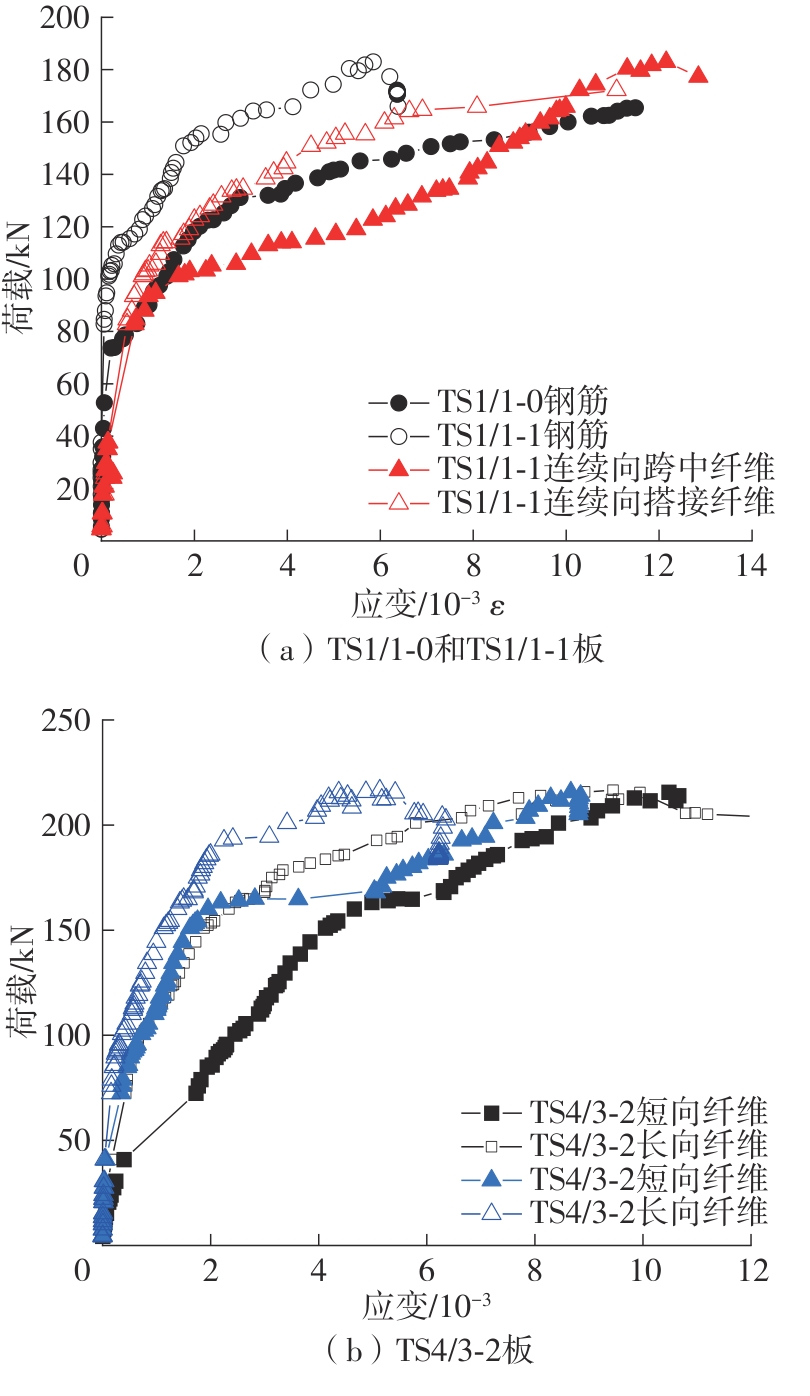
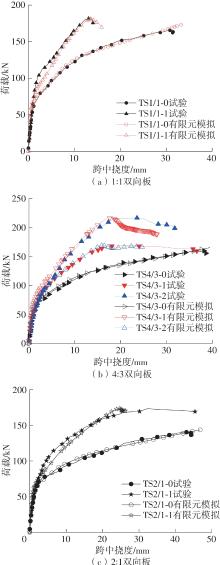
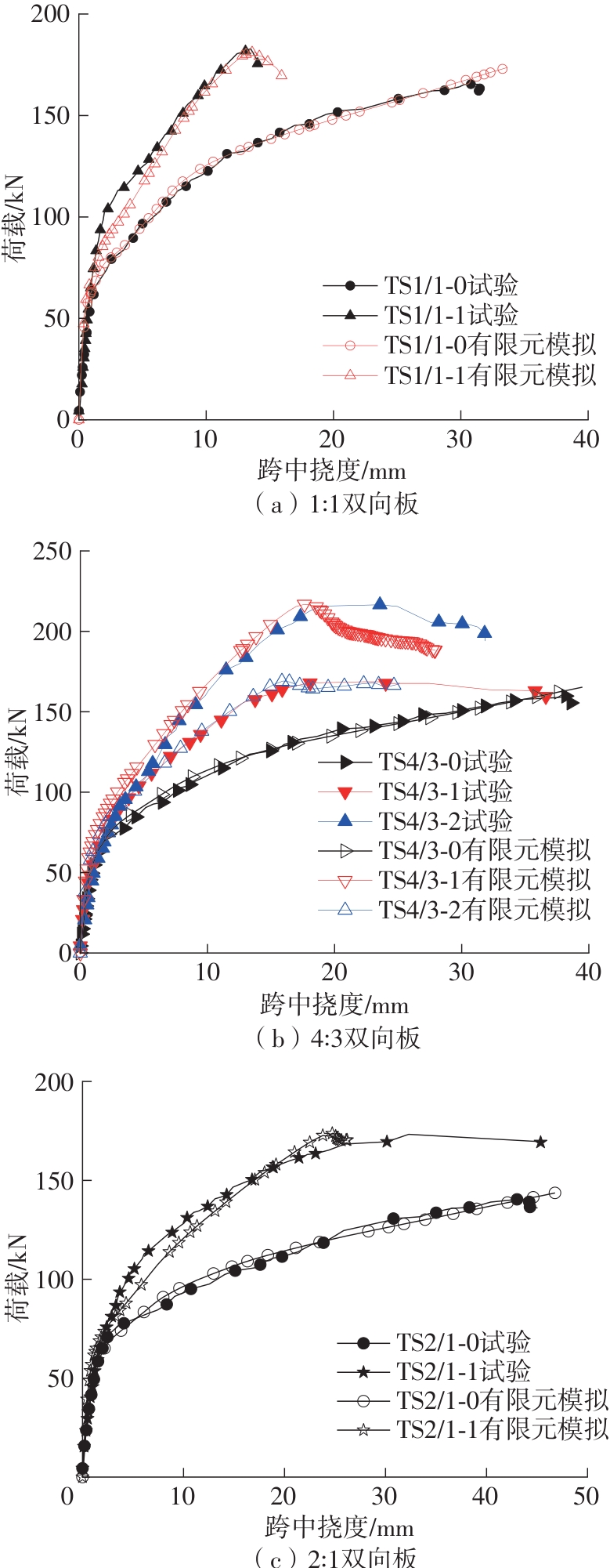
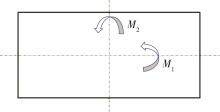
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 115-123.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240043
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
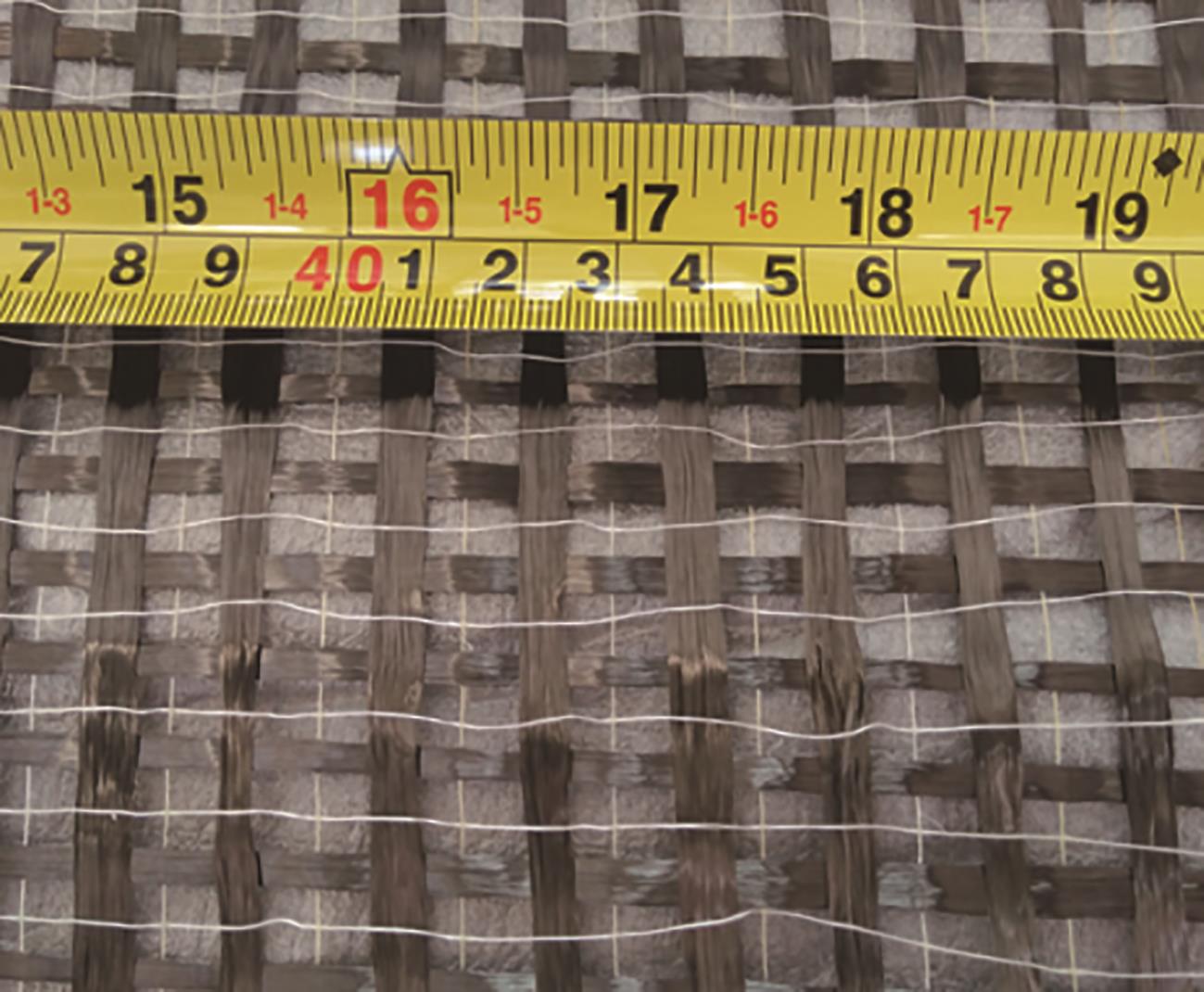
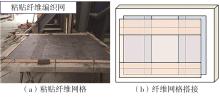
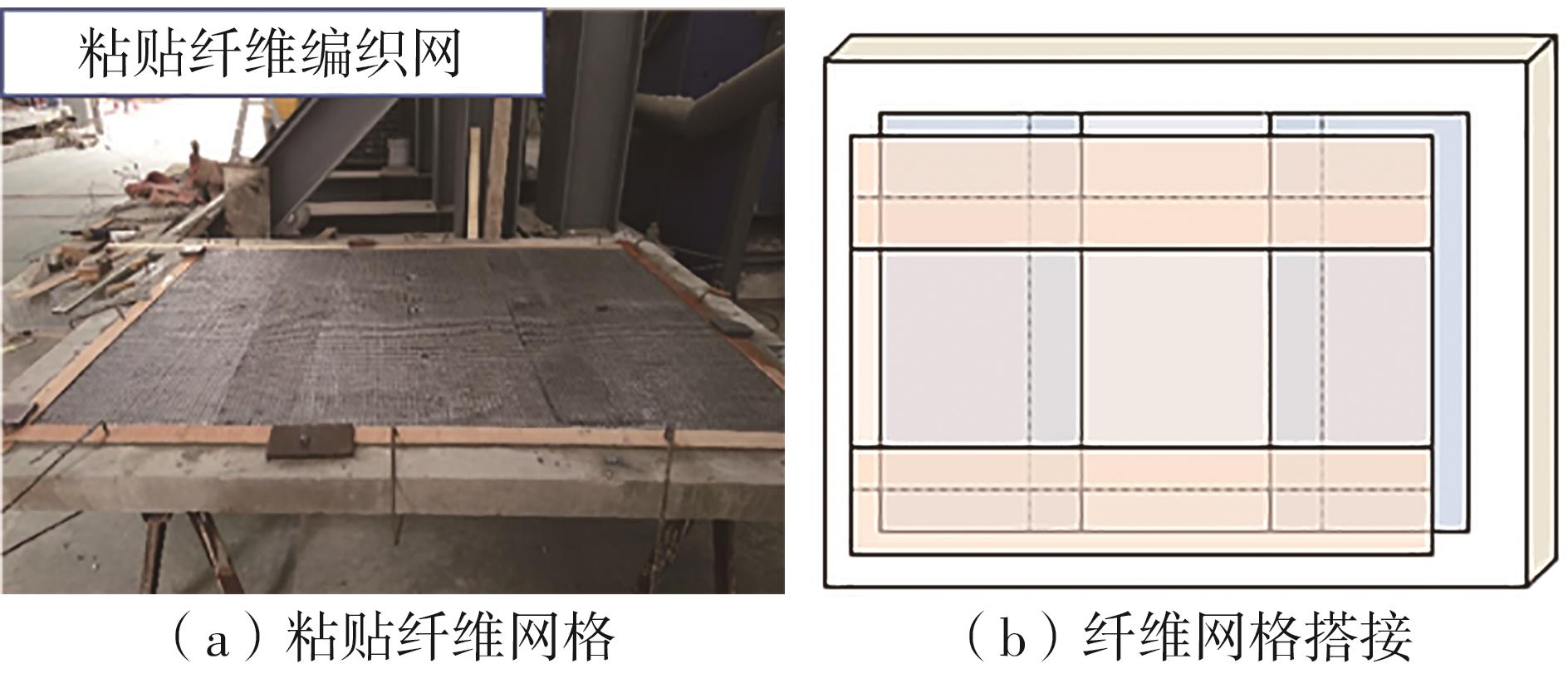
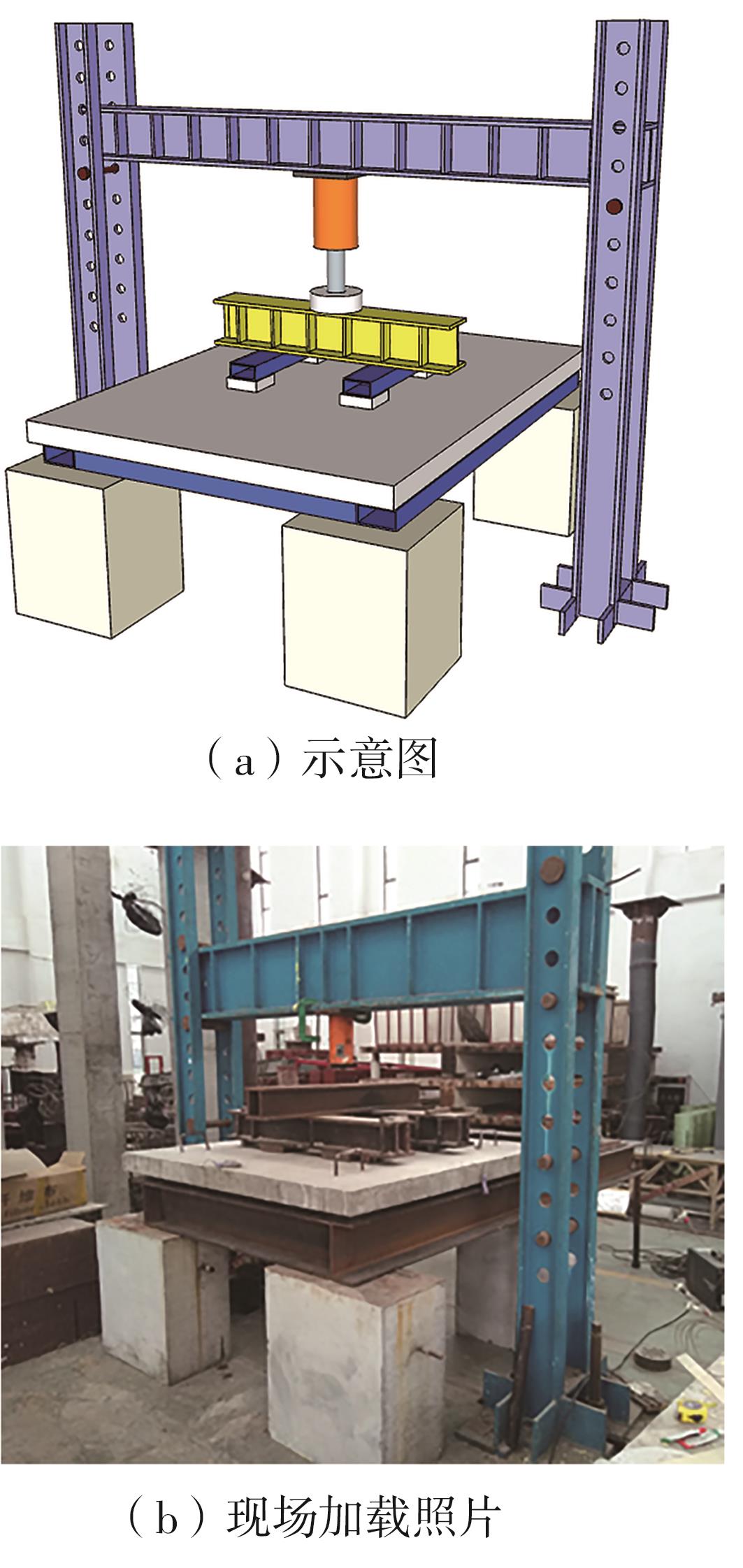
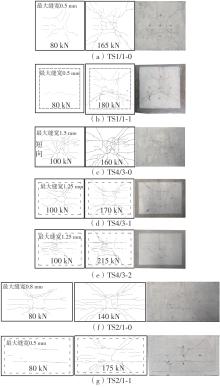
Flexural Performance of Two-Way Slabs Strengthened with Textile Reinforced Geopolymer Mortar
ZHANG Haiyan1,2, CHEN Haibiao2, WU Bo1,2, LI Mengyuan3
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building and Urban Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
3.Zhejiang Highway Technicians College,Hangzhou 310023,Zhejiang,China