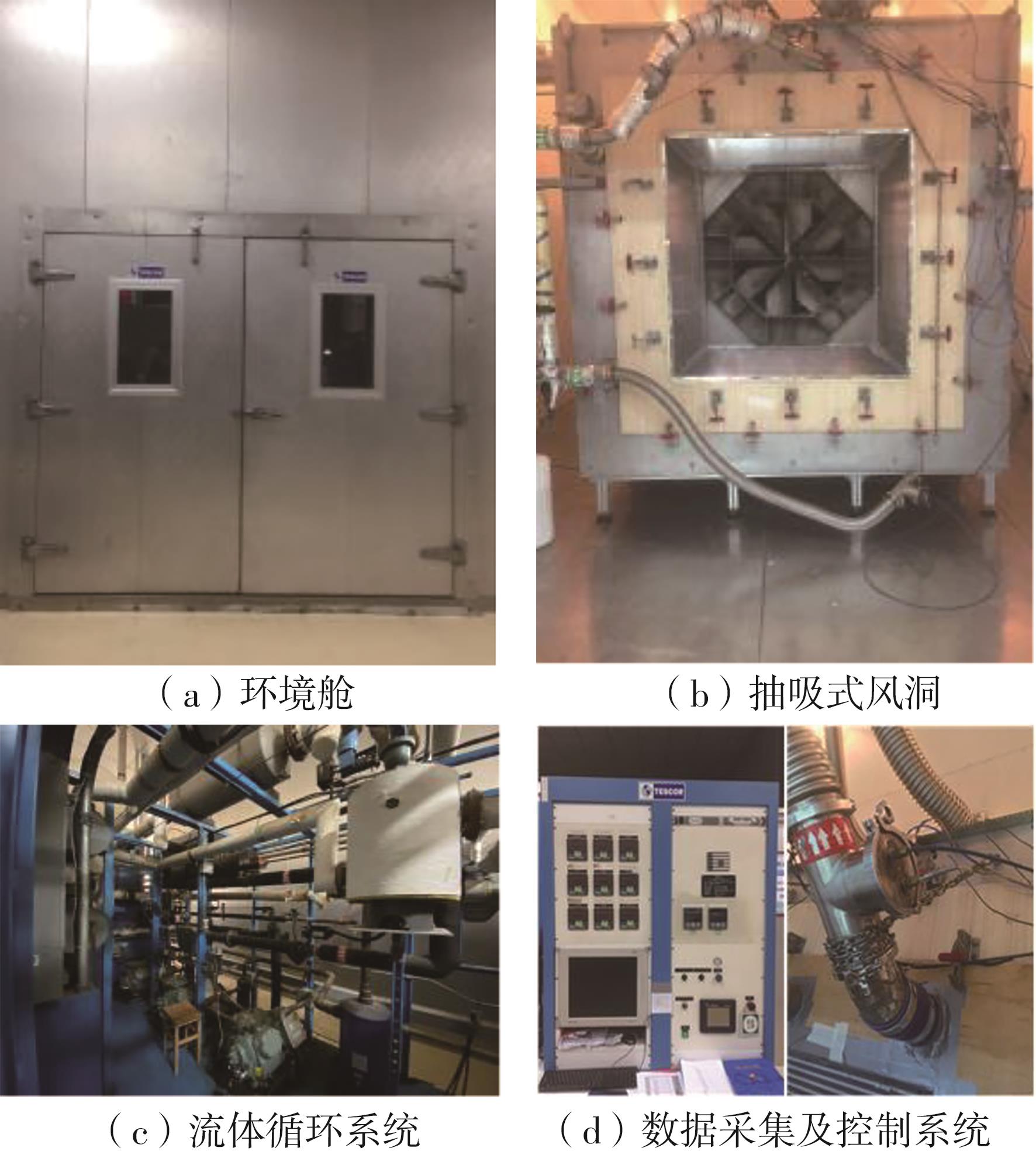
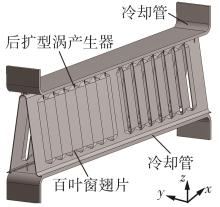
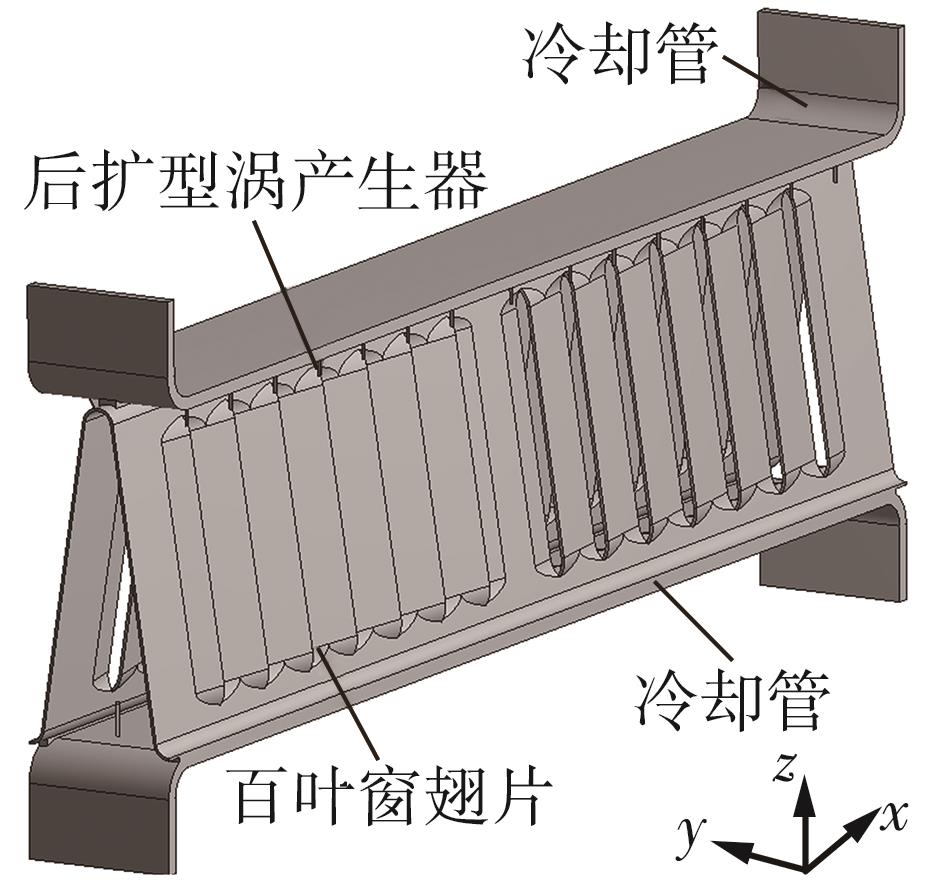
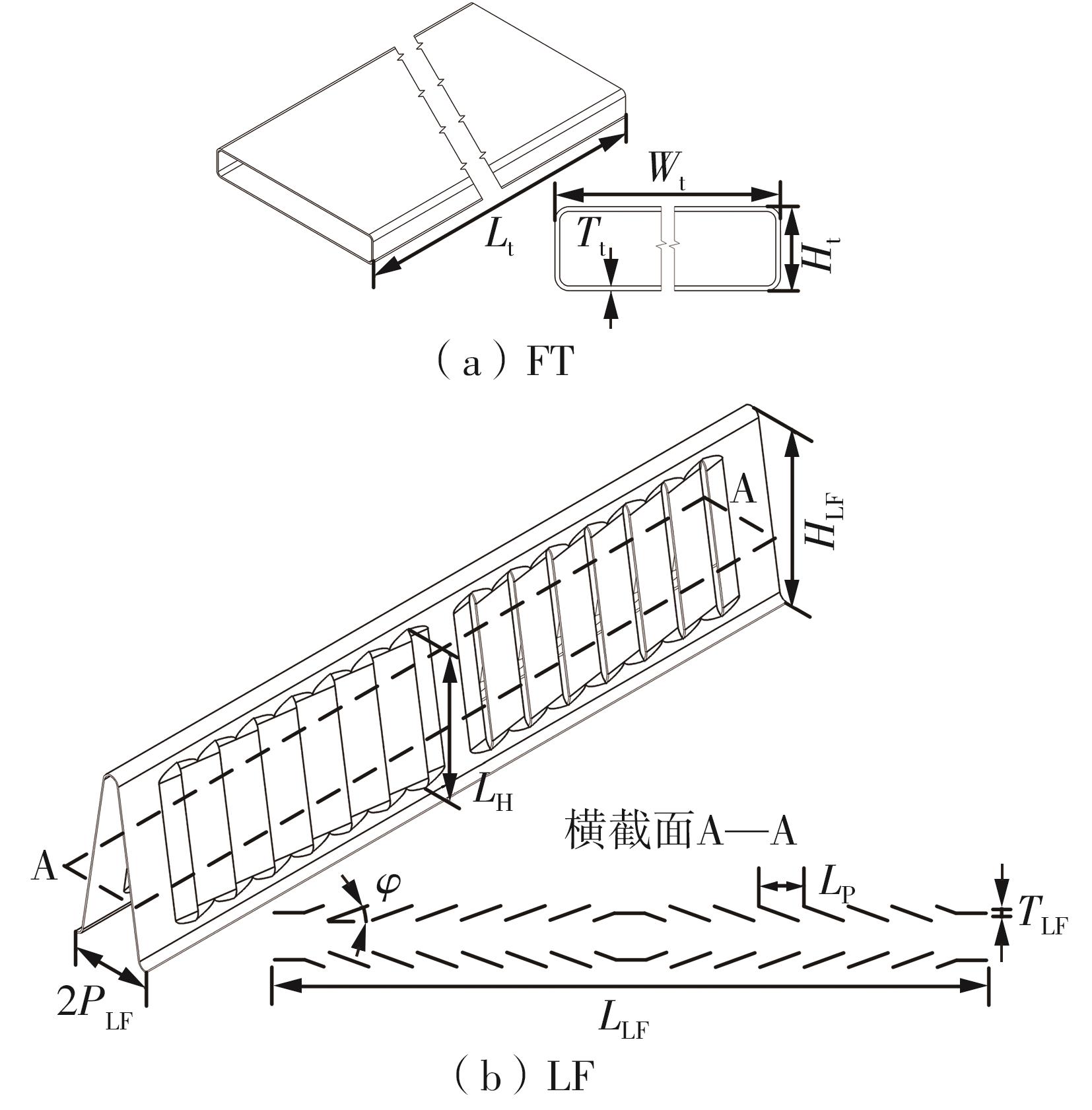
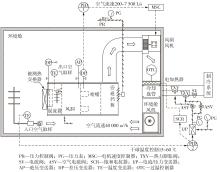
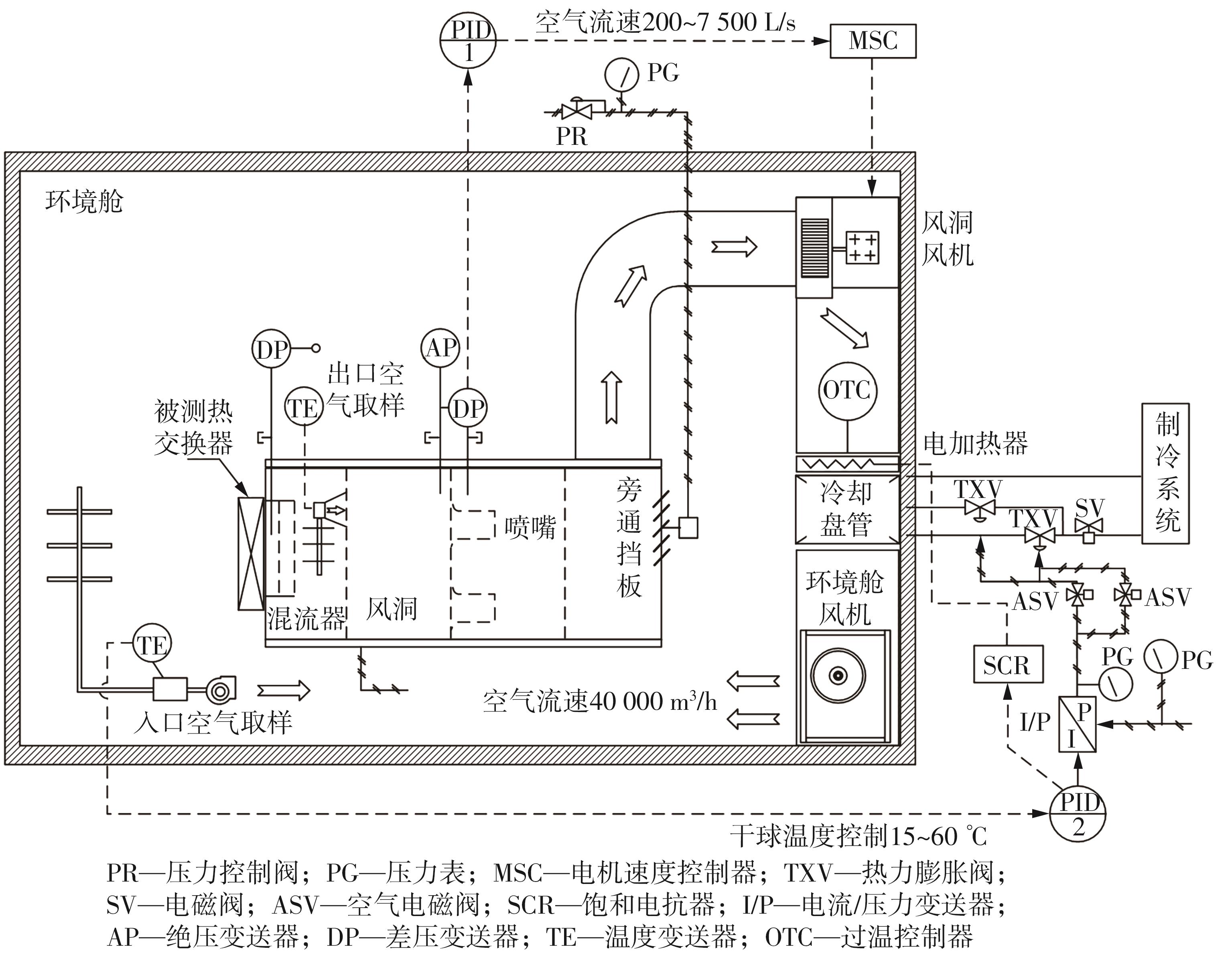
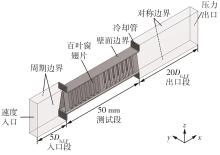
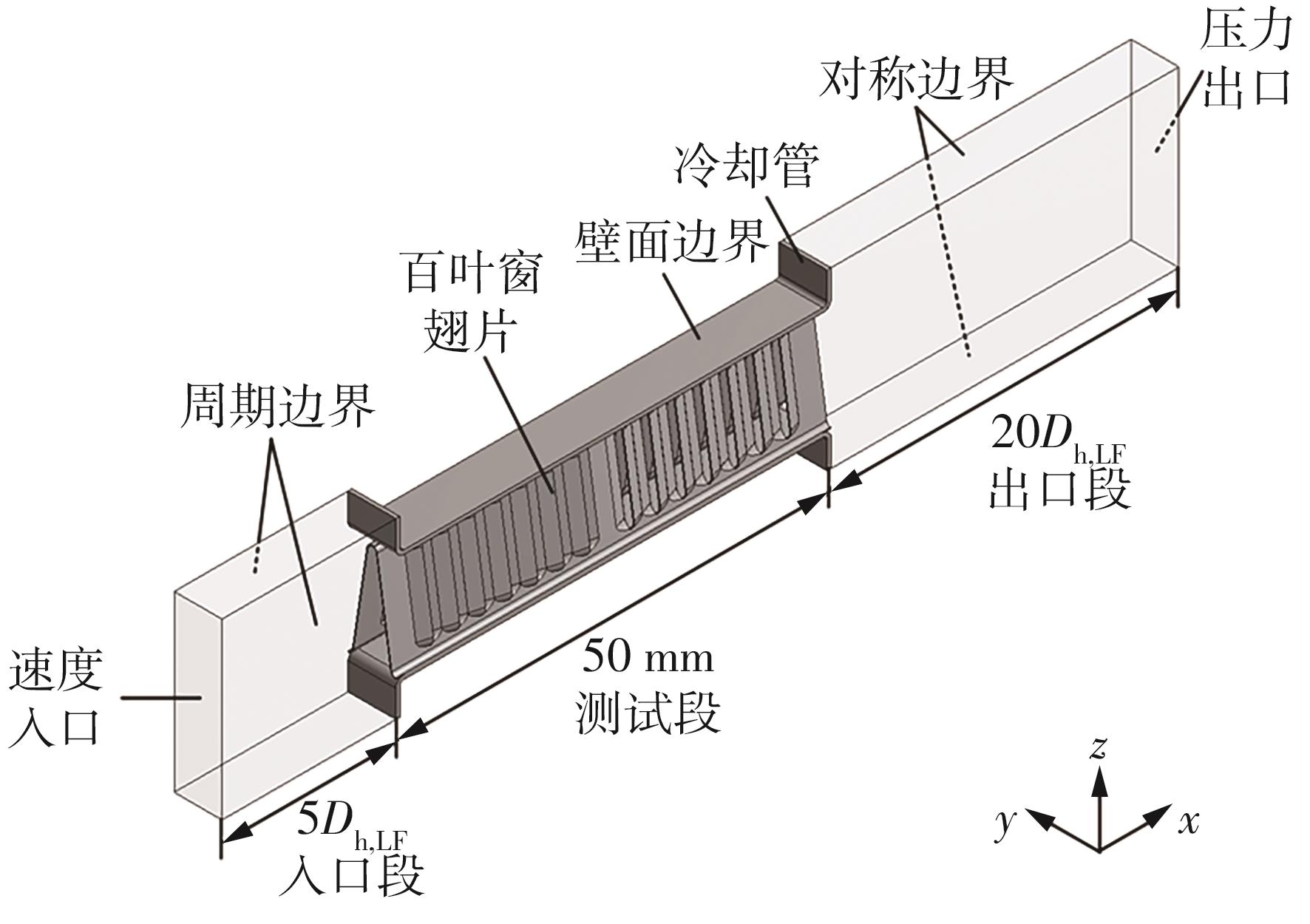
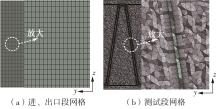
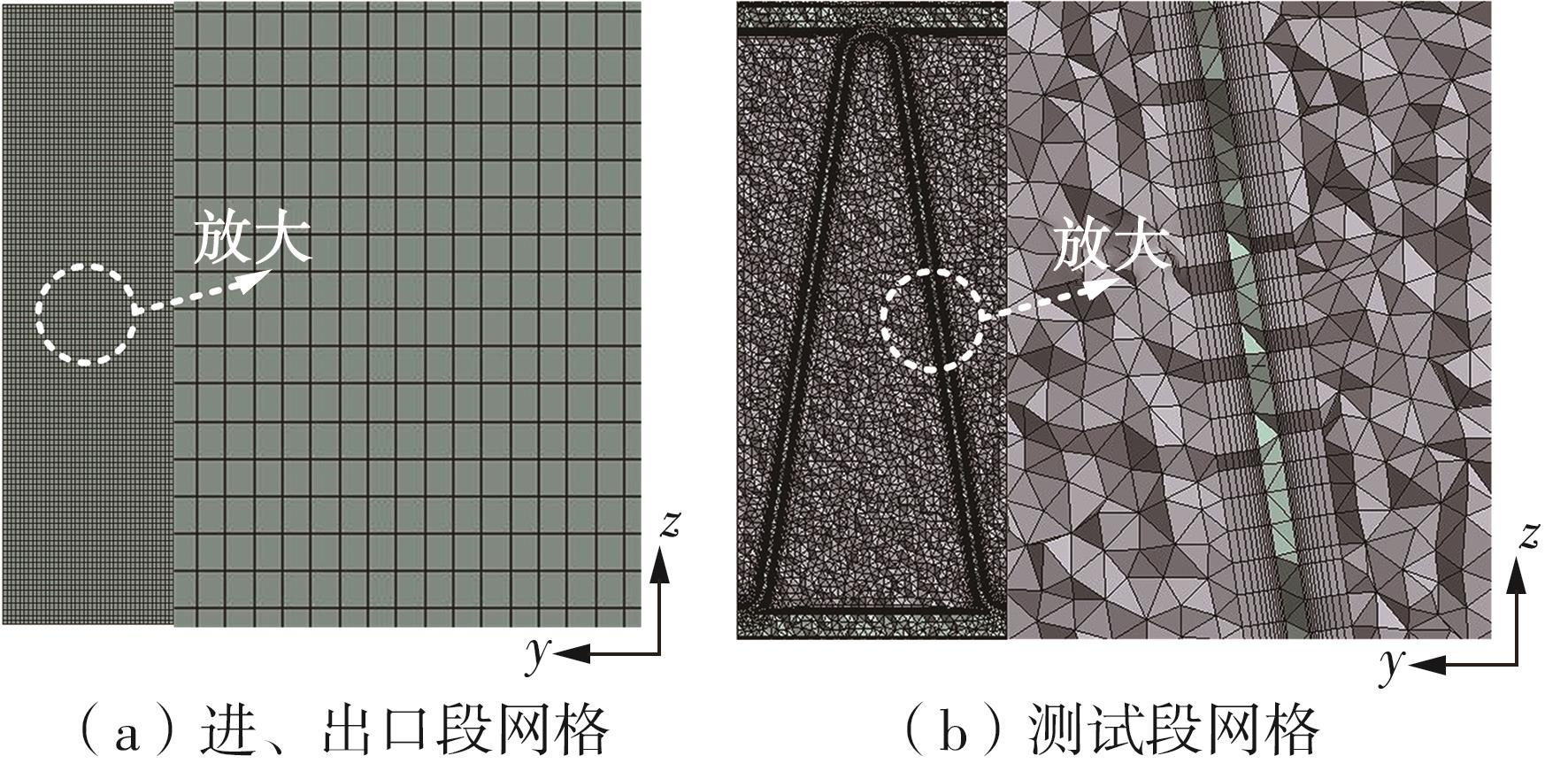
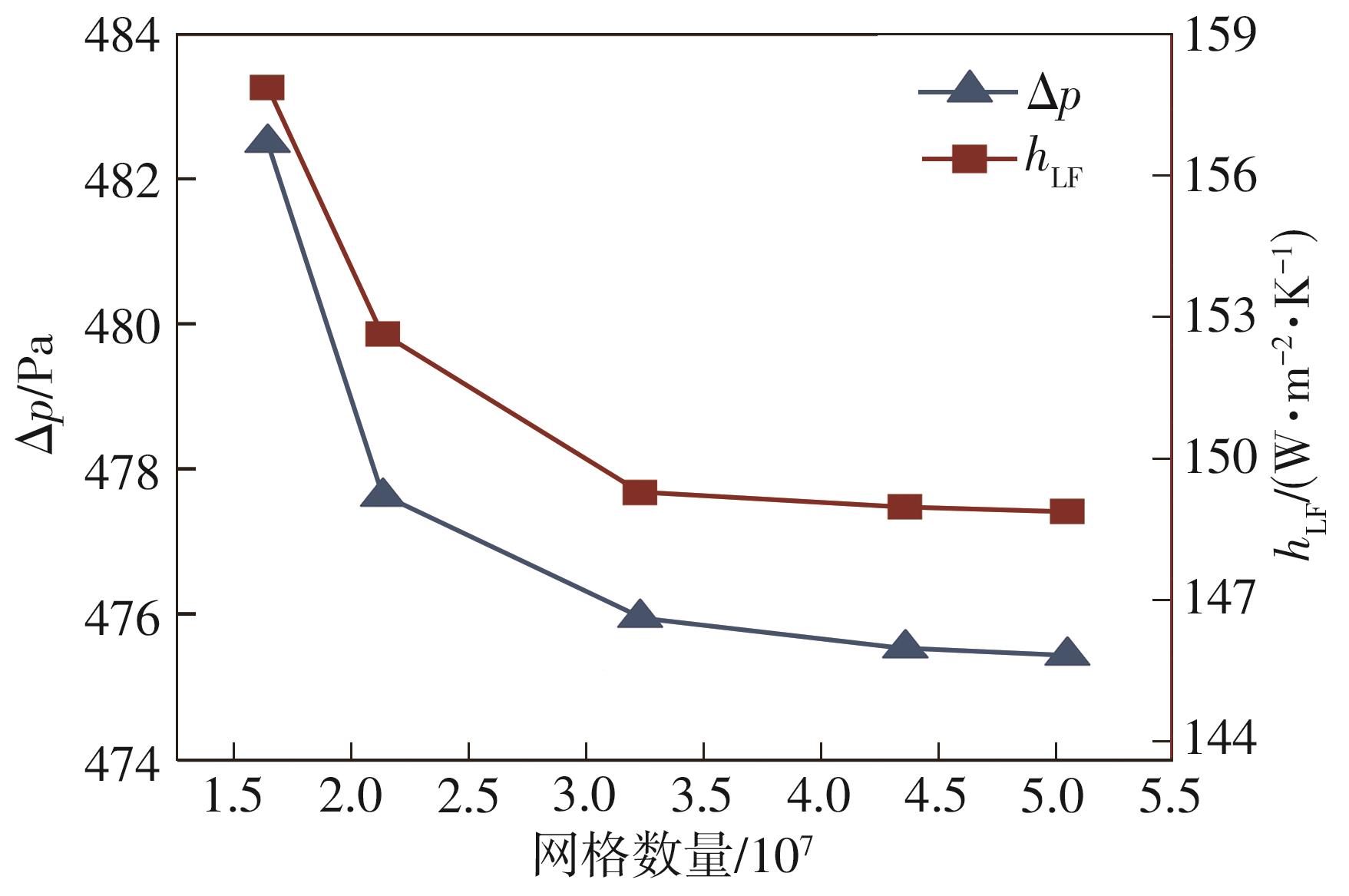
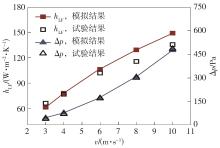
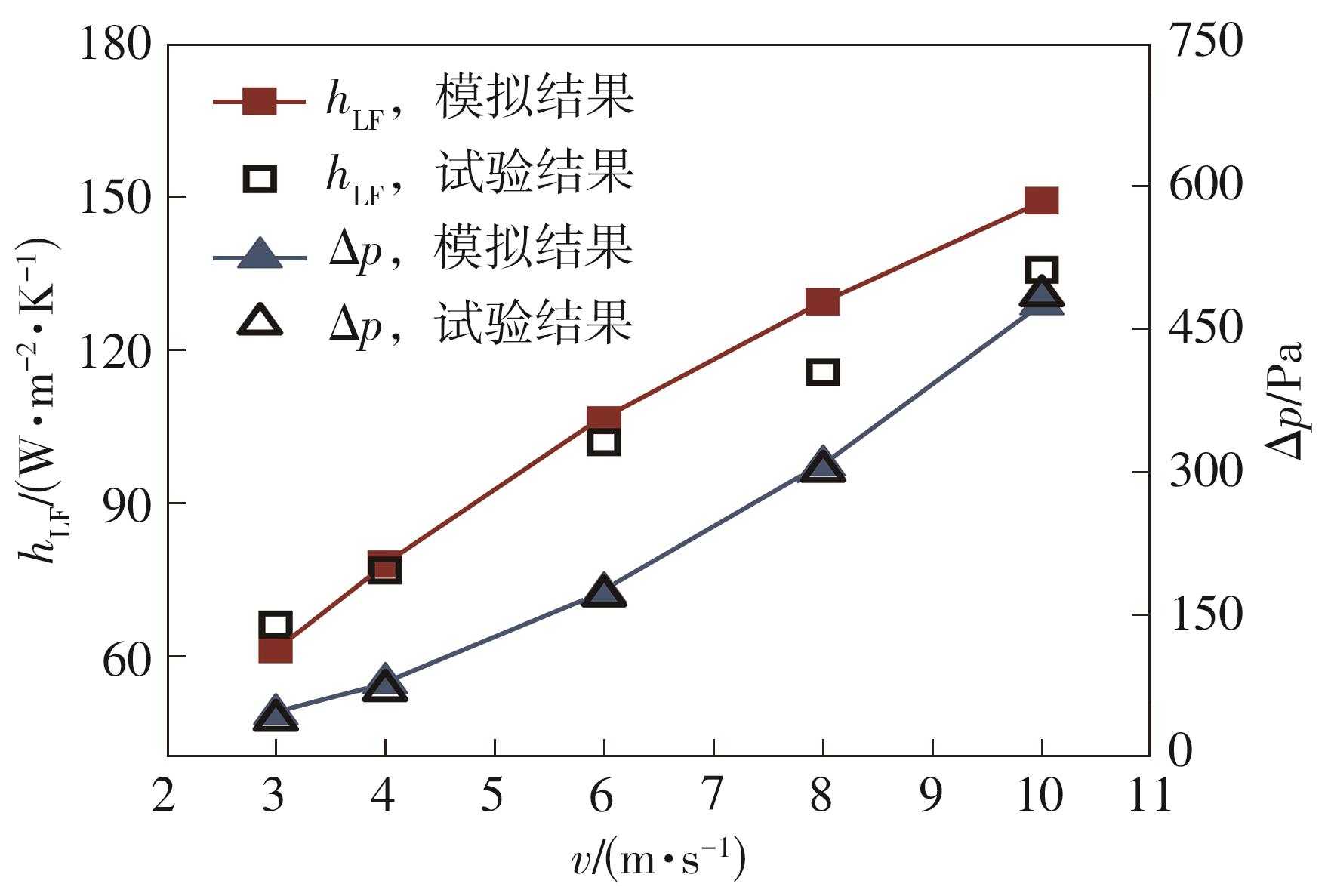
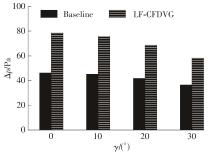
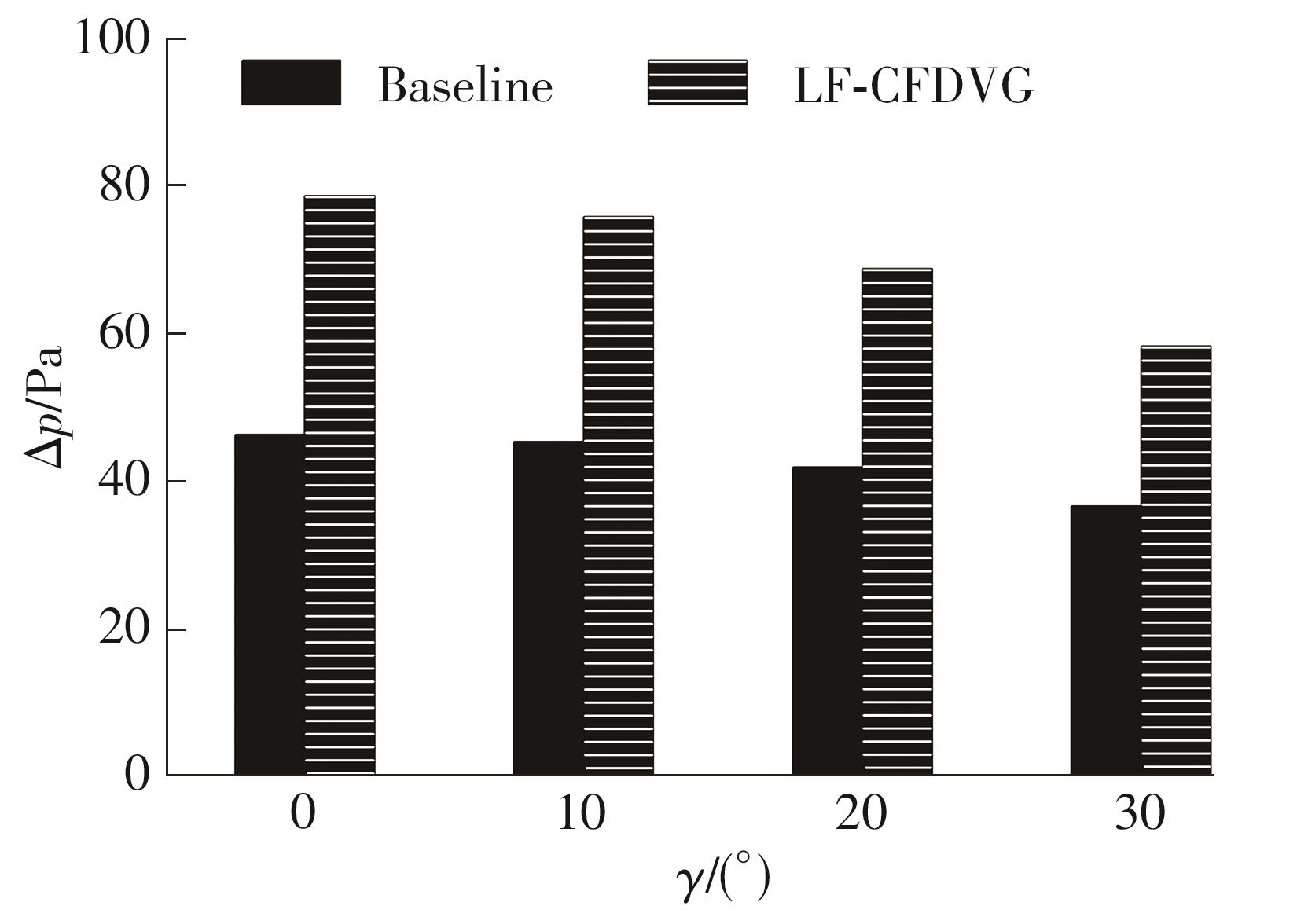
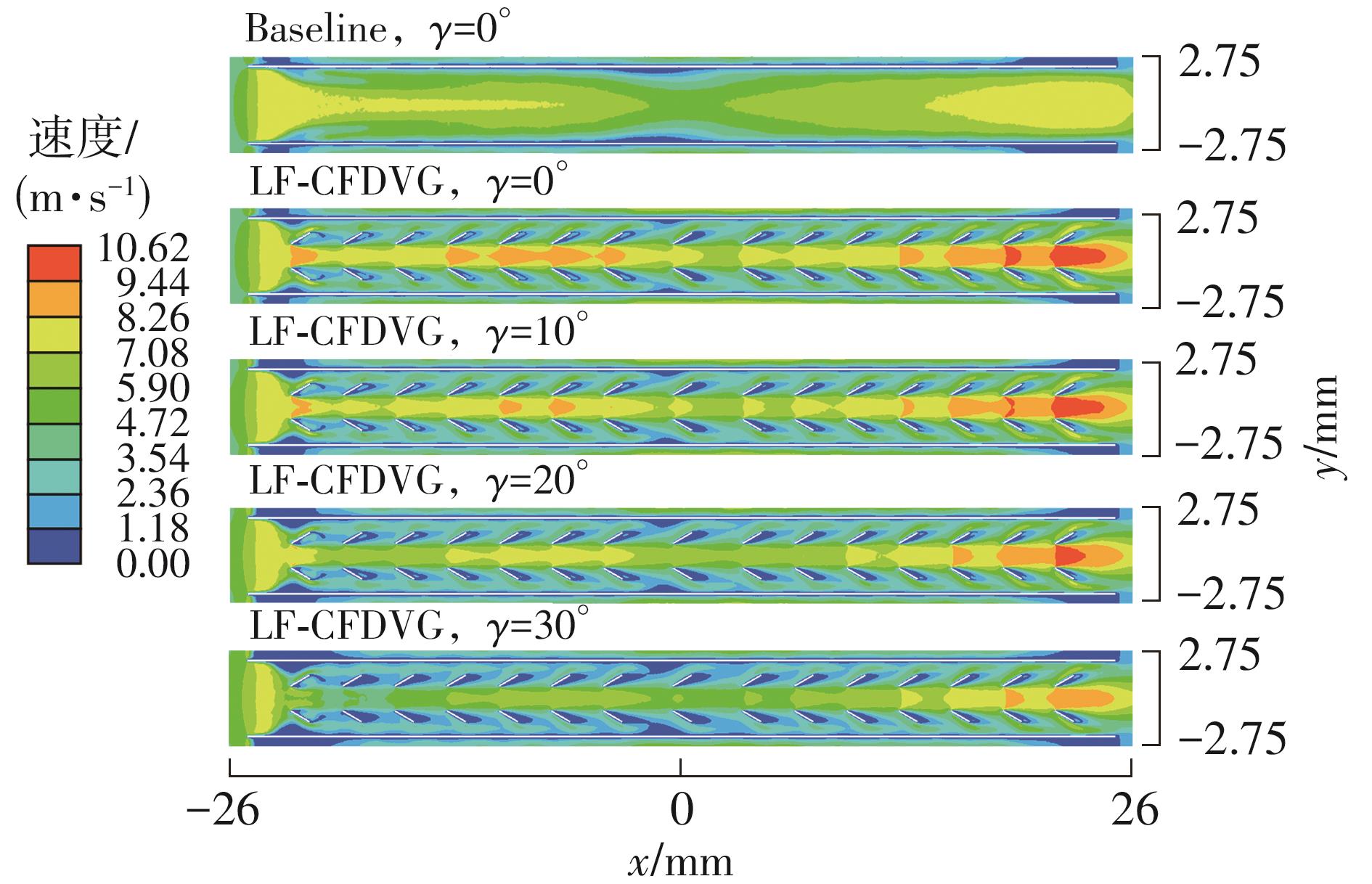
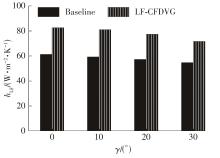
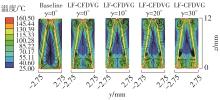
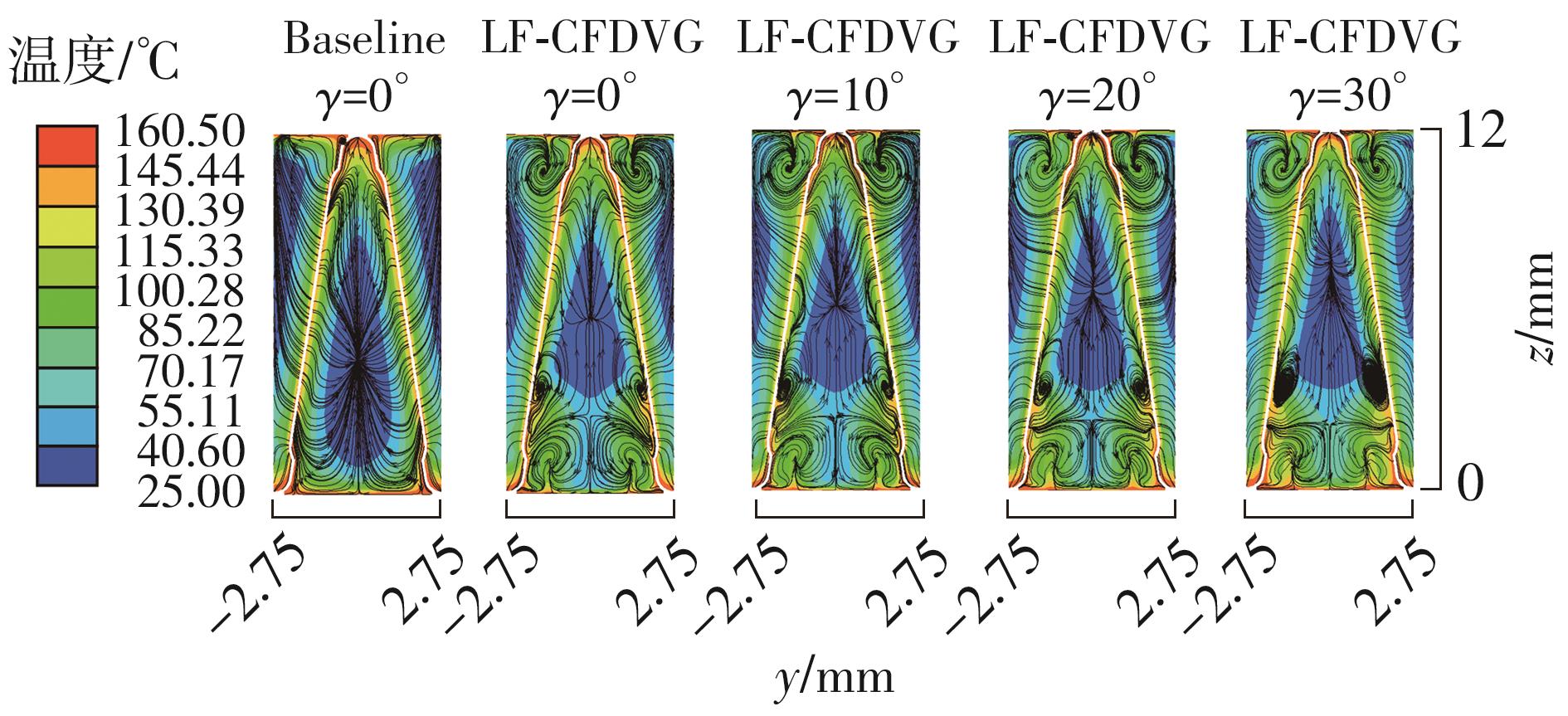
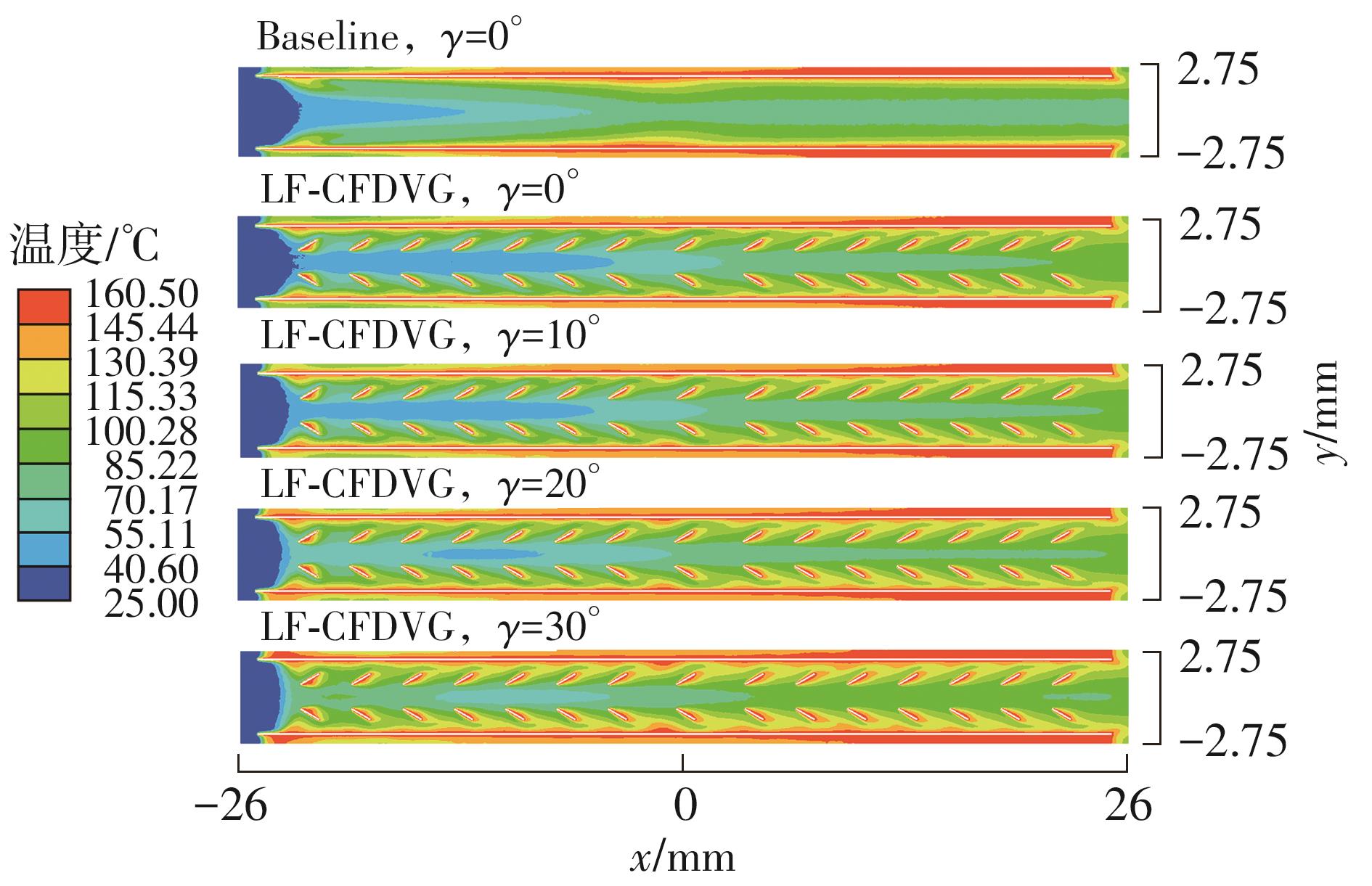
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (7): 12-20.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220701
Special Issue: 2023年机械工程
• Mechanical Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
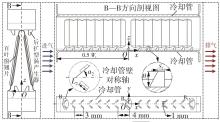
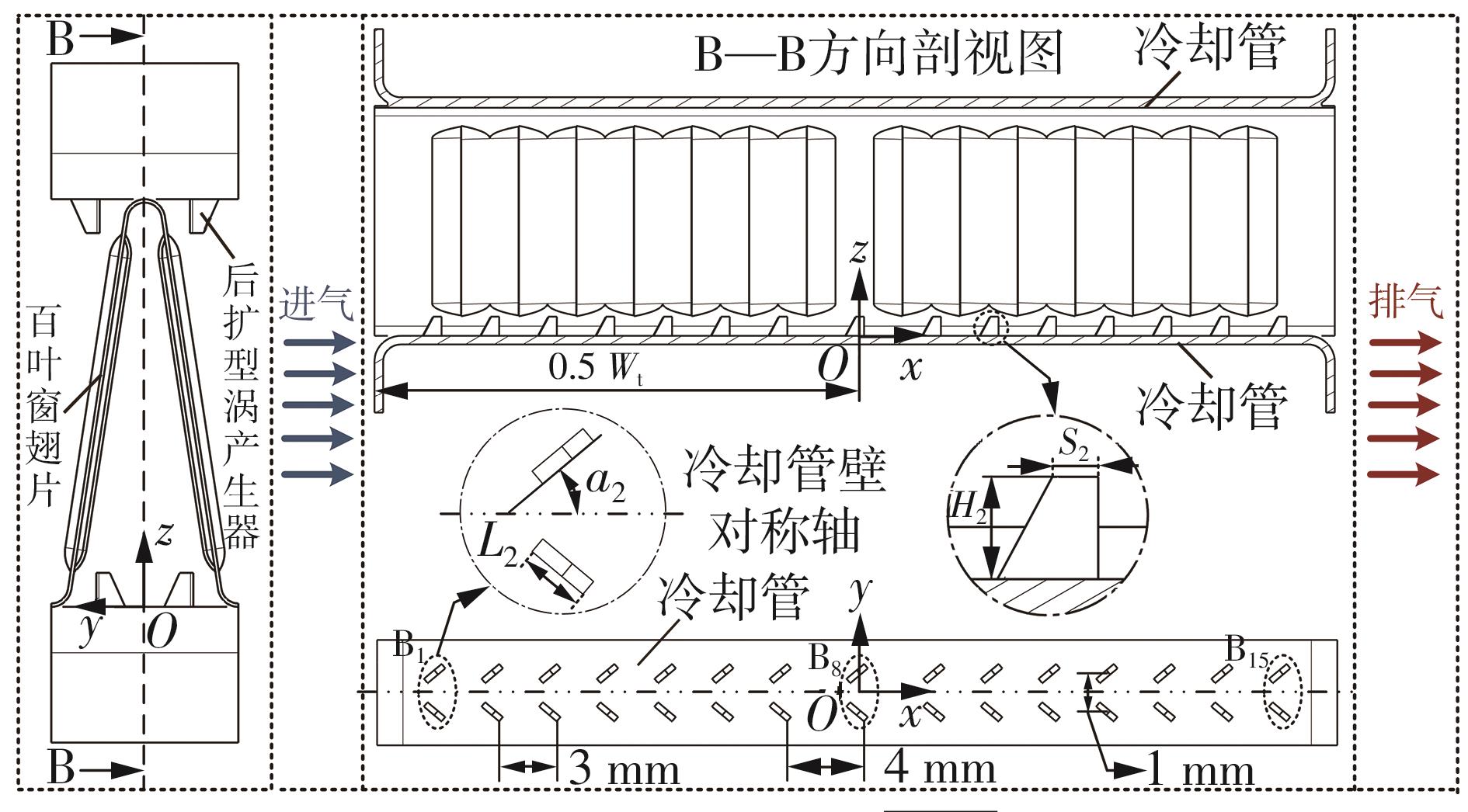
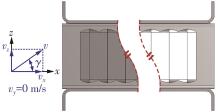
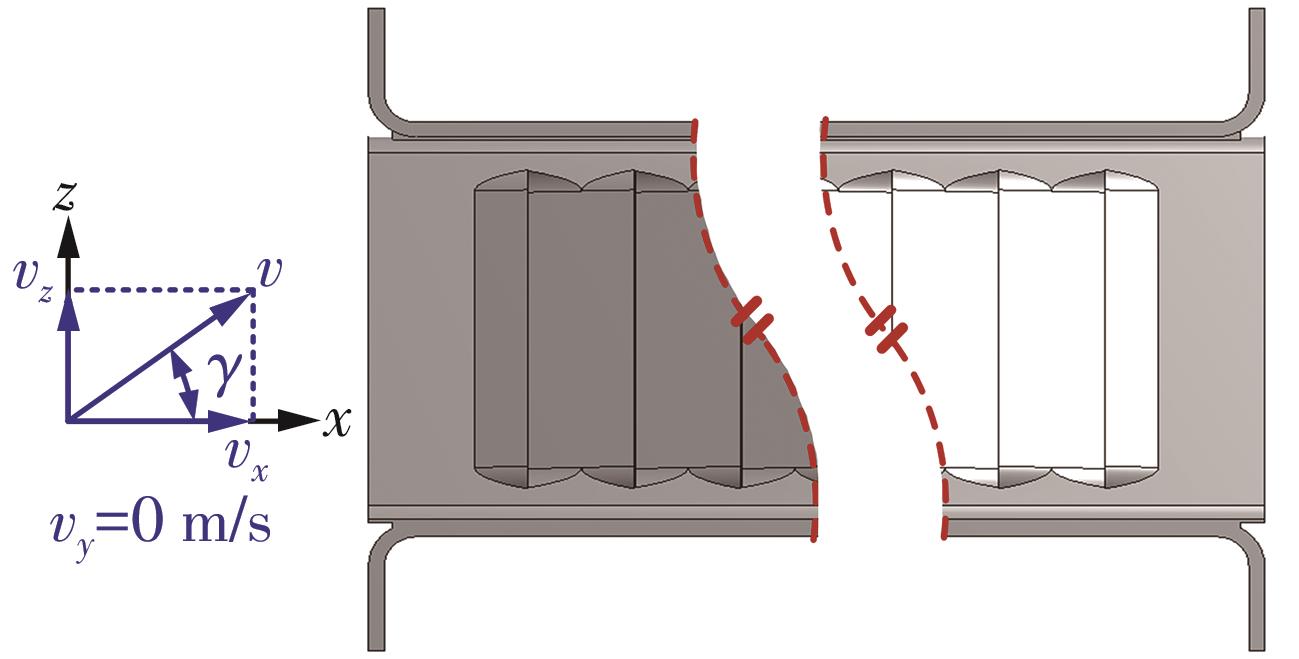
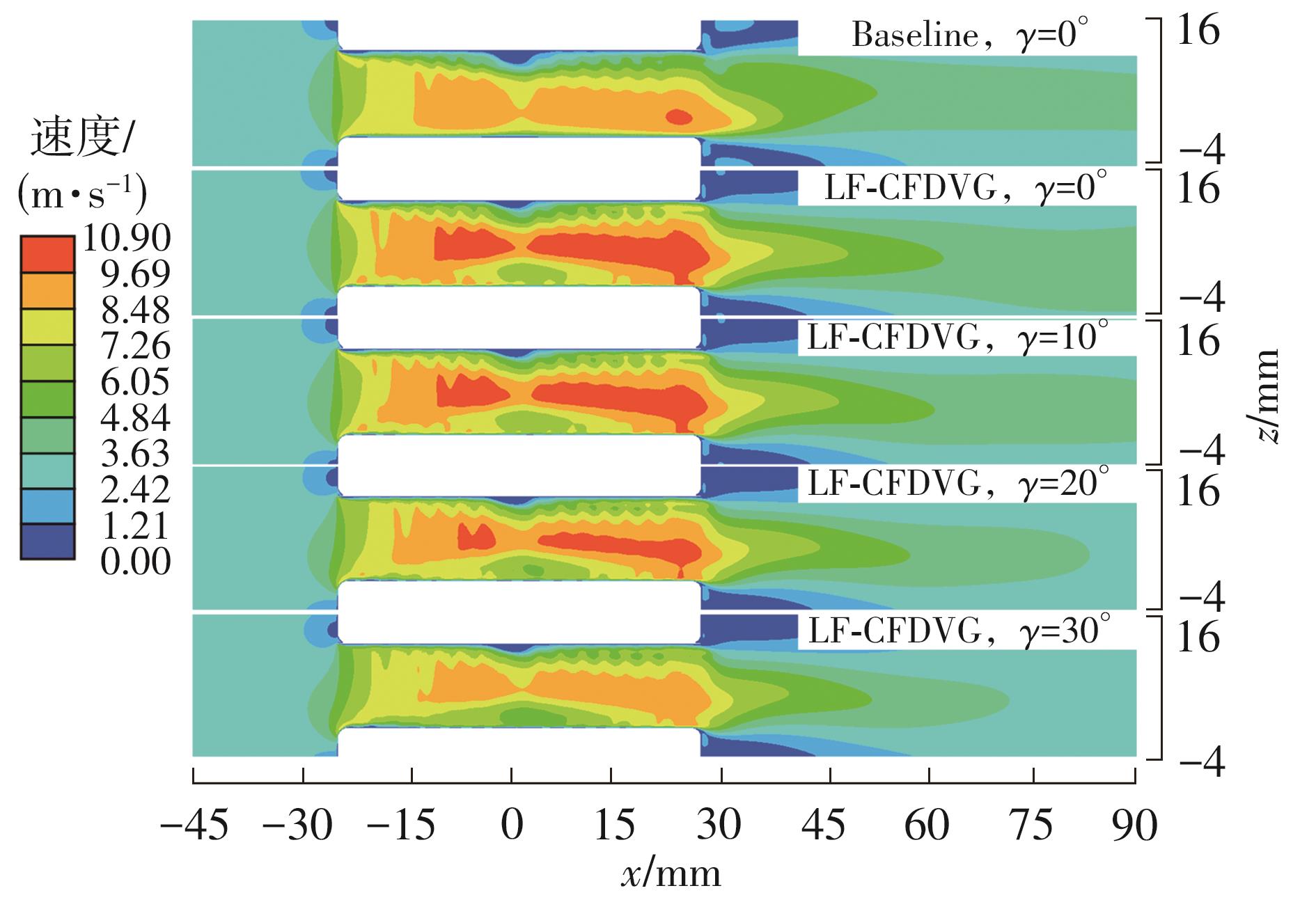
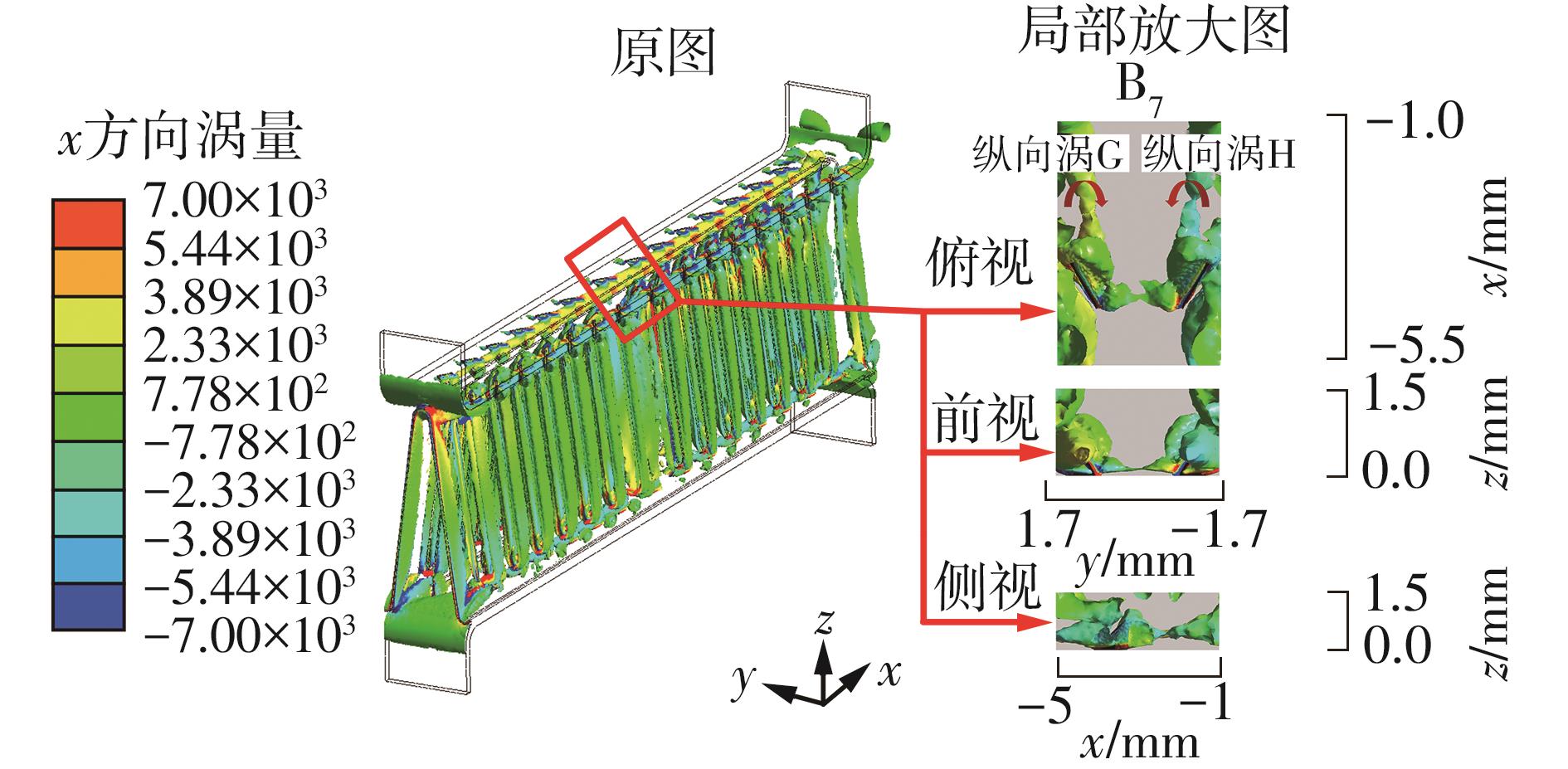
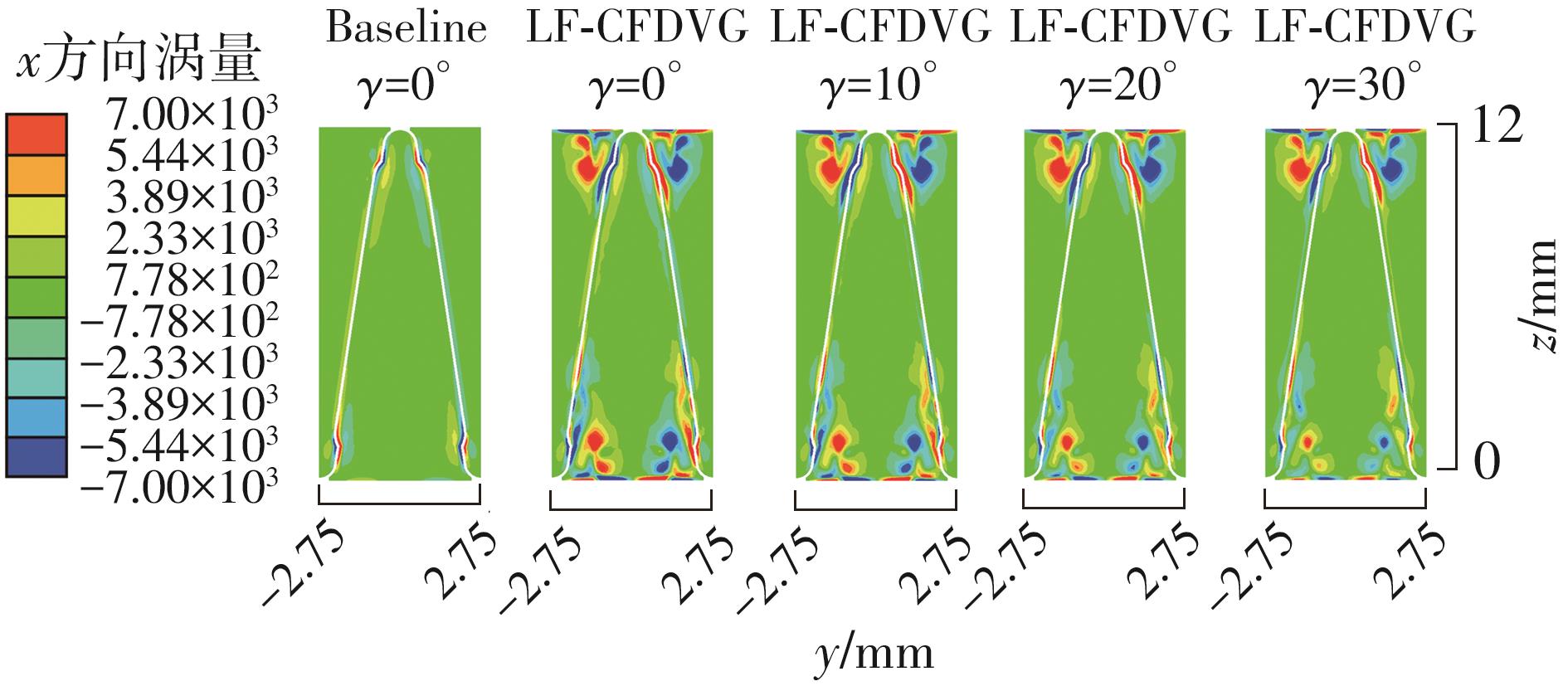
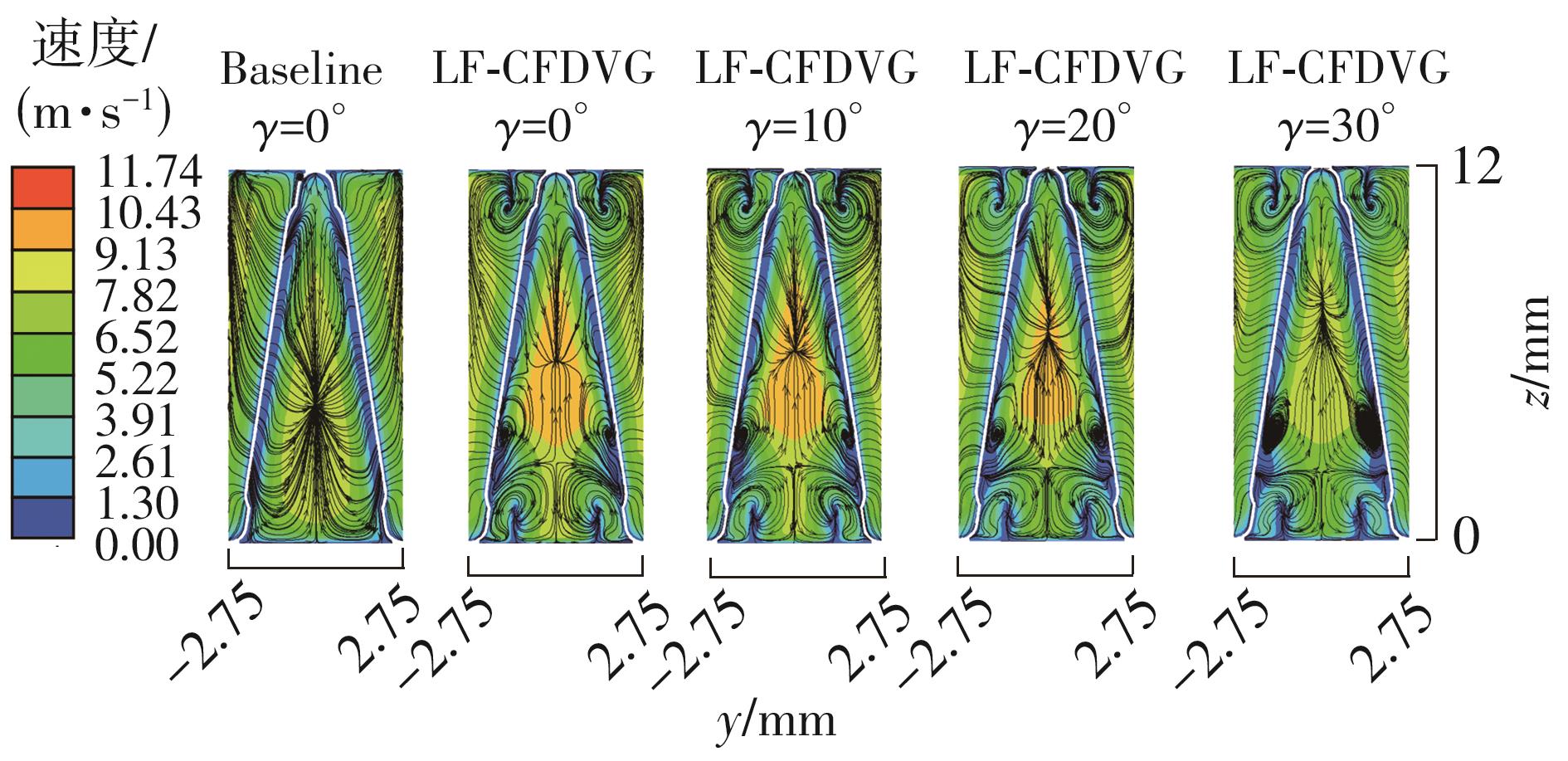
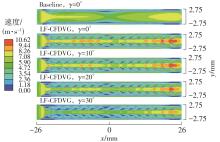
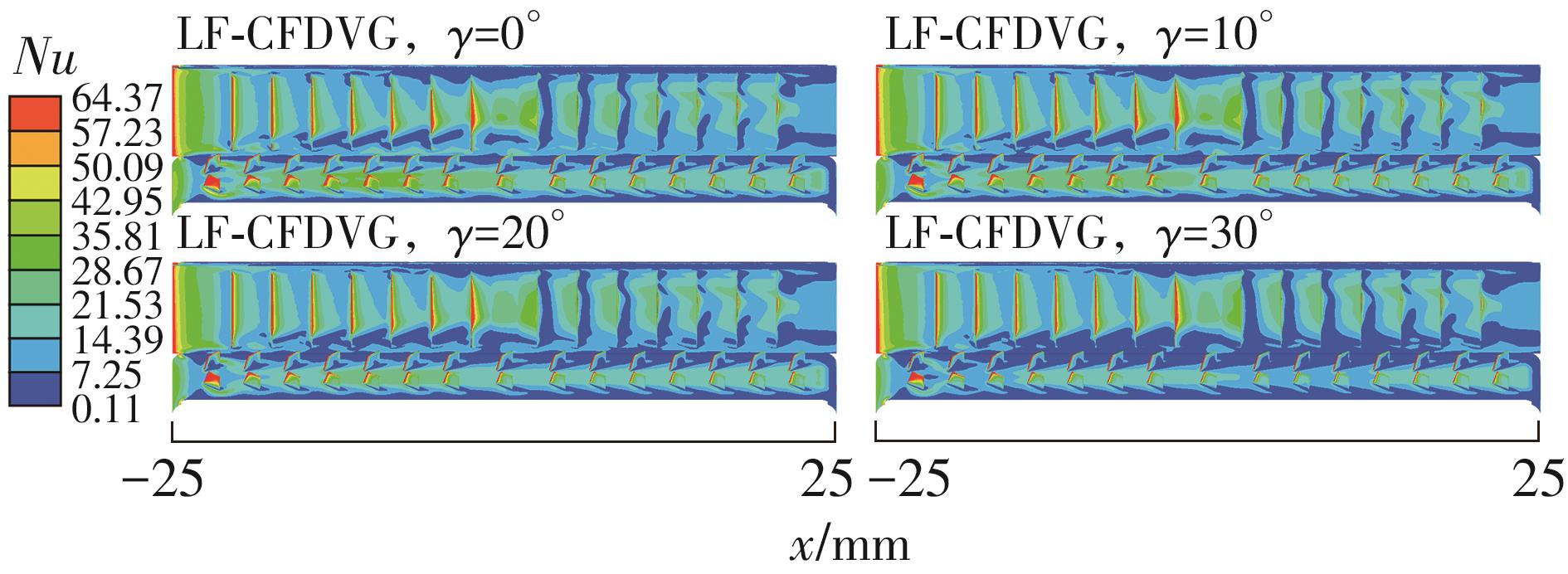
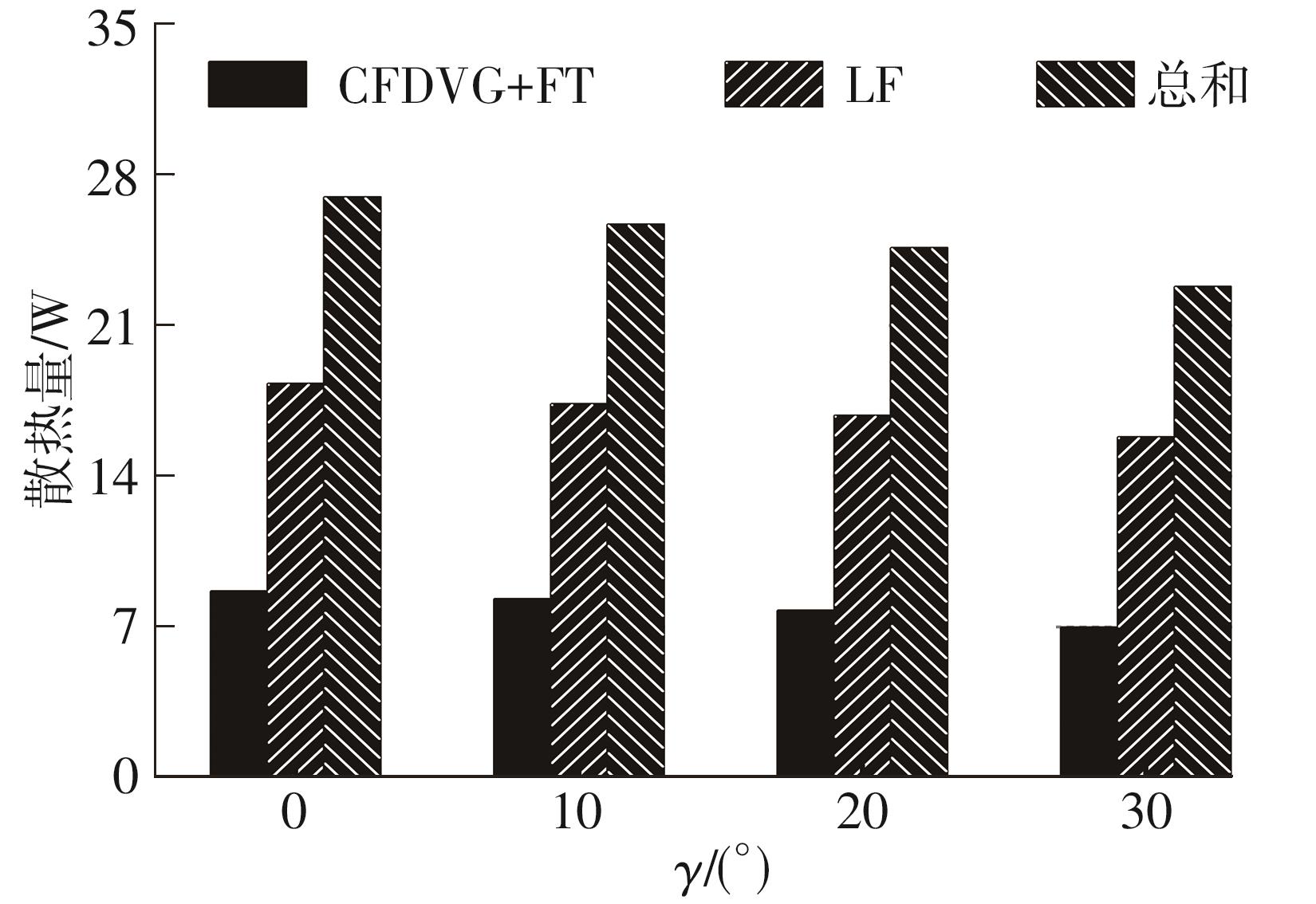
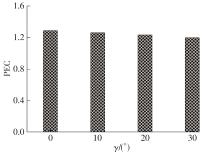
Influence of Inflow Direction on Thermal-Hydraulic Performance of Louvered Fin-Common Flow Down Vortex Generator
HU Xingjun LUO Yufei ZHANG Jinglong GUO Peng WANG Jingyu YU Tianming
- College of Automotive Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,Jilin,China
-
Received:2022-10-25Online:2023-07-25Published:2023-04-04 -
Contact:胡兴军(1976-),男,博士,教授,主要从事汽车空气动力学研究。 E-mail:hxj@jlu.edu.cn -
About author:胡兴军(1976-),男,博士,教授,主要从事汽车空气动力学研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51875238);the National Key R&D Program of China(2022YFE0208000)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HU Xingjun, LUO Yufei, ZHANG Jinglong, et al.. Influence of Inflow Direction on Thermal-Hydraulic Performance of Louvered Fin-Common Flow Down Vortex Generator[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 12-20.
share this article
| 1 | AWAIS M, BHUIYAN A A .Heat and mass transfer for compact heat exchanger (CHXs) design:a state-of-the-art review[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2018,127:359-380. |
| 2 | 中华人民共和国生态环境部 .中国移动源环境管理年报(2021) [EB/OL].(2021-09-11)[2022-08-16].. |
| 3 | WU J, LIU P, YU M,et al .Thermo-hydraulic performance and exergy analysis of a fin-and-tube heat exchanger with sinusoidal wavy winglet type vortex generators[J].International Journal of Thermal Sciences,2022,172:107274/1-18. |
| 4 | LOPES L D, YANAGIHARA J I .Heat exchanger:US006079487[P].2000-06-27. |
| 5 | LAWSON M J, THOLE K A .Heat transfer augmentation along the tube wall of a louvered fin heat exchanger using practical delta winglets[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2008,51:2346-2360. |
| 6 | DEZAN D J, SALVIANO L O, YANAGIHARA J I .Interaction effects between parameters in a flat-tube louvered fin compact heat exchanger with delta-winglets vortex generators[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2015,91:1092-1105. |
| 7 | DEZAN D J, SALVIANO L O, YANAGIHARA J I .Heat transfer enhancement and optimization of flat-tube multi-louvered fin compact heat exchangers with delta-winglet vortex generators[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2016,101:576-591. |
| 8 | PARK J, BYUN S, KIM D R,et al .Frost behavior of a louvered fin heat exchanger with vortex-generating fins[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2017,114:590-596. |
| 9 | HABIBIAN S H, ABOLMAALI A M, AFSHIN H .Numerical investigation of the effects of fin shape,antifreeze and nanoparticles on the performance of compact finned-tube heat exchangers for automobile radiator[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2018,133:248-260. |
| 10 | DEZAN D J, SALVIANO L O,JENOVENCIO,et al .Parametric investigation of heat transfer enhancement and pressure loss in louvered fins with longitudinal vortex generators[J].International Journal of Thermal Sciences,2019,135:533-545. |
| 11 | JOARDAR A, JACOBI A M .Impact of leading edge delta-wing vortex generators on the thermal performance of a flat tube,louvered-fin compact heat exchanger[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2005,48:1480-1493. |
| 12 | LI J, DANG C, HIHARA E .Heat transfer enhancement in a parallel,finless heat exchanger using a longitudinal vortex generator,part A:numerical investigation[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2019,128:87-97. |
| 13 | LI J, DANG C, HIHARA E .Heat transfer enhancement in a parallel,finless heat exchanger using a longitudinal vortex generator,part B:experimental investigation on the performance of finless and fin-tube heat exchangers[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2019,128:66-75. |
| 14 | 贾青,陈佳萍,杨志刚 .基于气动减阻和散热需求的主动格栅优化设计[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(2):264-275. |
| JIA Qing, CHEN Jiaping, YANG Zhigang .Active grille shutter optimal design based on aerodynamic drag reduction and heat dissipation requirements[J].Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2020,48(2):264-275. | |
| 15 | KIM M, YOUN B, BULLARD C W .Effect of inclination on the air-side performance of a brazed aluminum heat exchanger under dry and wet conditions[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2001,44:4613-4623. |
| 16 | HENRIKSSON L, DAHL E, GULLBERG P,et al .Experimental investigation of heat transfer rate and pressure drop through angled compact heat exchangers relative to the incoming airflow[J].SAE International Journal of Commercial Vehicles,2014,7(2):448-457. |
| 17 | CAO X, WANG X, SONG Q,et al .Experimental investigation on the heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of R600a in a minichannel condenser with different inclined angles[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2021,196:117227/1-11. |
| 18 | ZHANG J, HU X, LUO Y,et al .Effects of rectangular wing vortex generators on the thermal-hydraulic performance of louvered fin and flat tube heat exchanger[J].Journal of Thermal Science,2023,32(2):628-642. |
| 19 | SHAHSAVAR A, MORADI K, YILDIZ C,et al .Effect of nanoparticle shape on cooling performance of boehmite alumina nanofluid in a helical heat sink for laminar and turbulent flow regimes[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2022,217:107045/1-22. |
| 20 | 沙拉,塞库利克 .换热器设计技术[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2010. |
| 21 | 小约翰·D.安德森 .空气动力学基础[M].杨永,宋文萍,张正科,等译.北京:航空工业出版社,2014. |
| 22 | 林建忠,阮晓东,陈邦国,等 .流体力学[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2013. |
| 23 | SONDAERBY S K, MIRHOSSEINI M, REZANIA A,et al .Thermal-hydraulic performance of a corrugated cooling fin with louvered surfaces[J].Energy Procedia,2017,142:4077-4084. |
| [1] | ZHANG Yihan WANG Ping HU Jingfeng. Analysis of Nonlinear Rolling Damping and Rolling Motion of Asymmetric Catamaran [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(7): 26-33. |
| [2] | YING Rui, JIANG Jin, LI Yanhui, et al. Analysis of Flow Filed Characteristics and Particle Classification Performance of Inner Cone Hydrocyclone [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(4): 95-103. |
| [3] | . Transfer Function Representation of Dynamic Circulating Flow Rate of Torque Converter [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(7): 22-28. |
| [4] | Wang An-lin Cheng Wei Cao Yan Liu Wei-guo. Momentum Distribution Method of Blades of Hydraulic Torque Converter with Circumferential Uniform Acceleration [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(9): 135-140. |
| [5] | Yuan Xian-ju Guo Kong-hui . Investigation into Opening of a Pilot Relief Valve Located in a Semi-Active Damper#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(8): 91-98. |
| [6] | Gong Jin- ke Wang Yun- ke Jia Guo- hai. Simulation and Experimental Research on Performance of Decompression Engine Brake [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(9): 140-146. |
| [7] | Wang Shuo Su Yu-min Du Xin. Numerical Simulation of Planing Crafts Sailing in Calm Water and in Waves [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(4): 119-126. |
| [8] | Liu Jia-xin Qin Si-cheng Xu Zhen-yuan Zhang Ao Xi Yu Zhang Xue-lin. Comparative Analysis of Heat Exchange Performance of Vehicle Radiator Based on CFD Numerical Simulation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(5): 24-29. |
| [9] | Yan jun-wei Liu yang Zhou xuan Kang ying-zi. Energy-Saving Optimization of Air Conditioning Terminal Device Based on Numerical Simulation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(4): 144-149. |
| [10] | Chen Ke-fu Zeng Jin-song Feng Yu-cheng Li Jun. Flow and Simulation of Pulp Fiber Suspensions [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(10): 20-27. |
| [11] | Zeng Jin-song Chen Ke-fu Li Jun Xu Jun. CFD-Based Investigation into Flow Field of S-Type Discharger at the Bottom of High-Consistency Pulp-Bleaching Tower [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(1): 24-29. |
| [12] | Wu Jia-ming Deng Wei Lai Hua-wei . Numerical Simulation of Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Ducted Propeller in Turning Motion [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(7): 90-96. |
| [13] | Zhang De-man Li Shun-ming Men Xiu-hua . CFD Investigation into Pressure Loss of Single-Cylinder Engine Muffler [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(3): 129-132. |
| [14] | Xiao Yi-qing Li Chao Ou Jin-ping Song Li-li Li Qiu-sheng. CFD Approach to Evaluation of Wind Energy in Complex Terrain [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(9): 30-35. |
| [15] | Liu Jing Zhang Wen-wu Shao Jian-tao. CFD Simulation of Convective Heat-Transfer Coefficient of External Surfaces of Buildings [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(8): 94-98. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||