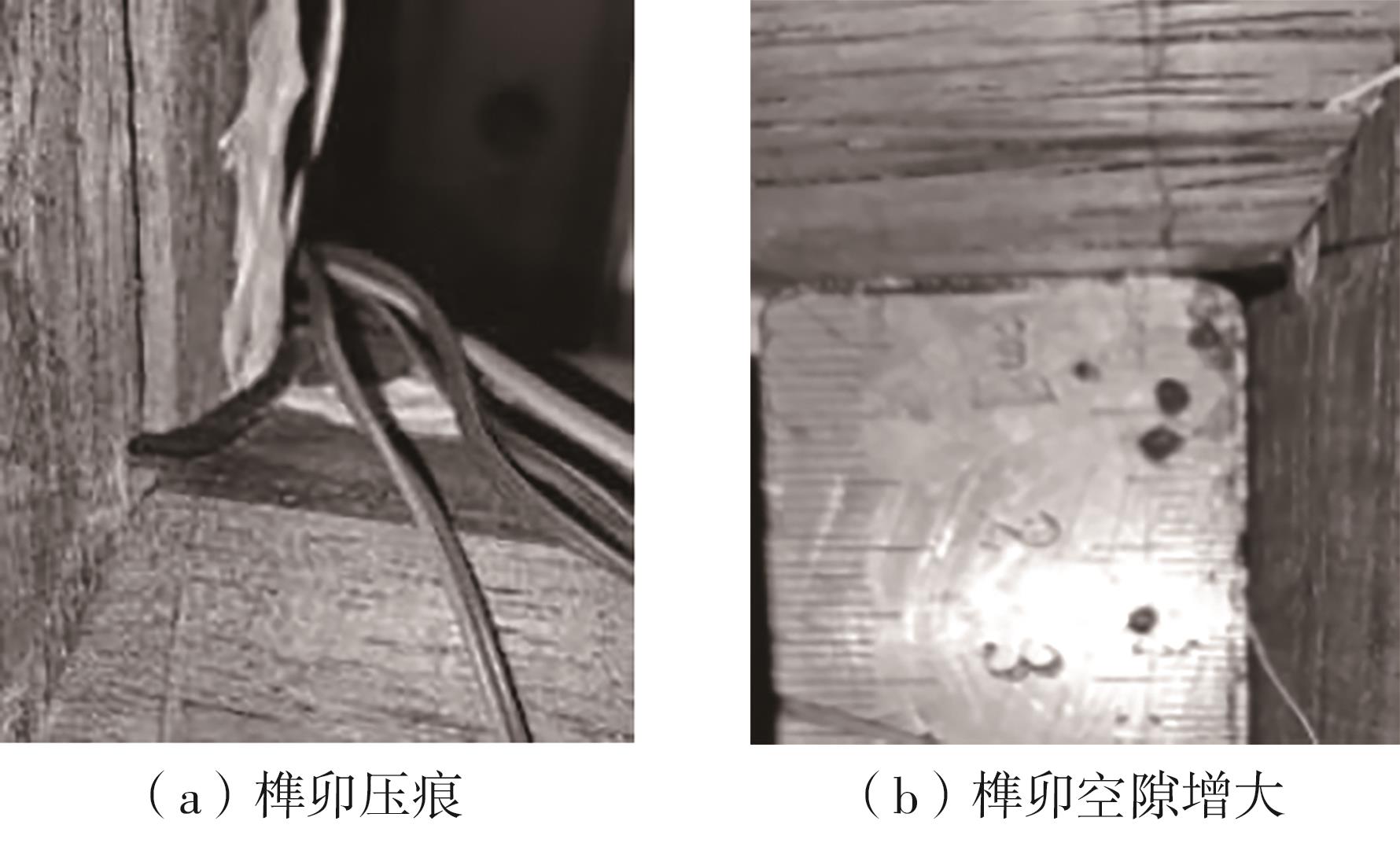
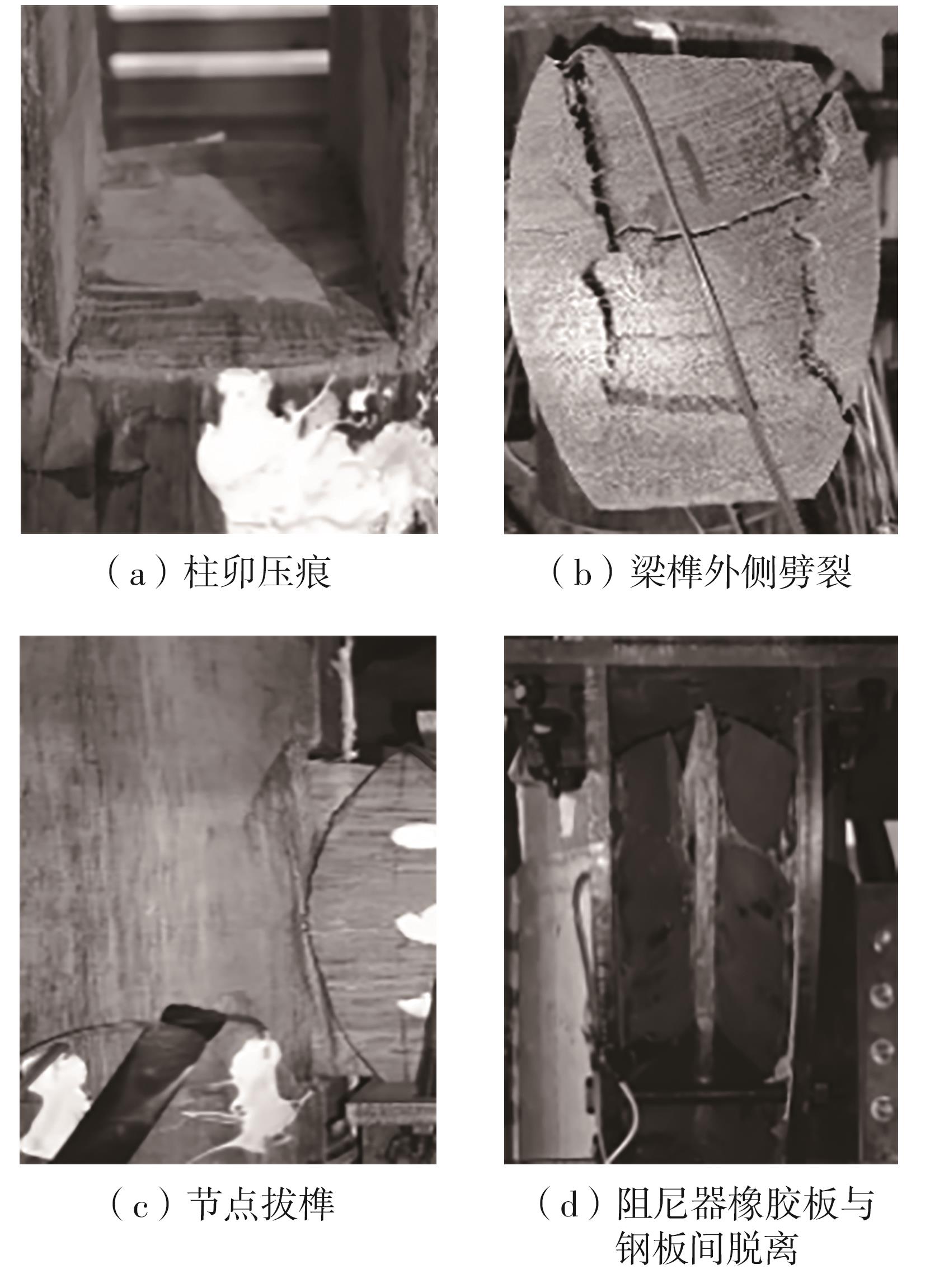
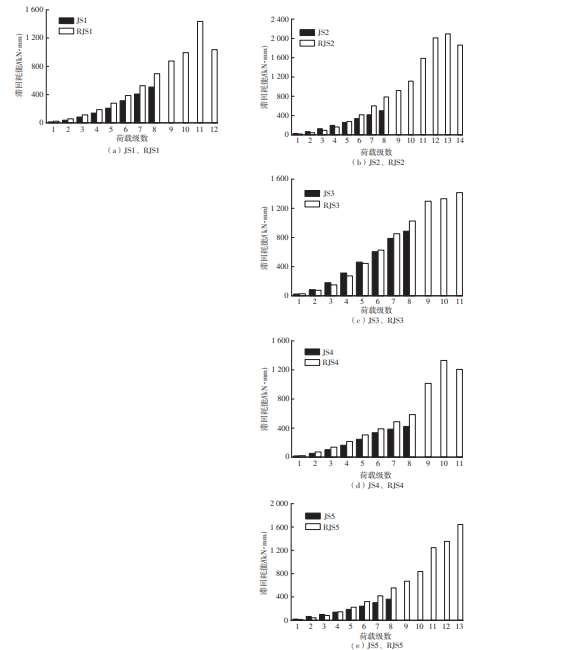
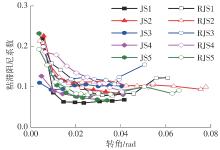
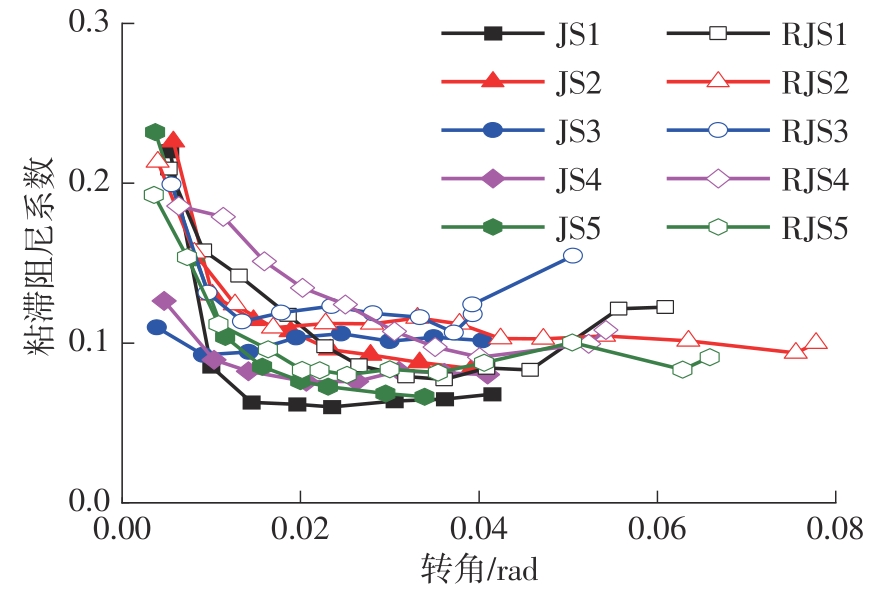
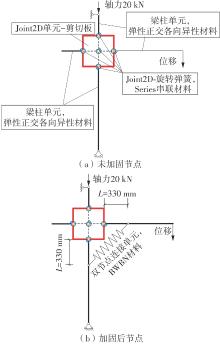
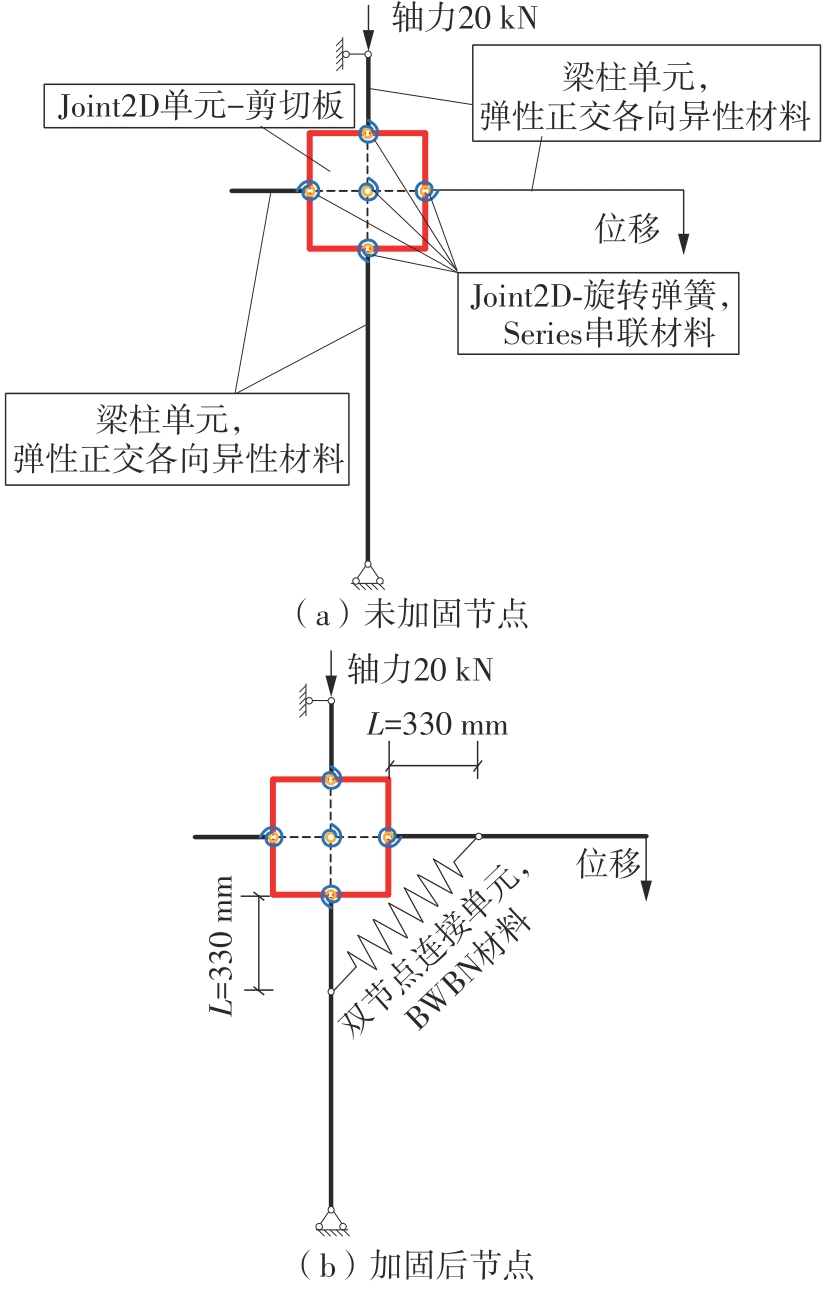
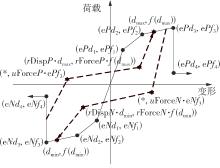
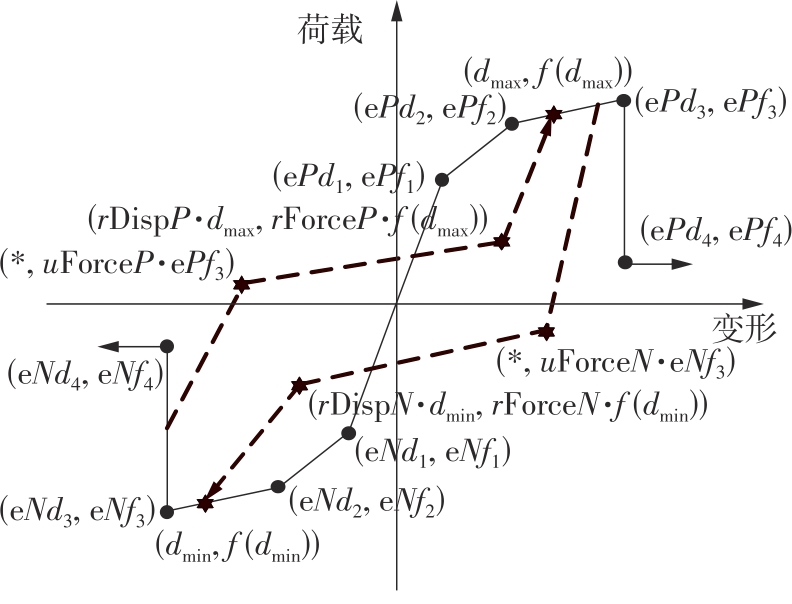
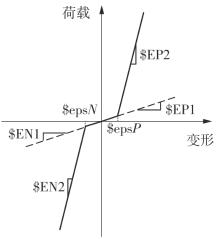
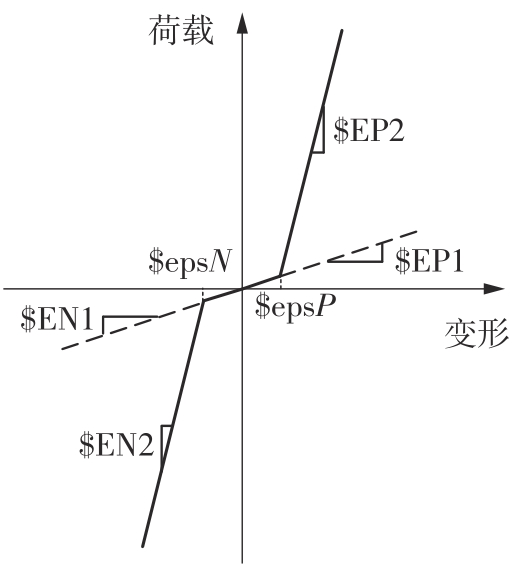
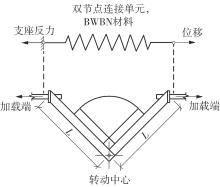
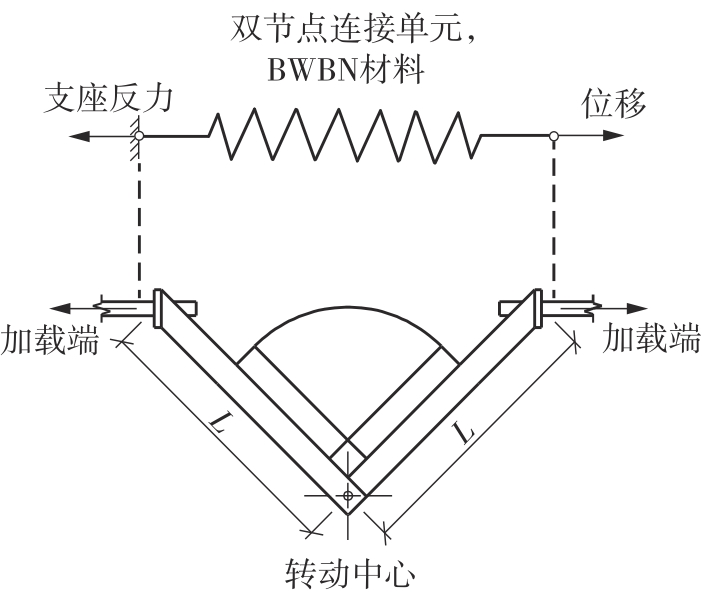
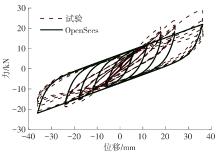
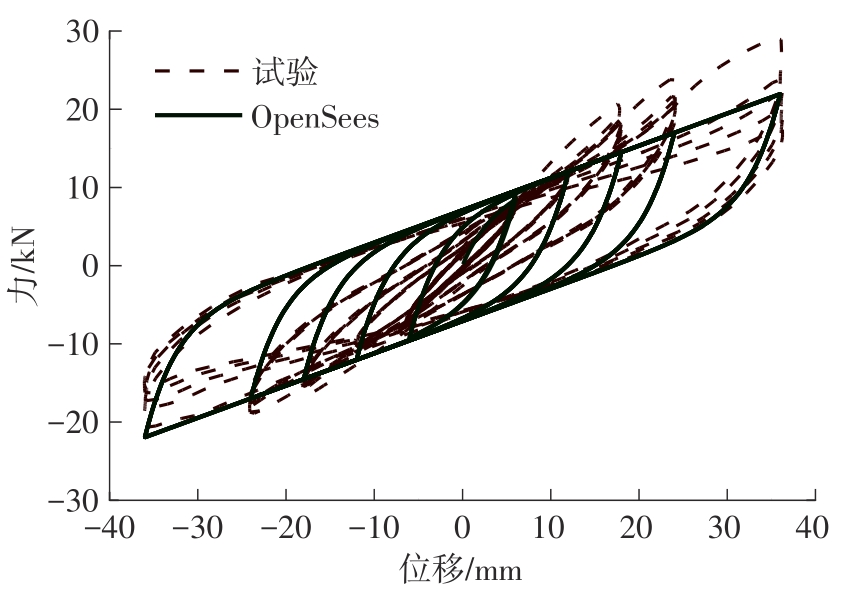
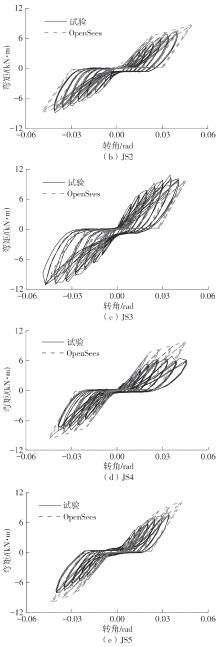
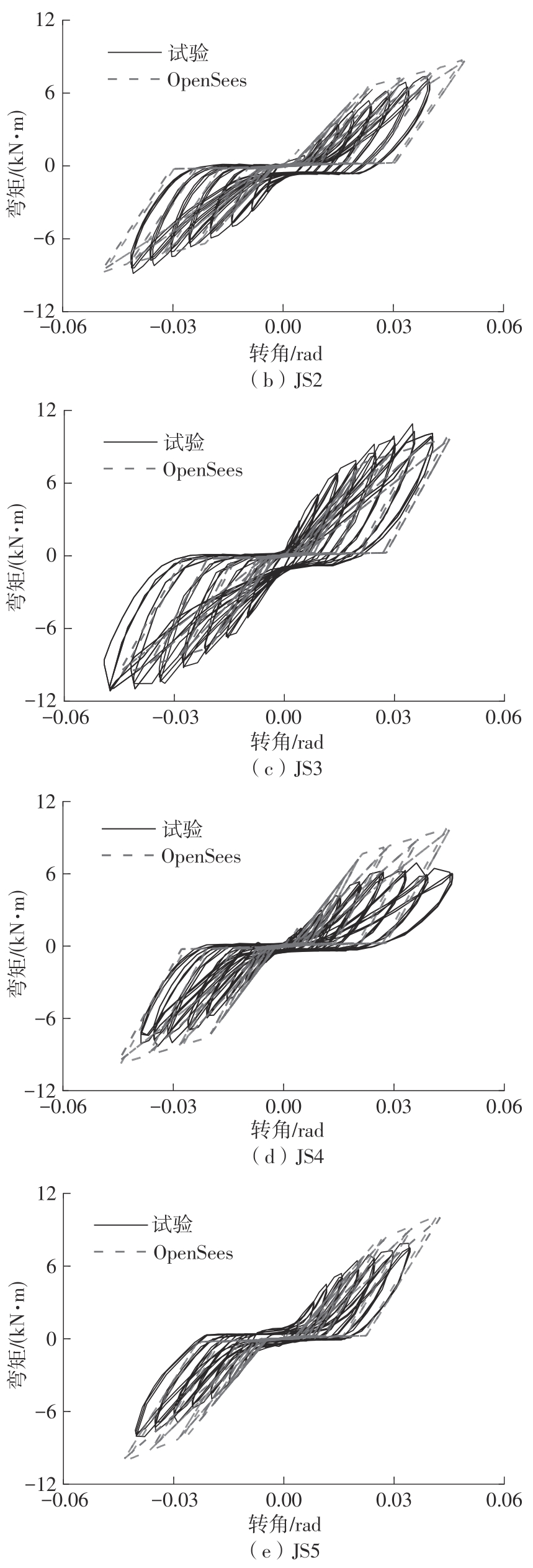
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 119-134.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230658
Special Issue: 2024年土木建筑工程
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Seismic Performance of Hoop Head Tenon Timber Joint with Added Corner Dampers
CHEN Qingjun1,2 LEI Jun2 LI Bingzhou2 ZUO Zhiliang2 CAI Jian1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building and Urban Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
3.Engineering Seismic Research Center of Guangdong,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-10-24Online:2024-07-25Published:2024-02-29 -
Contact:左志亮(1982—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事钢-混凝土组合结构、木结构研究。 E-mail:ctzlzuo@scut.edu.cn -
About author:陈庆军(1975—),男,博士,教授,主要从事木结构、混凝土结构等研究。E-mail: qjchen@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2021A1515012603)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Qingjun, LEI Jun, LI Bingzhou, et al. Seismic Performance of Hoop Head Tenon Timber Joint with Added Corner Dampers[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(7): 119-134.
share this article
| 1 | 潘毅,陈建,安仁兵,等 .山地古建筑木结构抗震性能研究评述[J].土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2022,44(2):10-21. |
| PANG Yi, CHEN Jian, AN Renbing,et al .A review seismic performance of ancient timber structures on sloped lands[J].Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2022,44(2):10-21. | |
| 2 | 谢启芳,赵鸿铁,薛建阳,等 .中国古建筑木结构榫卯节点加固的试验研究[J].土木工程学报,2008,41(1):28-34. |
| XIE Qifang, ZHAO Hongtie, XUE Jianyang,et al .An experimental study on the strengthening of mortise-tenon joints in ancient Chinese wooden buildings[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2008,41(1):28-34. | |
| 3 | 周乾,闫维明,李振宝,等 .古建筑榫卯节点加固方法振动台试验研究[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版),2011,43(6):70-78. |
| ZHOU Qian, YAN Wei-ming, LI Zhen-bao,et al .Aseismic strengthening methods on Chinese ancient tenon-mortise joint by shaking table tests[J].Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2011,43(6):70-78. | |
| 4 | 郇君虹,马东辉,郭小东,等 .扁钢加固半榫、透榫及燕尾榫抗震性能试验研究[J].北京工业大学学报,2019,45(8):763-771. |
| HUAN Junhong, MA Donghui, GUO Xiaodong,et al .Experimental study of aseismic behaviors of flexural tenon joint,through tenon joint and dovetail joint strengthened with flat steel devices[J].Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2019,45(8):763-771. | |
| 5 | 薛建阳,任国旗,张家珩,等 .角钢加固传统民居十字形半榫节点抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2021,42(1):103-112. |
| XUE Jianyang, REN Guoqi, ZHANG Jiaheng,et al .Experimental study on seismic performance of cross-shaped half-tenon joint reinforced by angle in traditional dwellings[J].Journal of Building Structures,2021,42(1):103-112. | |
| 6 | 金昱成,苏何先,潘文,等 .木结构榫卯节点抗震性能及加固对比试验研究[J].土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2022,44(2):138-147. |
| JIN Yucheng, SU Hexian, PAN Wen,et al .Experimental research on seismic performance and reinforcement comparison of mortise-tenon joints in timber structures[J].Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2022,44(2):138-147. | |
| 7 | 潘毅,王超,唐丽娜,等 .古建筑直榫节点扁钢与阻尼器加固比较研究[J].西南交通大学学报,2014.49(6):981-986,1031. |
| PAN Yi, WANG Chao, TANG Lina,et al .Comparative research on flat steel and damper strengthening of straight type of tenon-mortise joints[J].Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2014,49(6):981-986,1031. | |
| 8 | 高永林,陶忠,叶燎原,等 .传统穿斗木结构榫卯节点附加黏弹性阻尼器振动台试验[J].土木工程学报,2016,49(2):59-68. |
| GAO Yonglin, TAO Zhong, YE Liaoyuan,et al .Shaking table tests of mortise-tenon joints of a traditional Chuan-Dou wood structure attached with viscoelastic dampers[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2016,49(2):59-68. | |
| 9 | 高永林,陶忠,叶燎原,等 .带有黏弹性阻尼器穿斗木结构振动台试验研究[J].振动与冲击,2017,36(1):240-247. |
| GAO Yonglin, TAO Zhong, YE Liaoyuan,et al .Shaking table tests for a Chuan-dou timber building with viscoelastic dampers[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2017,36(1):240-247. | |
| 10 | XUE J, WU C, ZHANG X,et al .Effect of pre-tension in superelastic shape memory alloy on cyclic behavior of strengthened mortise-tenon joints[J].Construction and Building Materials,2020,241:118-136. |
| 11 | XUE J, WU C, ZHANG X,et al .Experimental study on seismic behavior of mortise-tenon joints strengthened with shape memory alloy[J].Engineering Structures,2020,218:110-839. |
| 12 | 聂雅雯,陶忠,高永林 .黏弹性阻尼器增强传统木结构燕尾榫节点试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2021,42(1):125-133. |
| NIE Yawen, TAO Zhong, GAO Yonglin .Experimental study on dovetail mortise-tenon joints with viscoelastic dampers in traditional timber structures[J].Journal of Building Structures,2021,42(1):125-133. | |
| 13 | 陆伟东,吴伟强,施程凯,等 .含内嵌卯口耗能器的榫卯节点抗震性能试验研究[J].土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2022,44(2):30-37. |
| LU Weidong, WU Weiqiang, SHI Chengkai,et al .Experimental study on seismic performance of mortise-tenon joint with embedded dampers[J].Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2022,44(2):30-37. | |
| 14 | 陆伟东,姜伟波,张坤,等 .含耗能雀替的榫卯节点抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2021,42(11):213-221. |
| LU Weidong, JIANG Weibo, ZHANG Kun,et al .Experimental study on seismic performance of mortise-tenon joints with Queti damper[J].Journal of Building Structures,2021,42(11):213-221. | |
| 15 | DAI B, GAO Y, TAO Z,et al .Fan shaped shear dampers strengthen mortise tenon joints in Chinese traditional timber structures[J].International Journal of Architectural Heritage,2022,17(7):1079-1092. |
| 16 | 肖旻,杨扬 .广府祠堂建筑尺度模型研究[J].华中建筑,2012,30(6):147-151. |
| XIAO Min, YANG Yang .Study on the scale mode of ancestral halls incanton[J].Huazhong Architecture,2012,30(6):147-151. | |
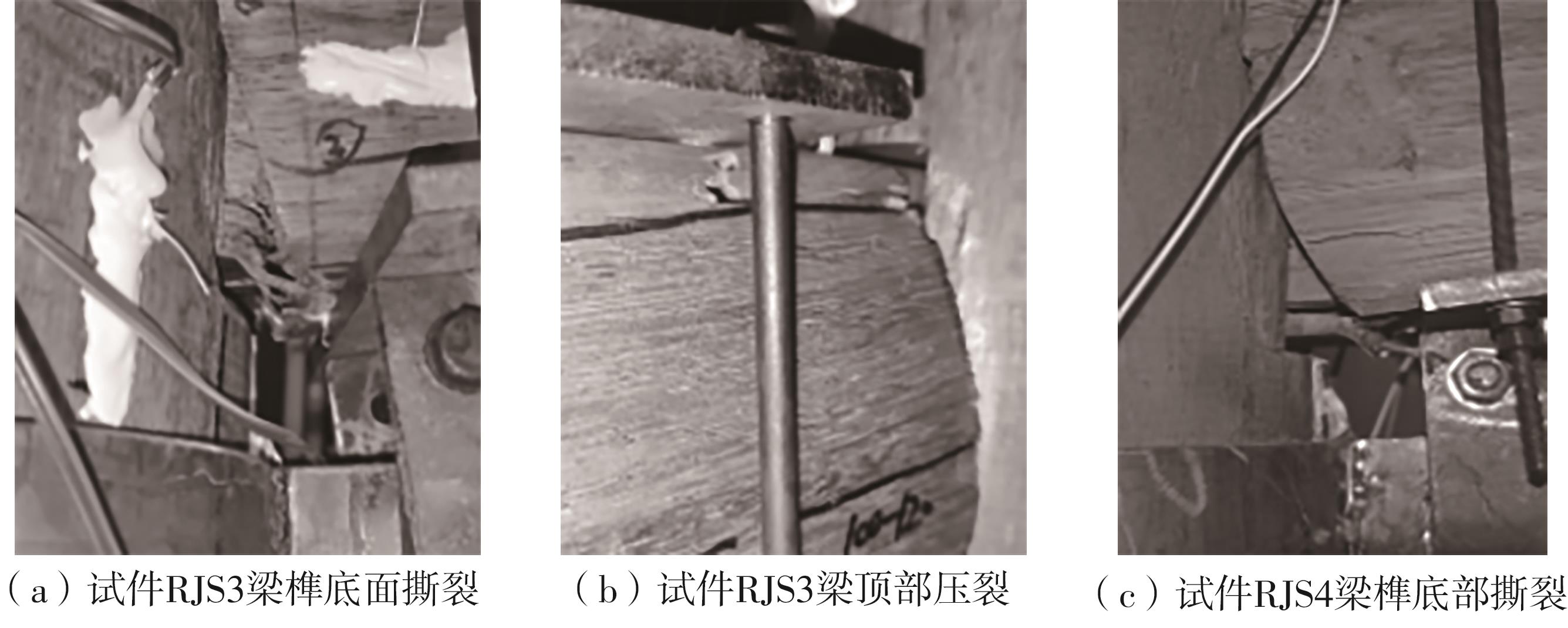
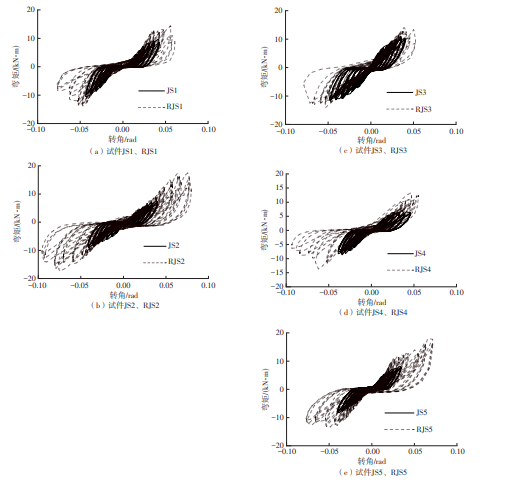
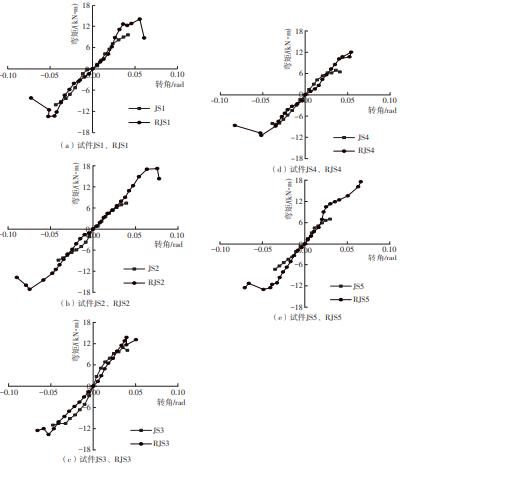
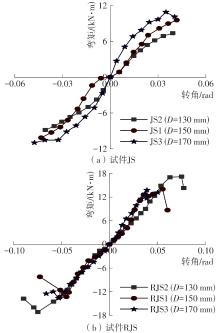
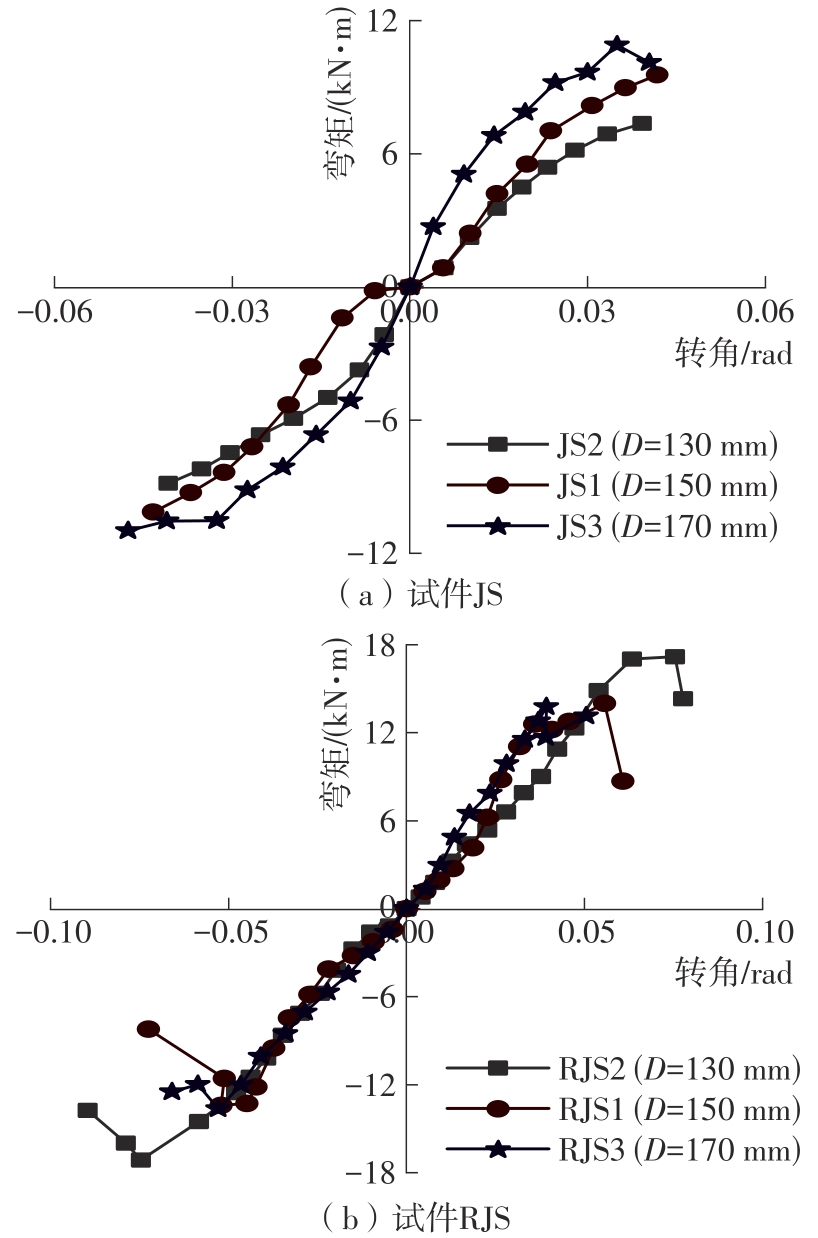
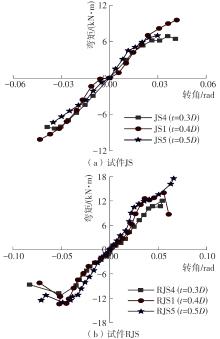
| 17 | 陈庆军,彭章锋,蔡健,等 .广府古建筑木结构箍头榫节点抗震性能研究[J].建筑结构学报,2019,40(10):168-179. |
| CHEN Qingjun, PENG Zhangfeng, CAI Jian,et al .Seismic behavior of hoop head tenon-mortise joint in ancient wood structures in Guangfu[J].Journal of Building Structures,2019,40(10):168-179. | |
| 18 | 常鹏,冯秋歌,韩乐,等 .松动残损下箍头榫节点抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2023,44(10):86-96. |
| CHANG Peng, FENG Qiuge, HAN Le,et al .Experimental study on seismic behavior of Gutou mortise-tenon joint with loose damage[J].Journal of Building Structures,2023,44(10):86-96. | |
| 19 | 陈庆军,李冰州,陈奕年,等 .雀替型阻尼器加固箍头榫木框架结构的抗震性能[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(4):9-20. |
| CHEN Qingjun, LI Bingzhou, CHEN Yinian,et al .Seismic performance of hoop head tenon frame structure reinforced by sparrow brace type damper[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023,51(4):9-20. | |
| 20 | 梁松,程从密,王绍怀,等 .土木工程材料(上册)[M].广州:华南理工大学出版社,2007. |
| 21 | 《木结构设计手册》编辑委员会 .木结构设计手册[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2021. |
| 22 | Forest Products Laboratory .Wood handbook—Wood as an engineering material,General Technical Report FPL-GTR-190[R].Madison:USA Department of Agriculture,Forest Service,Forest Products Laboratory,2010. |
| 23 | CHUN Q, YUE Z, PAN J .Experimental study on seismic characteristics of typical mortise-tenon joints of Chinese southern traditional timber frame buildings[J].Science China Technological Sciences,2011,54(9):2404-2411. |
| 24 | 薛建阳,任国旗,许丹,等 .传统民居穿斗式木结构栓榫节点抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2019,40(10):158-167. |
| XUE Jianyang, REN Guoqi, XU Dan,et al .Experimental study on seismic performance of dowel joints in traditional Chuan-Dou style timber structures[J].Journal of Building Structures,2019,40(10):158-167. | |
| 25 | The University of California .OpenSees User Documentation[EB/OL].[2023-09-24].. |
| 26 | 陈庆军,何永鹏,邱凯祥,等 .广府古建筑木结构箍头榫节点弯矩-转角关系理论分析[J].湖南大学学报报(自然科学版),2019,46(1):65-75. |
| CHEN Qingjun, HE Yongpeng, QIU Kaixiang,et al .Theoretical analysis on moment-rotation relationship of hoop head tenon-mortise joint for ancient timber structure in Guangfu[J].Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences),2019,46(1):65-75. |
| [1] | DING Faxing, CAI Yongqiang, WANG Liping, et al.. Seismic Performance Analysis of Welded Multi-Cavity Double Steel Plate-Concrete Composite Shear Wall [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 15-25. |
| [2] | ZHEN Xiaoxia, LIU Guiyuan, DONG Chunguang, et al. Study on Natural Vibration Characteristics of Cable Network-Damper System [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 61-71. |
| [3] | CHEN Qingjun, LI Bingzhou, CHEN Yinian, et al. Seismic Performance of Hoop Head Tenon Frame Structure Reinforced by Sparrow Brace Type Damper [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 9-20. |
| [4] | ZHENG Yifeng QIAN Shengyu . Study on the application of viscous dampers and steel dampers to bridge transverse vibration control [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(12): 89-100. |
| [5] | HUANG Haibin, WANG Yanchao, LIU Yazhou, et al. Seismic Performance of CFT Column-to-Beam Joints with Detached Vertical Stiffeners [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(3): 55-66. |
| [6] | XU Yan TONG Chuan LI Jianzhong. Simplified Dynamic Model for Cable-Stayed Bridge with Longitudinal Viscous Damper [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(4): 90-98. |
| [7] | MA Hongwei CHEN Fengshou. Optimal Arrangement of Dampers Based on Coarse-Grained Parallel Genetic Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(11): 104-112. |
| [8] |
ZENG Fanliang HUANG Yansheng ZHOU Jing.
Reliability Verification for Seismic Capacity Utilization Factors of Structure
|
| [9] | JIN Tianhe LIU Zhiming REN Zunsong LI Xiang. Study of Combination Damping Characteristics Effect of High-Speed Train Damper#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 116-124. |
| [10] |
LI Peizhen SHU Xin YANG Jinping .
Parametric Analysis of Structure with Additional Viscoelastic Dampers Considering Soil-Structure Dynamic Interaction
|
| [11] | LI Guojie LI Liping Subhash Rakheja SHANGGUAN Wenbin . Research on dynamic characteristics of a magneto-rheological damper featuring piston bypass holes [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(12): 66-73,102. |
| [12] | GUO Yi-ming WEI Yu-ming SHANGGUAN Wen-bin. Robust Optimal Matching of Rubber-Type Torsional Vibration Damper for Engine Crankshaft [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(2): 75-83,107. |
| [13] | SHANGGUAN Wen-bin CHEN Cheng-feng LI Li-ping YU Hong QI Zhen-ning. Analysis of Vibration Isolation Performances of Vehicle Suspension System Based on Vibrational Power Flow Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(2): 23-29,38. |
| [14] | GUO Meng LIU Zhi-yuan HUANG Wei WANG Shuang-jiao YUAN Quan . Experiment on Seismic Performance of Earthquake Damage Frame Strengthened with Aerated Concrete Block Composite Wall [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(10): 117-124. |
| [15] | Yuan Xian-ju Guo Kong-hui . Investigation into Opening of a Pilot Relief Valve Located in a Semi-Active Damper#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(8): 91-98. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||