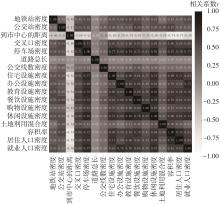
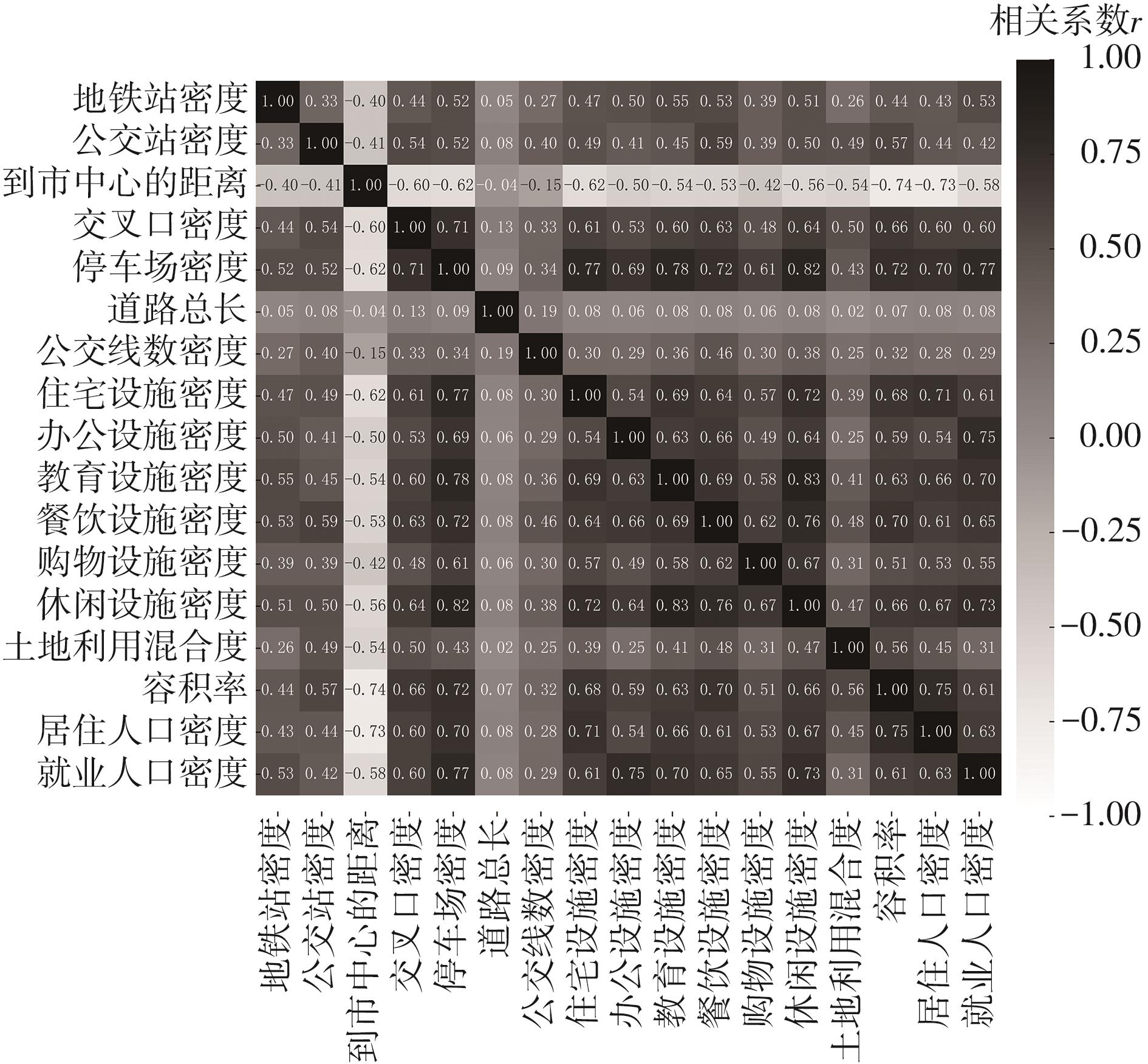
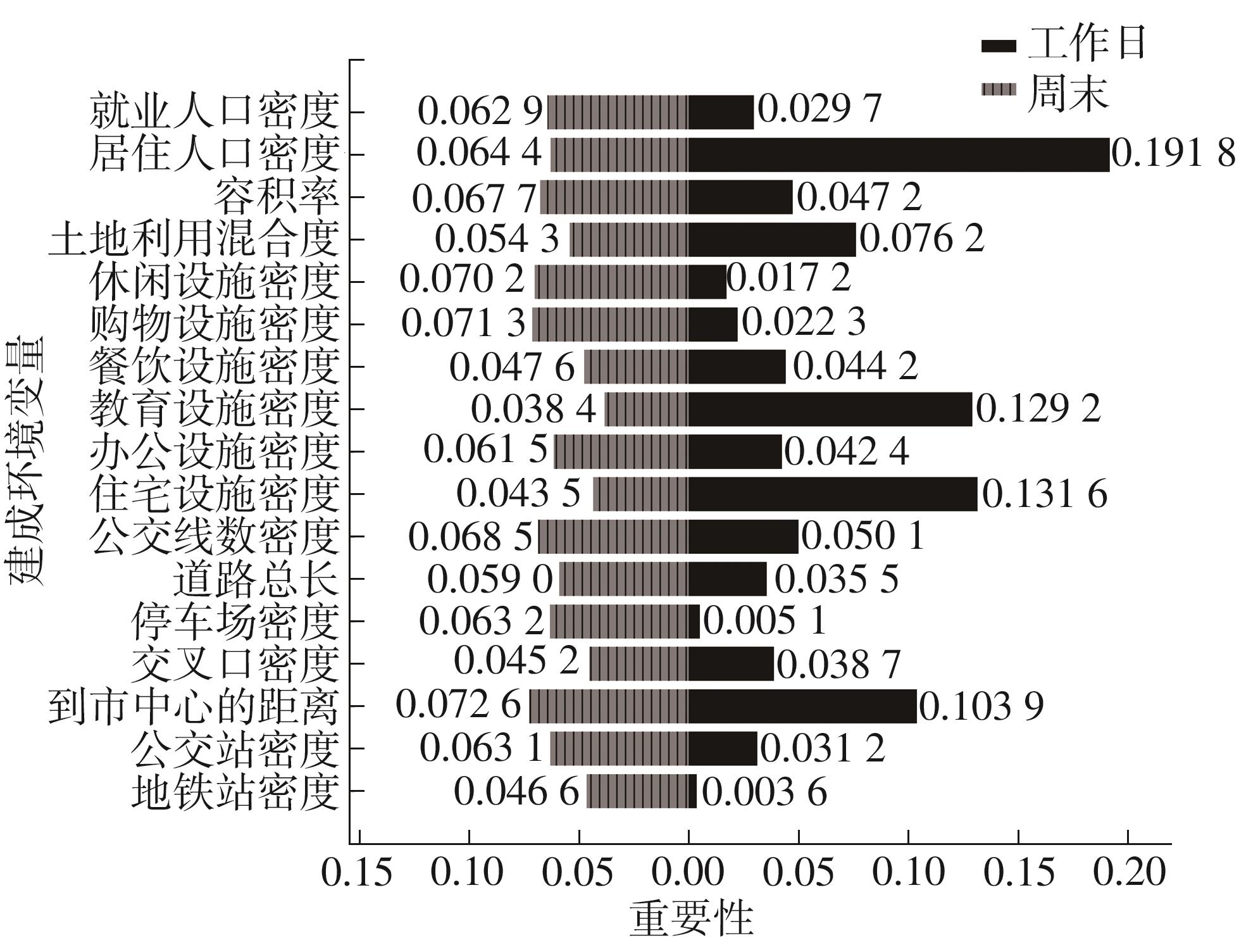
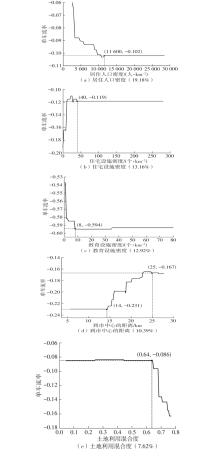
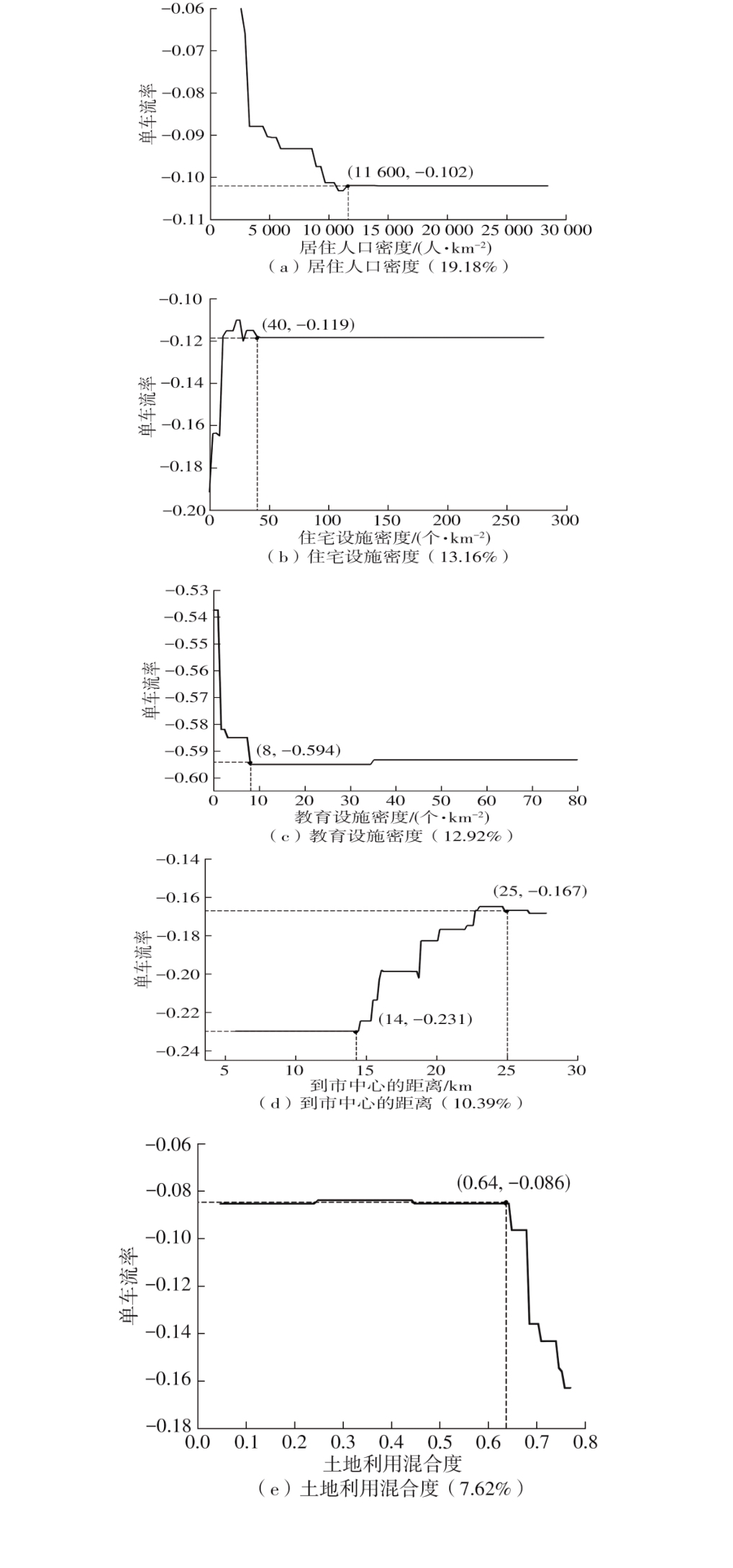
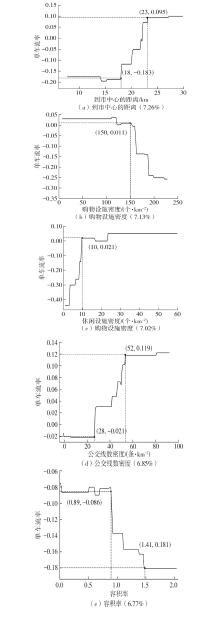
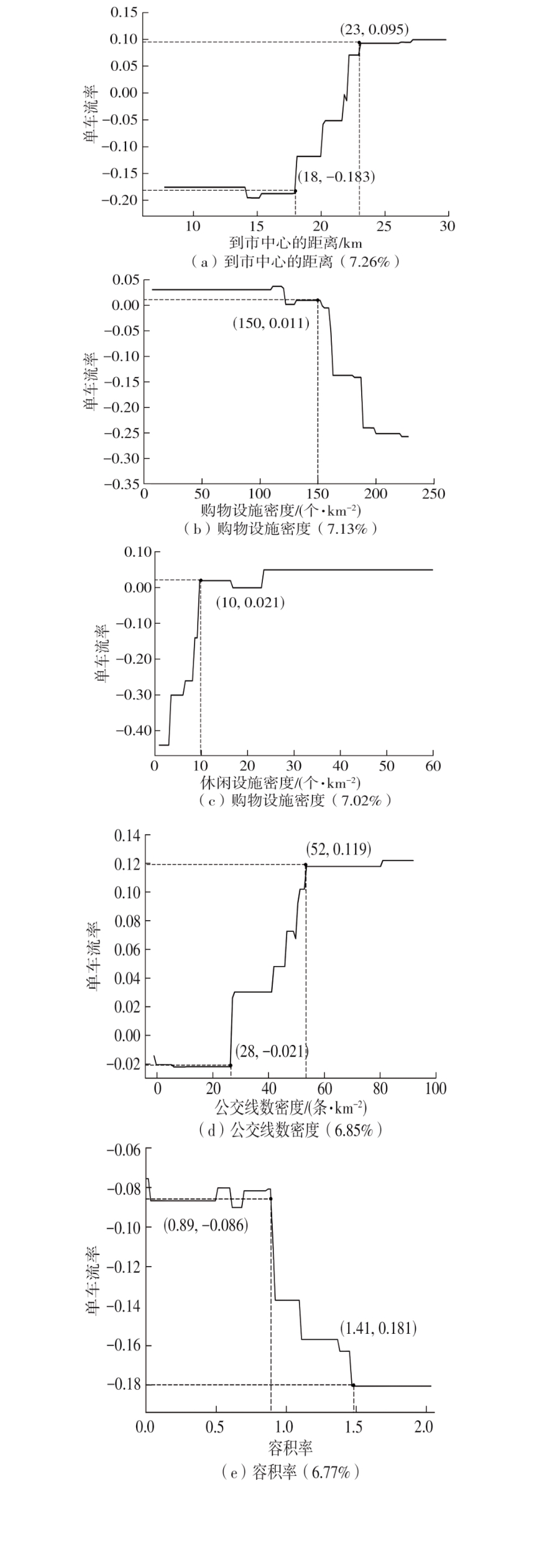
| 1 |
DU Y C, DENG F W, LIAO F X .A model framework for discovering the spatio-temporal usage patterns of public free-floating bike-sharing system[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2019,103:39-55.
|
| 2 |
LI W X, CHEN S W, DONG J S,et al .Exploring the spatial variations of transfer distances between dockless bike-sharing systems and metros[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2021,92:1-11.
|
| 3 |
PAL A, ZHANG Y .Free-floating bike sharing:Solving real-life large-scale static rebalancing problems[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2017,80:92-116.
|
| 4 |
YANG H T, ZHANG Y B, ZHONG L Z,et al .Exploring spatial variation of bike sharing trip production and attraction:a study based on Chicago’s Divvy system[J].Applied Geography,2020,115:1-11.
|
| 5 |
EL-ASSI W, MAHMOUD M S, HABIB K N .Effects of built environment and weather on bike sharing demand:a station level analysis of commercial bike sharing in Toronto[J].Transportation,2017,44(3):589-613.
|
| 6 |
莫海彤,魏宗财,翟青 .老城区共享单车出行特征及影响因素研究——以广州为例[J].南方建筑,2019(1):7-12.
|
|
MO Haitong, WEI Zongcai, ZHAI Qing .Travel behaviors and influencing factors of bike sharing in old town:the case of Guangzhou[J].South Architecture,2019(1):7-12.
|
| 7 |
MATEO-BABIANO I, BEAN R, CORCORAN J,et al .How does our natural and built environment affect the use of bicycle sharing?[J].Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice,2016,94:295-307.
|
| 8 |
曹小曙,罗依 .中国大陆城市建成环境与共享单车配置的关系[J].中山大学学报(自然科学版),2020,59(1):77-85.
|
|
CAO Xiaoshu, LUO Yi .Relationship between built environment and bikeshare allocation in the mainland of China[J].Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni(Natural Science Edition),2020,59(1):77-85.
|
| 9 |
ALCORN L G, JIAO J F .Bike-sharing station usage and the surrounding built environments in major Texas cities[J].Journal of Planning Education and Research,2019(7):1-14.
|
| 10 |
WANG X Z, LINDSEY G, SCHONER J E,et al .Modeling bike share station activity:Effects of nearby businesses and jobs on trips to and from stations[J].Journal of Urban Planning and Development,2016,142(1):04015001.
|
| 11 |
严亚磊,于涛,沈丽珍 .共享单车出行的建成环境影响机制——以上海市为例[J].上海城市规划,2020(6):85-91.
|
|
YAN Yalei, YU Tao, SHEN Lizhen .The impact mechanism of built environment on shared bikes travel:a case study of Shanghai[J].Shanghai Urban Planning Review,2020(6):85-91.
|
| 12 |
DING C, CAO X Y, WANG Y P .Synergistic effects of the built environment and commuting programs on commute mode choice[J].Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice,2018,118:104-118.
|
| 13 |
MA T, LIU C, ERDOGAN S .Bicycle sharing and public transit:does Capital Bikeshare affect Metrorail ridership in Washington,DC?[J].Transportation Research Record,2015,2534(1):1-9.
|
| 14 |
ZHAO D, ONG G P, WANG W,et al .Effect of built environment on shared bicycle reallocation:A case study on Nanjing,China[J].Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice,2019,128:73-88.
|
| 15 |
上海市交通委员会 .2020年上海市互联网租赁自行车经营服务报告[EB/OL].[2021-01-15]..
|
| 16 |
吴文静,景鹏,贾洪飞,等 .基于K均值聚类与随机森林算法的居民低碳出行意向数据挖掘[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(7):105-111.
|
|
WU Wenjing, JING Peng, JIA Hongfei,et al .Low carbon travel intention data mining for residents based on k-means clustering and random forest algorithm[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2019,47(7):105-111.
|
| 17 |
FAGHIH-IMANI A, ELURU N, EL-GENEIDY A M,et al .How land-use and urban form impact bicycle flows:evidence from the bicycle-sharing system (BIXI) in Montreal[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2014,41:306-314.
|
| 18 |
GUO D S, ZHU X, JIN H,et al .Discovering spatial patterns in origin‐destination mobility data[J].Transactions in GIS,2012,16(3):411-429.
|
| 19 |
CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C .Xgboost:a scalable tree boosting system[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd Acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining,USA:ACM,2016:785-794.
|
| 20 |
MOLNAR C,Interpretable machine learning[M].USA:Leanpub,2020:147-154.
|
| 21 |
高楹,宋辞,郭思慧,等 .接驳地铁站的共享单车源汇时空特征及其影响因素[J].地球信息科学学报,2021,23(1):155-170.
|
|
GAO Ying, SONG Ci, GUO Sihui,et al .Spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of source and sink of dockless sharing bicycles connected to subway stations[J].Journal of Geo-Information Science,2021,23(1):155-170.
|
| 22 |
ZHAO J B, WANG J, DENG W .Exploring bikesharing travel time and trip chain by gender and day of the week[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2015,58:251-264.
|
| 23 |
马新卫,季彦婕,金雨川,等 .基于时空地理加权回归的共享单车需求影响因素分析[J].吉林大学学报(工学版),2020,50(4):1344-1354.
|
|
MA Xinwei, JI Yanjie, JIN Yuchuan,et al .Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in dockless bikeshare usage demand[J].Joural of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition),2020,50(4):1344-1354.
|
| 24 |
WANG F R, ROSS C L .Machine learning travel mode choices:comparing the performance of an extreme gradient boosting model with a multinomial logit model[J].Transportation Research Record,2018,2672(47):35-45.
|
| 25 |
孔静 .无桩式共享单车站点需求预测及调度路径优化研究[D].西安:长安大学,2018.
|
| 26 |
ZHANG Y, THOMAS T, BRUSSEL M,et al .Exploring the impact of built environment factors on the use of public bikes at bike stations:case study in Zhongshan,China[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2017,58:59-70.
|