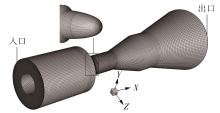
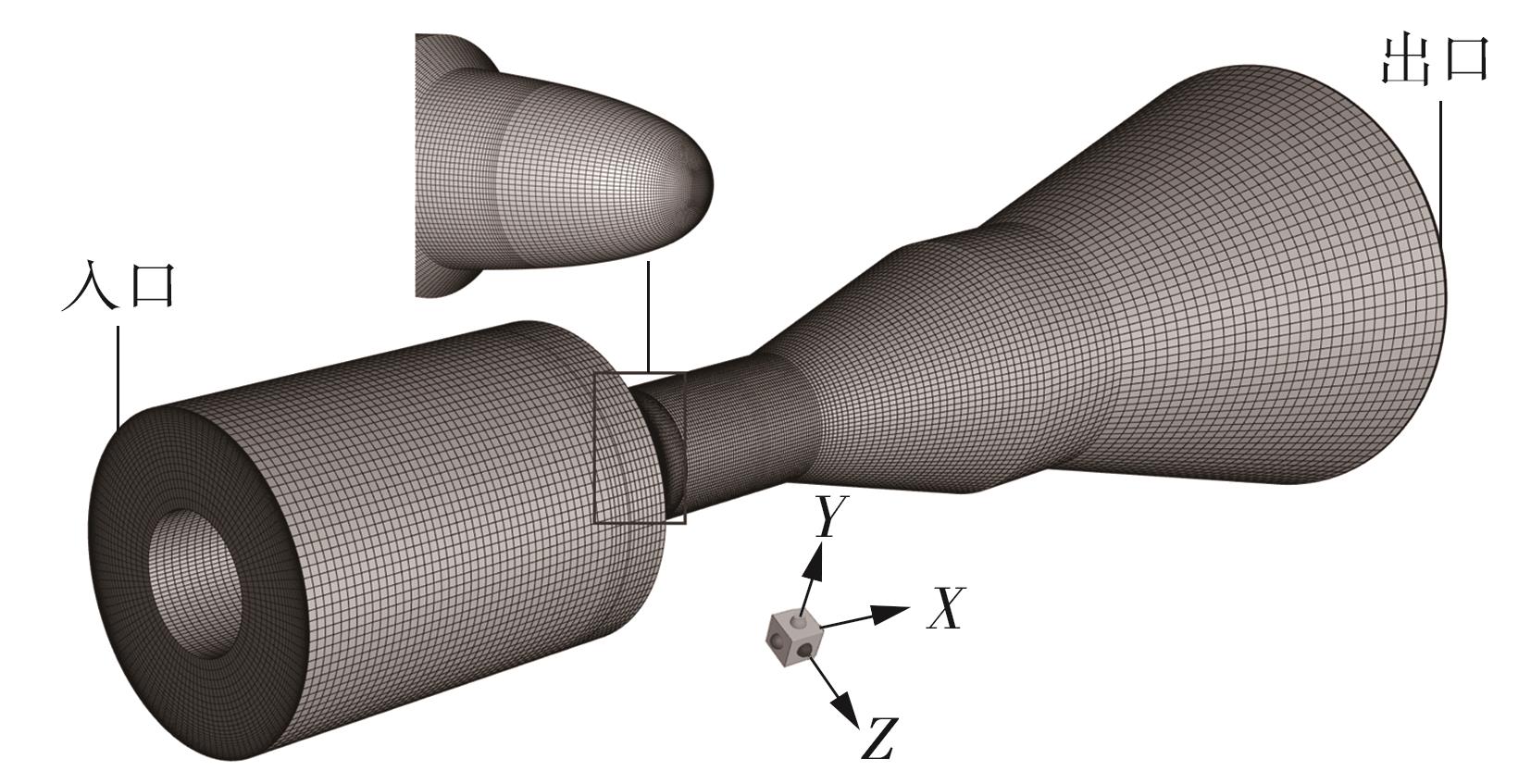
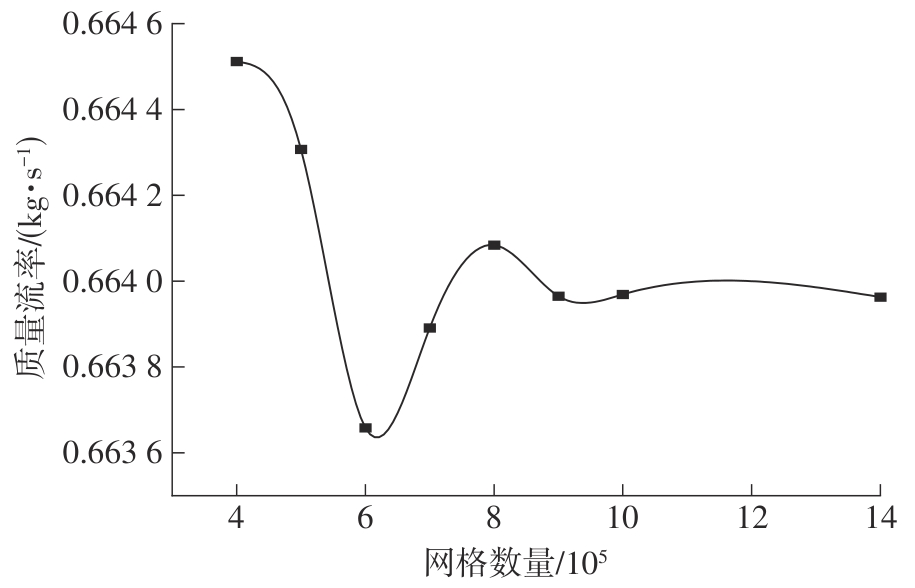
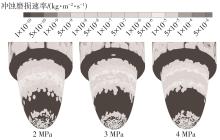
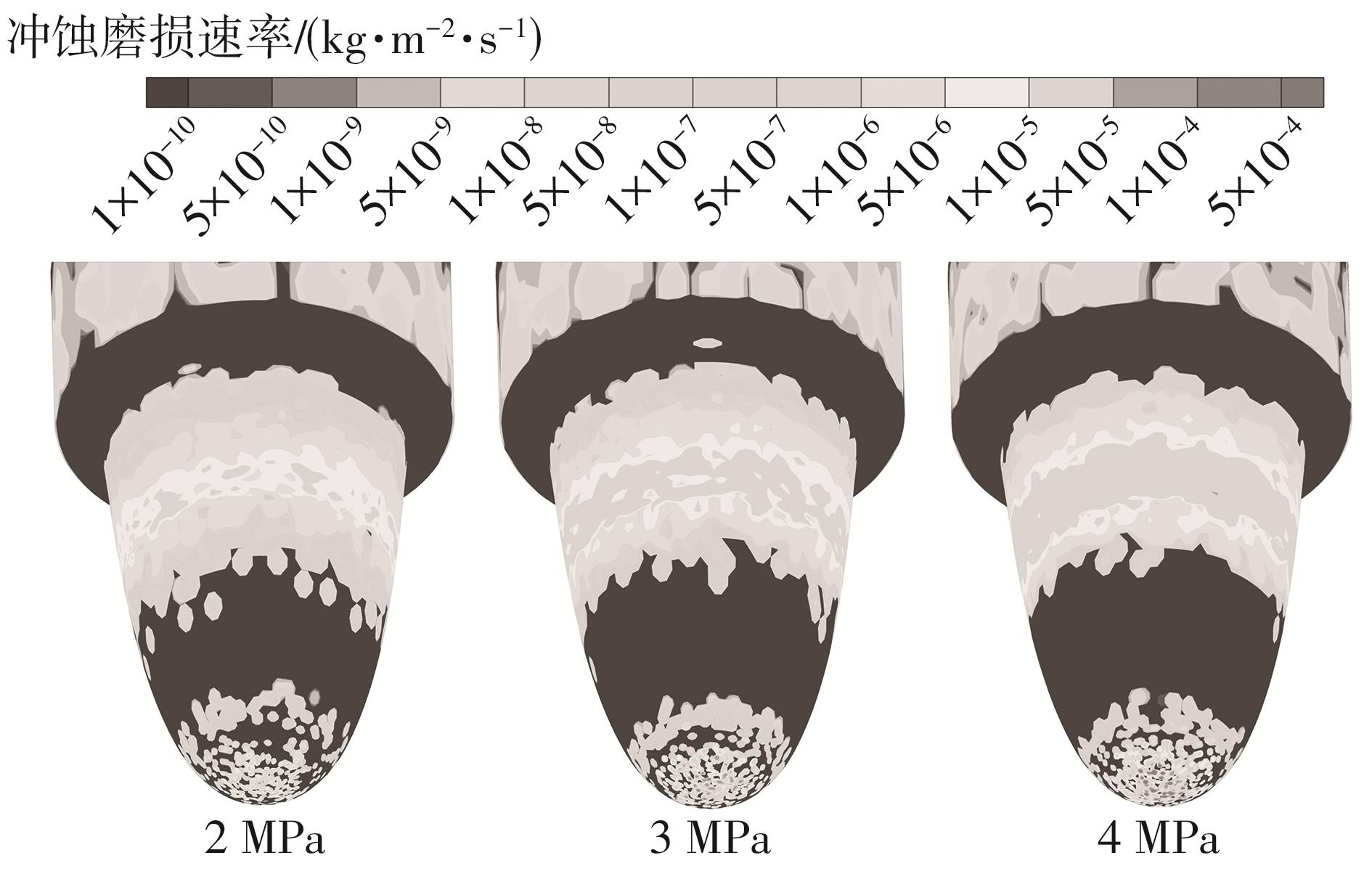
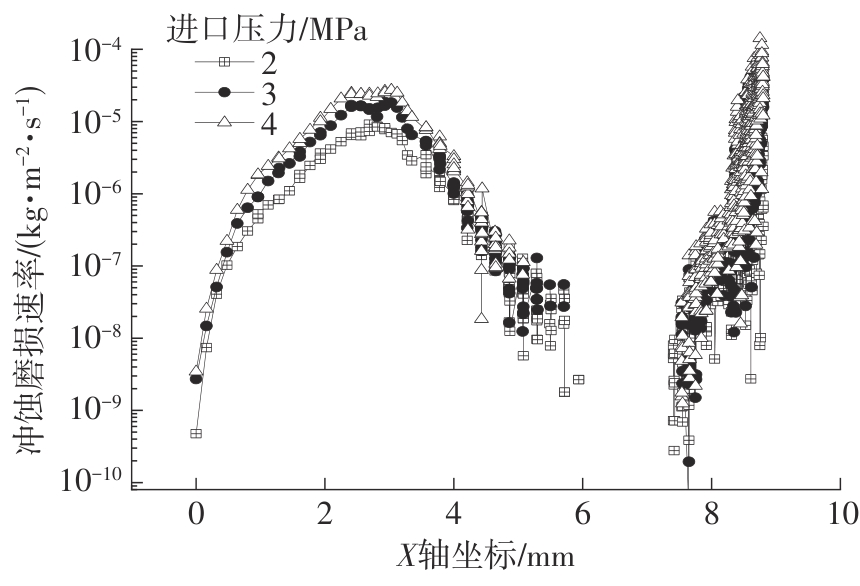
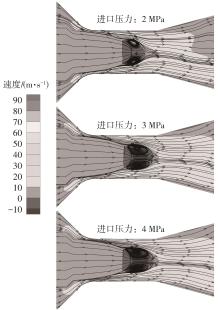
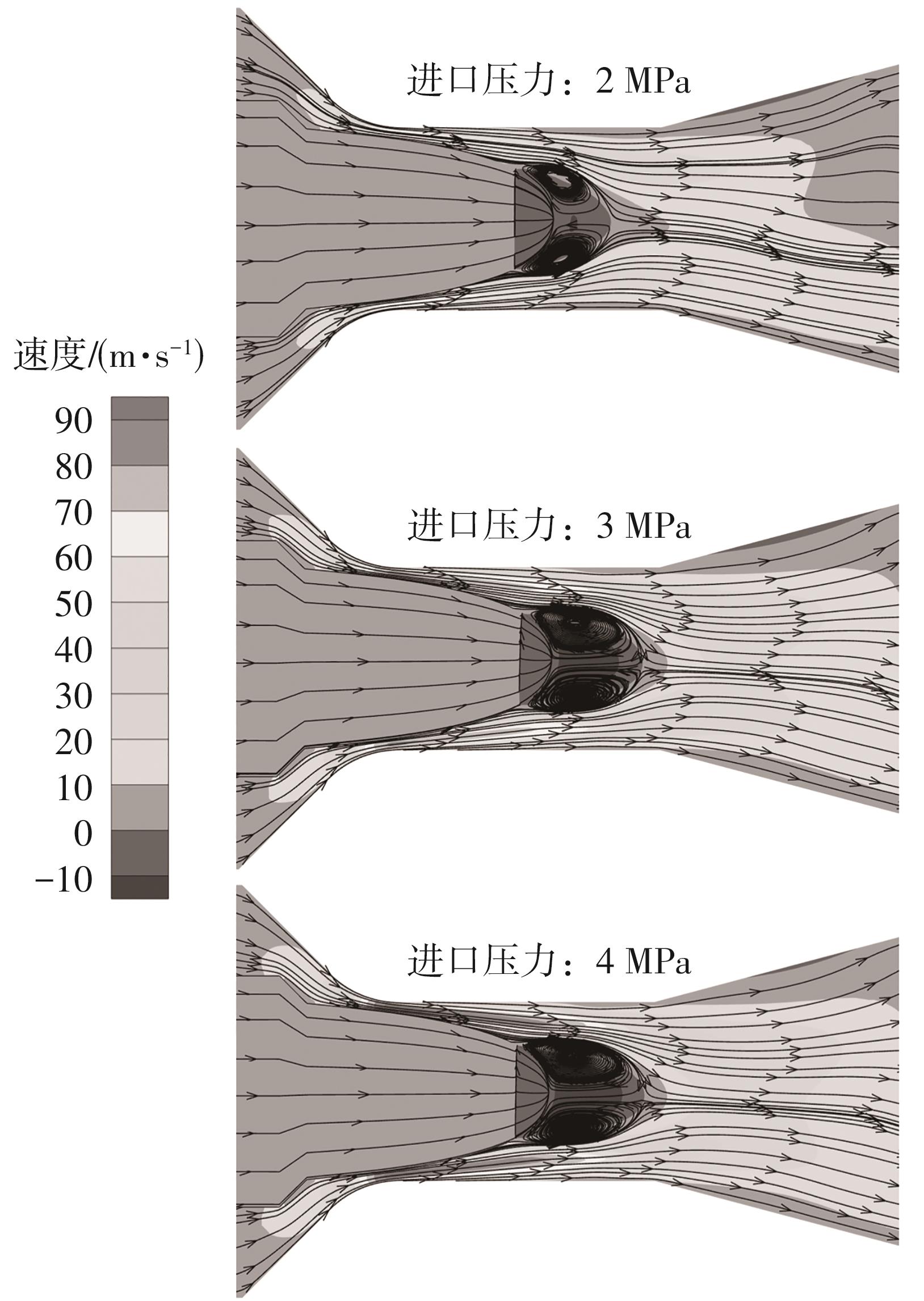
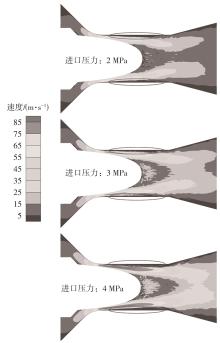
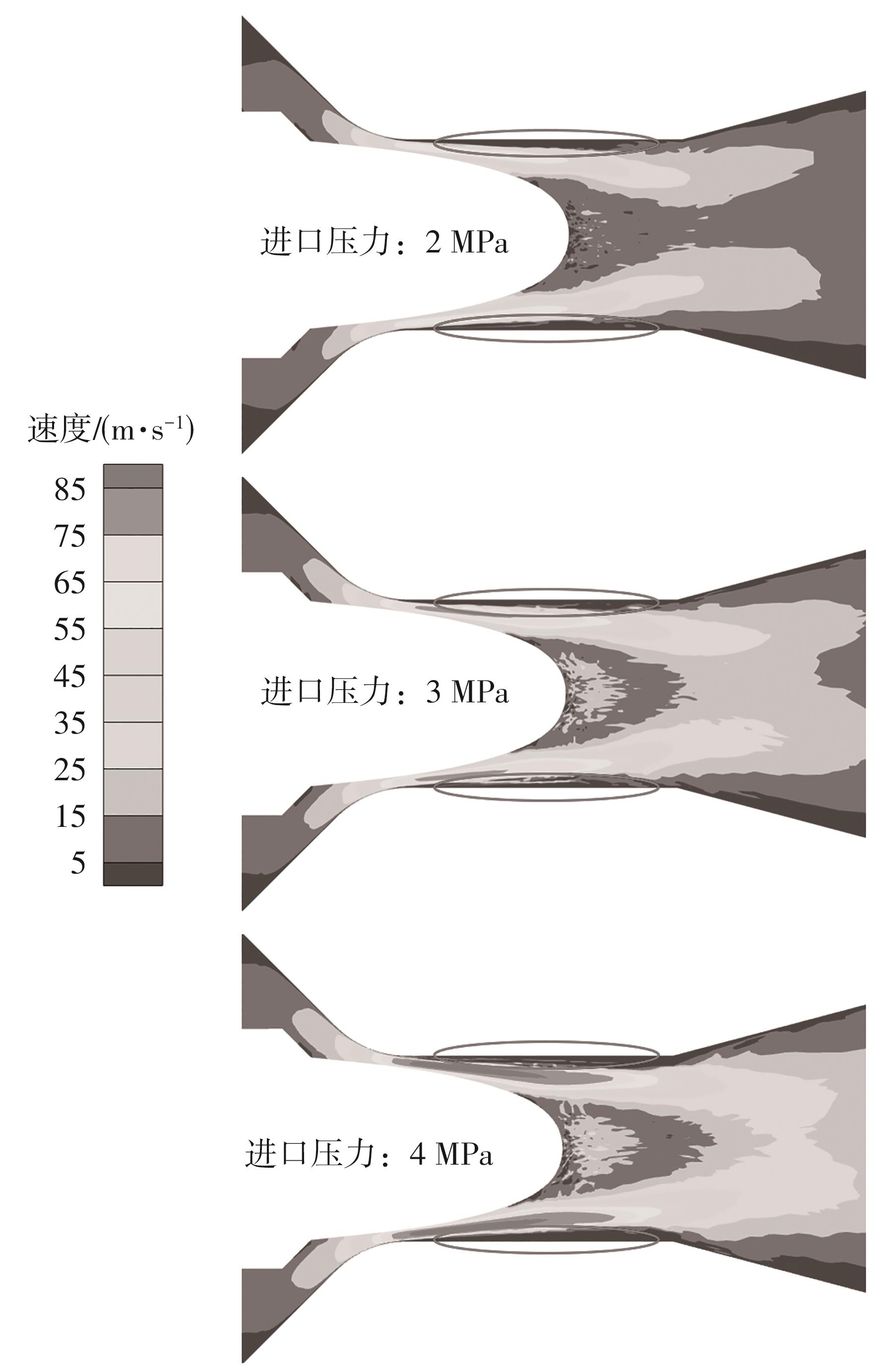
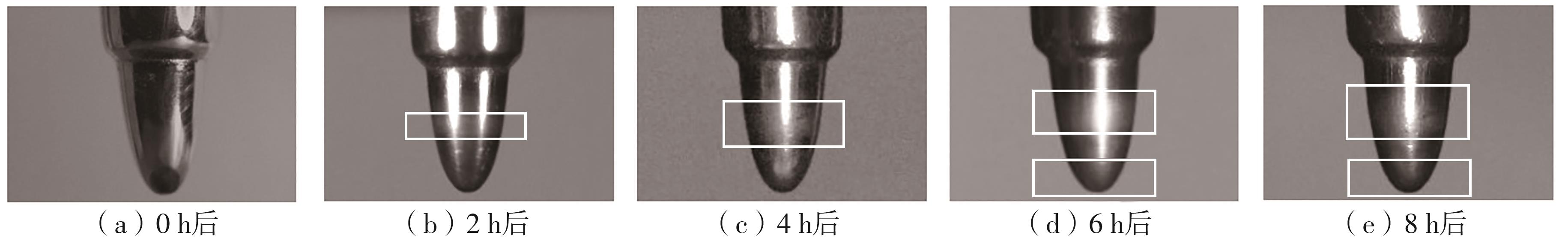
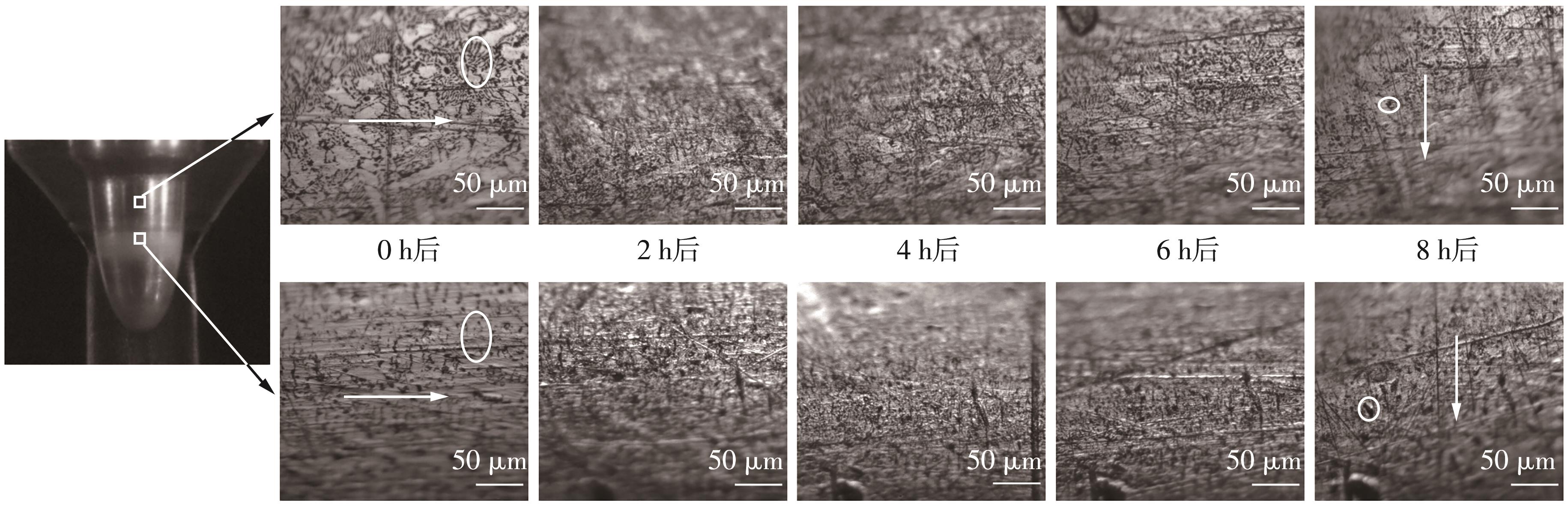
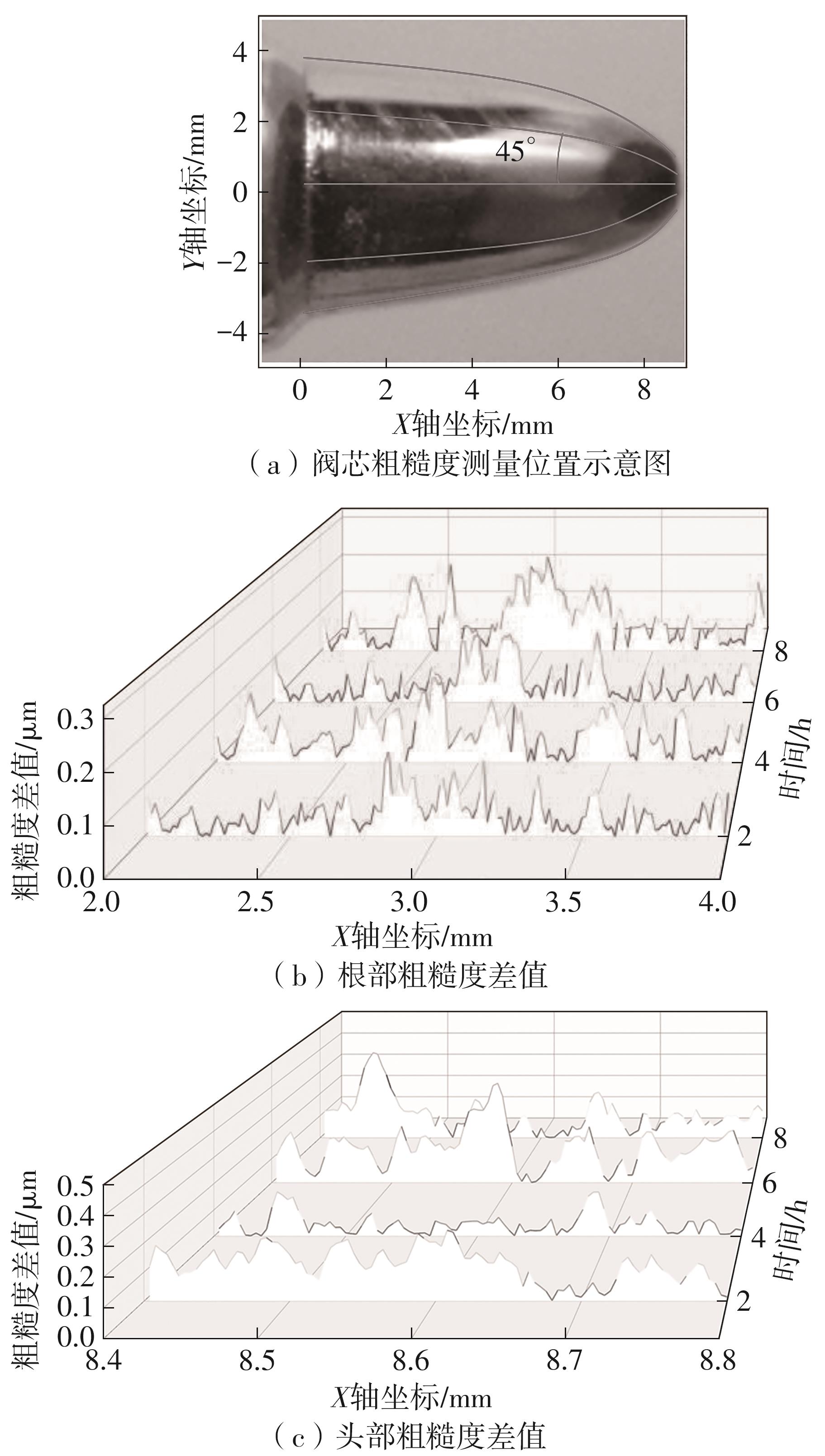
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 109-118.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240304
Special Issue: 2024年流体动力与机电控制工程
• Fluid Power & Mechatronic Control Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Simulated and Experimental Investigation into Coupled Wear of Cavitation and Erosion in Regulating Valves
LIU Xiumei1 MA Xuemin1 LI Beibei1 ZHAO Qiao2 LI Shiyang1 WU Siyu1 HAN Rui1
- 1.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou 221116,Jiangsu,China
2.College Student Innovation Training Center,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou 221116,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2024-06-12Online:2024-12-25Published:2024-09-23 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51875559);the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province(BK20242085)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Xiumei, MA Xuemin, LI Beibei, et al. Simulated and Experimental Investigation into Coupled Wear of Cavitation and Erosion in Regulating Valves[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(12): 109-118.
share this article
| 1 | 康红普,王国法,王双明,等 .煤炭行业高质量发展研究[J].中国工程科学,2021,23(5):130-138. |
| KANG Hongpu, WANG Guofa, WANG Shuangming,et al .High-quality development of China’s coal industry[J].Chinese Engineering Science,2021,23(5):130-138. | |
| 2 | LIU X, HE J, XIE Y,et al .Investigation on unsteady cavitation flow and excited pressure fluctuations in regulating valve[J].Machines,2022,10(1):32-32. |
| 3 | WEI M, JI H, YANG L .Axial vibration in a poppet valve based on fluid-structure interaction[J].Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part C:Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science,2015,229(17):3266-3273. |
| 4 | HABIBNEJAD D, AKBARZADEH P, SALAVATIPOUR A,et al .Cavitation reduction in the globe valve using oblique perforated cages:a numerical investigation[J].Flow Measurement and Instrumentation,2022,83:102-110. |
| 5 | OU G,OU Y, ZHRNG Z,et al .Investigation on failure process and structural improvement of a high-pressure coal water slurry valve[J].Engineering Failure Analysis,2019,96:1-17. |
| 6 | 王世强 .基于重叠网格的阀芯振荡诱导空化的研究[D].兰州:兰州理工大学,2023. |
| 7 | QIU N, XUN D, ZHU H,et al .Impact of re-entrant jet and shedding cloud cavity on the distribution of cavitation erosion[J].Ocean Engineering,2024,307:118111/1-19. |
| 8 | 孙毅,祝利豪,毛亚郎,等 .近球壁射流空泡溃灭对微细颗粒破碎效果的影响[J].中国机械工程,2020,31(24):2910-2917,2923. |
| SUN Yi, ZHU Lihao, MAO Yalang,et al .Effects of bubble collapse of near-ball wall jet flows on crushing effectiveness of fine particles[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2020,31(24):2910-2917,2923. | |
| 9 | IJIRI M,OGI T, YOSHIMURA T,et al .Effect of multifunction cavitation on microstructure and plane bending fatigue properties of low-alloy steel[J].Results in Materials,2024,22:100578/1-8. |
| 10 | AMARENDRA H J, CHAUDHAIR G P, NATH S K .Synergy of cavitation and slurry erosion in the slurry pot tester[J].Wear,2012,290/291:25-31. |
| 11 | JIN H, ZHENG F, LI S,et al .The role of sand particles on the rapid destruction of the cavitation zone of hydraulic-turbines[J].Wear,1986,112(2):199-205. |
| 12 | 张逸群,武晓亚,李根生,等 .天然气水合物旋转空化射流冲蚀性能研究[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版),2022,53(3):909-923. |
| ZHANG Yiqun, WU Xiaoya, LI Gensheng,et al .Study on swirling cavitating jet for natural gas hydrate[J].Journal of Central South University (Natural Science Edition),2022,53(3):909-923. | |
| 13 | 陈海舰,刘峰斌,郭诒大,等 .微颗粒对超声空蚀影响的试验研究[J].摩擦学学报,2022,42(3):461-469. |
| CHEN Haijian, LIU Fengbin, GUO Yida,et al .Experimental study of the effect of microparticles on ultrasonic cavitation[J].Journal of Tribology,2022,42 (3):461-469. | |
| 14 | 蔡腾飞,潘岩,王啸林,等 .自振空化射流冲蚀模式与机制研究[J].机械工程学报,2024,60(6):378-385. |
| CAI Tengfei, PAN Yan, WANG Xiaolin,et al .Study on erosion pattern and mechanism of self-excited cavitating waterjet[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2024,60(6):378-385. | |
| 15 | 杨俊峰,孙淑贞,孙帅辉,等 .泥沙浓度对水力机械材料磨损及磨蚀特性的影响[J].水力发电学报,2024,43(7):51-60. |
| YANG Junfeng, SUN Shuzhen, SUN Shuaihui,et al .Influence of sediment concentration on abrasion and erosion characteristics of hydraulic machinery materials[J].Journal of Hydroelectric Power,2024,43(7):51-60. | |
| 16 | 范文睿,孙龙刚,郭鹏程,等 .冲击式水轮机内部流动与泥沙磨损特性研究进展[J].水动力学研究与进展(A辑),2023,38(5):774-793. |
| FAN Wenrui, SUN Longgang, GUO Pengcheng,et al .Advances in internal flow and sediment erosion characteristics of Pelton turbines[J].Hydrodynamics Research and Progress A,2023,38(5):774-793. | |
| 17 | HAUGEN K, KVERNVOLD O, RONOLD A,et al .Sand erosion of wear-resistant materials:erosion in choke valves[J].Wear,1995,186(1):179-188. |
| 18 | QIU N, XU P, ZHU H,et al .Cavitation morphology and erosion on hydrofoil with slits[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2024,275:109345/1-17. |
| 19 | ZHENG Z,OU G, YI Y,et al .A combined numerical-experiment investigation on the failure of a pressure relief valve in coal liquefaction[J].Engineering Failure Analysis,2016,60:326-340. |
| 20 | NAN L, ARABNEJAD H, SHIRAZI S A,et al .Experimental study of particle size,shape and particle flow rate on erosion of stainless steel[J].Powder Technology,2018,336:70-79. |
| 21 | PENG D, DONG S, WANG Z,et al .Characterization of the solid particle erosion of the sealing surface materials of a ball valve[J].Metals,2021,11(2):263-280. |
| 22 | 王军军,李志均,黄伟九 .沙粒粒径和外电位对黄铜腐蚀磨损的影响[J].摩擦学学报,2016,36(4):406-412. |
| WANG Junjun, LI Zhijun, HUANG Weijiu .Effect of particle size and electrochemical potential on erosion behavior of brass in liquid-solid solution[J].Journal of Tribology,2016,36(4):406-412. | |
| 23 | 邓宽海,程金亮,林元华,等 .基于气-固两相流喷嘴实验的20G钢冲蚀机理研究[J].表面技术,2024,53(17):50-61. |
| DENG Kuanhai, CHENG Jinliang, LIN Yuanhua,et al .Erosion mechanism of 20G steel based on gas-solid two-phase flow nozzle experiment[J].Surface Technology,2024,53(17):50-61. | |
| 24 | MARGOT X, HOYAS S, GIL A,et al .Numerical modelling of cavitation:validation and parametric studies[J].Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics,2014,6:15-24. |
| 25 | 郝常乐,党建军,陈长盛,等 .基于双向流固耦合的超空泡射弹入水研究[J].力学学报,2022,54(3):678-687. |
| HAO Changle, DANG Jianjun, CHEN Changsheng,et al .Numerical study on water entry process of supercavitating projectile by considering bidirectional fluid structure interaction effect[J].Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2022,54(3):678-687. | |
| 26 | FORDER A, THEW M, HARRISON D .A numerical investigation of solid particle erosion experienced within oilfield control valves[J].Wear,1998,216(2):184-193. |
| 27 | BO C, PING C, YUAN Q .Numerical simulation of particle erosion in the vertical-upward-horizontal elbow under multiphase bubble flow[J].Powder Technology,2022,404:117437/1-13. |
| 28 | ERLEI S, YUN P L, QUAN L Z,et al .Numerical analysis of permeability rebound and recovery during coalbed methane extraction: implications for CO2 injection methods[J].Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2021,149:93-104. |
| 29 | 陈青,黄志强,孔祥伟,等 .基于多录井参数特征同步的溢流事故监测研究[J/OL].(2024-09-12)[2024-09-30].. |
| CHEN Qing, HUANG Zhiqiang, KONG Xiangwei,et al .Study on overflow accident monitoring based on synchronous features of multiple well logging parameters[J/OL].(2024-09-12)[2024-09-30].. |
| [1] | LIU Guoyong, GAO Shize, ZHU Dongmei. Analysis of Extrusion Law of Large-Scale and Small-Scale Aluminum Profiles with Hollow Thin Wall for Rails [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(5): 45-55. |
| [2] | DING Xiaobin, XIE Yuxuan, SHI Yu. Crack Extension Analysis of Rock-Like Material Based on the Improved Contact Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 146-158. |
| [3] | YU Mingquan, ZHAO Jiyun, MAN Jiaxiang, et al.. Study of Distribution Structure for High Water-Based Hydraulic Motor [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(9): 19-29. |
| [4] | LU Zhimin, LI Bohang, TANG Wen, et al. Optimization Simulation of Ammonia Injection in SCR DeNO x System of Coal-Fired Power Plant [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(8): 62-70. |
| [5] | LIU Dingping, ZHANG Xiangyang, CHEN Aihua, et al. Numerical Analysis of Performance of Cyclone-Tube Demister Based on Orthogonal Design [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(6): 89-96. |
| [6] | MA Xiangjun, WANG Zhen, YAO Zhiqiang, et al. Numerical Simulation on Melt Flow Characteristics of UHMWPE in Eccentric Rotor Extruder [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(5): 114-121. |
| [7] | DAI Gonglian, CHEN Kun, GE Hao, et al. Research on Numerical Simulation of Rail Non-contact Nondestructive Testing Technology [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 44-52. |
| [8] | LI Shuxun, HU Yinggang, LI Cheng, et al. Optimization of Body Profile Line of Axial Flow Control Valve Based on Surrogate Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(3): 41-52. |
| [9] | TIAN Lifeng, GUO Meiqi, DING Hao, et al. On Aero-optical Effect and Control of Supersonic Boundary Layer [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 137-146. |
| [10] | YU Mingquan, ZHAO Jiyun, MAN Jiaxiang, et al.. Study on Flow Distribution Mechanism of Low Speed High Torque Hydraulic Motor [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(11): 101-109. |
| [11] | DU Jianming, FANG Qian , WANG Gan, et al. Characteristics of Transient Pressure and Pressure Gradient of a High-Speed Train Travelling Through a Double-Track Tunnel [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 58-68. |
| [12] | GONG Nan, LI Peizhen, HE Xuming. Design of an Innovative Eddy Current Replaceable Coupling Beam and Its Numerical Analysis [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 25-34. |
| [13] | DU Jianming, FANG Qian, LI Jianye. Influences of Train to Tunnel Area Ratio on Aerodynamic Pressure Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Tunnel Wall [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 56-64. |
| [14] | YANG Chen, WANG Fenglei, WU Jiayi, et al. Analysis of Shell-Side Thermal-Hydraulic Performance of Hybrid Smooth and Spirally Corrugated Tubes [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 137-144. |
| [15] | HUANG Si, ZHANG Guoran, TANG Zirui, et al. Fluid-Solid Coupling Analysis of Spherical Storage Tank under Wind Load [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 67-75. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||