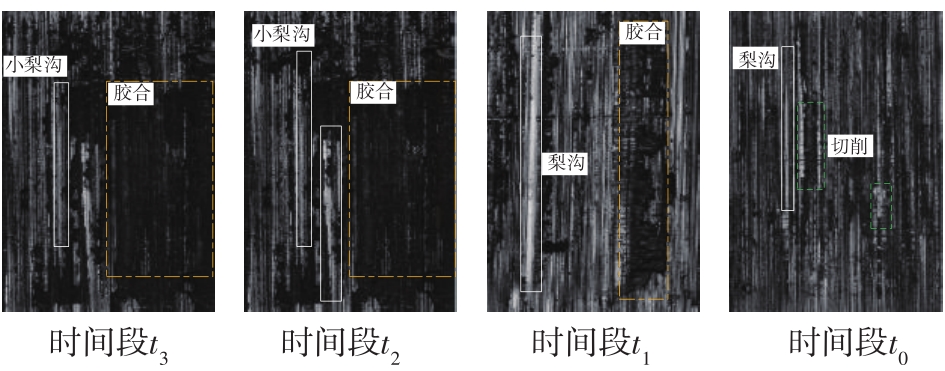
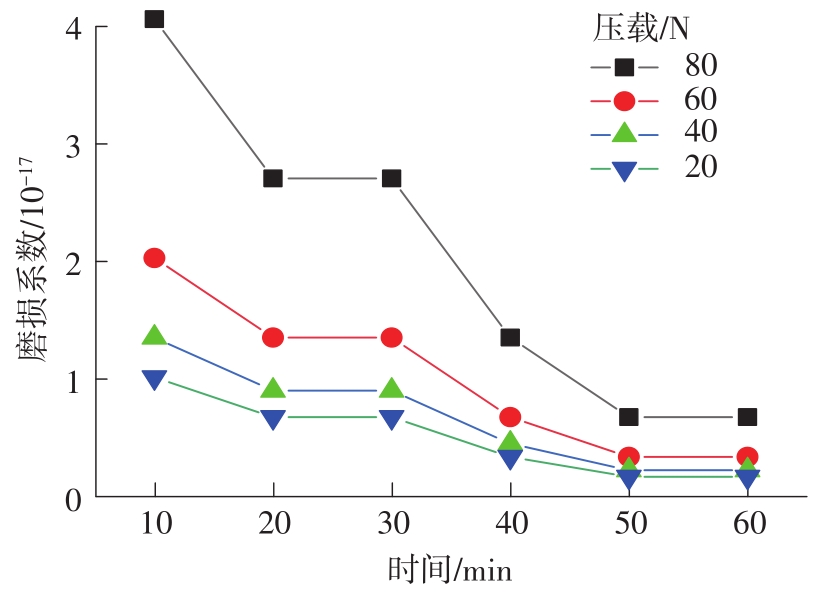
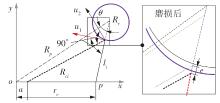
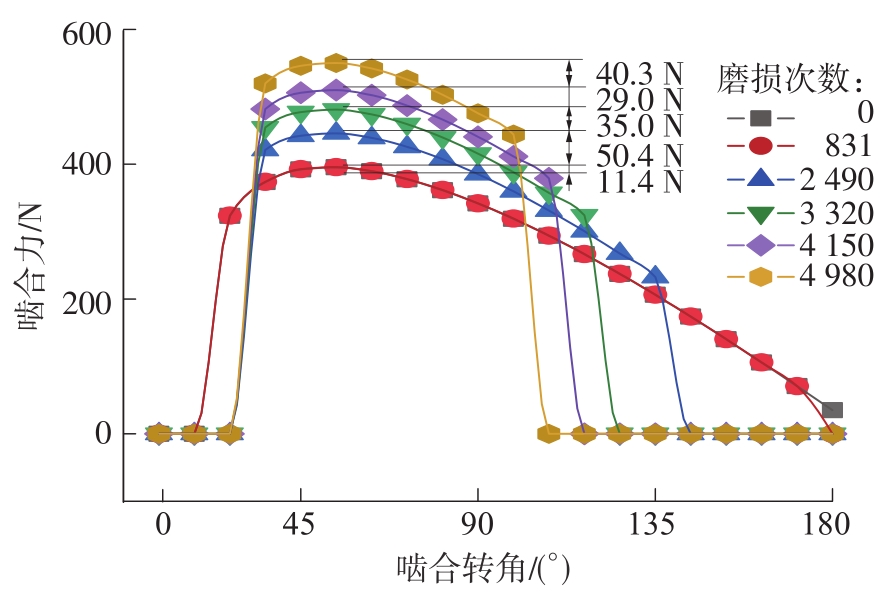
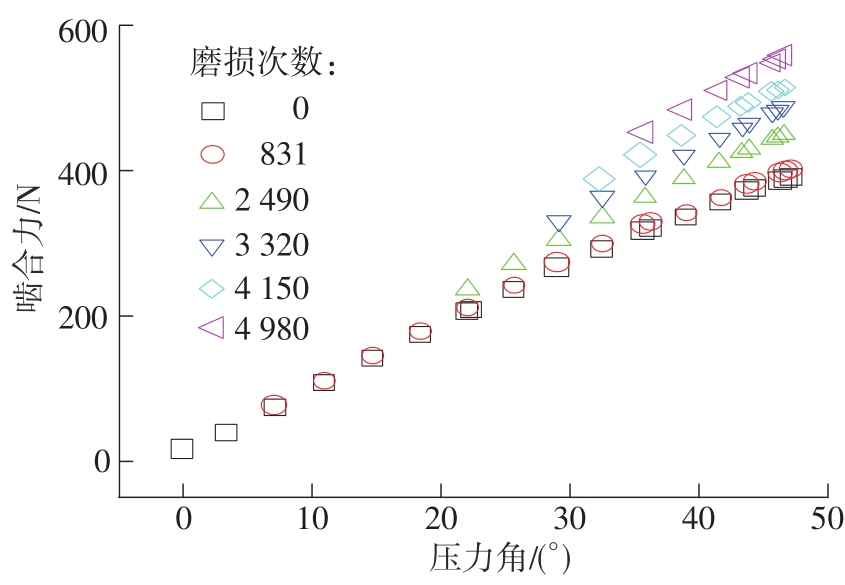
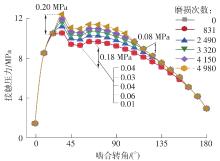
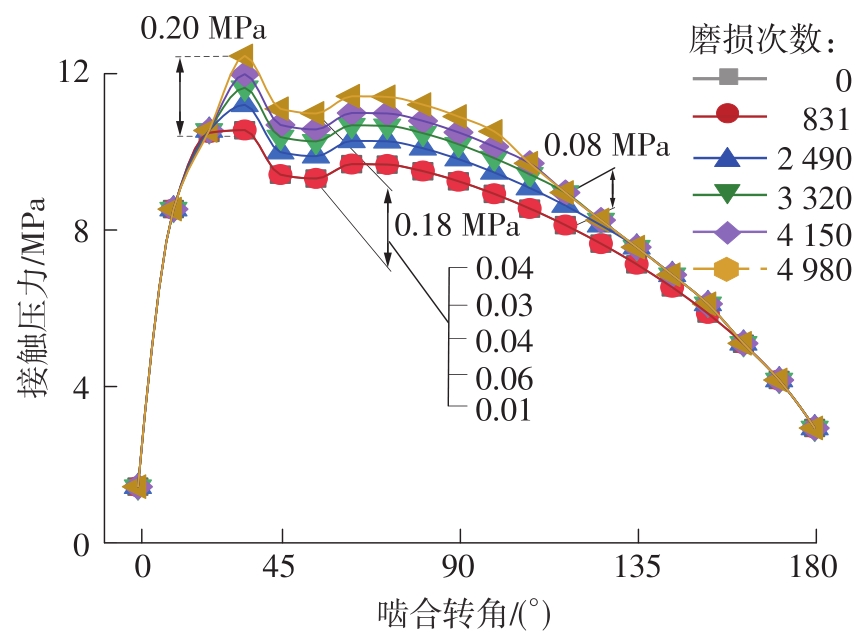
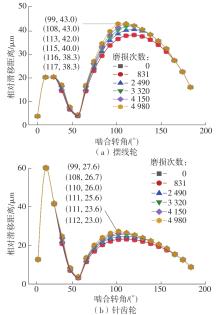
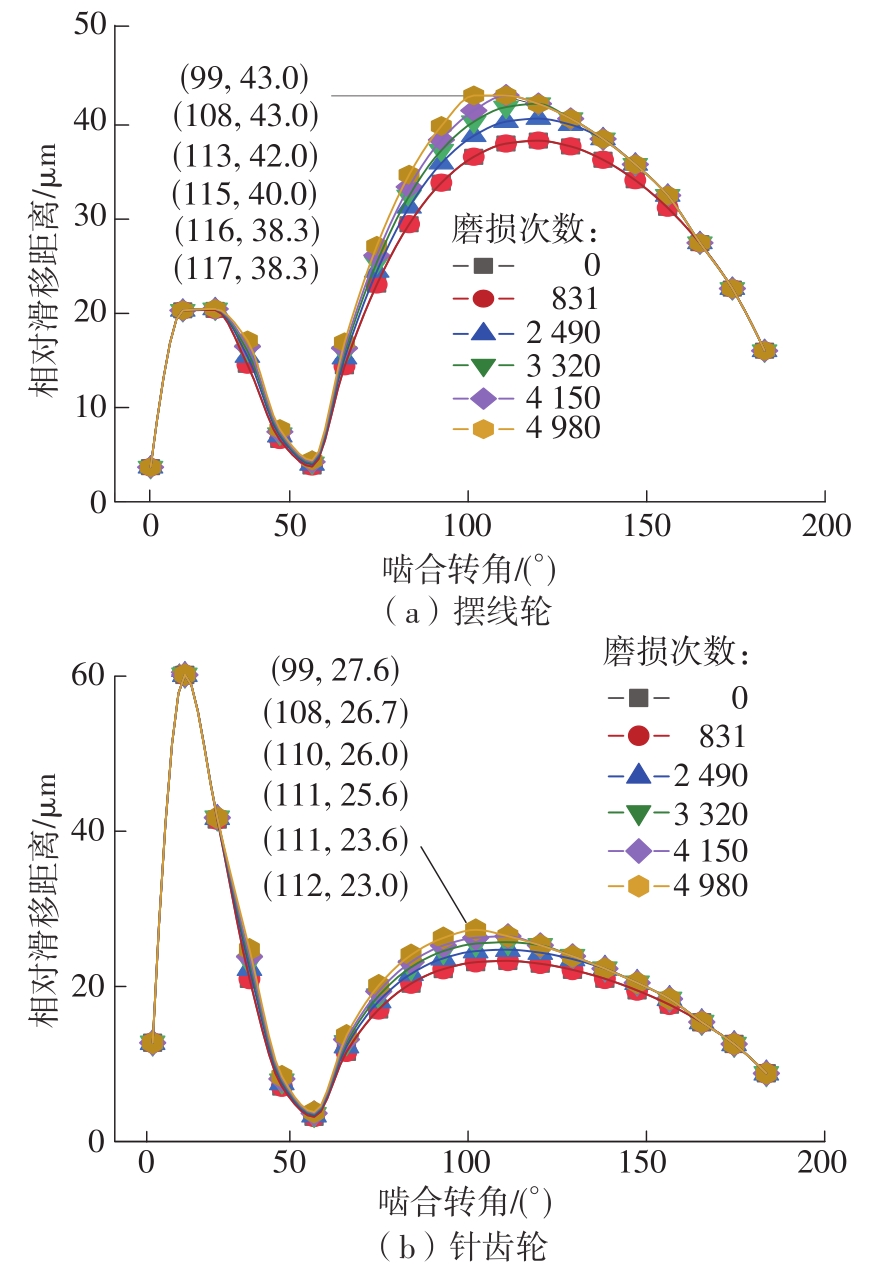
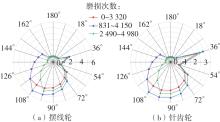
| 1 |
刘义才,高俊 .工业机器人产业发展现状与对策研究[J].中国商论,2021(18):174-176.
|
|
LIU Yicai, Gao Jun .Research on the development status and countermeasures of industrial robot industry[J].China Business Theory,2021(18):174-176.
|
| 2 |
JOCHEN S, CLAUDIO Z, RUSTAM S .Let’s push things forward:a survey on robot pushing[J].Frontiers in Robotics and AI,2020,7:8/1-18.
|
| 3 |
殷埝生 .我国工业机器人发展现状及未来发展探究[J].中国新通信,2020,22(20):135-136.
|
|
YIN Niansheng .Research on the development status and future development of industrial robots in China[J].China New Communications,2020,22(20):135-136.
|
| 4 |
沈智宪,乔百杰,罗巍,等 .齿轮磨损故障动态响应特征与诊断指标研究[J].机械工程学报,2021,57(17):120-131.
|
|
SHEN Zhixian, QIAO Baijie, LUO Wei,et al .Study on dynamic response characteristics and diagnosis indexes of gear wear fault[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2021,57(17):120-131.
|
| 5 |
PHAM A D, AHN H J .Efficiency analysis of a cycloid reducer considering tolerance[J].Journal of Friction and Wear,2017,38(6):490-496.
|
| 6 |
机器人用精密行星摆线减速器: [S].
|
| 7 |
XU H, SHI Z Y, YU B,et al .Optimal measurement speed and its determination method in the transmission precision evaluation of precision reducers[J].Applied Sciences,2019,9(10):1-11.
|
| 8 |
陆龙生,张飞翔,唐恒,等 .基于优化承载能力的RV减速器摆线齿轮齿廓的等距-移距修形[J].中国机械工程,2019,30(17):2022-2029.
|
|
LU Longsheng, ZHANG Feixiang, TANG Heng,et al .Isometric shift modification of cycloidal gear profile of RV reducer based on optimized bearing capacity[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2019,30(17):2022-2029.
|
| 9 |
REN Z, MAO S, GUO W,et al .Tooth modification and dynamic performance of the cycloidal drive[J].Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2017,85:857-866.
|
| 10 |
LIN K S, CHAN K Y, LEE J J .Kinematic error analysis and tolerance allocation of cycloidal gear reducers[J].Mechanism and Machine Theory,2018,124:73-91.
|
| 11 |
HSIEH C F, ALFONSO F A .Performance prediction method of cycloidal speed reducers[J].Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering,2019,41(4):1-15.
|
| 12 |
WANG H, SHI Z Y, YU S B,et al .Transmission performance analysis of RV reducers influenced by profile modification and load[J].Applied Sciences,2019,9(19):1-19.
|
| 13 |
QIAO X T, AHANG L b, CHEN C S,et al .Study on transient contact performance of meshing transmission of cycloid gear and needle wheel in RV reducer[J].The Journal of Engineering,2020,2020(14):1001-1004.
|
| 14 |
XU L X, CHEN B K, LI C Y .Dynamic modelling and contact analysis of bearing-cycloid-pinwheel transmission mechanisms used in joint rotate vector reducers[J].Mechanism and Machine Theory,2019,137:432-458.
|
| 15 |
郑钰馨,奚鹰,李梦如,等 .基于密切值法的RV减速器传动受力影响分析[J].中国工程机械学报,2017,15(2):153-157,164.
|
|
ZHENG Yuxin, XI Ying, LI Mengru,et al .Analysis of transmission force influence of RV reducer based on osculating value method[J].Chinese Journal of Construction Machinery,2017,15(2):153-157,164.
|
| 16 |
黄彬,常安全,潘安霞,等 .机器人用关节减速器的失效分析及改善措施[J].金属热处理,2021,46(2):223-227.
|
|
HUANG Bin, CHANG Anquan, PAN Anxia,et al .Failure analysis and improvement measures of joint reducer for robot[J].Metal Heat Treatment,2021,46(2):223-227.
|
| 17 |
苏建新,李晨 .RV减速器摆线轮磨损量的数值计算与分析[J].机械传动,2021,45(4):41-45,57.
|
|
SU Jianxin, LI Chen .Numerical calculation and analysis of cycloidal gear wear of RV Reducer[J].Mechanical Transmission,2021,45(4):41-45,57.
|
| 18 |
ARCHARD J F .Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces[J].Journal of Applied Physics,1953,24:981-988.
|
| 19 |
LANKARANI H M, NIARAVESH P E .A contact force model with hysteresis damping for impact analysis of multibody systems[J].Journal of Mechanical Design,1990,112(3):369-376.
|
| 20 |
MA J, QIAN L f, CHEN G S,et al .Dynamic analysis of mechanical systems with planar revolute joints with clearance[J].Mechanism and Machine Theory,2015,94:148-164.
|