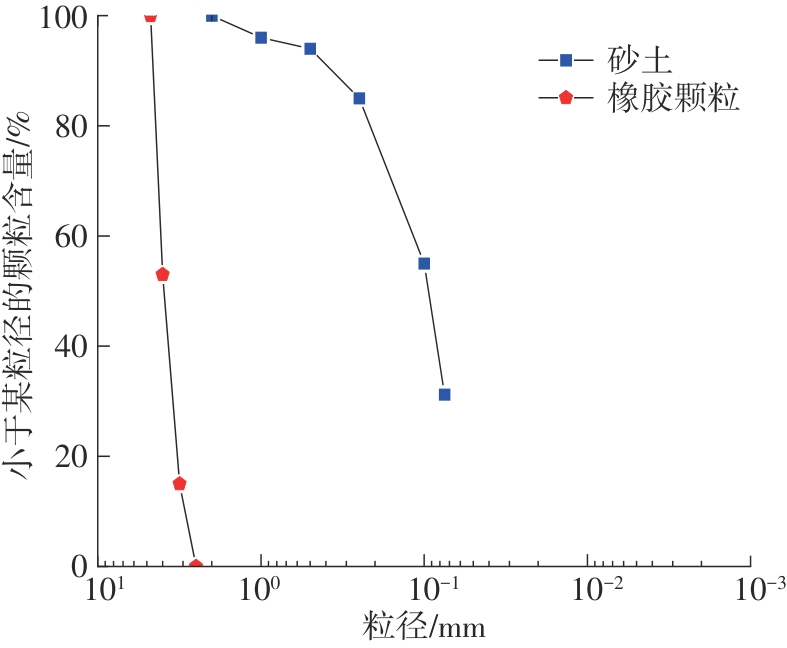
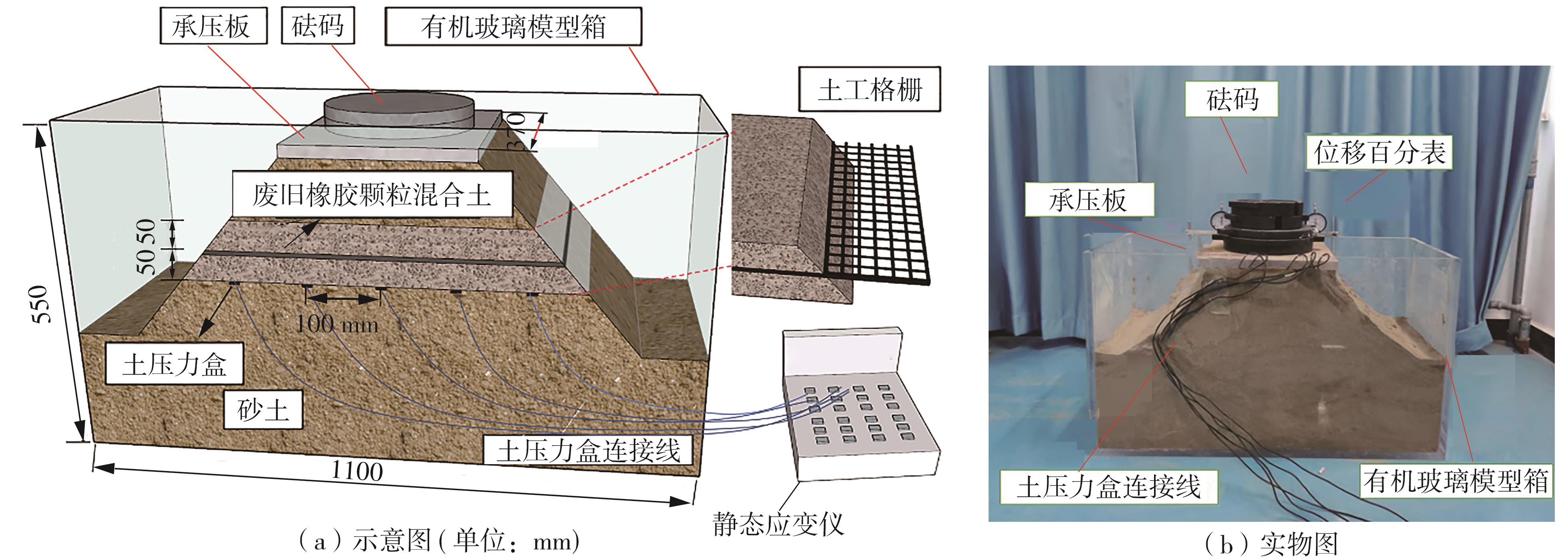
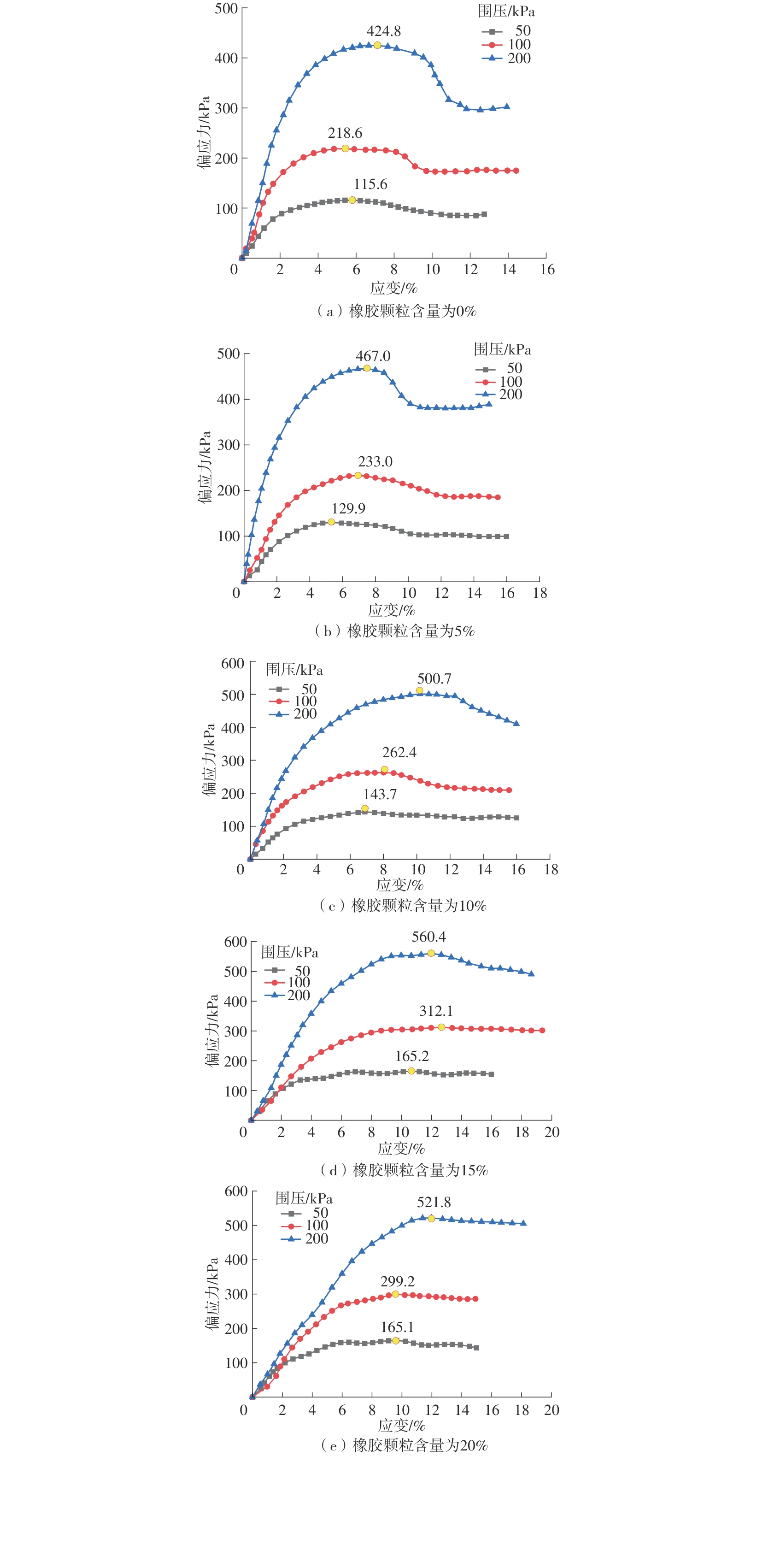
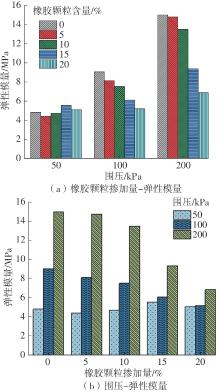
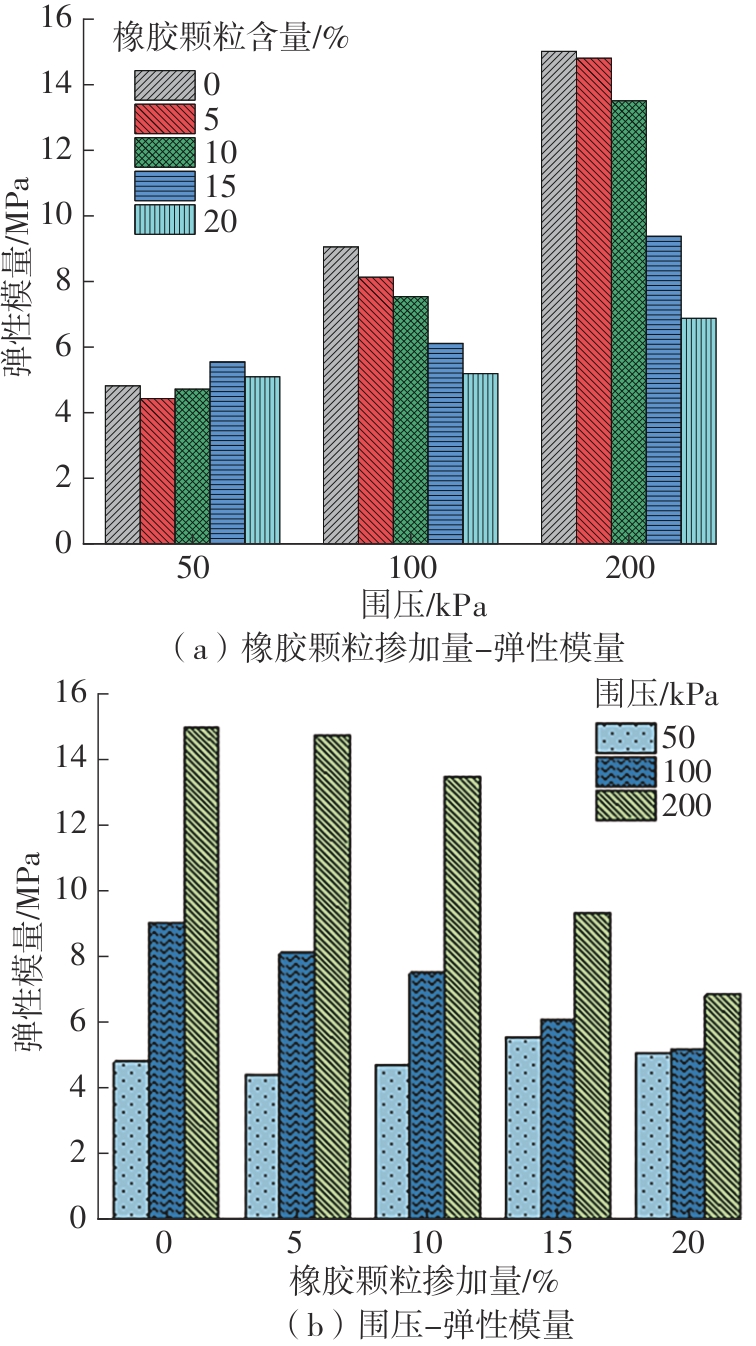
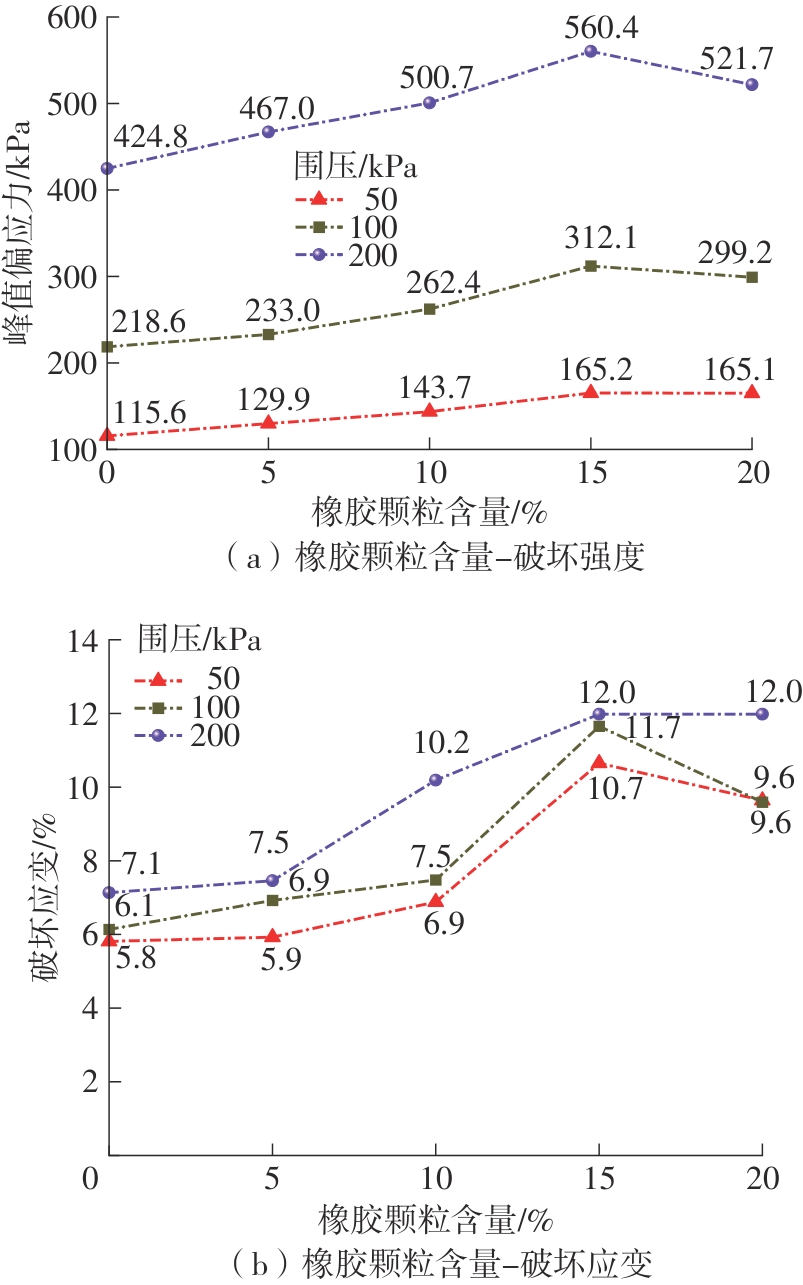
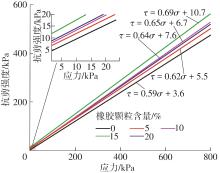
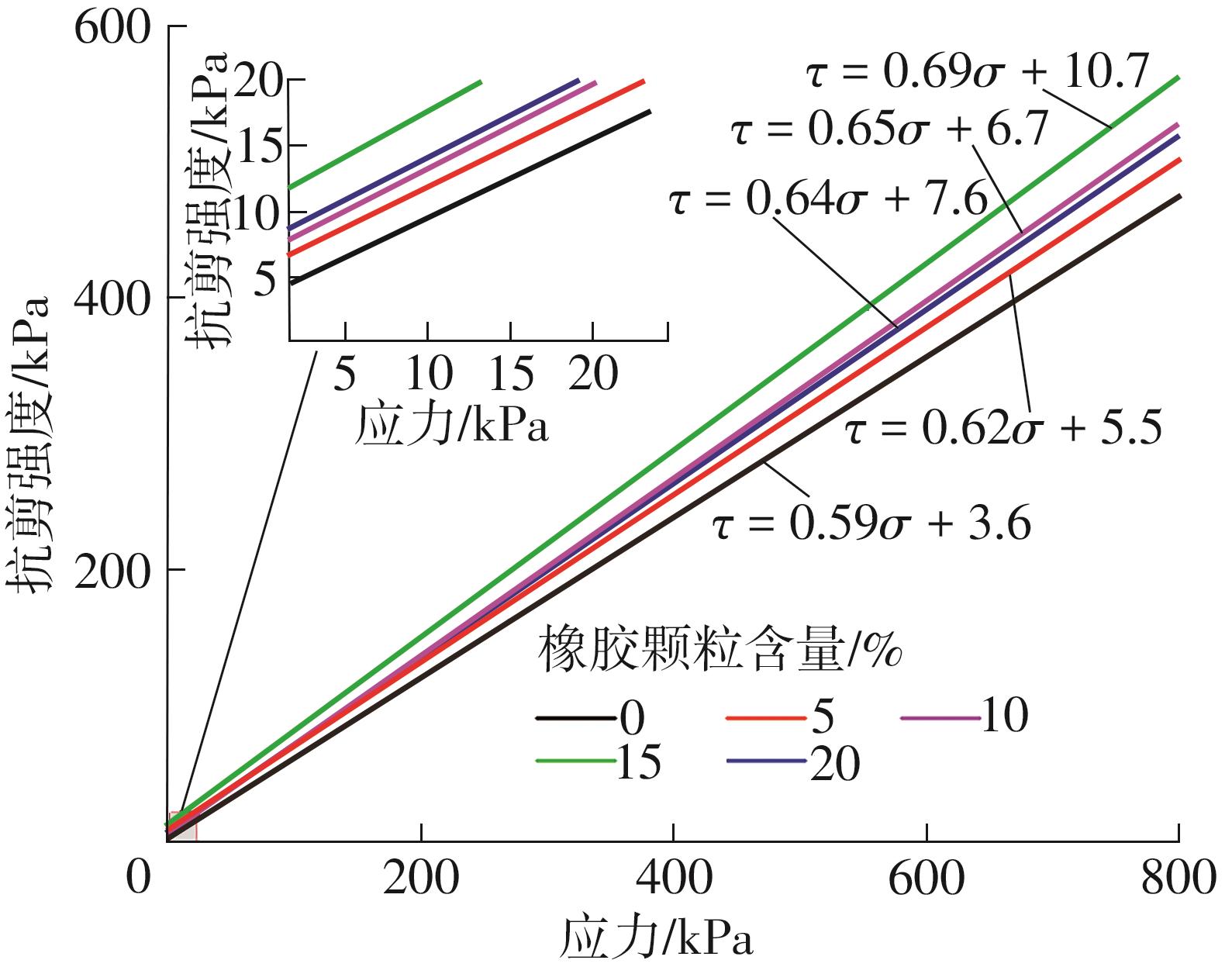
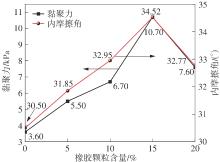
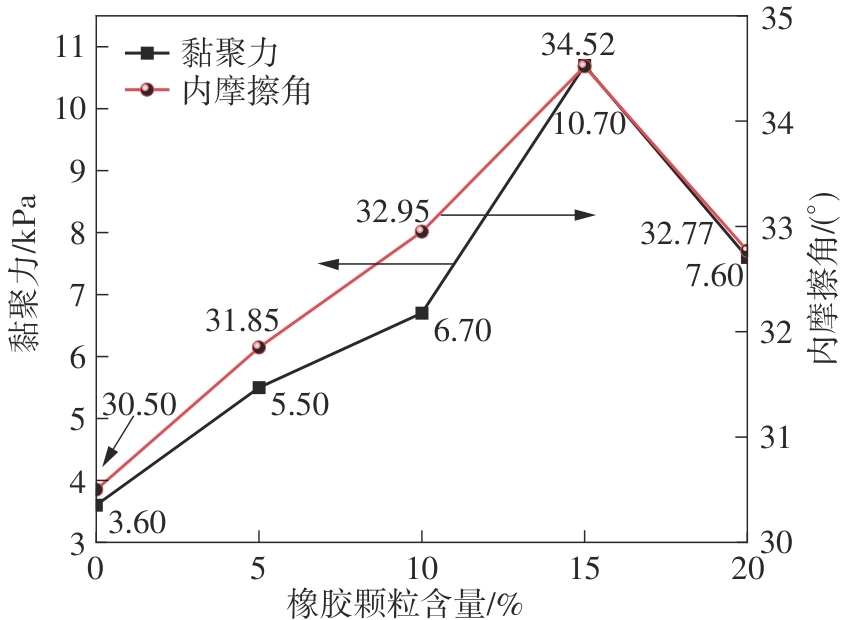
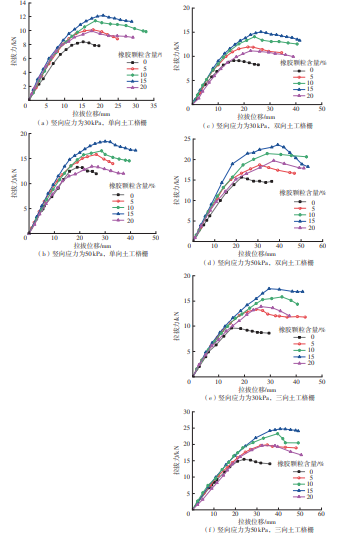
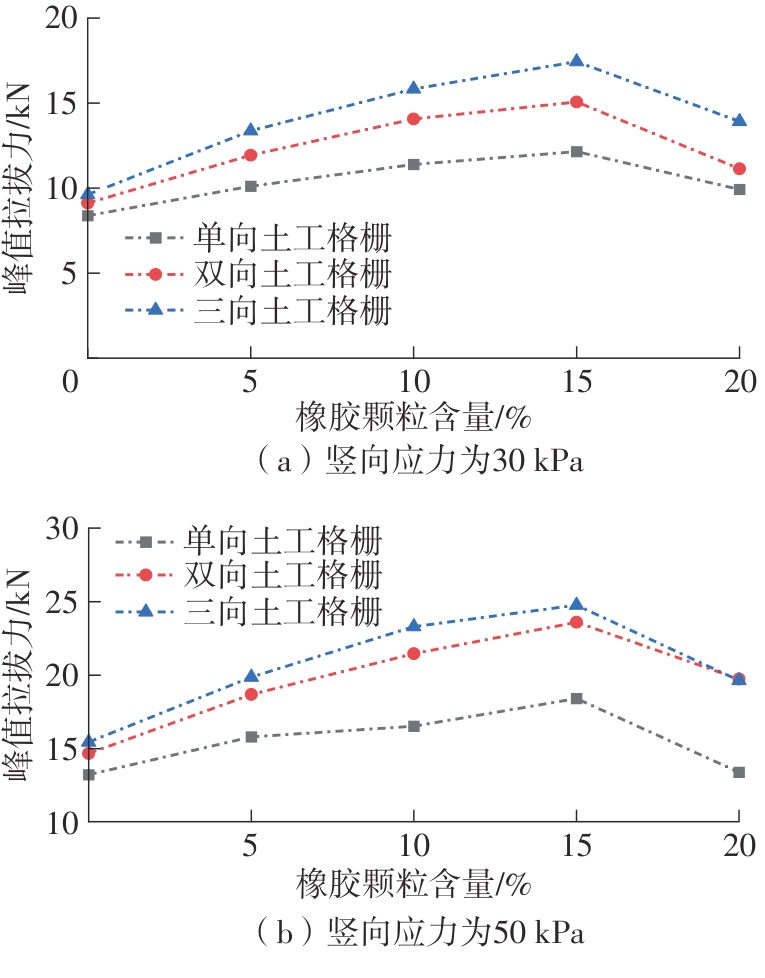
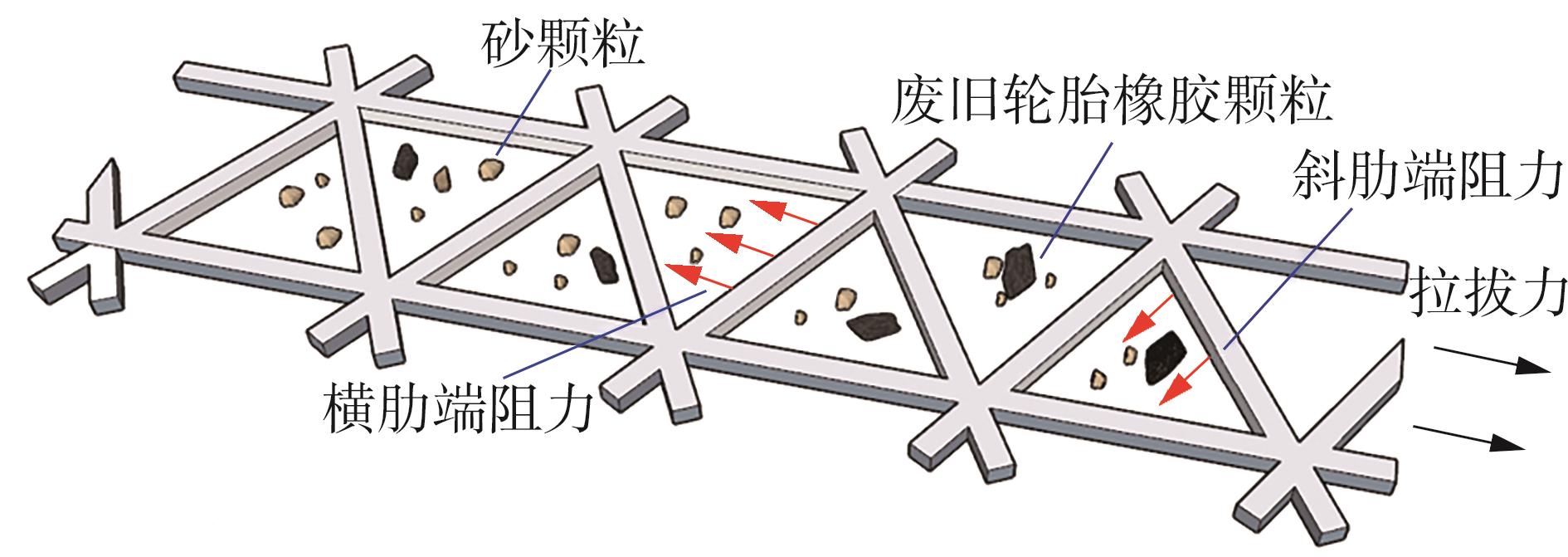
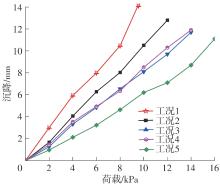
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 124-135.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240291
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Stability Study of Reinforced Embankment with Rubber Particles Mixed Soil
LI Tao1, LI Yue1, SHU Jiajun1, ZHANG Ruihai1, LIU Bo1,2
- 1.School of Mechanics and Civil Engineering,China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing,Beijing 100083,China
2.National Key Laboratory for Disaster Prevention,Control and Intelligent Construction of Tunnel Engineering,Beijing 100083,China
-
Received:2024-06-06Online:2025-02-25Published:2025-02-03 -
About author:李涛(1981—),男,博士,教授,主要从事岩土工程和城市地下工程研究。E-mail: lit@cumtb.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(42172319)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Tao, LI Yue, SHU Jiajun, ZHANG Ruihai, LIU Bo. Stability Study of Reinforced Embankment with Rubber Particles Mixed Soil[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(2): 124-135.
share this article
| 1 | 刘丽莎,田锋 .废旧轮胎的回收处理及资源化现状研究[J].新型工业化,2021,11(5):58-59. |
| LIU Lisha, TIAN Feng .Research on recycling and resource utilization of waste tires[J].The Journal of New Industrialization,2021,11(5):58-59. | |
| 2 | LI B, HUANG M S, ZENG X W .Dynamic behavior and liquefaction analysis of recycled-rubber sand mixtures[J].Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2016,28(11):1-14. |
| 3 | LI L H, LIU S S, XIAO H L,et al .Experimental investigation on reinforcement effect of sustainable materials for different subgrades[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,343(7):130944/1-14. |
| 4 | LI L H, YANG J C, XIAO H L,et al .Behavior of tire-geogrid-reinforced retaining wall system under dynamic vehicle load[J].International Journal of Geomechanics,2020,20(4):04020017/1-12. |
| 5 | LI H B, LI W B, TEMITOPE A A,et al .Analysis of the influence of production method,crumb rubber content and stabilizer on the performance of asphalt rubber[J].Applied Sciences,2020,10(16):5447/1-18. |
| 6 | WANG H N, YOU Z P, MILLS-BEALE J,et al .Laboratory evaluation on high temperature viscosity and low temperature stiffness of asphalt binder with high percent scrap tire rubber[J].Construction and Building Materials,2012,26(1):583-590. |
| 7 | WANG T, XIAO F P, AMIRKHANIAN S,et al .A review on low temperature performances of rubberized asphalt materials[J].Construction and Building Materials,2017,145(4):483-505. |
| 8 | KOK B V, COLAK H .Laboratory comparison of the crumb-rubber and SBS modified bitumen and hot mix asphalt[J].Construction and Building Materials,2011,25(8):3204-3212. |
| 9 | GHAVIBAZOO A, ABDELRAHMAN M .Composition analysis of crumb rubber during interaction with asphalt and effect on properties of binder[J].International Journal of Pavement Engineering,2013,14(5):517-530. |
| 10 | JEONG K D, LEE S J, AMIRKHANIAN S N,et al .Interaction effects of crumb rubber modified asphalt binders[J].Construction and Building Materials,2010,24(5):824-831. |
| 11 | ZHOU C X, TAN Y Q .Study on anti-icing performance of pavement containing a granular crumb rubber asphalt mixture[J].Road Materials and Pavement Design,2009,10(1):281-294. |
| 12 | BRESSI S, COLINAS-ARMIJO N, DI MINO G .Analytical approach for the mix design optimisation of bituminous mixtures with crumb rubber[J].Materials and Structures,2018,51(1):48-59. |
| 13 | CHEN H L, LI D D, MA X,et al .Mesoscale analysis of rubber particle effect on young’s modulus and creep behaviour of crumb rubber concrete[J].International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design,2021,17(3):659-678. |
| 14 | 刘志恒,陈徐东,胡良鹏,等 .重复冲击下高温后橡胶自密实混凝土动态力学性能[J].工程科学与技术,2023,55(4):169-178. |
| LIU Zhiheng, CHEN Xudong, HU Liangpeng,et al .Investigation on the dynamic mechanical properties of thermally treated rubberized self-compacting concrete under repeated impact[J].Advanced Engineering Sciences,2023,55(4):169-178. | |
| 15 | ZHU X B, MIAO C W, LIU J P,et al .Influence of crumb rubber on frost resistance of concrete and effect mechanism[J].Procedia Engineering,2012,27(1):206-213. |
| 16 | REN R, LIANG J F, LIU D W,et al .Mechanical behavior of crumb rubber concrete under axial compre-ssion[J].Advances in Concrete Construction,2020,9(3): 249-256. |
| 17 | ASSAGGAF R A, ALI M R, AL-DULAIJAN S U,et al .Properties of concrete with untreated and treated crumb rubber-a review[J].Journal of Materials Research and Technology-Jmr & T,2021,11(1):1753-1798. |
| 18 | AL-TAYEB M M, BAKAR B H ABU, ISMAIL H,et al .Impact resistance of concrete with partial replacements of sand and cement by waste rubber[J].Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering,2012,51(12):1230-1236. |
| 19 | XU X Q, ZHANG Z G, HU Y G .Bearing strength of crumb rubber concrete under partial area loading[J].Materials,2020,13(11):2446/1-26. |
| 20 | AKBARI M, TAHAMTAN M H N, FALLAH-VALUKOLAEE S,et al .Investigating fracture characteristics and ductility of lightweight concrete containing crumb rubber by means of WFM and SEM methods[J].Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics,2022,117(1):103148/1-15. |
| 21 | RICHARDSON A, COVENTRY K, EDMONDSON V,et al .Crumb rubber used in concrete to provide freeze-thaw protection (optimal particle size)[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2016,112(1):599-606. |
| 22 | OTIENO M, MUSHUNJE K .Creep deformation characteristics of rubberised structural concrete[J].Construction and Building Materials,2021,312(6):125418/1-10. |
| 23 | 顾建波,周恩全,姚缘 .橡胶混合土路用性能研究[J].交通科技与管理,2024,5(4):111-113. |
| GU Fangbo, ZHOU Enquan, YAO Yuan .Study on performance of rubber mixed earth road[J].Traffic Technology and Management,2024,5(4):111-113. | |
| 24 | YADAV J S, TIWARI S K. Influence of crumb rubber on the geotechnical properties of clayey soil[J].Environment Development and Sustainability,2018,20(6):2565-2586. |
| 25 | 刘路路,蔡国军,刘晓燕 .橡胶-砂轻质填料压缩特性及颗粒破碎研究[J].中国矿业大学学报,2020,49(5):882-888. |
| LIU Lulu, CAI Guojun, LIU Xiaoyan .Investigation on compression and particle breakage characteristics of rubber-sand lightweight filler[J].Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2020,49(5):882-888. | |
| 26 | 刘飞禹,李昊泽,符军,等 .橡胶砂级配对混合土体剪切特性影响研究[J].岩土力学,2023,44(3):663-672. |
| LIU Feiyu, LI Haoze, FU Jun,et al .Effect of rubber-sand mixtures gradation on shear characteristics of mixed soil[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2023,44(3): 663-672. | |
| 27 | DAS S, BHOWMIK D .Small-strain dynamic beha-vior of sand and sand-crumb rubber mixture for different sizes of crumb rubber particle[J].Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2020,32(11):04020334/1-9. |
| 28 | 李丽华,肖衡林,唐辉明,等.轮胎碎片-砂混合土抗剪性能优化试验研究[J].岩土力学,2013,34(4):1063-1067. |
| LI Lihua, XIAO Henglin, TANG Huiming,et al .Shear performance optimizing of tire shred-sand mixture[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(4):1063-1067. | |
| 29 | 周海 .砂土-橡胶颗粒轻质混合料强度与剪胀特性试验研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2021. |
| 30 | 蔡永明,王志杰,齐逸飞,等 .土工格栅加筋橡胶碎石动力特性试验研究[J].岩土力学,2024,45(1):87-96,107. |
| CAI Yongming, WANG Zhijie, QI Yifei,et al .Experimental study on dynamic properties of geogrid reinforced rubber gravel[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2024,45(1):87-96,107. | |
| 31 | SOL-SANCHEZ M, MORENO-NAVARRO F, PEREZ R,et al .Defining the process of including sustainable rubber particles under sleepers to improve track beha-viour and performance[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,227(15):178-188. |
| 32 | 刘方成,王将,吴孟桃,等 .土工格栅加筋橡胶砂应力-应变特性试验[J].吉林大学学报(工学版),2023,53(9):2542-2553. |
| LIU Fangcheng, WANG Jiang, WU Mengtao,et al .Stress-strain characteristics of geogrid reinforced[J].Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2023,53(9):2542-2553. | |
| 33 | 公路土工试验规程: [S]. |
| 34 | 杨晋华 .季节性冻土区粉砂土的力学特性研究[D].包头:内蒙古科技大学,2019. |
| 35 | BERGADO D T, CHAI J C, MIURA N. Prediction of pullout resistance and pullout force-displacement relationship for inextensible grid reinforcements[J].Soils and Foundations,1996,36(4):11-22. |
| [1] | Wang Yi-min Li Qing-zhen Gao Shui-qin. Experimental Investigation into Effect of Differential Settlement on Working Performance of Geogrid Reinforced Embankment [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(9): 68-74. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||