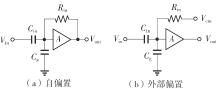
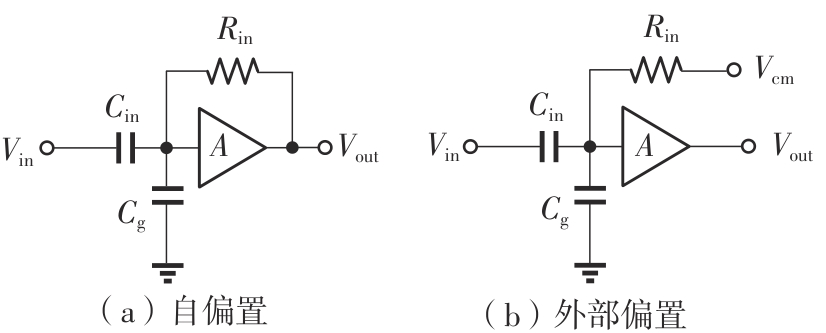
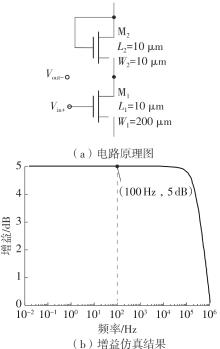
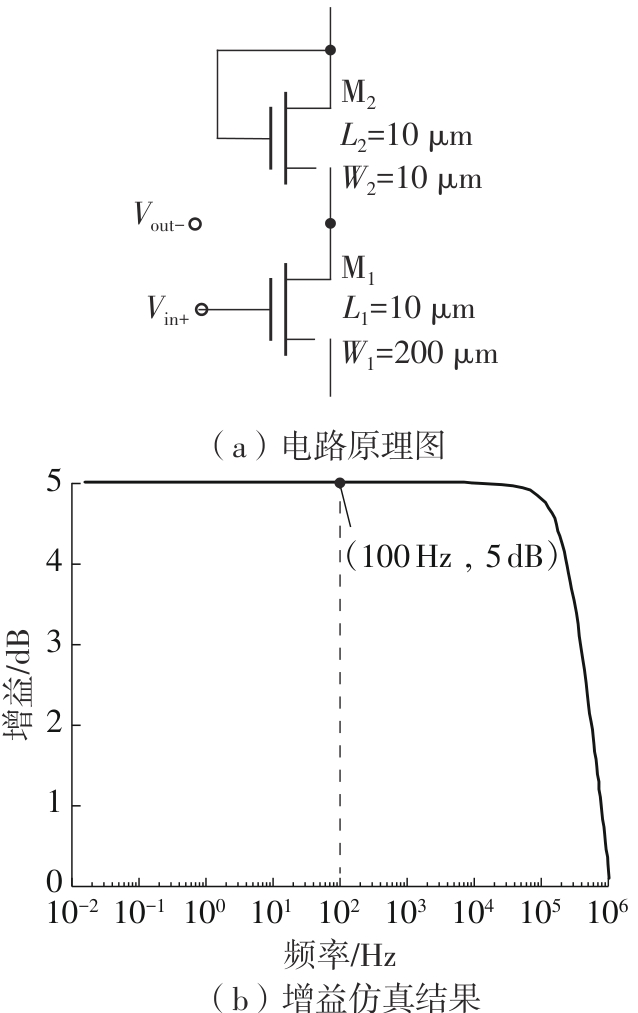
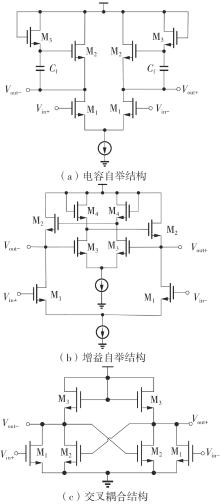
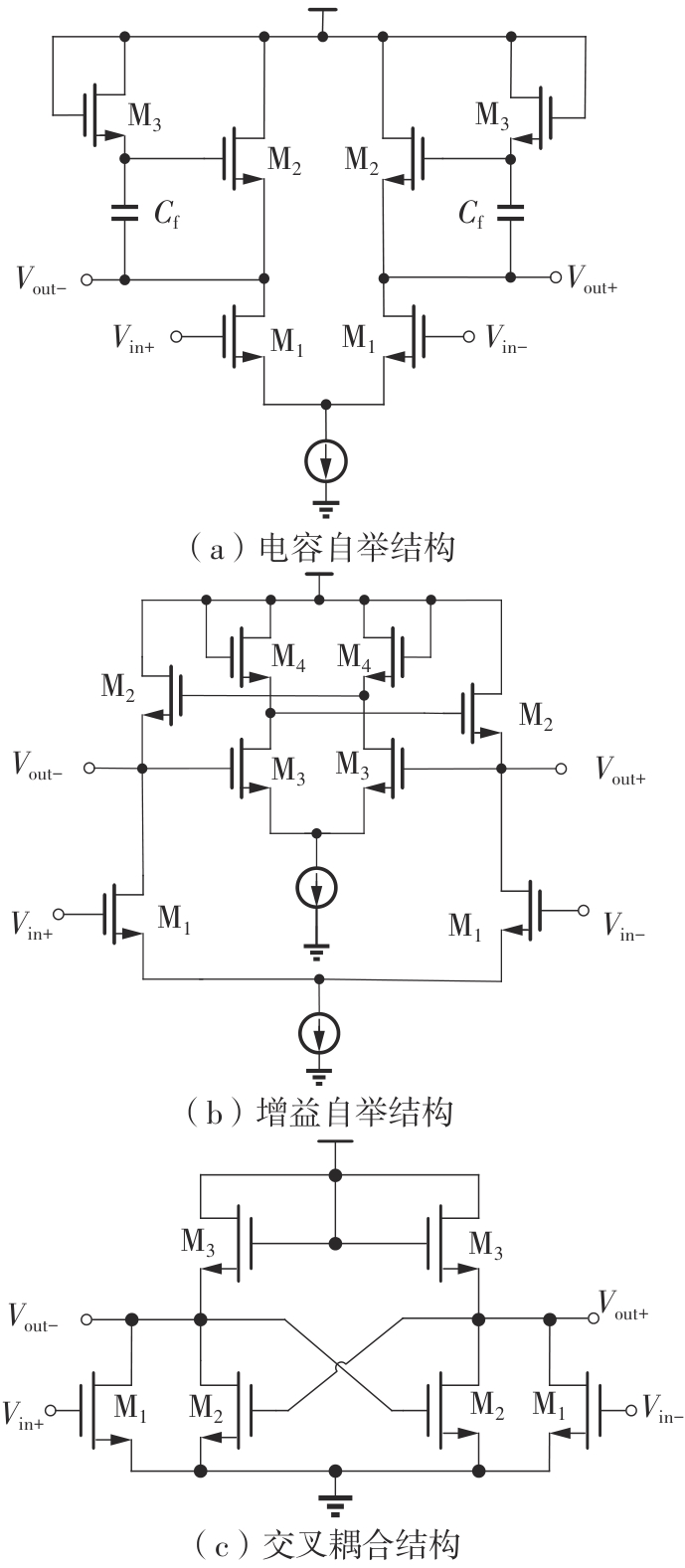
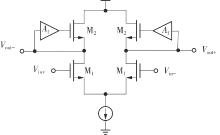
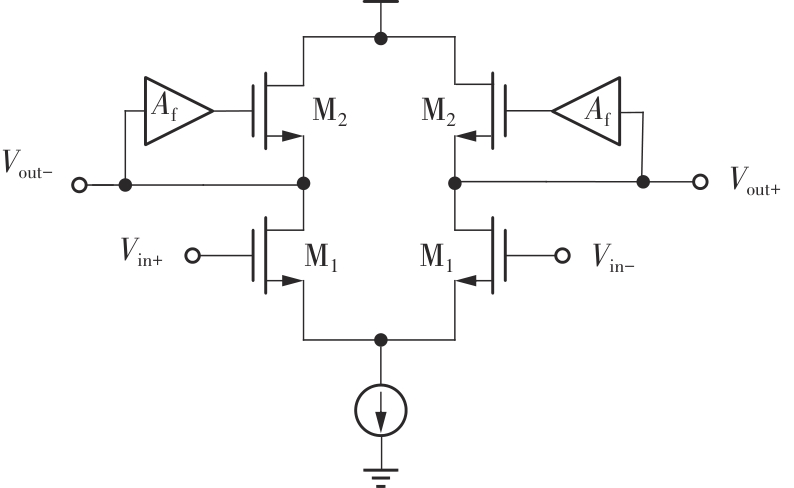
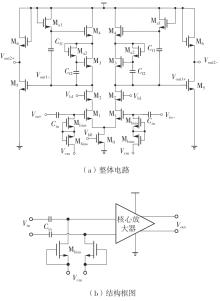
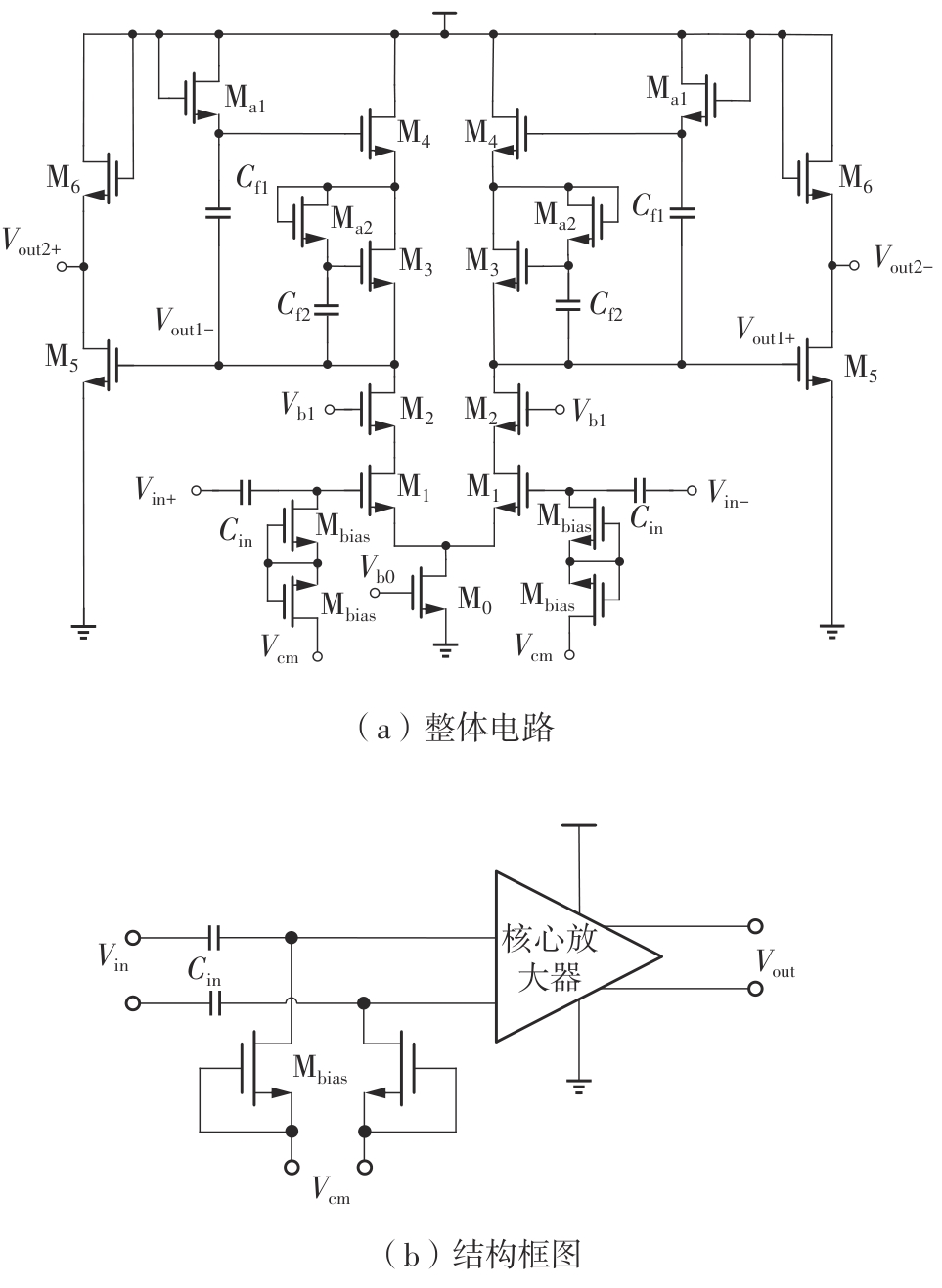
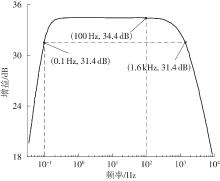
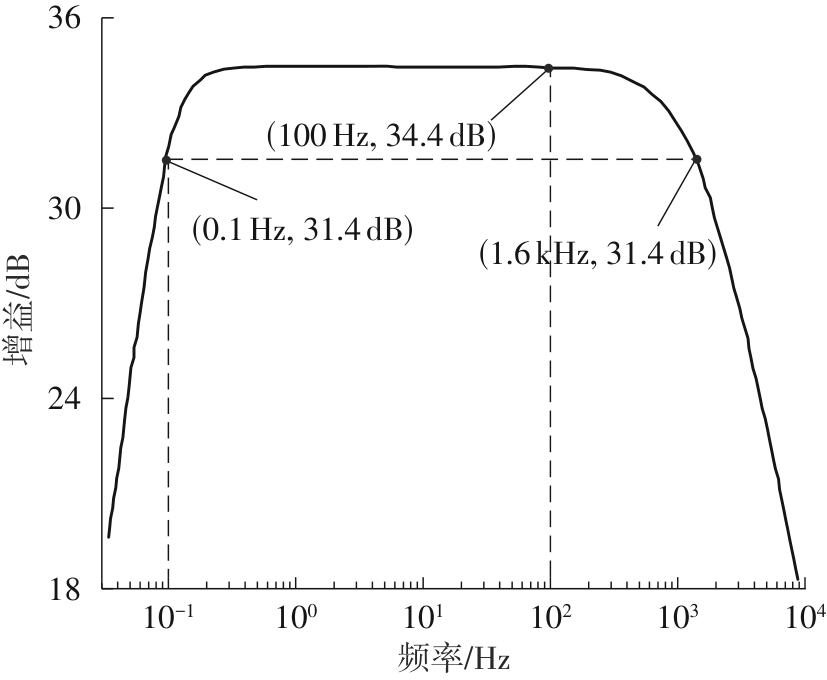
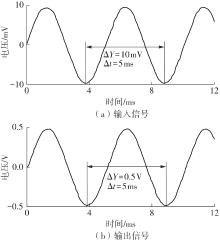
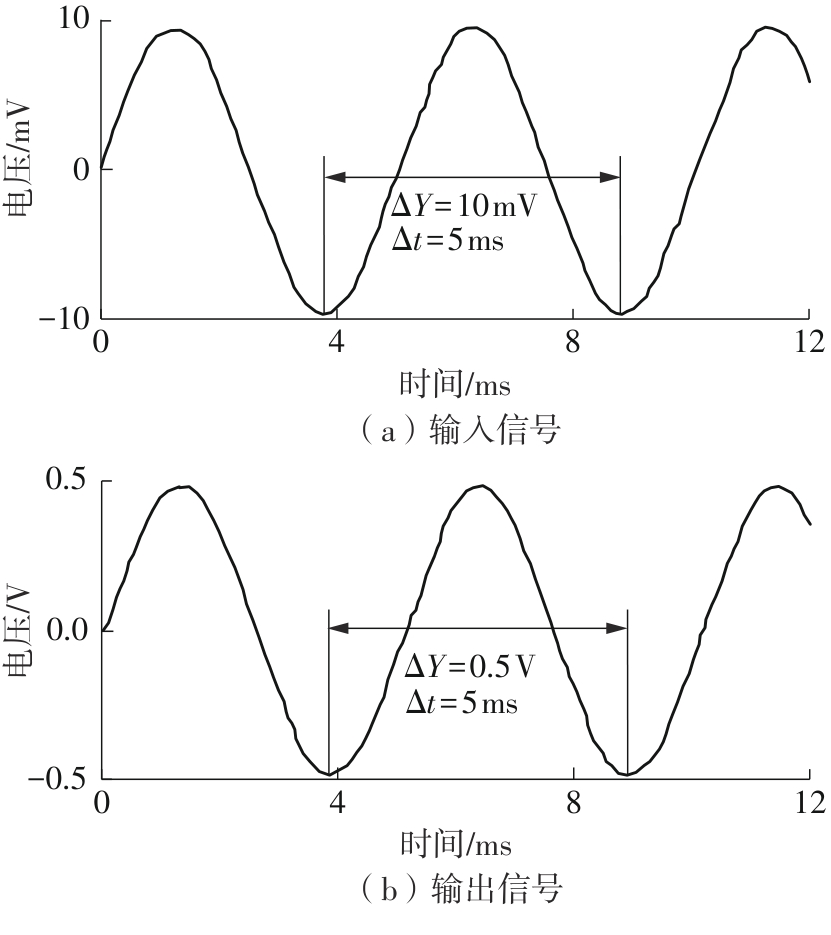
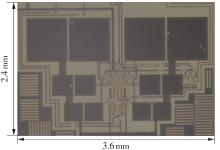
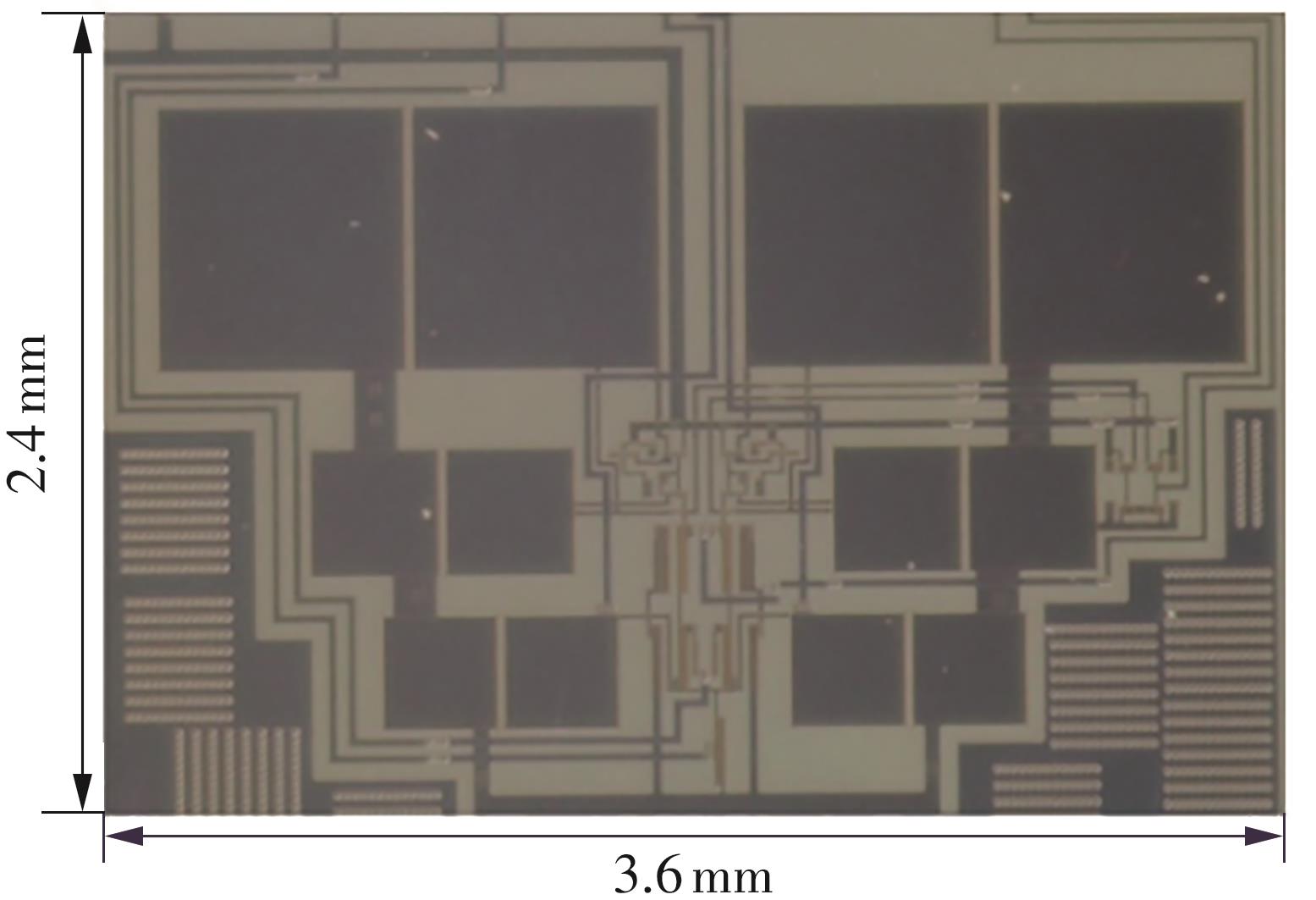
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 80-87.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240296
• Electronics, Communication & Automation Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
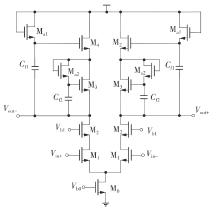
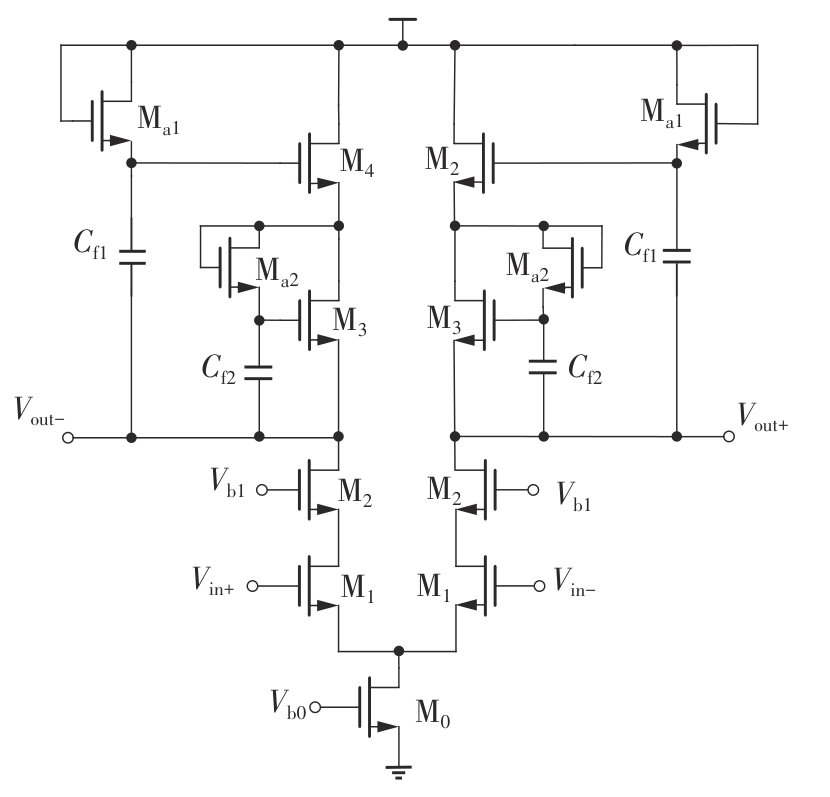
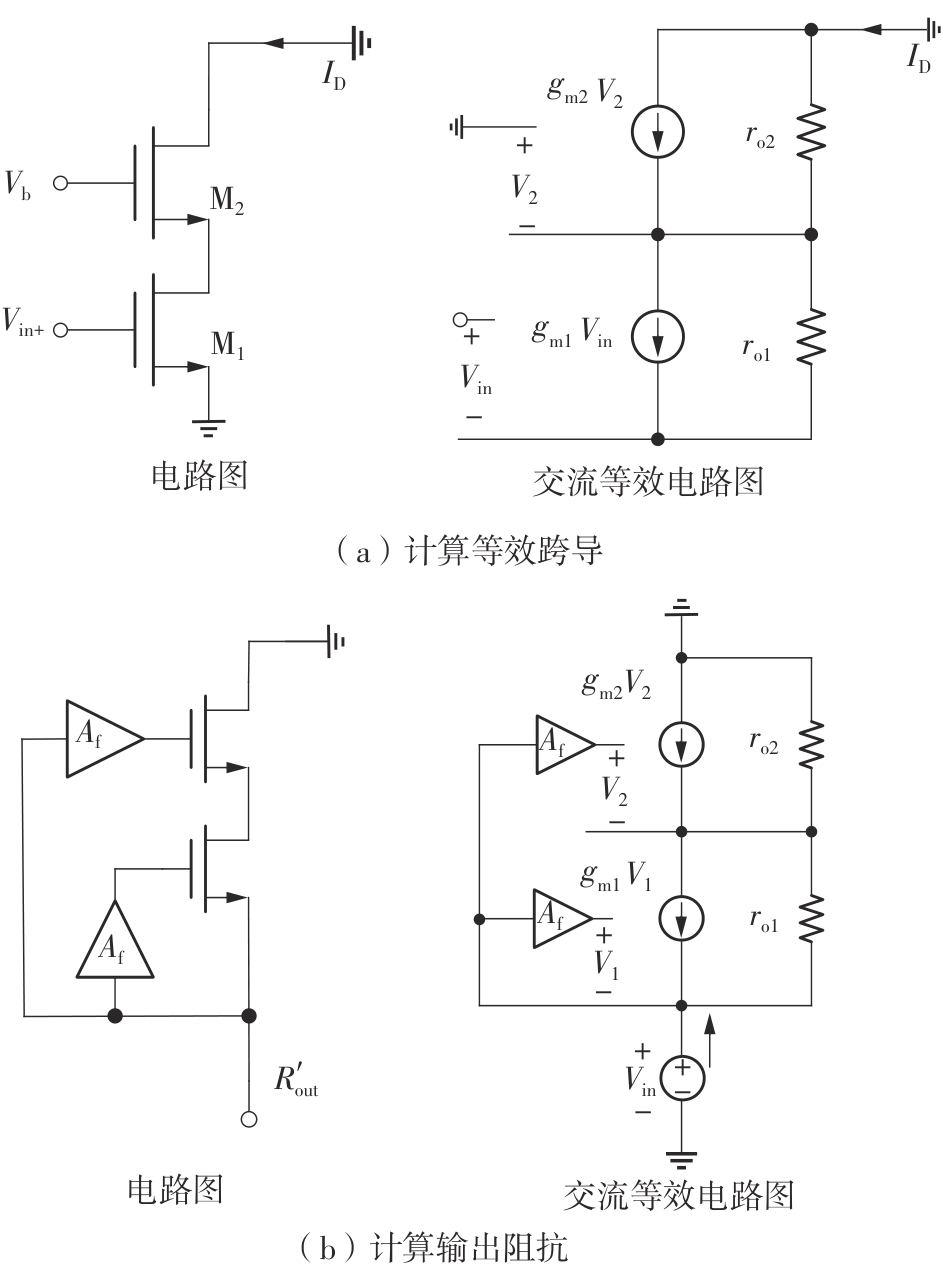
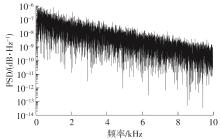
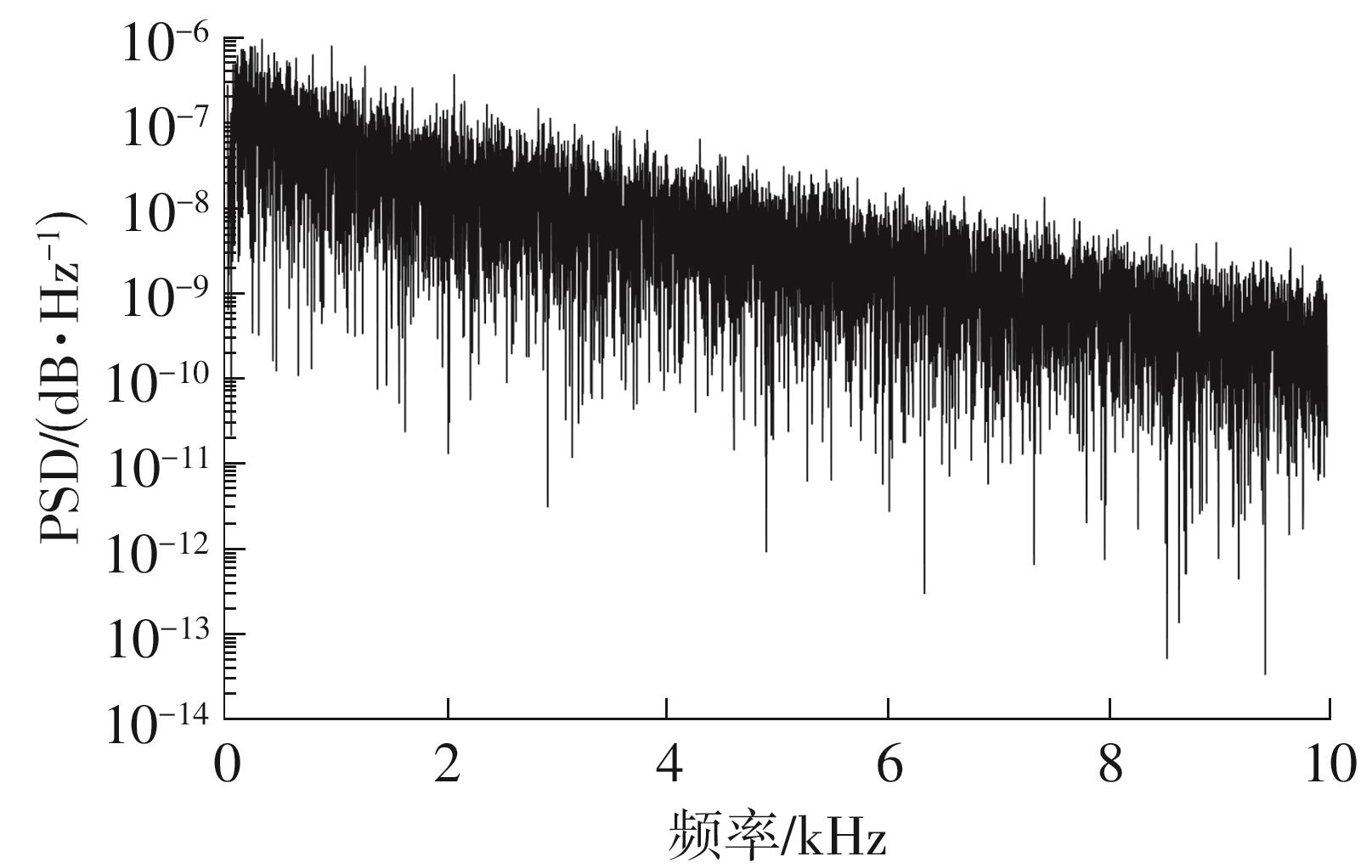
Research on High-Gain MO-TFT Heart Rate Signal Detection Preamplifier
WU Zhaohui( ), CHEN Jialin, ZHAO Mingjian, LI Bin(
), CHEN Jialin, ZHAO Mingjian, LI Bin( )
)
- School of Microelectronics,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 511442,Guangdong,China