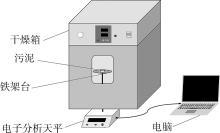
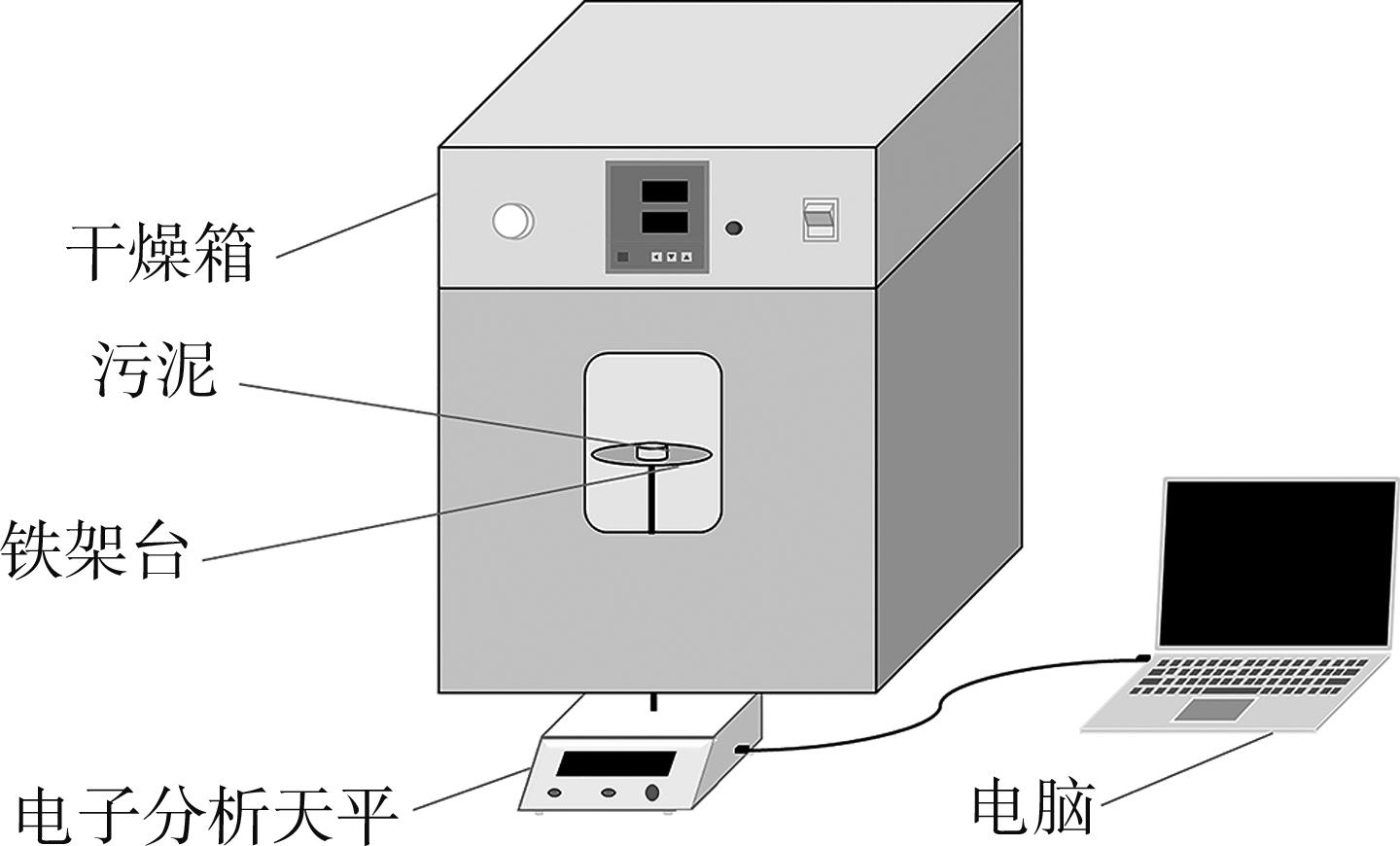
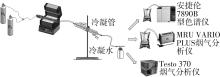
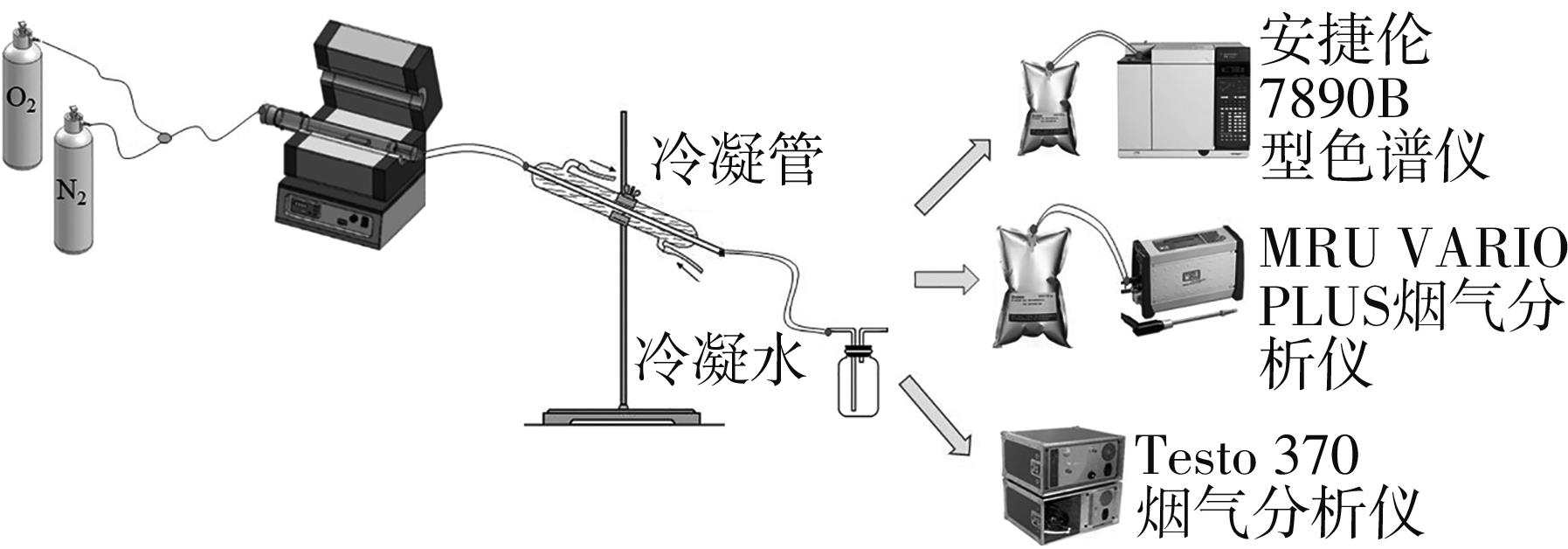
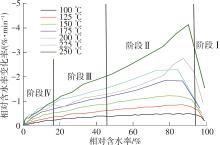
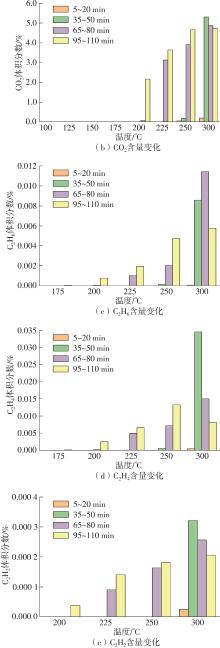
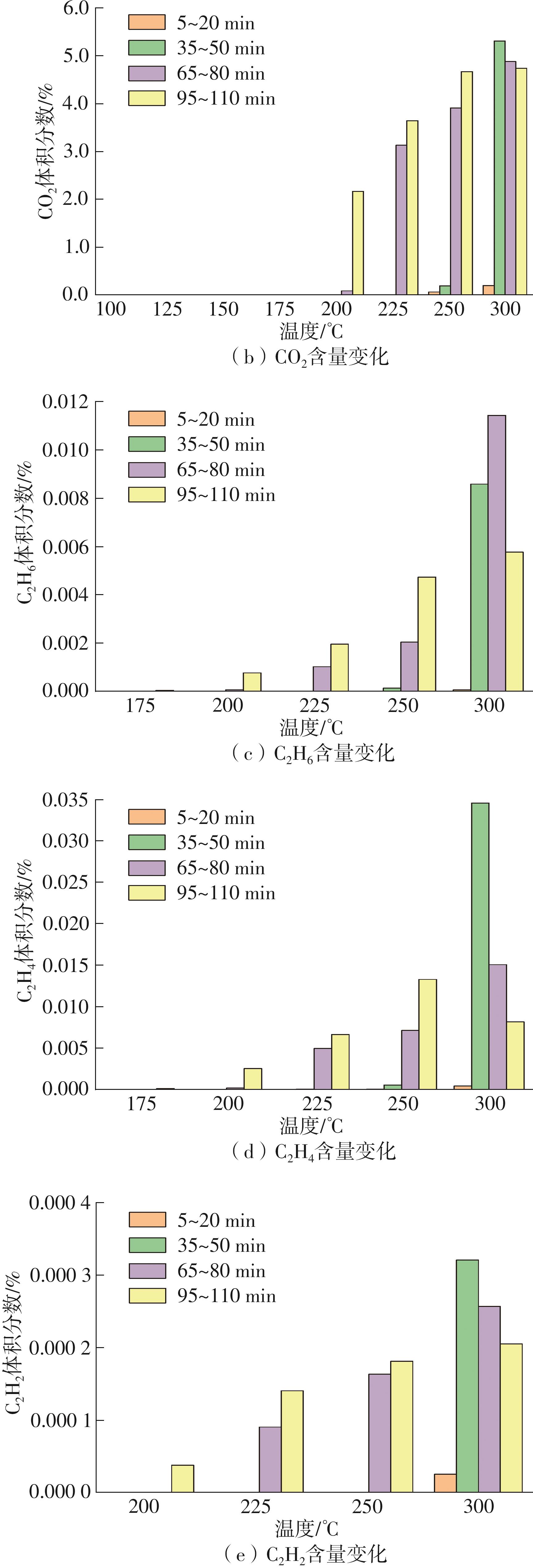
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (8): 92-101.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210726
Special Issue: 2022年环境科学与技术
• Environmental Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Experimental Study on Thermal Drying Characteristics and Pollutant Discharge Law of Municipal Sludge
LIAO Yanfen QIU Mengze CHEN Shunkai MA Xiaoqian
- School of Electric Power Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2021-11-16Online:2022-08-25Published:2022-04-08 -
Contact:廖艳芬(1976-),女,教授,博士生导师,主要从事固体废弃物清洁高效利用研究。 E-mail:yfliao@scut.edu.cn -
About author:廖艳芬(1976-),女,教授,博士生导师,主要从事固体废弃物清洁高效利用研究。 -
Supported by:the Guangdong Province Key Field Research and Development Program(2020B1111380001)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIAO Yanfen, QIU Mengze, CHEN Shunkai, et al . Experimental Study on Thermal Drying Characteristics and Pollutant Discharge Law of Municipal Sludge[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(8): 92-101.
share this article
Table 3
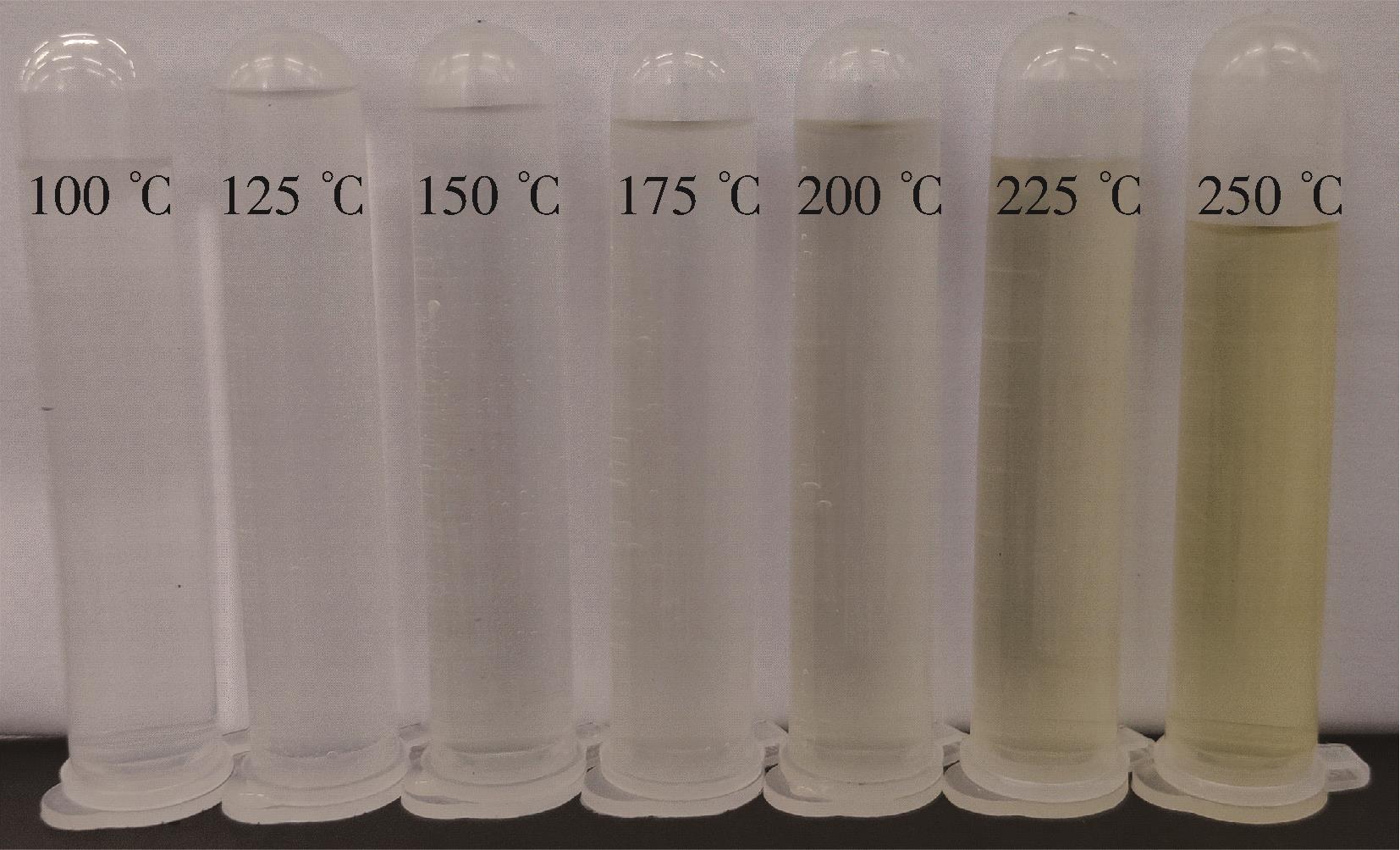
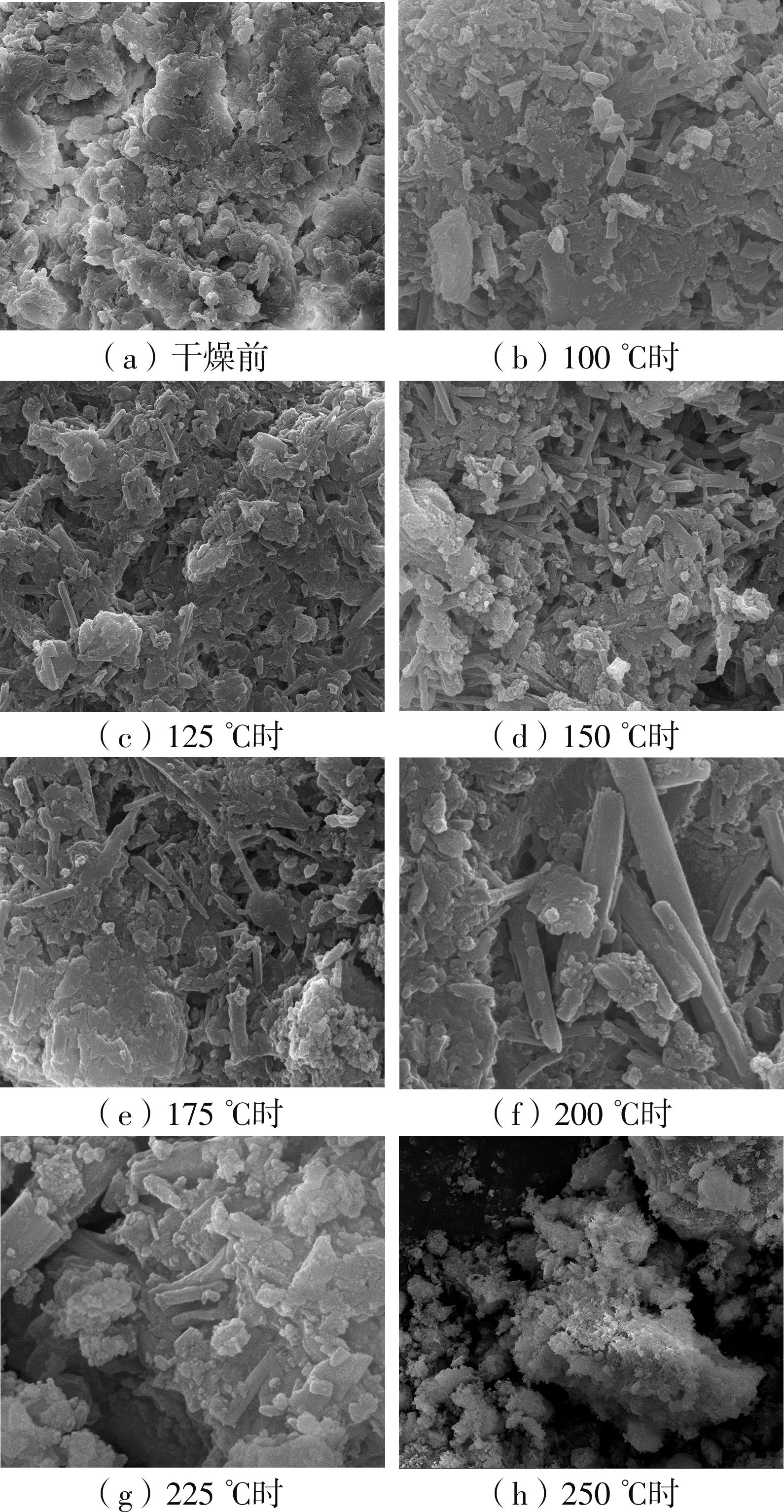
Proximate analysis, ultimate analysis results and calorific value of sludge residue (dry basis)"
| 实验组次 | 工业分析结果/% | 元素分析结果/% | 高位热值/ (kJ·kg-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灰分 | 挥发分 | 固定碳 | C | H | O1) | N | S | ||
125 ℃组 150 ℃组 175 ℃组 200 ℃组 225 ℃组 250 ℃组 275 ℃组 300 ℃组 | 45.56 48.81 69.80 72.20 73.09 76.88 77.03 76.52 | 50.31 47.07 26.13 24.29 23.68 21.01 21.18 20.59 | 4.13 4.12 4.07 3.51 3.23 2.11 1.79 2.89 | 12.5 12.59 13.34 11.8 11.47 9.49 8.7 10.06 | 3.593 3.676 2.099 1.676 1.71 1.454 1.293 1.379 | 34.862 31.236 10.176 9.843 9.245 7.945 8.944 7.889 | 1.72 1.76 1.84 1.63 1.57 1.2 1.01 1.2 | 1.765 1.928 2.745 2.851 2.915 3.031 3.023 2.952 | 4 470 4 400 4 220 3 420 3 300 2 380 2 150 2 830 |
| 1 | YANG G, ZHANG G M, WANG H C .Current state of sludge production,management,treatment and disposal in China[J].Water Research,2015,78:60-73. |
| 2 | 黄瑛,张董 .国内外污泥处理处置技术研究与应用现状[J].环境工程,2015,33(s1):600-604. |
| HUANG Ying, ZHANG Dong .Research and application status of sludge treatment and disposal technology at home and abroad[J].Environmental Engineering,2015,33(s1):600-604. | |
| 3 | KOBAYASHI N, OKADA K, TACHIBANA Y,et al .Drying behavior of sludge with drying 494 accelerator[J].Dry Technol,2020,38(1/2):38-47. |
| 4 | 李博,王飞,严建华,等 .污水处理厂污泥干化焚烧处理可行性分析[J].环境工程学报,2012,6(10):3399-3404. |
| LI Bo, WANG Fei, YAN Jianhua,et al .Feasibility analysis of sludge drying and incineration treatment in sewage treatment plant[J].Environmental Engineering Journal,2012,6(10):3399-3404. | |
| 5 | 洪博文,薛红琳,车卫彤,等 .污泥干化及协同焚烧处置技术分析[J].能源与节能,2020(6):86-88. |
| HONG Bowen, XUE Honglin, CHE Weitong,et al .Analysis of sludge drying and co-incineration disposal technology[J].Energy and Energy Conservation,2020(6):86-88. | |
| 6 | 邓文义,严建华,李晓东,等 .造纸污泥干化及焚烧系统污染物排放特性[J].燃烧科学与技术,2008(6):545-550. |
| DENG Wen-yi, YAN Jian-hua, LI Xiao-dong,et al .Papermaking sludge drying and pollutant emission cha-racteristics of incineration systems[J].Combustion Science and Technology,2008(6):545-550. | |
| 7 | 鲁南,李博,王飞,等 .深圳市污水处理厂剩余污泥干化特性研究[J].环境污染与防治,2011,33(10):59-62,72. |
| LU Nan, LI Bo, WANG Fei,et al .Study on the drying characteristics of surplus sludge in Shenzhen sewage treatment plant[J].Environmental Pollution and Control,2011,33(10):59- 62,72. | |
| 8 | 汪家兴,刘欢,刘鹏,等 .深度脱水污泥的热干化特性[J].化工学报,2017,68(6):2491-2500. |
| WANG Jiaxing, LIU Huan, LIU Peng,et al .Thermal drying characteristics of deeply dewatered sludge[J].CIESC Journal,2017,68(6):2491-2500. | |
| 9 | GOMEZ-RICO M F, FULLANA A, FONT R .Volatile organic compounds released from thermal drying of se-wage sludge[J].WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment,2008,111:425-433. |
| 10 | WANG J, SALMAN C A, WANG B,et al .Integrating sludge drying in biomass fueled CHP plants[J].Energy,Ecology and Environment,2021,6(1):1-12. |
| 11 | PARLAK N, OZDEMIZ S, YETILMEZSOY K,et al .Mathematical modeling of thin-layer solar drying of poultry abattoir sludge[J].International Journal of Environmental Research,2021,15(1):177-190. |
| 12 | GUO J L, ZHENG L, LI Z F .Microwave drying behavior,energy consumption,and mathematical modeling of sewage sludge in a novel pilot-scale microwave drying system[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,777:146109. |
| 13 | LI X, HU YN, CHEN L,et al .Method for improving of activated sludge drying by the appropriate foaming pre-treatment[C]∥Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences.Dali:EDP Sciences,2021:02038. |
| 14 | MA X-W, WENG H-X, ZHANG J-J .Difference and cause analysis of drying characteristics of different shapes sludge[J].China Environmental Science,2011,31(5):803-809. |
| 15 | LI B, WANG F, CHI Y,et al .Study on optimal energy efficiency of a sludge drying-incineration combined system[J].Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management,2014,16(4):684-692. |
| 16 | YANG J, YU W, LI P S,et al .Experimental study on drying characteristics of sewage sludge at low temperature[C]∥Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Coal Combustion.Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science & Technology Press,2007:576-581. |
| 17 | LI H, ZOU S X, LI C C .Liming pretreatment reduces sludge build-up on the dryer wall during thermal drying[J].Drying Technology,2012,30(14):1563-1569. |
| 18 | AVSAR Y, SARAL A, ILHAN F,et al .Vacuum-assisted thermal drying of wastewater treatment sludge[J].Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association,2021,71(3):293-303. |
| 19 | 俞燕,胡晓亮,施捷,等 .污泥干化全流程废气治理研究[J].中国设备工程,2021(14):253-254. |
| YU Yan, HU Xiaoliang, SHI Jie,et al .Research on waste gas treatment in the whole process of sludge drying[J].China Equipment Engineering,2021(14):253-254. | |
| 20 | 翁焕新,章金骏,刘瓉,等 .污泥干化过程氨的释放与控制[J].中国环境科学,2011,31(7):1171-1177. |
| WENG Huanxin, ZHANG Jinjun, LIU Zan,et al .Release and control of ammonia during sludge drying process[J].China Environmental Science,2011,31(7):1171-1177. | |
| 21 | 刘亚军,王磊,邓文义,等 .市政污泥热力干化污染物排放研究[J].广东化工,2017,44(23):13-14. |
| LIU Yajun, WANG Lei, DENG Wenyi,et al .Research on pollutant discharge from thermal drying of municipal sludge[J].Guangdong Chemical Industry,2017,44(23):13-14. | |
| 22 | LI T, FAN Y, LI H,et al .Excess sludge disintegration by discharge plasma oxidation:efficiency and underlying mechanisms[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,774:145127. |
| 23 | XU D, LI J, LIU J,et al .Rapid aerobic sludge granulation in an integrated oxidation ditch with two-zone clarifiers[J].Water Research,2020,175:115704. |
| 24 | 汤连生,张龙舰,罗珍贵 .污泥中水分布形式划分及脱水性能研究[J].生态环境学报,2017,26(2):309-314. |
| TANG Liansheng, ZHANG Longjian, LUO Zhengui .Study on the distribution of water in sludge and its dewatering performance[J].Journal of Ecological Environment,2017,26(2):309-314. | |
| 25 | 陈泽成,黄汉廷,韦献革,等 .污泥干化废气特性及其治理技术研究进展[J].环境保护科学,2020,46(5):66-73. |
| CHEN Zecheng, HUANG Hanting, WEI Xiange,et al .Research progress on the characteristics of sludge drying waste gas and its treatment technology[J].Environmental Protection Science,2020,46(5):66-73. | |
| 26 | 周杰,吴敏,牛明星,等 .污泥干化过程恶臭气体释放的研究进展[J].中国给水排水,2015,31(4):25-27. |
| ZHOU Jie, WU Min, NIU Mingxing,et al .Research progress on the release of odorous gases during sludge drying[J].China Water & Wastewater,2015,31(4):25-27. | |
| 27 | 丁洁华 .污泥热干化过程恶臭污染物排放特性研究[D].廊坊:华北科技学院,2017. |
| 28 | 魏盟盟,刘帅,桂本,等 .污泥中脂肪族硫低温热解下含硫气体的释放特性[J].燃烧科学与技术,2015,21(1):71-76. |
| WEI Mengmeng, LIU Shuai, GUI Ben,et al .Release characteristics of sulfur-containing gas under low-temperature pyrolysis of aliphatic sulfur in sludge[J].Combustion Science and Technology,2015,21(1):71-76. | |
| 29 | 郦春蓉 .市政污泥间壁式干燥过程污染物排放研究[J].广东化工,2019,46(12):49-50. |
| LI Chunrong .Research on pollutant emission during the partition drying process of municipal sludge[J].Guangdong Chemical Industry,2019,46(12):49-50. | |
| 30 | 李安峰,骆坚平,黄丹,等 .污泥干化冷凝水水质特征分析[J].环境工程学报,2015,9(1):253-256. |
| LI Anfeng, LUO Jianping, HUANG Dan,et al .Analysis of water quality characteristics of sludge drying condensate[J].Environmental Engineering Journal,2015,9(1):253-256. | |
| 31 | 王兴润,金宜英,王志玉,等 .污水污泥间壁热干燥实验研究[J].环境科学,2007(2):407-410. |
| WANG Xingrun, JIN Yiying, WANG Zhiyu,et al .Experimental study on thermal drying of sewage sludge partition[J].Environmental Science,2007(2):407-410. | |
| 32 | 牛宇锟 .污泥低温碳化裂解液资源化技术研究[D].太原:太原理工大学,2020. |
| [1] | ZHANG Heng, HUANG Junguang, LI Weike, et al. Influence of Electroosmosis-Calcium Chloride Treatment on the Deformation of Sodium Sulfate Saline Soil [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 53-60. |
| [2] | Yu Qijun, Ma Ting, Zhang Tongsheng, et al. Effect of particle size on hydration kinetics and microstructure development of recycled brick powder-cement pastes [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(11): 63-73. |
| [3] | TAN Haibing, LI Shu, WANG Jing, et al. Influence of Solution Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Property of GH4099 Alloy [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(8): 136-143. |
| [4] | CHEN Weiping, LI Bing, LING Zicheng, et al. Influence of Ce Addition on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance to Molten Aluminum of Fe-Cr-B Alloys [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(9): 73-79. |
| [5] | WEI Xiaolan, LIN Guoqing, DING Jing, et al. Simulation and Experiment Investigation into Specific Heat Capacity Enhancement of Nitrate Molten Salt Nanofluid [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(9): 46-55. |
| [6] | ZHOU Tao, HE Lin, TIAN Pengfei, et al. Prediction Model of Microstructure Evolution in Shear Zone During Cutting Process [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(1): 82-92. |
| [7] | SU Fenghua FENG Wenying YUAN Xi. Numerical Simulation of an Oil Cooler Based on Multi-Scale Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(5): 112-117. |
| [8] | XU Daofen, CHEN Kanghua, XING Jun, et al. Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of 2219 Aluminum Alloy Forging's Joint by TIG Welding [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(3): 116-125. |
| [9] |
YIN Xiaolong DENG Wenjun ZHANG Jiayang PI Yunyun .
Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al 7075 Alloy Prepared by Cryogenic-Temperature Extrusion Machining
|
| [10] | ZHANG Heng MA Qinguo HU He NIU Fujun. Experimental Research on the Effect of Using Calcium Chloride and Electroosmosis to Reinforce Silt Clay [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 119-125. |
| [11] | LI Peisheng WANG Zhaotai ZHAO Wandong ZHONG Yuan ZHANG Ying. Simulation of Liquid Infiltration Process for Reparation of Composite Materials by Multi-Component Pseudopotential LBM [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(7): 7-15. |
| [12] | ZHOU Zhaoyao LUO Jiehan ZOU Chunhua ZOU Chunya. Microstructure and Property of Capacitor-Discharging Projection Welding Joints of T-Type Galvanized Nuts to Hot-Stamping Steels [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(10): 81-87. |
| [13] | Lǚ Fei TIAN Zongjun LIANG Huixin XIE Deqiao SHEN Lida XIAO Meng. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of AlSi10Mg Aluminum Alloy Fabricated by Laser Melting Deposition [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(10): 117-125. |
| [14] | YANG Yi-bo PU Yong-qiang YAN Wei-jun GUO Wen-ying WANG Heng-chang. Microstructure and Chloride Ion Dissolution Characteristics of Soda Residue [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(5): 82-89. |
| [15] | ZHOU Zhao-yao CAO Xiao-bing QIN Jie XIAO Zhi-yu. Effects of Mechanical Vibration on Microstructure and Properties of A356 Aluminum Alloy During Squeeze Casting [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(2): 46-51. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||