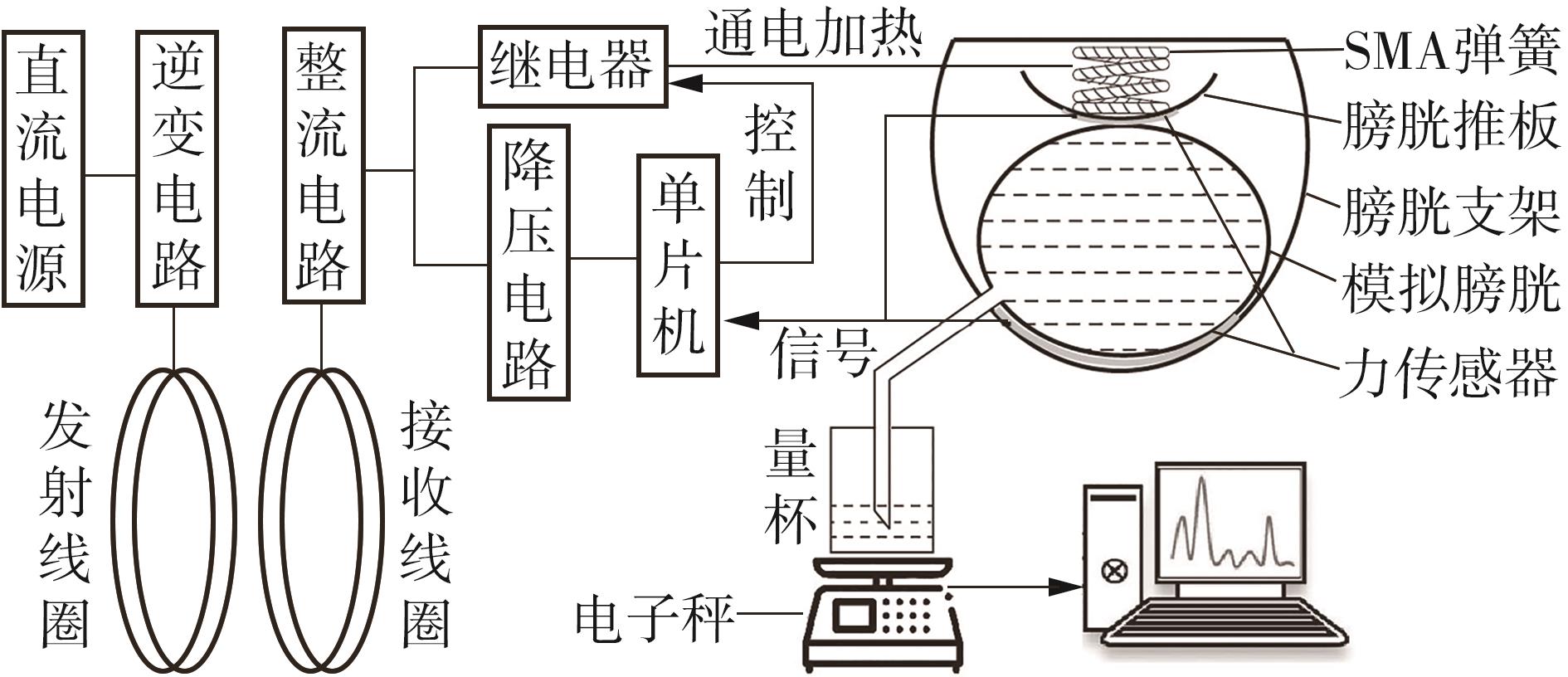
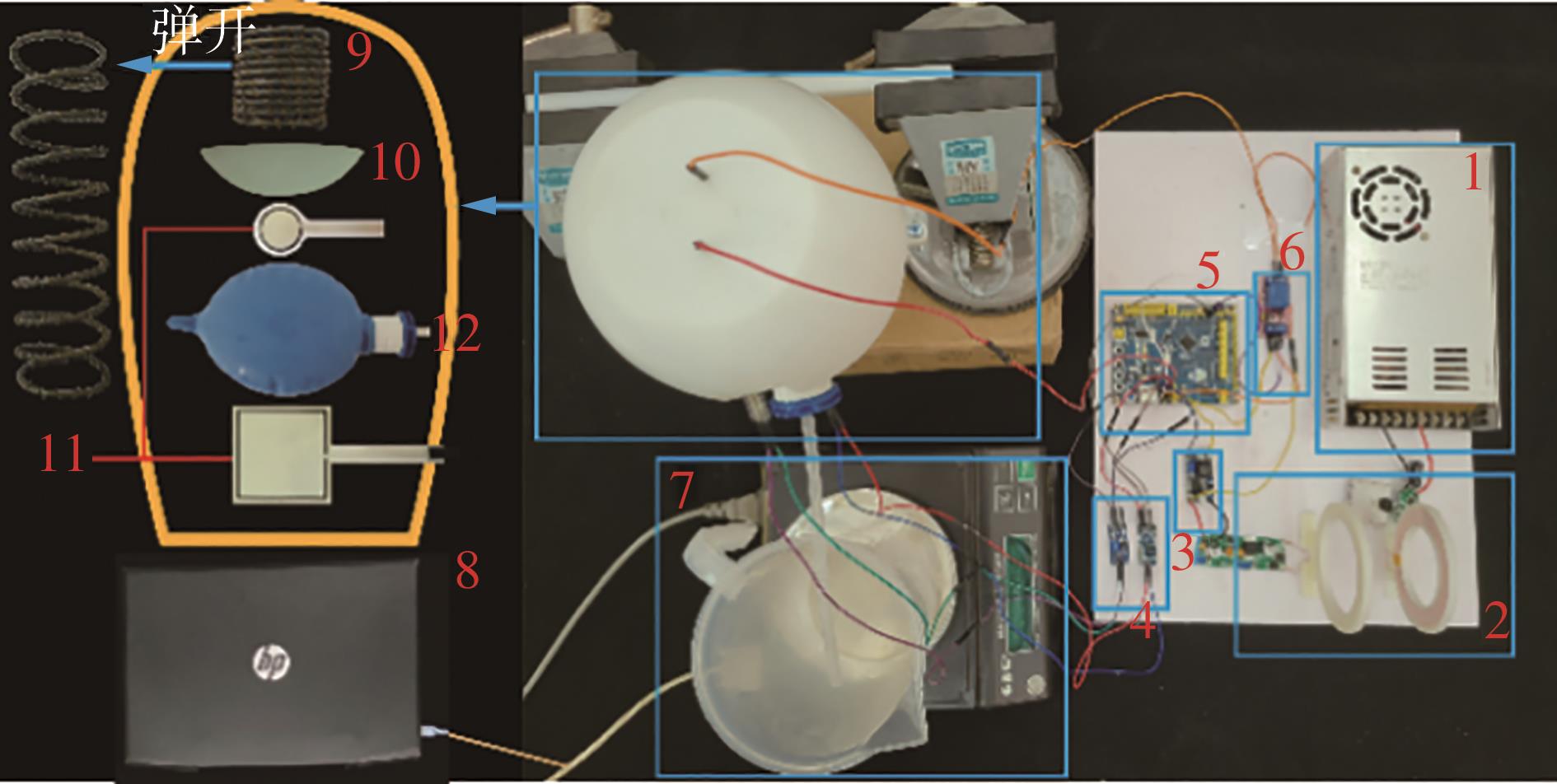
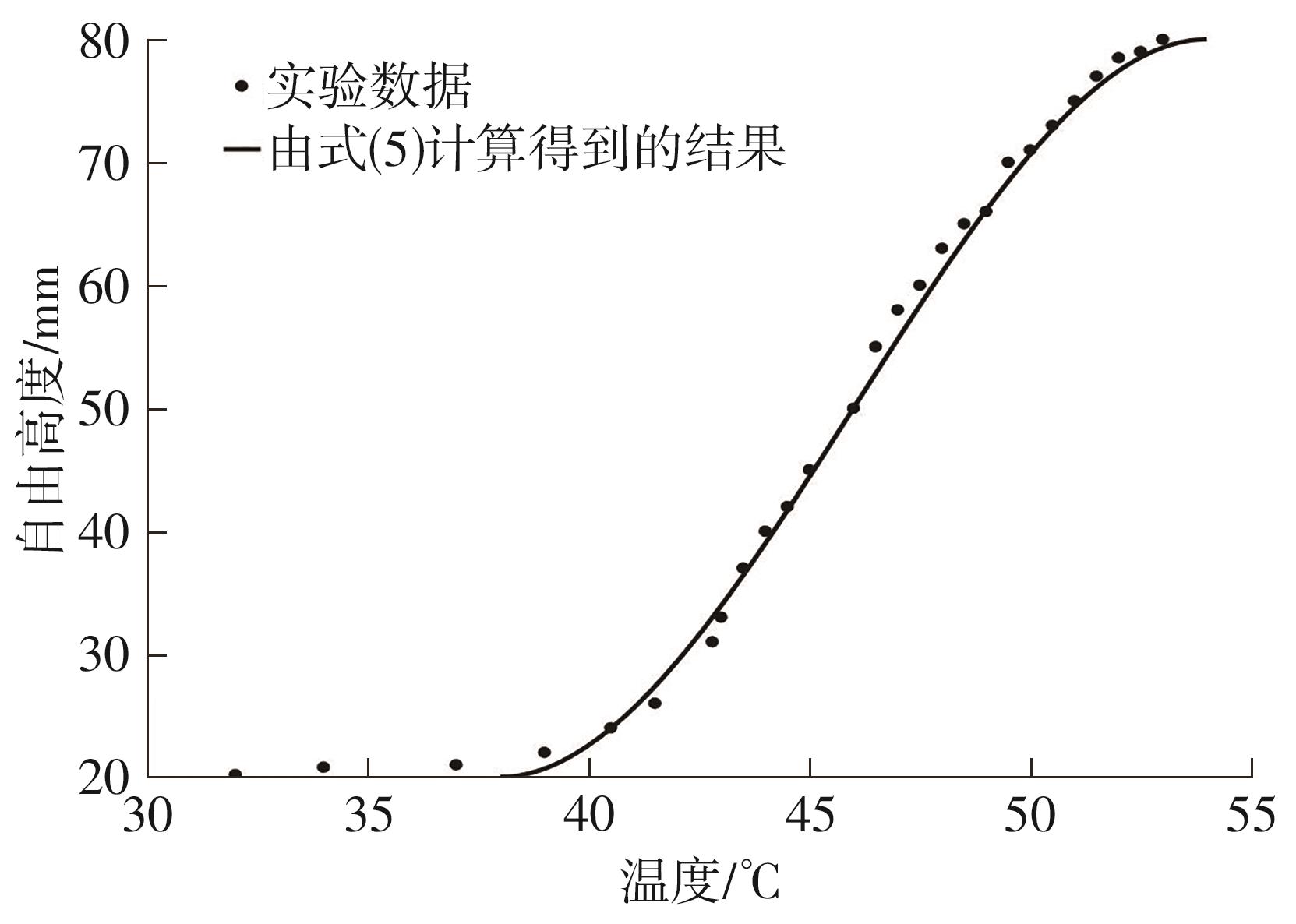
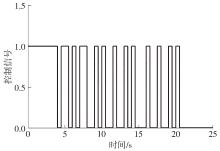
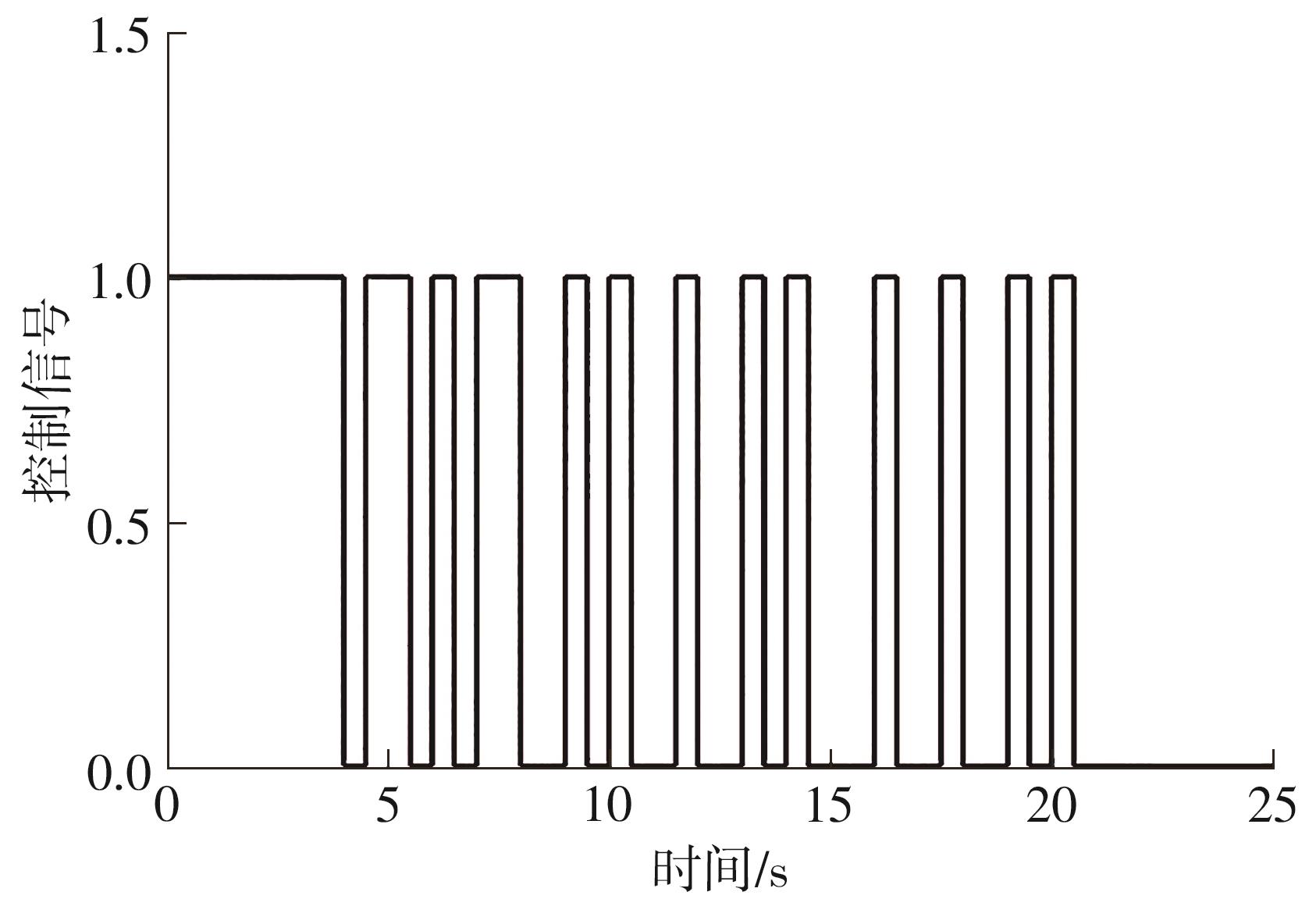
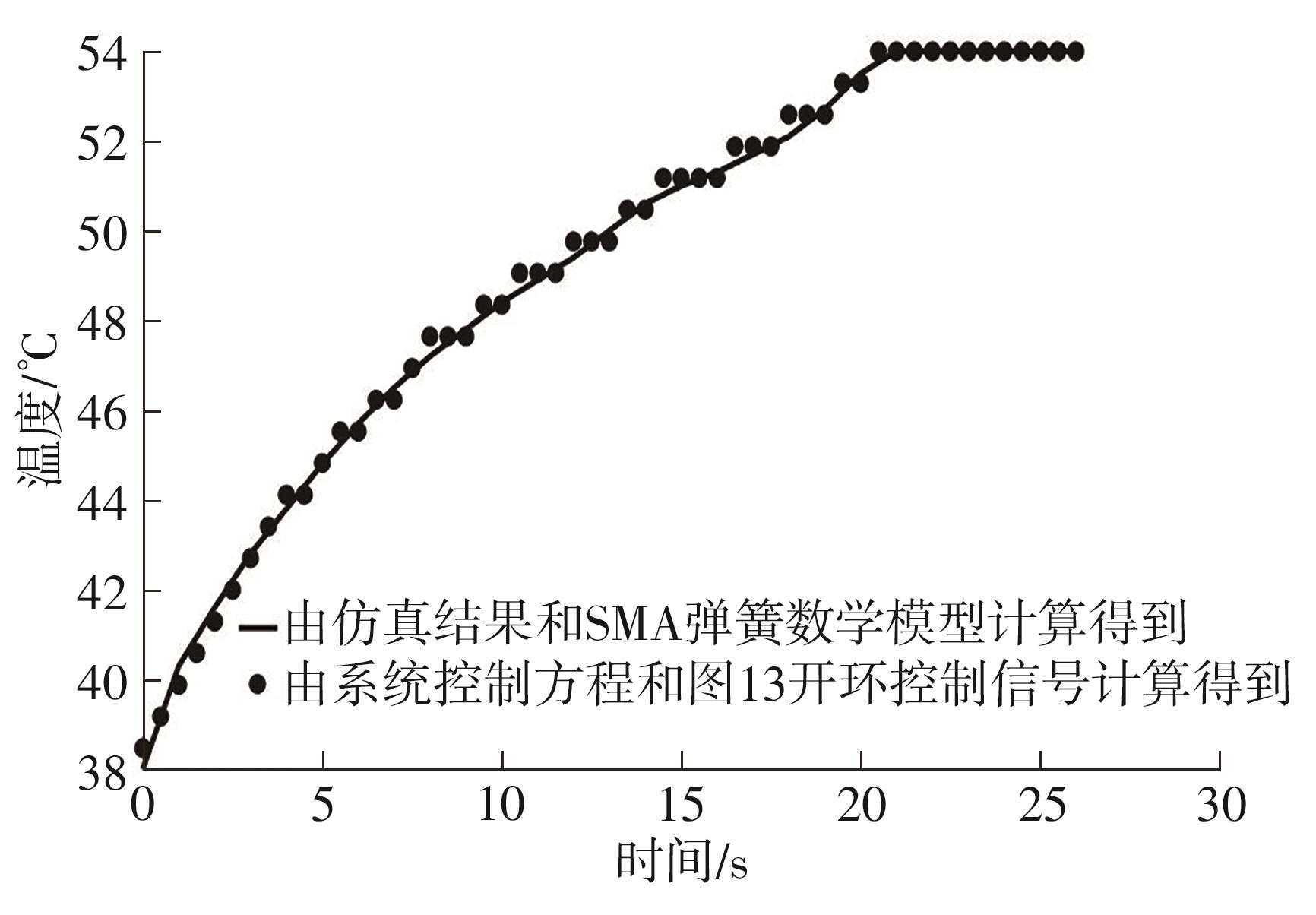
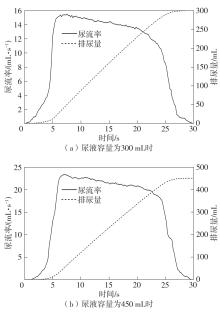
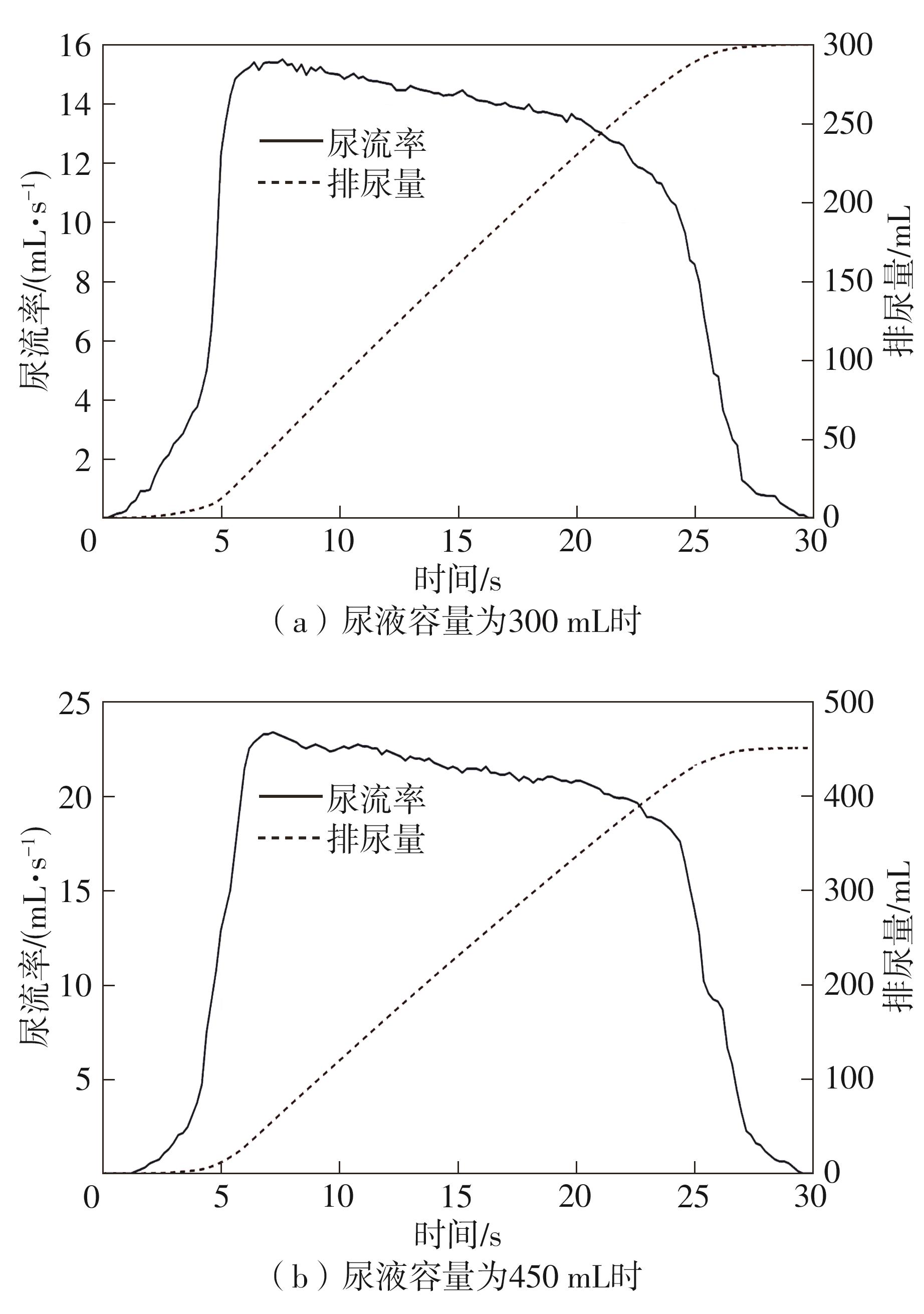
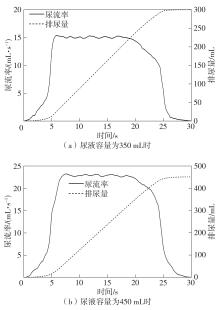
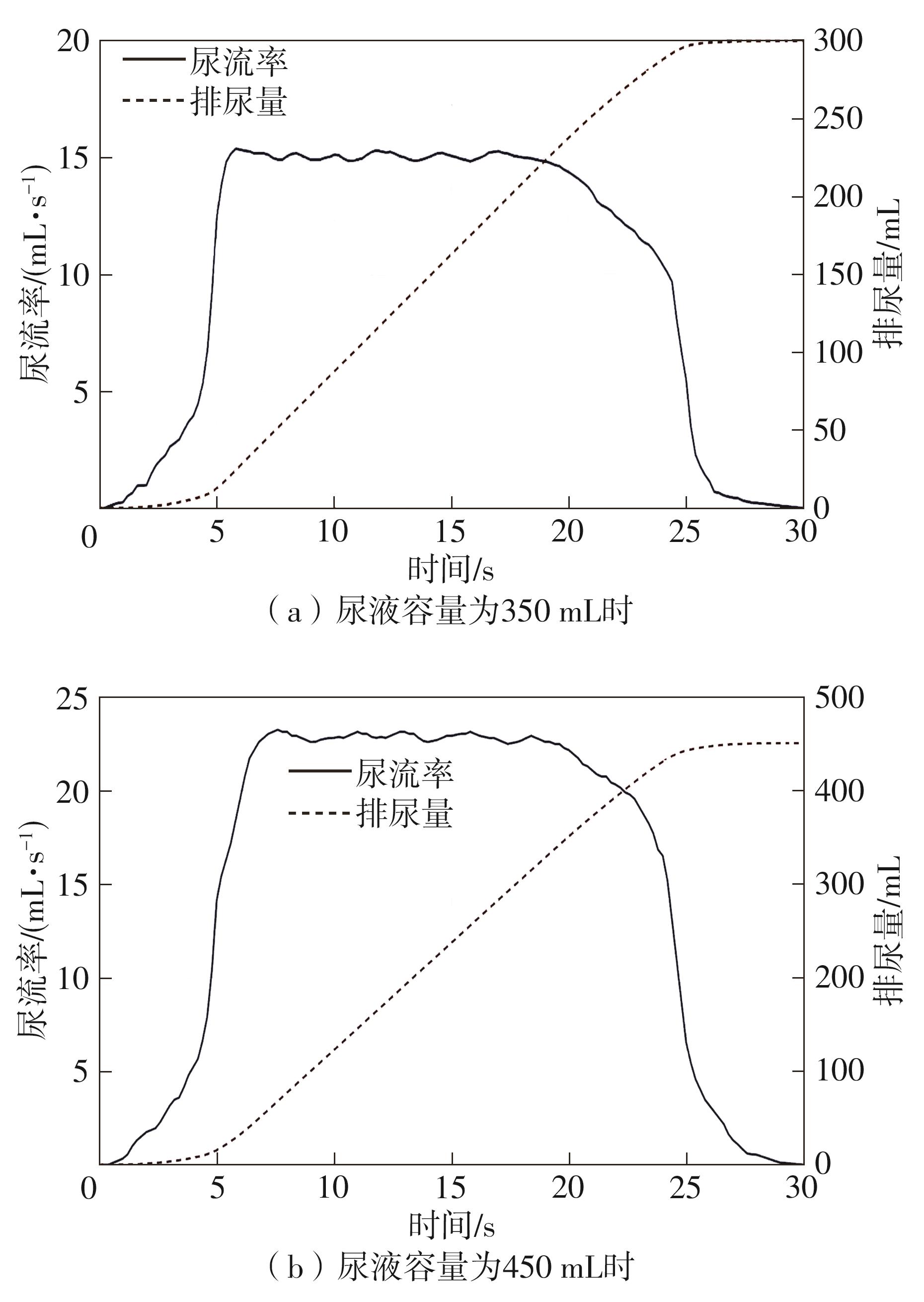
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 73-80.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230398
• Mechanical Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
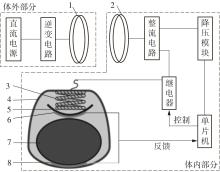
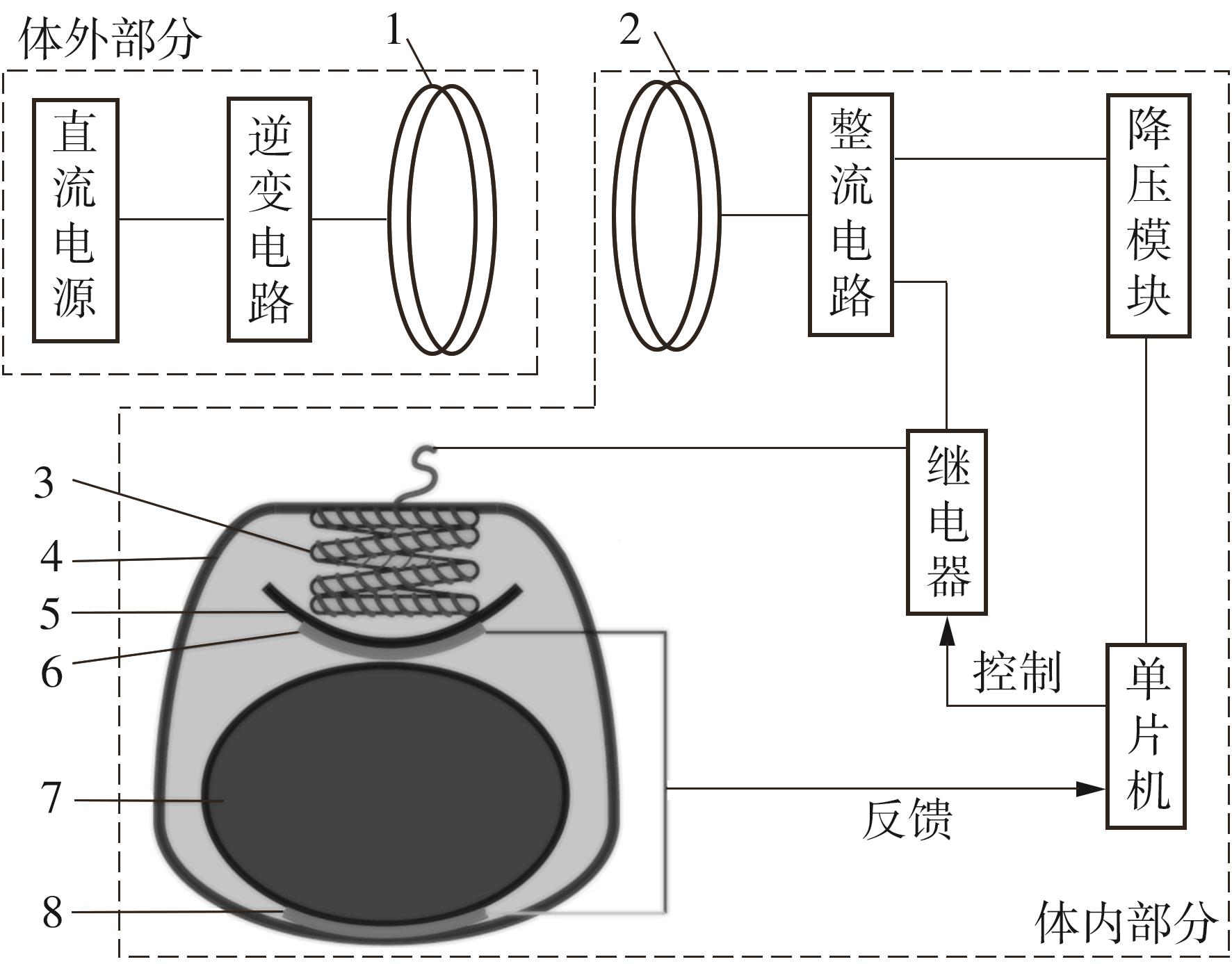
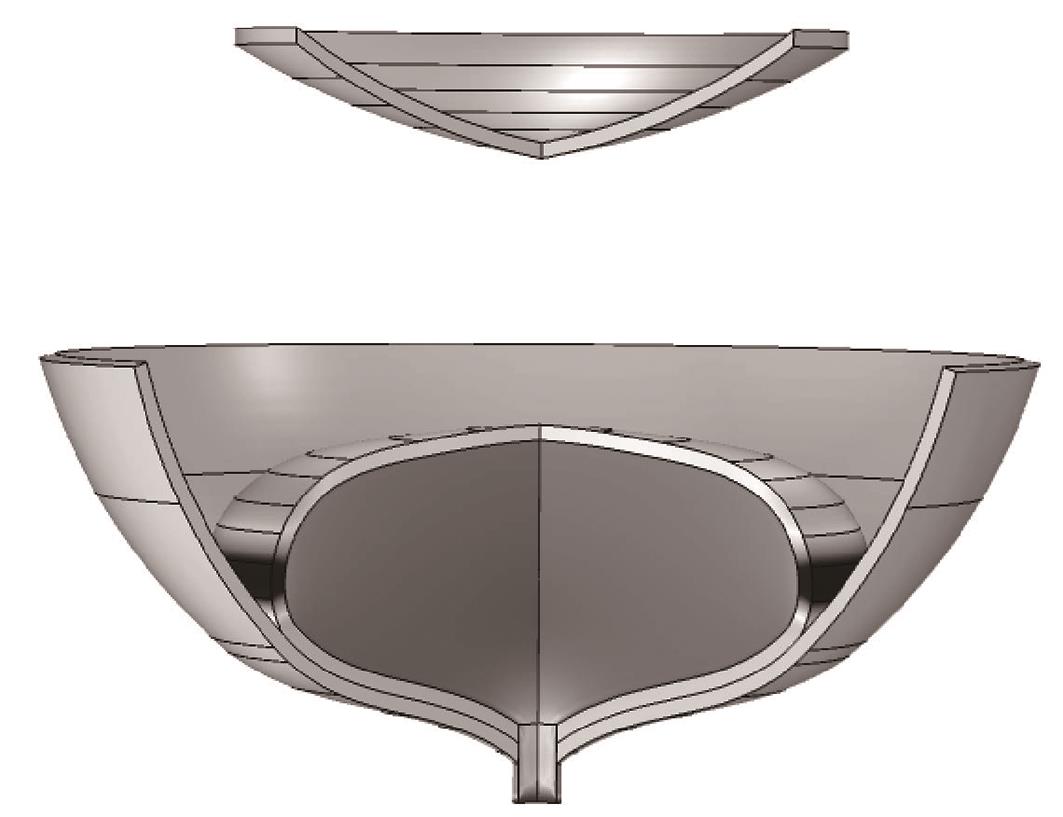
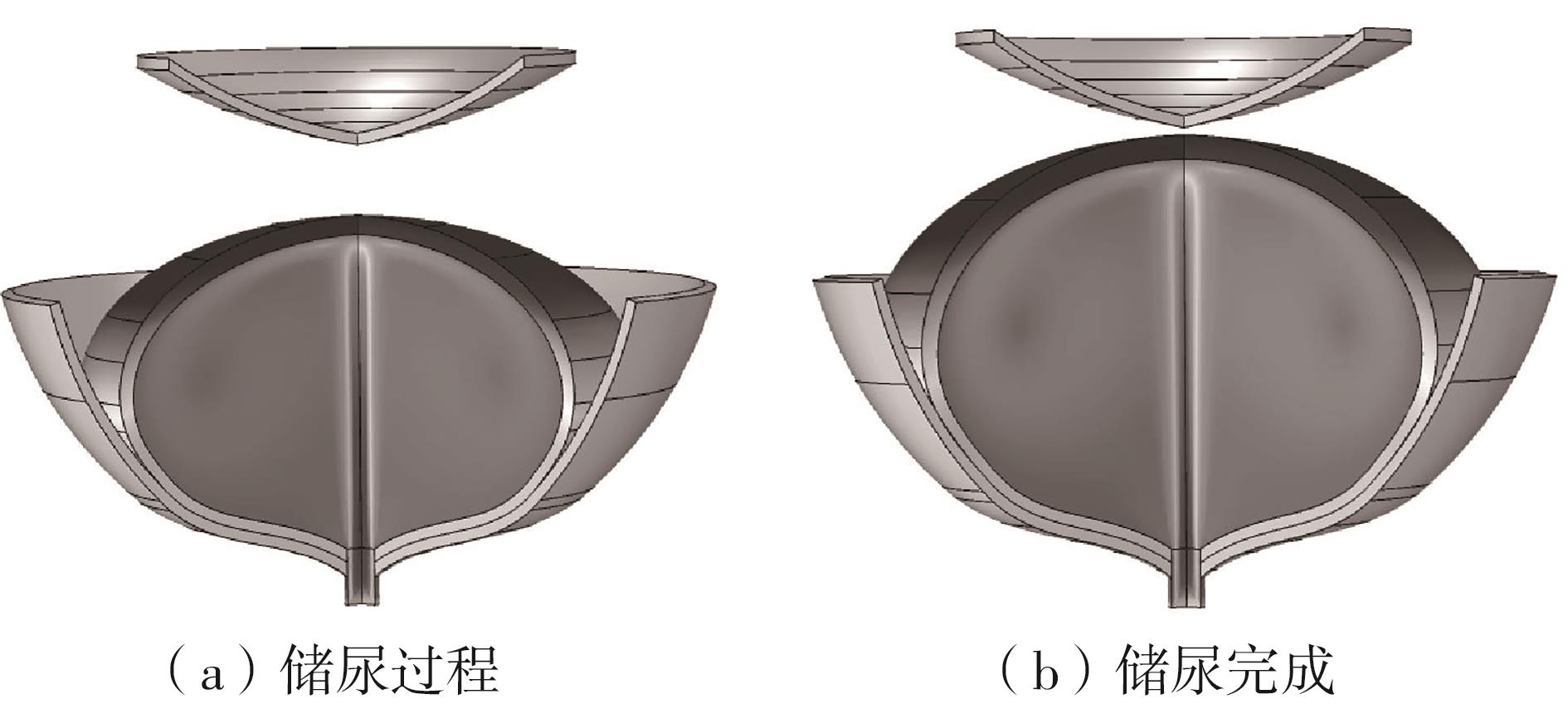
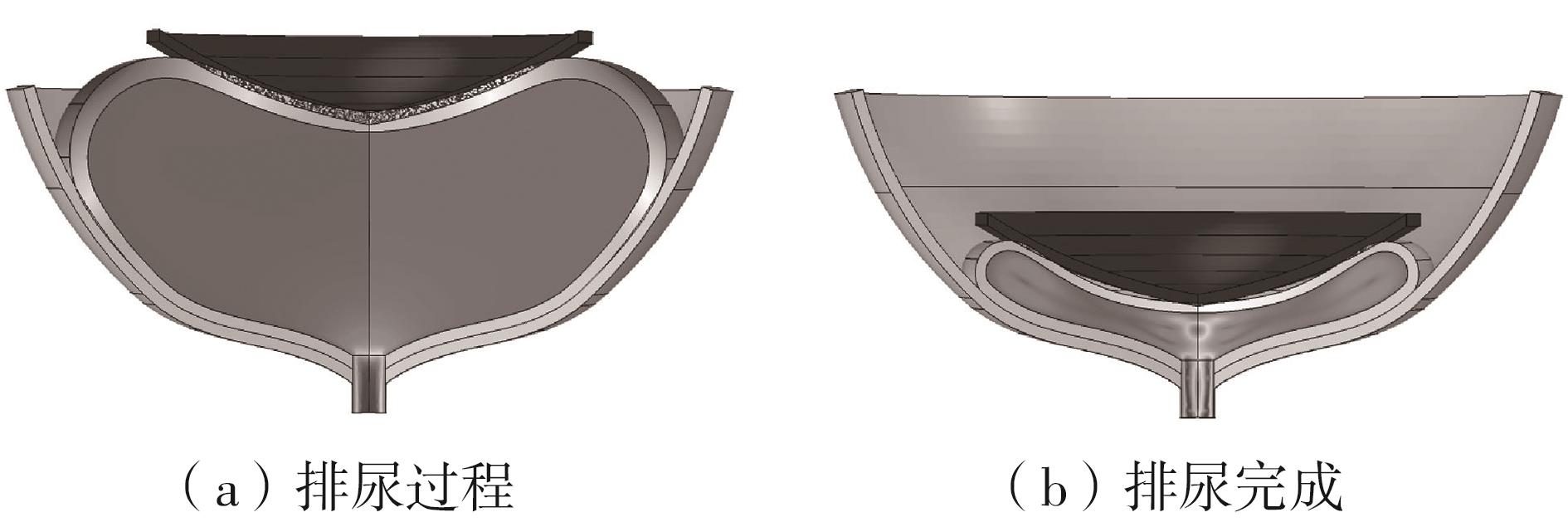
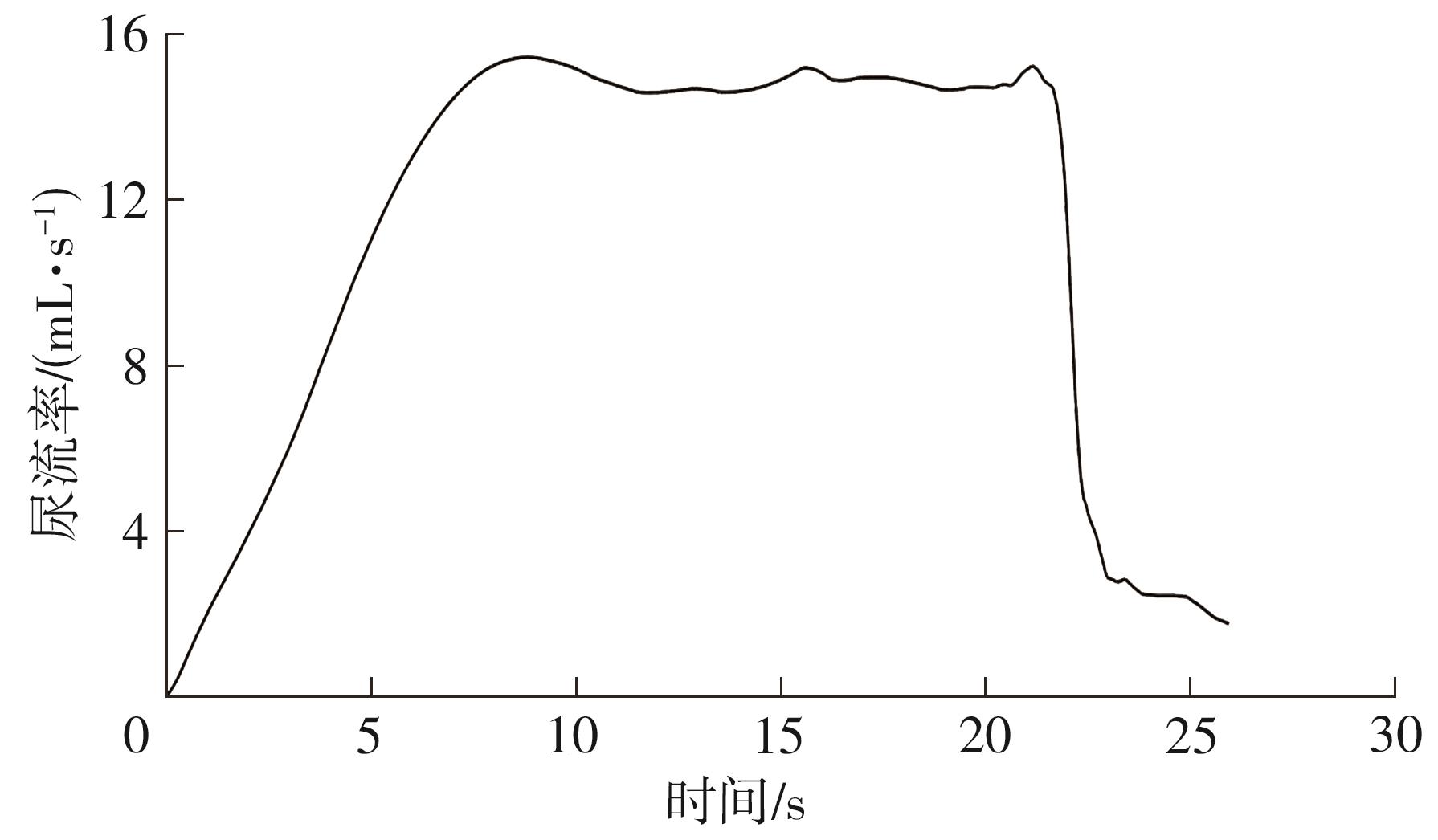
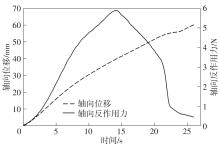
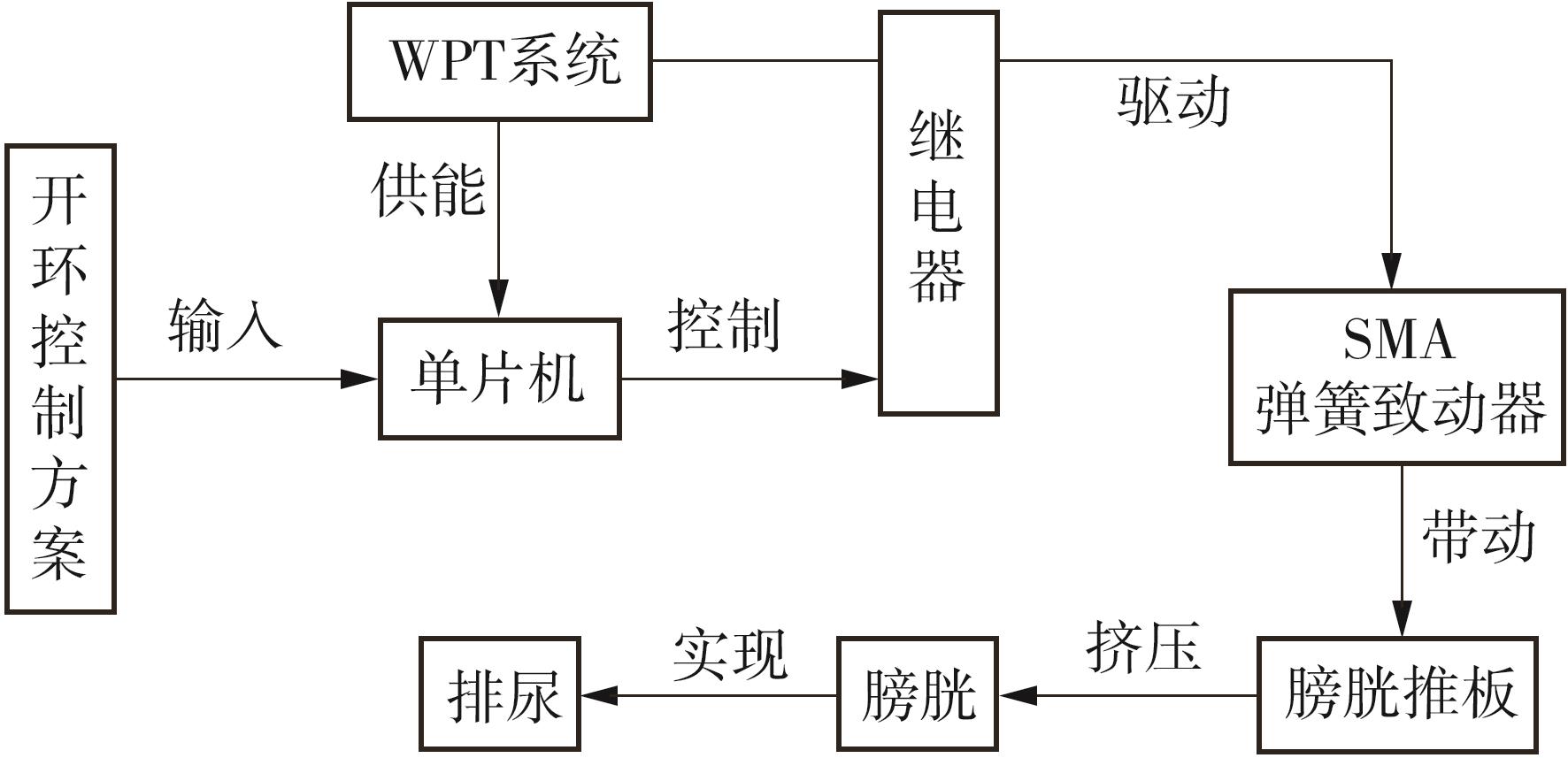
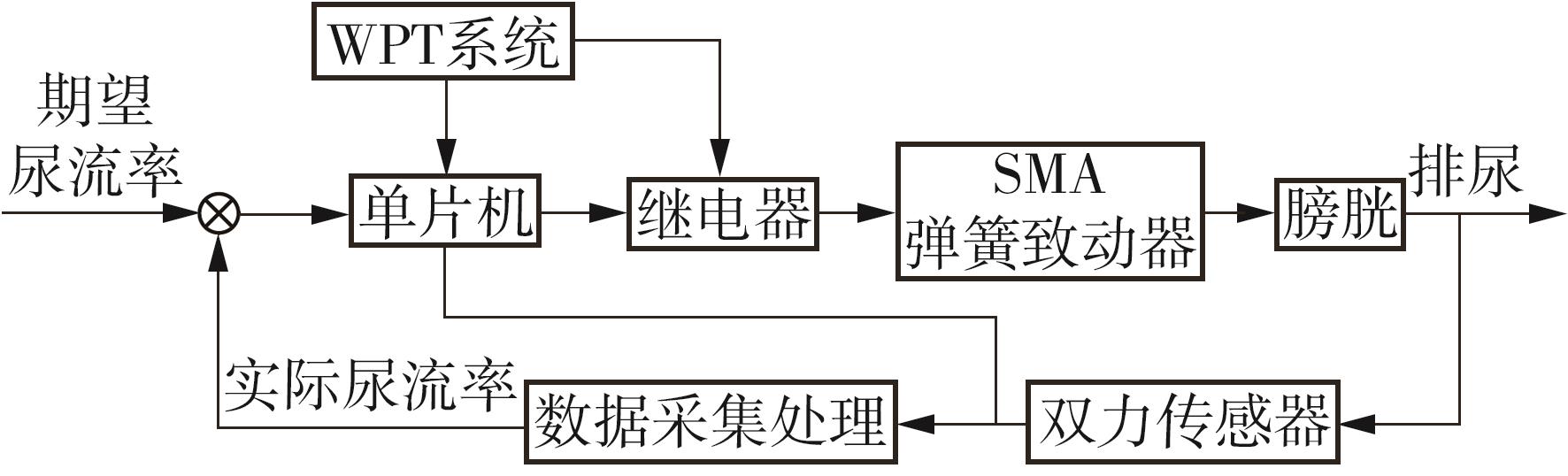
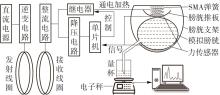
Artificial Bladder Detrusor System Driven by Shape Memory Alloy
- School of Electromechanical Engineering,Guangdong University of Technology,Guangzhou 510006,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-06-12Online:2024-06-25Published:2023-12-27 -
About author:李笑(1962—),男,博士,教授,主要从事机电液智能控制与应用、生物医疗器械等研究。E-mail: lixiao@gdut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52075101)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Xiao, LI Yapeng. Artificial Bladder Detrusor System Driven by Shape Memory Alloy[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(6): 73-80.
share this article
| 1 | METE U K, POWELL C R .Review of current neurogenic bladder best practices and international guidelines[J].Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports,2020,15:283-295. |
| 2 | LI X, GUAN T, ZHOU D,et al .Design and investigation of bladder power pump driven by an external electromagnet[J].Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology,2014,28:3589-3596. |
| 3 | YANG X, AN C, LIU S,et al .Soft artificial bladder detrusor[J].Advanced Healthcare Materials,2018,7(6):1701014/1-9. |
| 4 | HASSANI F A, GAMMAD G G L, MOGAN R P,et al .Design and anchorage dependence of shape memory alloy actuators on enhanced voiding of a bladder[J].Advanced Materials Technologies,2018,3(1):1700184/1-12. |
| 5 | HASSANI F A, PEH W Y X, GAMMAD G G L,et al .A 3D printed implantable device for voiding the bladder using shape memory alloy (SMA) actuators[J].Advanced Science,2017,4(11):1700143/1-10. |
| 6 | HASSANI F A, JIN H, YOKOTA T,et al .Soft sensors for a sensing-actuation system with high bladder voiding efficiency[J].Science Advances,2020,6(18):eaba0412/1-8. |
| 7 | KIGUCHI K, SAKAMOTO Y, NAKASHIMA K,et al .Development of an urination assist system - a bladder compressing system with a link-work mechanism[C]∥Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics.[S.l.]:IEEE,2007. |
| 8 | 聂帆宇,李笑,李晓刚 .超声汽化蒸汽驱动的膀胱动力泵尿道阀研究[J].机床与液压,2017,45(1):9-15. |
| NIE Fan-yu, LI Xiao, LI Xiao-gang .Research of the urethral valve for bladder power pump driven by ultrasonic-vaporized steam[J].Machine Tool & Hydraulics,2017,45(1):9-15. | |
| 9 | 胡振,李笑,关婷 .超声汽化蒸汽驱动的尿道阀的仿真与实验[J].中国机械工程,2015,26(13):1789-1793. |
| HU Zhen, LI Xiao, GUAN Ting .Simulation and experiments for urethral valve driven by ultrasonic-vaporized steam[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2015,26(13):1789-1793. | |
| 10 | CASAGRANDE G, IBRAHIMI M, SEMPRONI F,et al .Hydraulic detrusor for artificial bladder active voiding[J].Soft Robotics,2023,10(2):269-279 |
| 11 | 陈忠,崔拮,双卫兵 .神经源性膀胱[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009. |
| 12 | KUMAT S S .A robotic device to assist with in-vivo measurement of human pelvic organ tissue properties[D].[S.l.]:[s.n.],2018. |
| 13 | BUSH M B, LIEDL B, WAGENLEHNER F,et al .A finite element model validates an external mechanism for opening the urethral tube prior to micturition in the female[J].World Journal of Urology,2015,33:1151-1157. |
| 14 | MOHD J J, LEARY M, SUBIC A .Designing shape memory alloy linear actuators:a review[J].Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures,2017,28(13):1699-1718. |
| 15 | BRINSON L, BEKKER A, HWANG S .Deformation of shape memory alloys due to thermo-induced transformation[J].Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures,1996,7(1):97-107. |
| [1] | DU Yunwei, WANG Ronghui, ZHEN Xiaoxia, et al. Calculation of Elastic Stiffness of Shear Connector in Steel Concrete Bridge Tower Joint Section [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 76-87. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xueguang LIU Chunguo LIANG Jiye. A 3D Die Compensation Method Based on Interpolation Solution and FE Simulation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(7): 100-108. |
| [3] |
PAN Difu CHEN Jun BAO Tianzhe HAN Kun .
Application of Multi-Output Support Vector Regression Hybrid Model in Locomotive Secondary Spring Loads Adjustment
|
| [4] |
PAN Difu CHEN Jun BAO Tianzhe HAN Kun .
Application of Multi-Output Support Vector Regression Hybrid Model in Locomotive Secondary Spring Loads Adjustment
|
| [5] | HE Wei ZHU Liang-sheng HU Jin-peng. Impact of Lingding Navigation Channel on Fresh Salt-Water Mixing in Dry Season [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(4): 138-144. |
| [6] | Teng Fei Liang Ji-cai Zhang Wan-xi Wang Xue Gao Song. Springback Prediction of Rectangular Profiles During Three-Dimension Stretch Bending Forming [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(2): 107-113. |
| [7] | Xia Qin-xiang Wang Ting Chen Zhi-ping Zhao Xue-zhi Qiu Zun-wen. Forming Quality Control of Multi-Position Progressive Stamping Based on Numerical Simulation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(7): 80-85. |
| [8] | Liang Ji- cai Teng Fei Gao Song Chen Guang- yi Wei Zhi- yong. Multi- Objective Optimization of Flexible Three- Dimensional Stretch-Bending Forming Process of rectangular Hollow Aluminum Profiles [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(9): 143-148. |
| [9] | Li Min Zhang Ya-nan Gong Zhen-bang. Development of Robot for Inspecting Exterior of Tubes of Heat Exchangers in Nuclear Power Plants [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(8): 48-53. |
| [10] | Ling Yu-hong Peng Hui-hong Zhang Shuai. A Novel SMA Damper and Its Vibration Reduction Performance [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(6): 119-125. |
| [11] | Ling Yu-hong Peng Hui-hong Zhang Shuai. Mechanical Behavior of Superelastic NiTi Wires [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(4): 131-135,155. |
| [12] | Yang Xiang-an Ruan Feng Zhou Chi. Multi-Objective Optimization of Forming Process of Sheet Metal Based on Springback Control [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(12): 7-13. |
| [13] | Liu Qiang Ruan Feng Xue Xin Zhou Chi . Compensation Control of Springback Torsion for 3D Irregular Stamping Parts [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(9): 93-97. |
| [14] | . Horizontal Earthquake Isolating Function of the Vertical Spring-steel Rolling Base Isolation Seismic System [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2003, 31(6): 20-25. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||