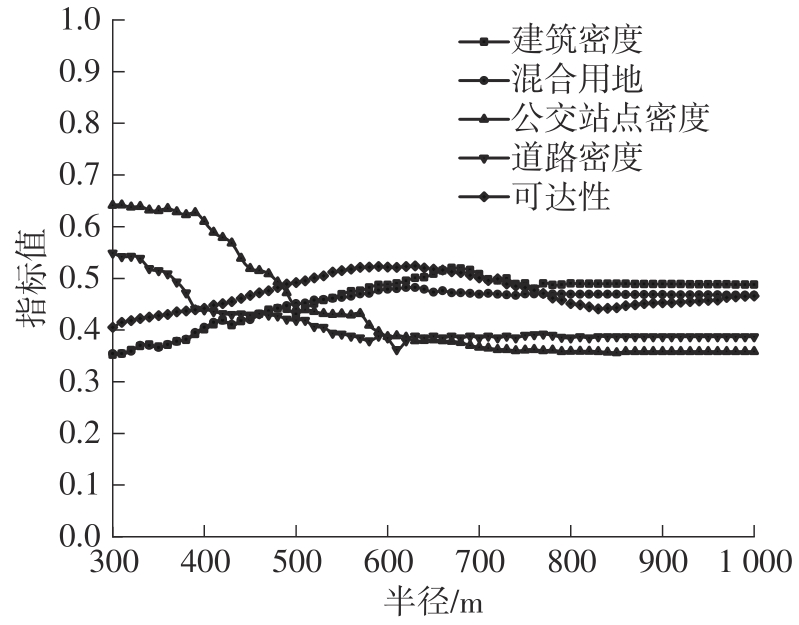
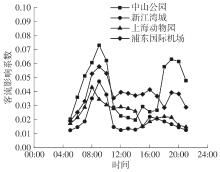
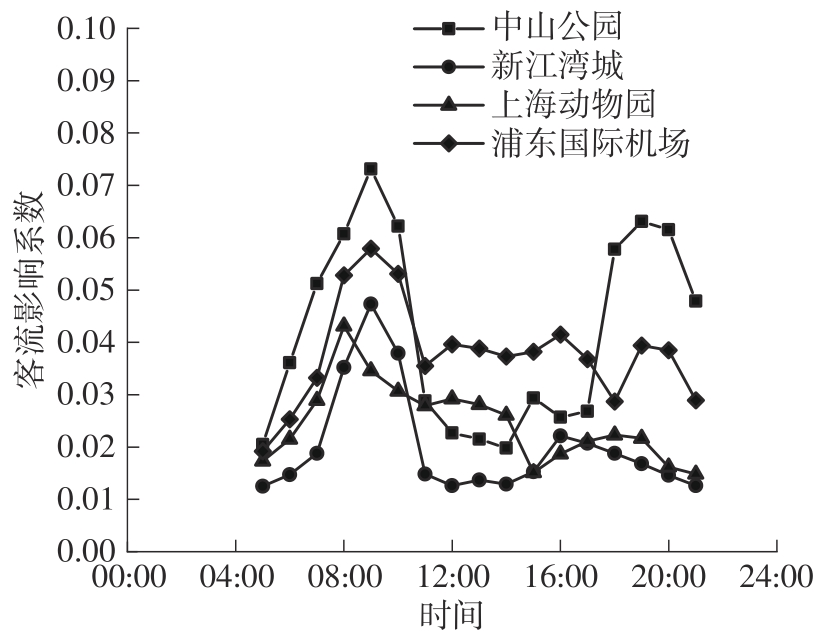
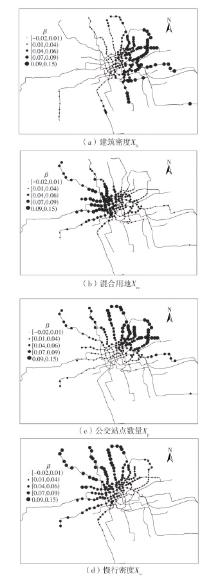
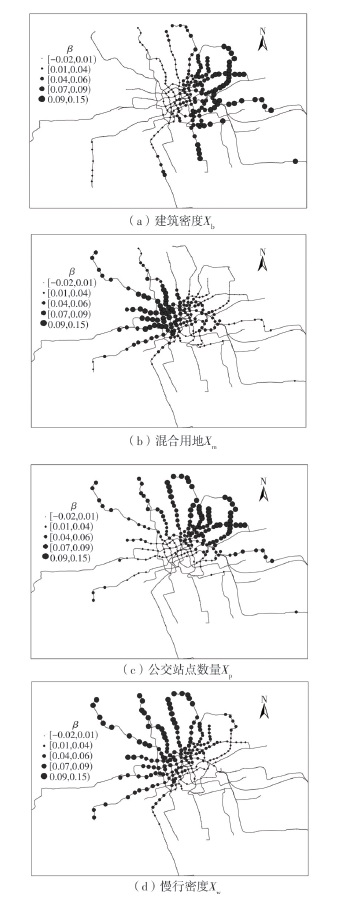
| 1 |
SUNG H, CHOI K, LEE S,et al .Exploring the impacts of land use by service coverage and station-level accessibility on rail transit ridership[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2014,36:134-140.
|
| 2 |
王淑伟,孙立山,郝思源,等 .基于精细化用地的轨道客流直接估计模型[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2015,15(3):37-43.
|
|
WANG Shu-wei, SUN Li-shan, HAO Si-yuan,et al .Station level transit ridership direct estimation model based on precise land use[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2015,15(3):37-43.
|
| 3 |
ZHAO J, DENG W, SONG Y,et al .What influences metro station ridership in China? insights from Nanjing[J].Cities,2013,35:114-124.
|
| 4 |
孔祥夫,杨家文 .土地利用视角下的轨道站点客流预测——以深圳市为例[J].地理科学,2018,38(12):2074-2083.
|
|
KONG Xiangfu, YANG Jiawen .A new method for forecasting station-level transit ridership from land-use perspective: the case of Shenzhen City[J].Geographical Science,2018,38(12):2074-2083.
|
| 5 |
崔叙,喻冰洁,梁朋朋,等 .基于“客流-用地”的城市轨道交通站点类型识别与空间再平衡研究——以成都市为例[J].现代城市研究,2021(7):68-79.
|
|
CUI Xu, YU Bingjie, LIANG Pengpeng,et al .Urban rail transit station type identification and job-housing spatial rebalancing based on passenger flow and land use: taking Chengdu as an example[J].Modern Urban Research,2021(7):68-79.
|
| 6 |
RODRIGUEZ D A, KANG C D .A typology of the built environment around rail stops in the global transit-oriented city of Seoul,Korea[J].Cities,2020,100:102663/1-12.
|
| 7 |
YU Z, ZHU X, LIU X .Characterizing metro stations via urban function:thematic evidence from transit-oriented development (TOD) in Hong Kong[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2022,99:103299/1-11.
|
| 8 |
岂常禄,胡昊 .基于混合地理加权回归的城市轨道交通站点客流预测研究[J].铁道科学与工程学报,2021,18(7):1903-1909.
|
|
QI Changlu, HU Hao .Research on ridership forecast of urban rail transit station based on mixed geographic weighted regression[J].Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2021,18(7):1903-1909.
|
| 9 |
DING C, CAO X, LIU C .How does the station-area built environment influence metrorail ridership? using gradient boosting decision trees to identify non-linear thresholds[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2019,77:70-78.
|
| 10 |
DU Q, ZHOU Y, HUANG Y,et al .Spatiotemporal exploration of the non-linear impacts of accessibility on metro ridership[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2022,102:103380/1-17.
|
| 11 |
IBRAEVA A, CORREIA G, SILVA C,et al .Transit-oriented development:a review of research achievements and challenges[J].Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice,2020,132:110-130.
|
| 12 |
谭佩珊,麦可,张亚涛,等 .利用多源城市数据划定地铁站点吸引范围[J].地球信息科学学报,2021,23(4):593-603.
|
|
TAN Peishan, Ke MAI, ZHANG Yatao,et al .Identifying the catchment area of metro stations using multi-source urban data[J].Journal of Geo-Information Science,2021,23(4):593-603.
|
| 13 |
姜莉,温惠英 .空间耦合连接性的TOD测度模型构建及应用研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21(4):239-247.
|
|
JIANG Li, WEN Hui-ying .TOD Measurement model with spatial coupling connectivity[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2021,21(4):239-247.
|
| 14 |
高德辉,许奇,陈培文,等 .城市轨道交通客流与精细尺度建成环境的空间特征分析[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21(6):25-32.
|
|
GAO De-hui, XU Qi, CHEN Pei-wen,et al .Spatial characteristics of urban rail transit passenger flows and fine-scale built environment[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2021,21(6):25-32.
|
| 15 |
LIU J, WANG B, XIAO L .Non-linear associations between built environment and active travel for working and shopping:an extreme gradient boosting approach[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2021,92:103034/1-12.
|
| 16 |
DING C, CAO X, NAESS P .Applying gradient boosting decision trees to examine non-linear effects of the built environment on driving distance in Oslo[J].Transportation Research,Part A:Policy and Practice,2018,110:107-117.
|
| 17 |
李亮,赵星,张海燕,等 .基于时空维度变量的杭州市轨道交通站点聚类研究[J].北京交通大学学报,2022,46(4):31-42.
|
|
LI Liang, ZHAO Xing, ZHANG Haiyan,et al .Clustering research on Hangzhou metro station based on spatio-temporal variables[J].Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University,2022,46(4):31-42.
|
| 18 |
戢晓峰,乔新 .建成环境对行人交通事故严重程度的非线性影响[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2023,23(1):314-323.
|
|
JI Xiao-feng, QIAO Xin .Nonlinear influence of built environment on pedestrian traffic accident severity[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2023,23(1):314-323.
|
| 19 |
SHAO Q F, ZHANG W J, CAO X Y,et al .Threshold and moderating effects of land use on metro ridership in Shenzhen:implications for TOD planning[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2020,89:102878/1-12.
|