Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (10): 126-134.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230198
Special Issue: 2023绿色智慧交通系统专辑
• Green, Intelligent Traffic System • Previous Articles Next Articles
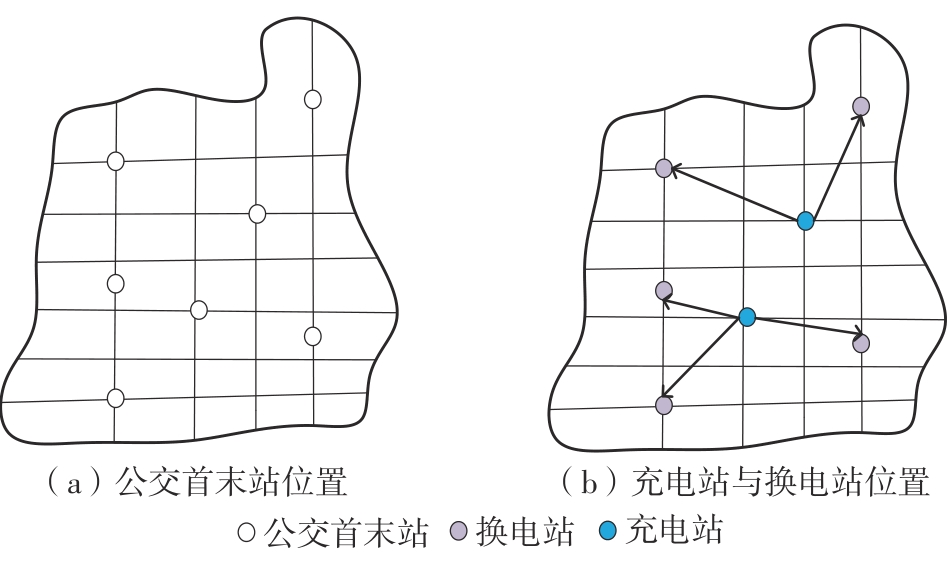
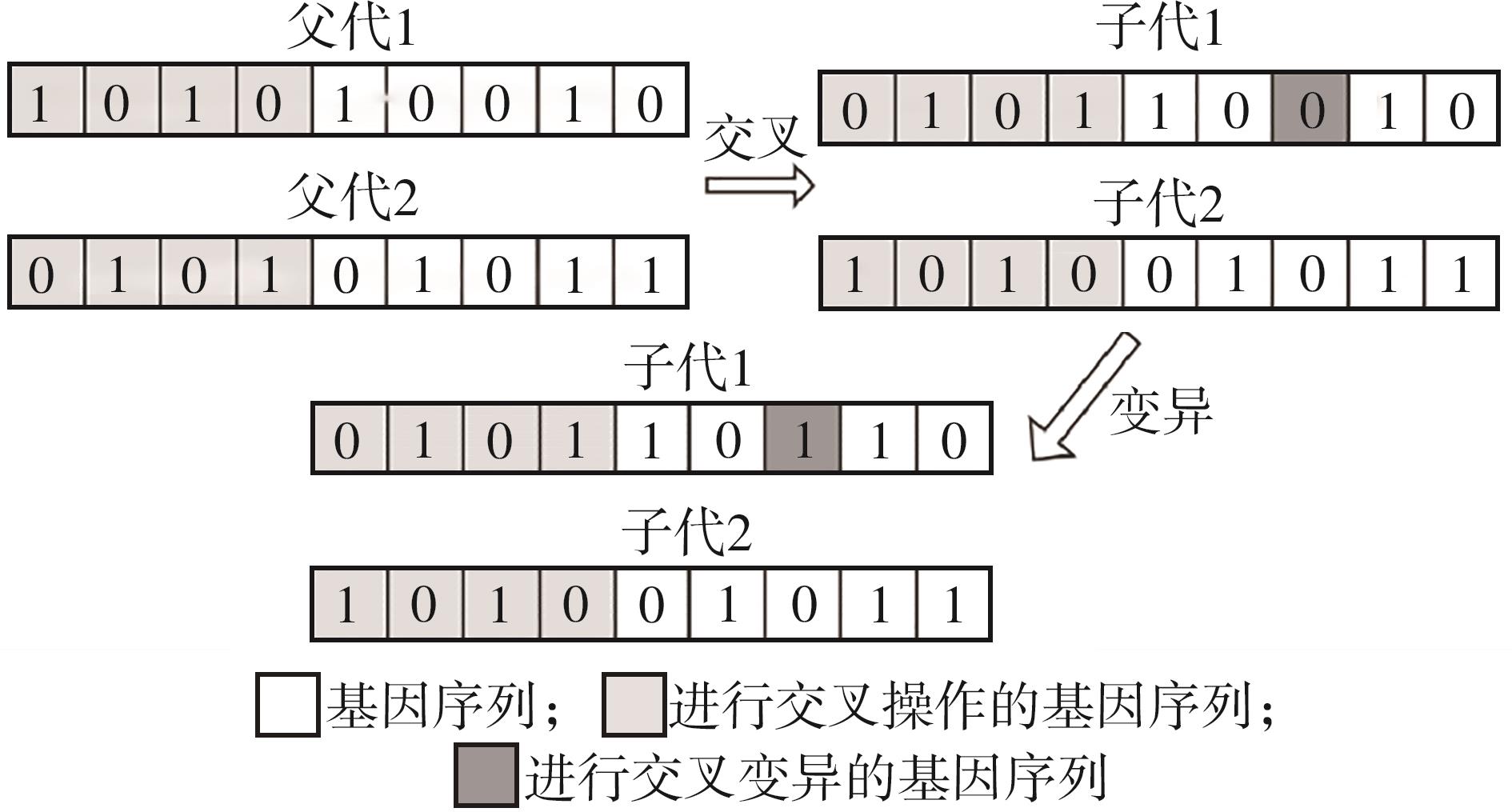
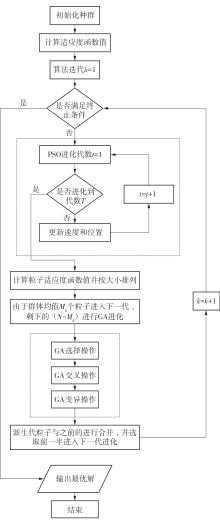
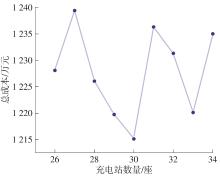
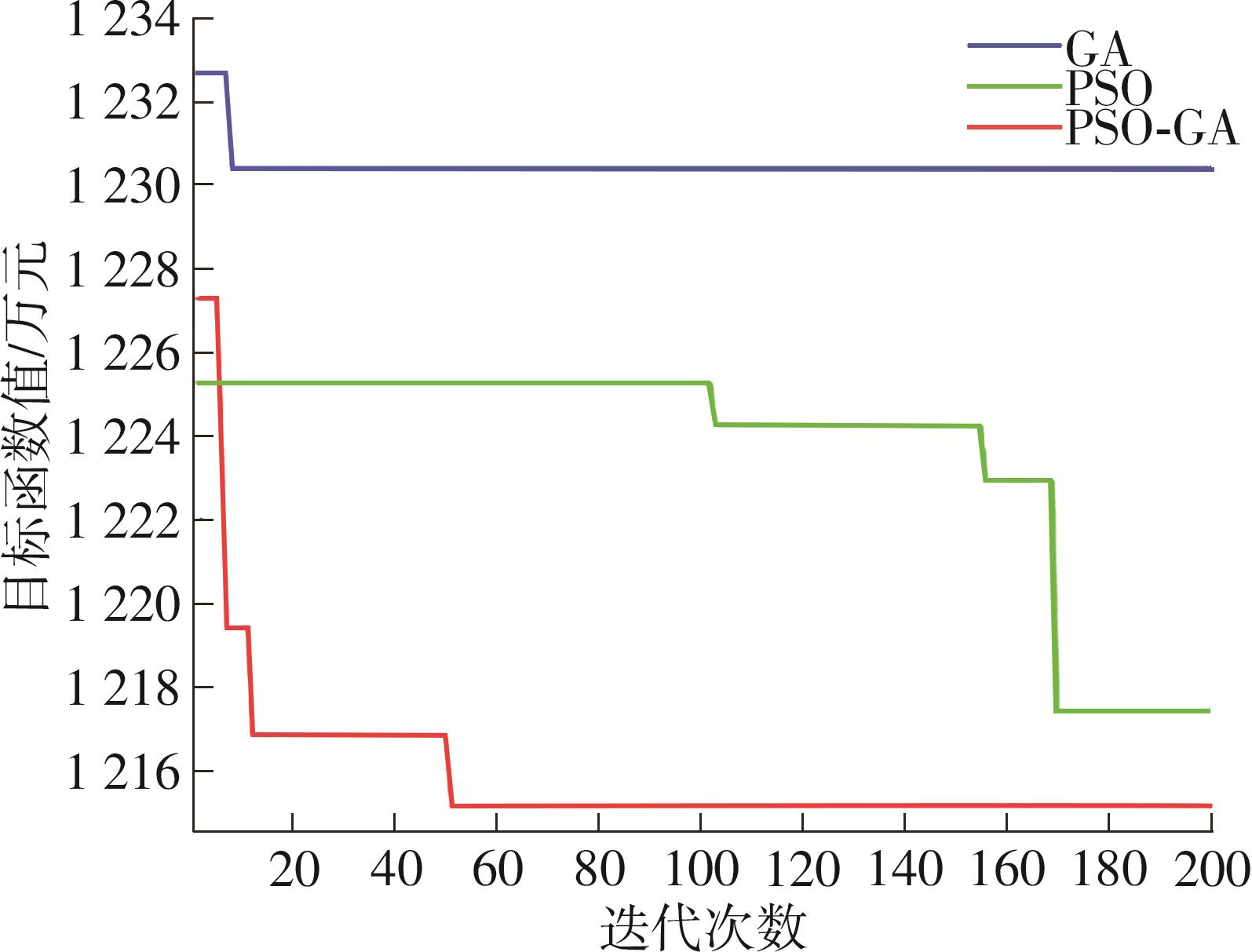
Location and Capacity Optimization Model of Battery-Swapped Electric Bus Charging Station
ZHANG Wenhui1 SU Jiaqi1 HA Zihong2 QIAO Xiaotian1 LIU Tuo1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang, China
2.Harbin Transportation Group Public Transport Co. , Ltd, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang, China