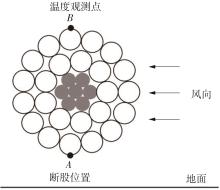
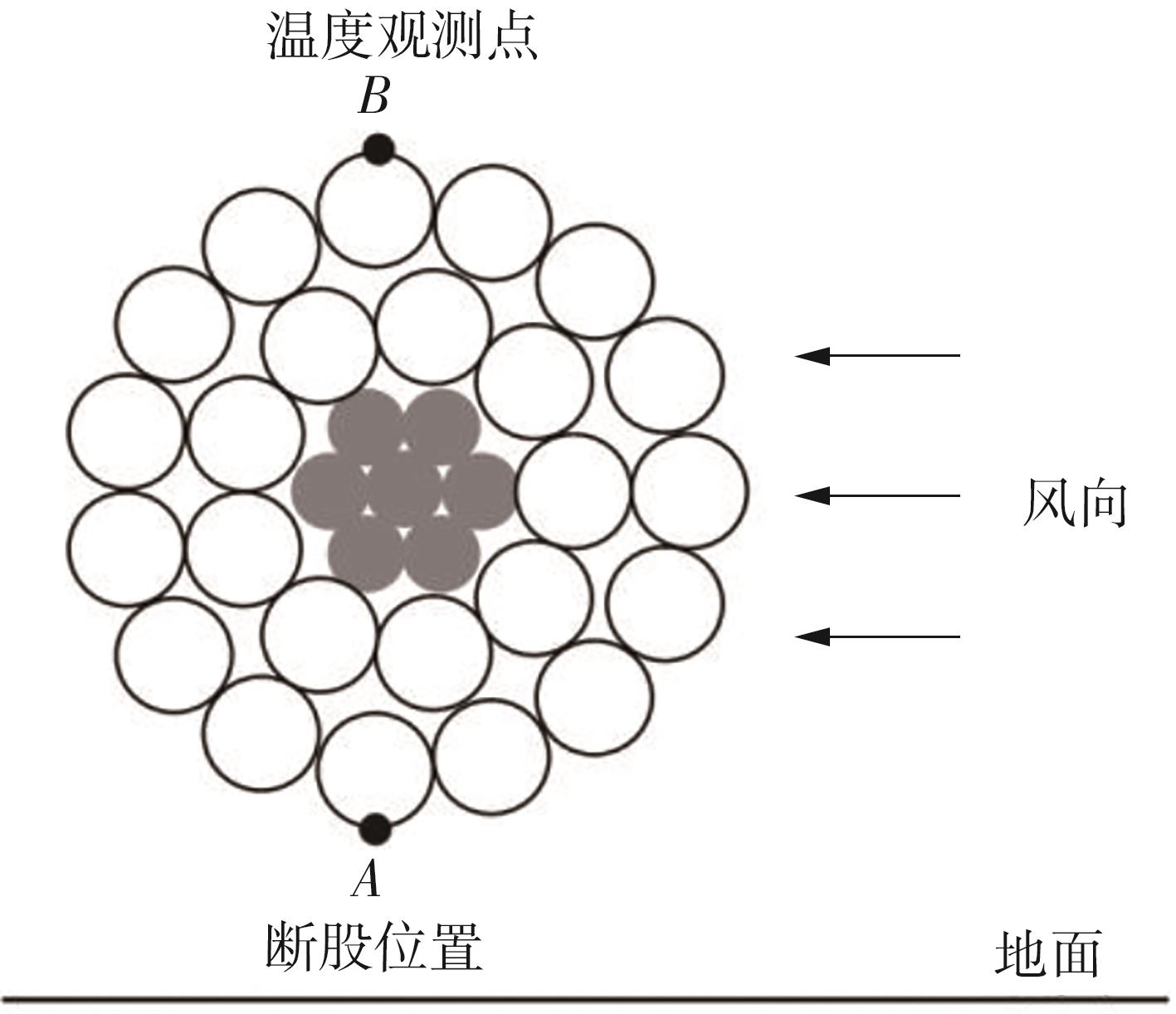
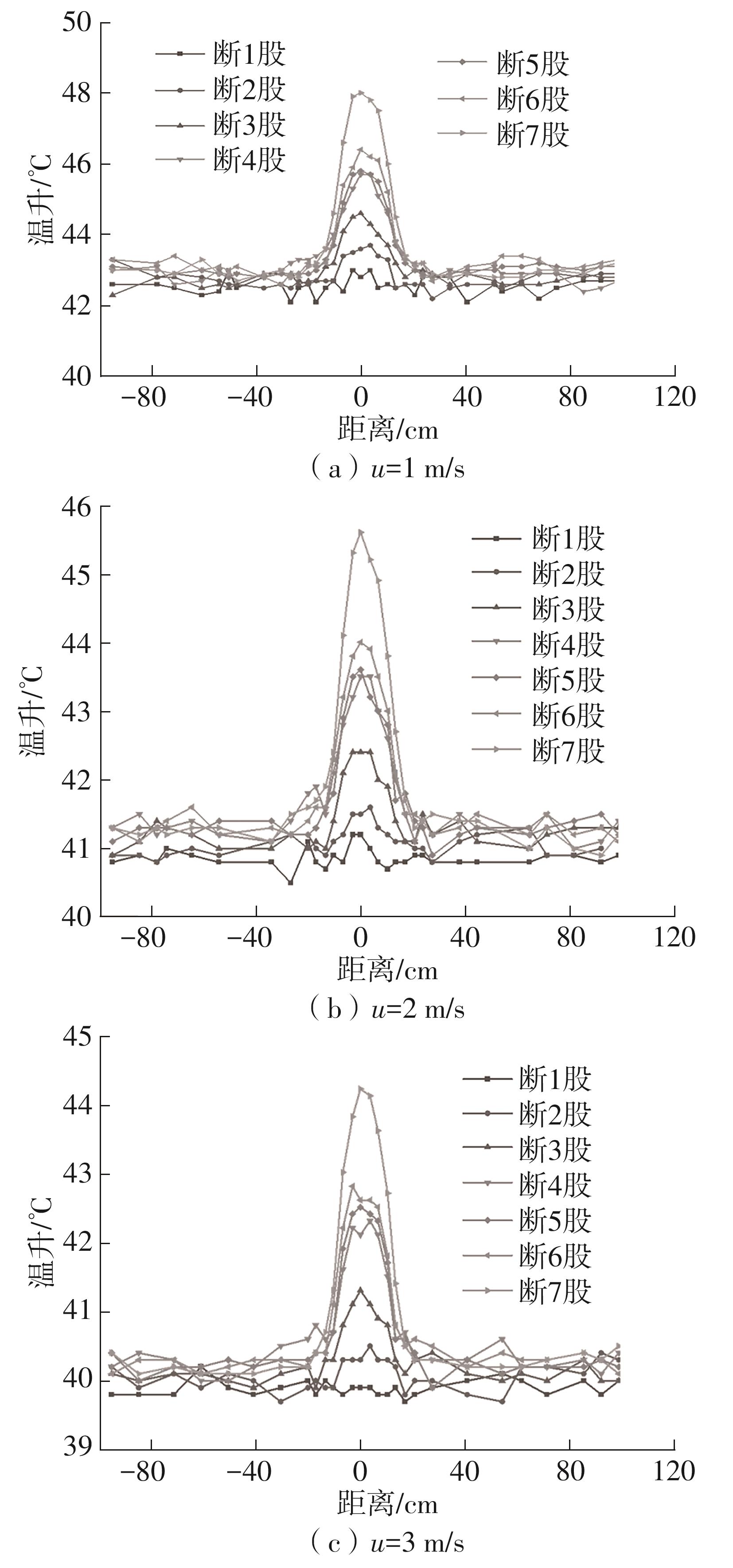
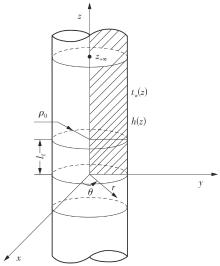
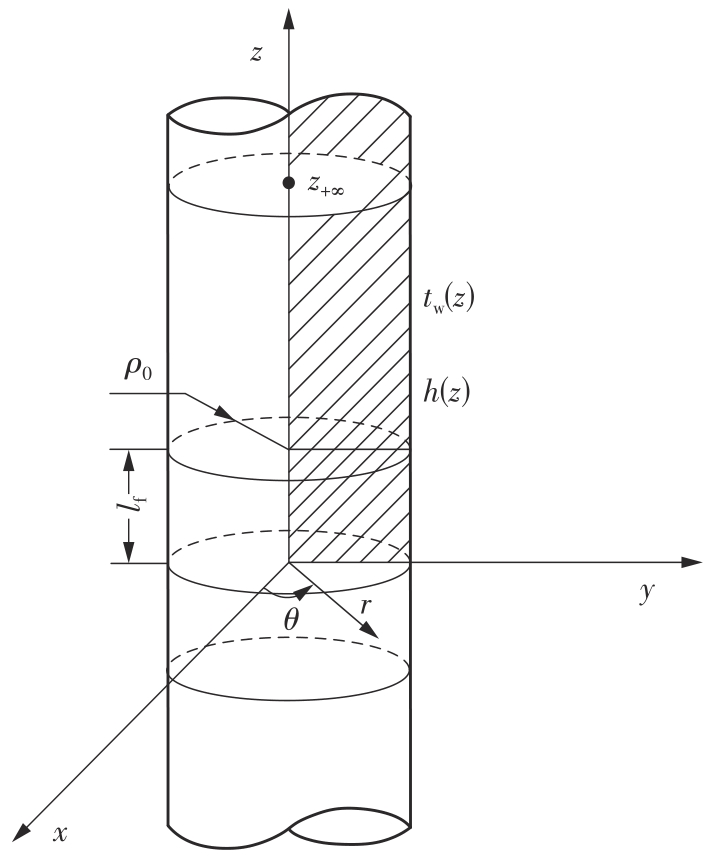
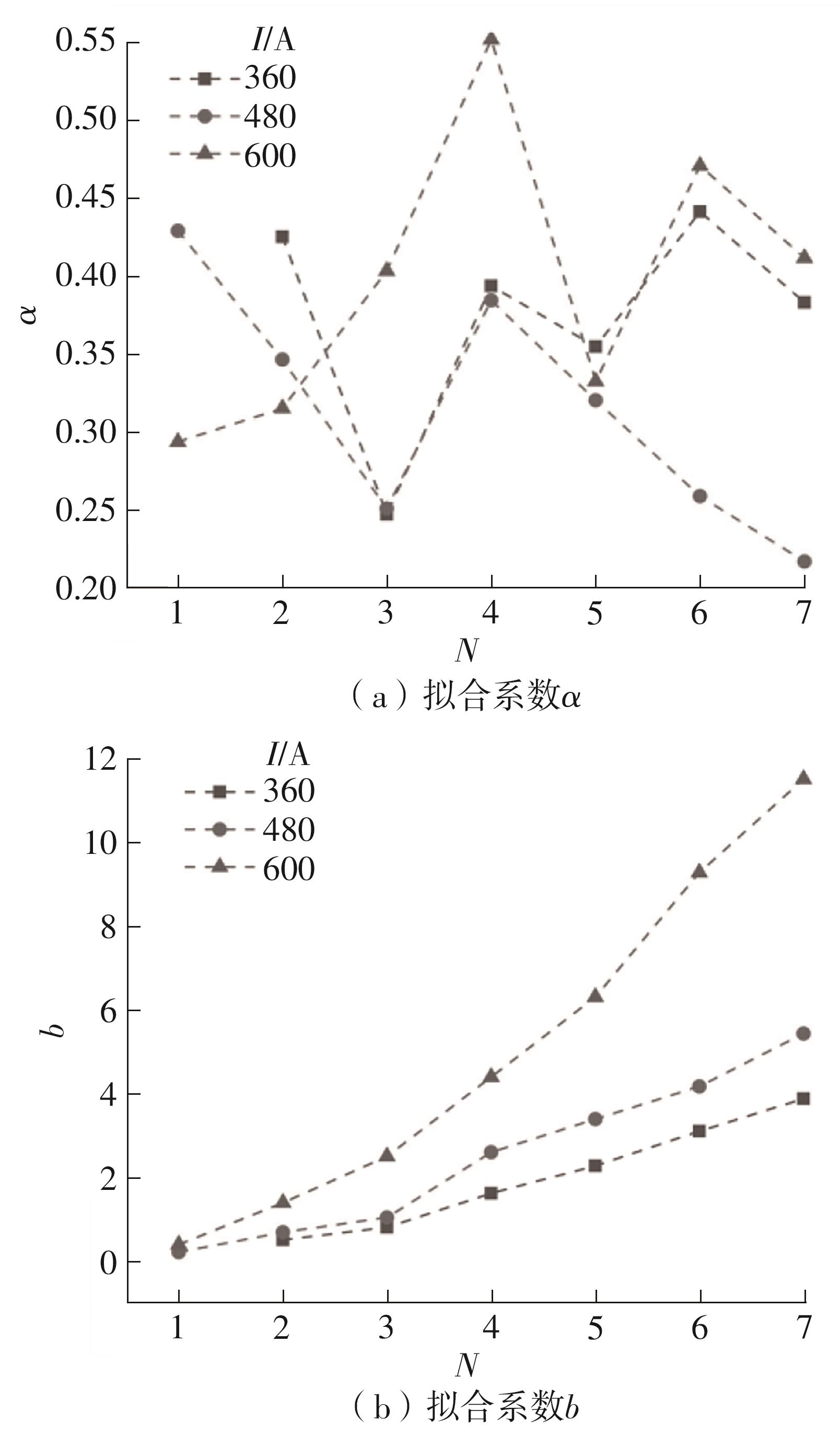
| 1 |
郭日彩,李明,徐晓东,等 .加快电网建设新技术推广应用的研究与建议[J].电网技术,2006,30(2):23-29.
|
|
GUO Ricai, LI Ming, XU Xiaodong,et al .Research and suggestions on speeding up dissemination and application of new technologies for power grid construction[J].Power System Technology,2006,30(2):23-29.
|
| 2 |
韩兴波,吴海涛,郭思华,等 .输电线路单导线覆冰和扭转的相互影响机制分析[J].电工技术学报,2022,37(17):4508-4516.
|
|
HAN Xingbo, WU Haitao, GUO Sihua,et al .Analysis of interaction mechanism between icing and torsion of single transmission lines[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2022,37(17):4508-4516.
|
| 3 |
MEYBER R A, SALAS F, DOMINGUES L,et al .Experimental study on the transformer effect in an ACSR cable [J].International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,2020,119(6):1058-1075.
|
| 4 |
MURPHY S, NIEBUR D .Solving the overhead transmission conductor heat balance equation using the newton raphson algorithm[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery,2021,36(6):3743-3751.
|
| 5 |
XIE P, FANG Z .Lightning performance of unshielded 220 kV transmission lines equipped with metal oxide arresters[J].IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility,2022,64(3):795-804.
|
| 6 |
LIU Q, JIA R, LIU Y,et al .Infrared image super-resolution reconstruction by using generative adversarial network with an attention mechanism[J].Applied Intelligence,2021,51(4):2018-2030.
|
| 7 |
徐奇伟,黄宏,张雪锋,等 .基于改进区域全卷积网络的高压引线接头红外图像特征分析的在线故障诊断方法[J].电工技术学报,2021,36(7):1380-1388.
|
|
XU Qiwei, HUANG Hong, ZHANG Xuefeng,et al .Online fault diagnosis method for infrared image feature analysis of high-voltage lead connectors based on improved R-FCN[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2021,36(7):1380-1388.
|
| 8 |
ZHU H, LI Q, TAO C,et al .Multispectral camouflage for infrared,visible,lasers and microwave with radiative cooling[J].Nature Communications,2021,12(1):1467-1481.
|
| 9 |
IEEE standard for calculating the current-temperature relationship of bare overhead conductors:IEEE Std 738-2012 [S].
|
| 10 |
Guide for thermal rating calculation of overhead lines:Technical Brochure 601 [S].
|
| 11 |
张辉,韩学山,王艳玲 .架空输电线路运行载流量分析[J].电网技术,2008,6(14):31-35.
|
|
ZHANG Hui, HAN Xueshan, WANG Yanling .Analysis on current carrying capacity of overhead lines being operated[J].Power System Technology,2008,6(14):31-35.
|
| 12 |
严伯伦,谢红刚,杨明 .微气象分析与载流量预测结合的动态线路增容方法[J].电力系统及其自动化学报,2022,34(12):137-144.
|
|
YAN Bolun, XIE Honggang, YANG Ming .Dynamic line rating method combining micrometeorological analysis and ampacity forecasting[J].Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2022,34(12):137-144.
|
| 13 |
FU X G, LIN G S, YANG X B .Parameter identification for current-temperature relationship of contact wire under natural convection[J].International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,2022,135(3):2101-2110.
|
| 14 |
BARTON T, MUSILEK P .Probabilistic forecasting of dynamic thermal line rating with temporal correlations[J].International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,2022,134(4):1074-1087.
|
| 15 |
DAMINOV I, PROKHOROV A, CAIRE R,et al .Assessment of dynamic transformer rating,considering current and temperature limitations[J].International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,2021,129(12):1187-1203.
|
| 16 |
带电设备红外诊断应用规范: [S].
|
| 17 |
李云红 .基于红外热像仪的温度测量技术及其应用研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2010.
|
| 18 |
架空输电线路运行规范: [S].
|
| 19 |
张怡,项中明,马超,等 .电网热稳定输送能力辅助决策系统[J].电网技术,2020,44(5):2000-2008.
|
|
ZHANG Yi, XIANG Zhongming, MA Chao,et al .Design of aided-decision system to improve thermal stability transport capacity of power grid[J].Power System Technology,2020,44(5):2000-2008.
|
| 20 |
胡剑,熊小伏,王建 .基于热网络模型的架空输电线路径向和周向温度计算方法[J].电工技术学报,2019,34(1):139-152.
|
|
HU Jian, XIONG Xiaofu, WANG Jian .Radial and circumferential temperature calculation method of overhead transmission lines based on thermal network model[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2019,34(1):139-152.
|
| 21 |
ZHANG X, YING Z, CHEN Y,et al .A thermal model for calculating axial temperature distribution of overhead conductor under laboratory conditions[J].Electric Power Systems Research,2019,166(15):223-231.
|
| 22 |
刘刚,李炀,陈垣,等 .基于电磁-热耦合模型的架空导线温度分布和径向温差的计算与实验验证[J].电力系统保护与控制,2018,46(7):7-13.
|
|
LIU Gang, LI Yang, CHEN Yuan,et al .Calculation and experiment verification on temperature distribution and radial temperature of overhead transmission line based on electromagnetic-thermal coupling fields[J].Power System Protection and Control,2018,46(7):7-13.
|
| 23 |
杨桢,张士成,杨立 .反射温度补偿法及其实验验证[J].光学精密工程,2010,18(9):1959-1964.
|
|
YANG Zhen, ZHANG Shicheng, YANG Li .Reflected temperature compensation method and its experimental verification [J].Optics and Precision Engineering,2010,18(9):1959-1964.
|
| 24 |
杨松,李文强,黄旭,等 .基于对流换热系数修正的钢箱梁温度场研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(4):47-58,64.
|
|
YANG Song, LI Wenqiang, HUANG Xu,et al .Study on temperature field of steel box girder based on modified convective heast transfer coefficient[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(4):47-58,64.
|
| 25 |
IEEE standard for calculating the current-temperature relationship of bare overhead conductors:IEEE 738-2012,2012 [S].
|
| 26 |
BITYUKO V K, KHUDAK Y I, GUSEIN-ZADE N G .Analytical derivation of the Stefan-Boltzmann law for integral radiance from Planck's law for spectral radiance[J].Bulletin of the Lebedev Physics Institute,2016,45(2):46-50.
|
| 27 |
110 kV~750 kV架空输电线路设计规范: [S].
|