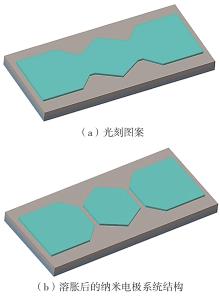
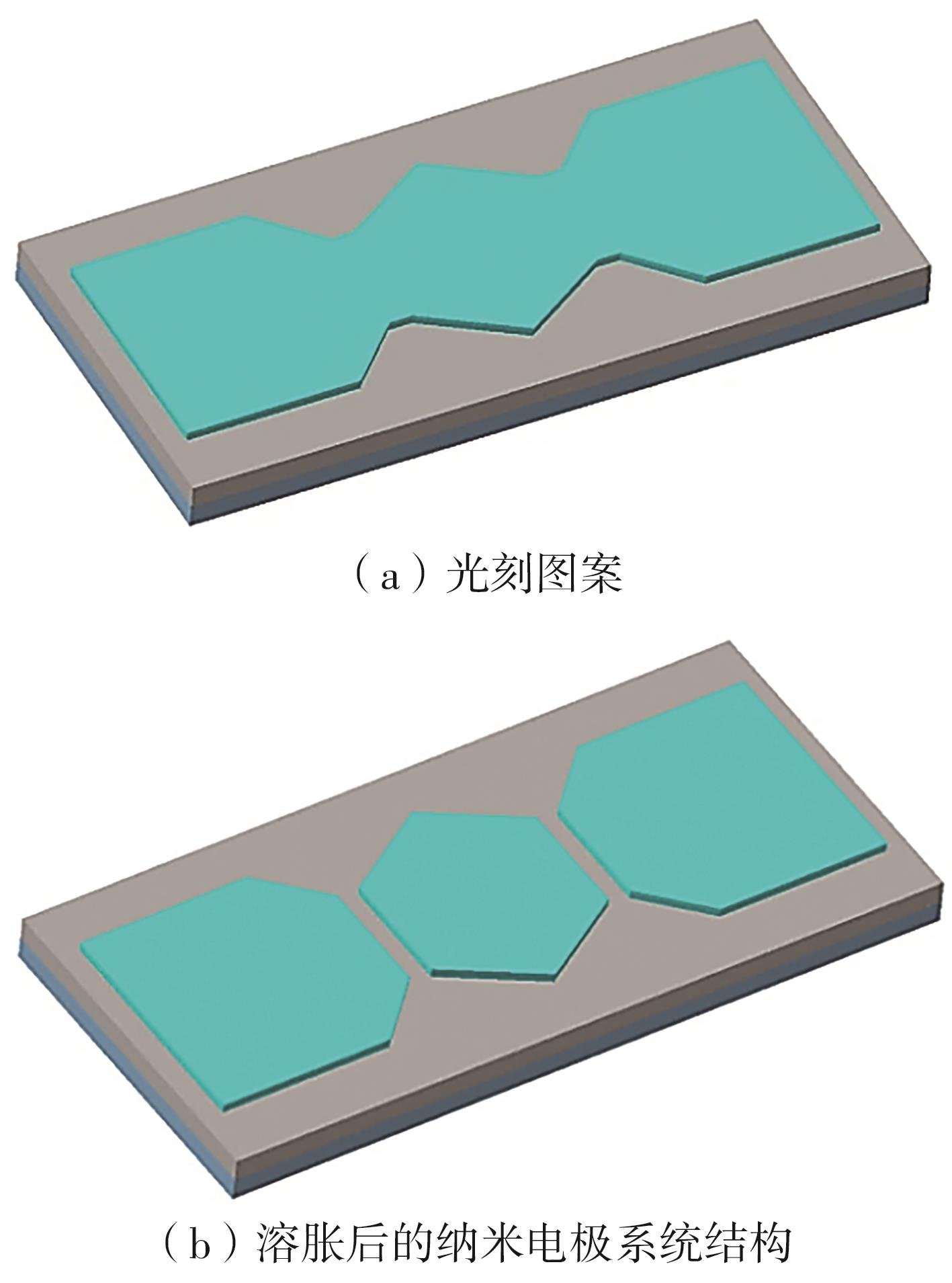
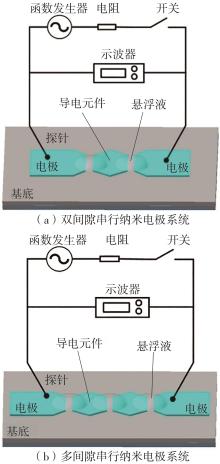
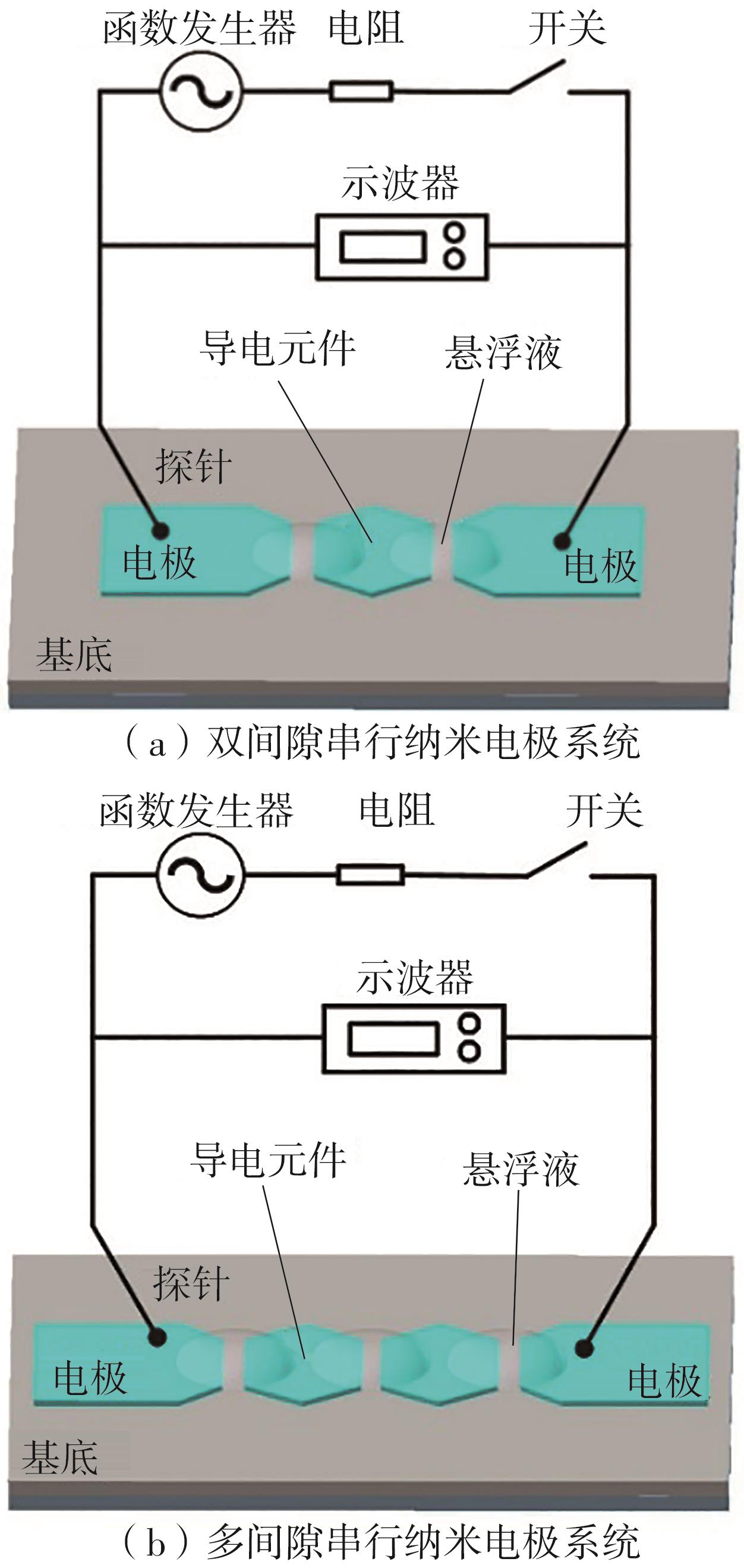
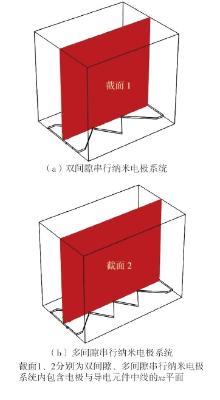
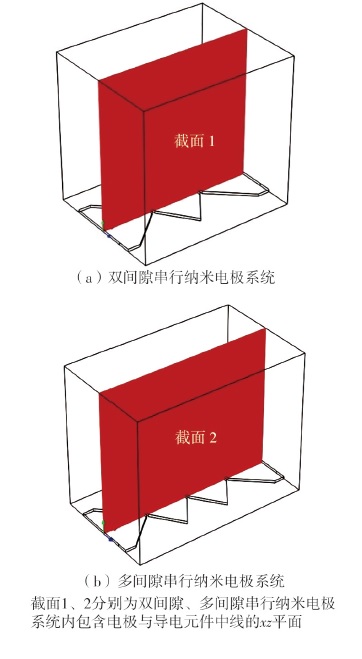
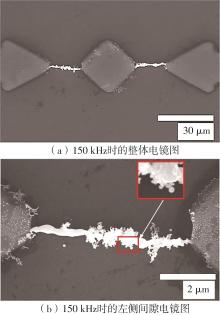
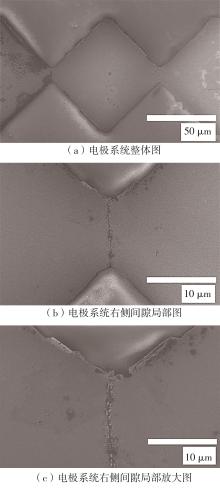
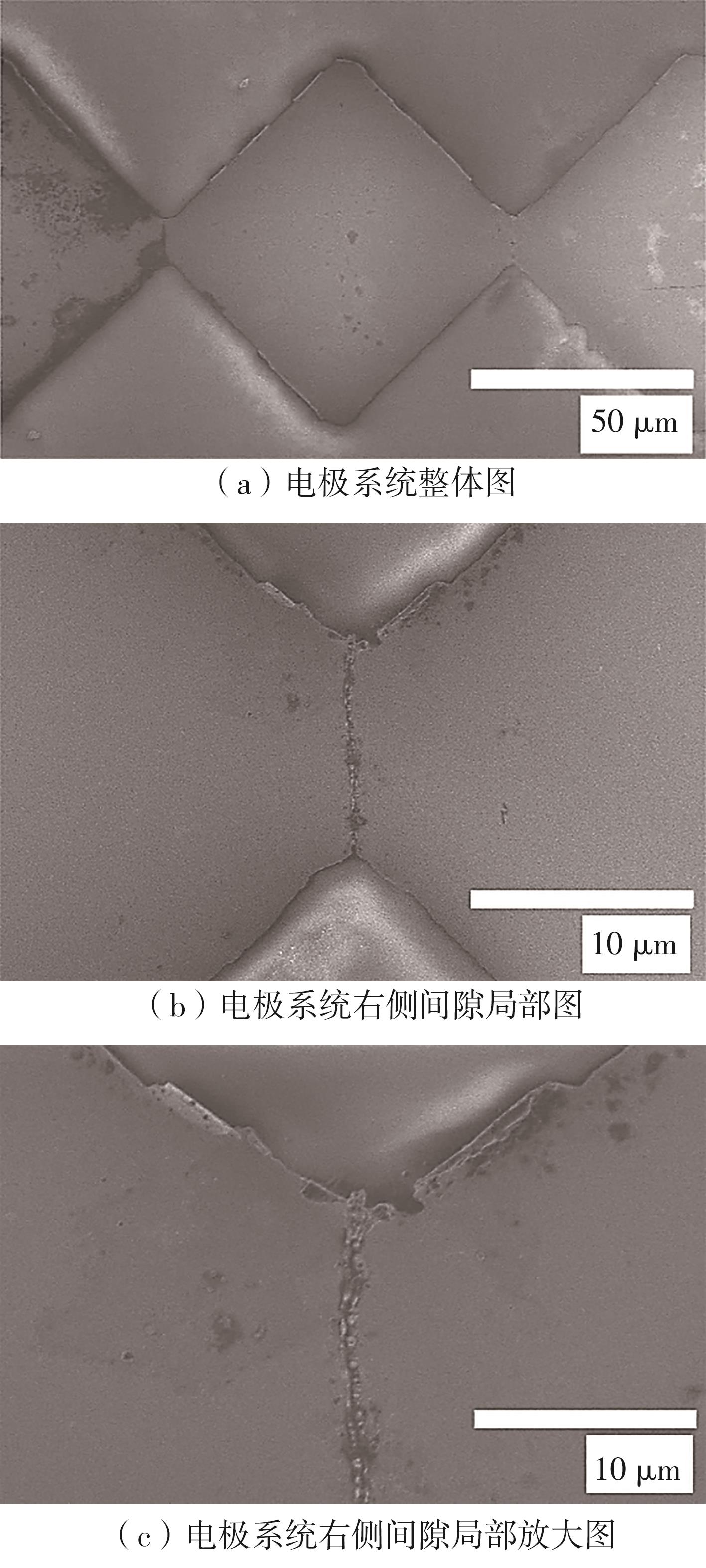
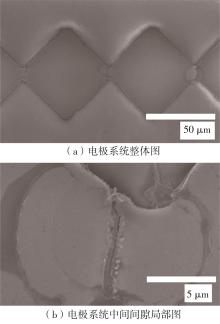
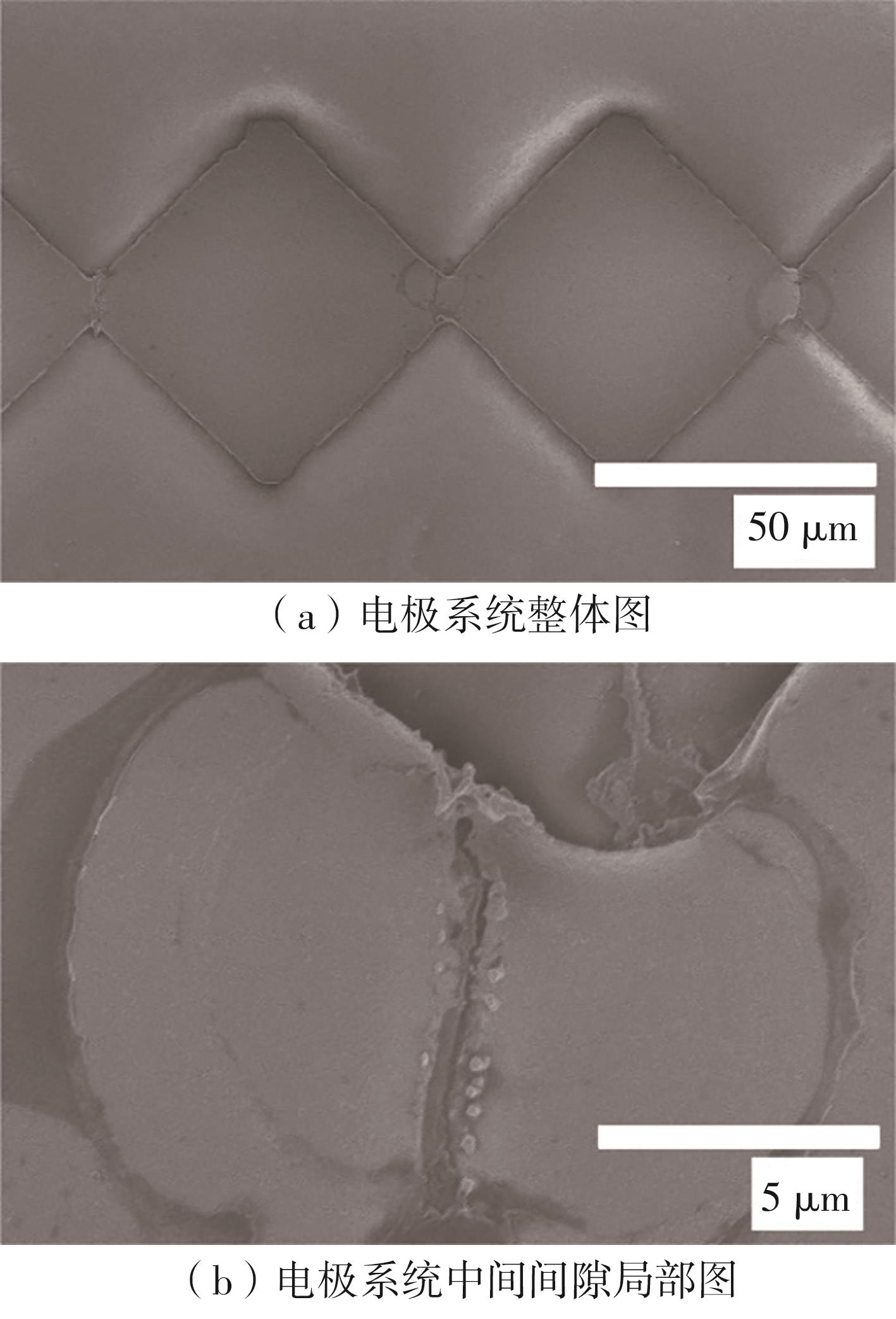
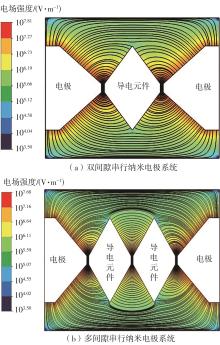
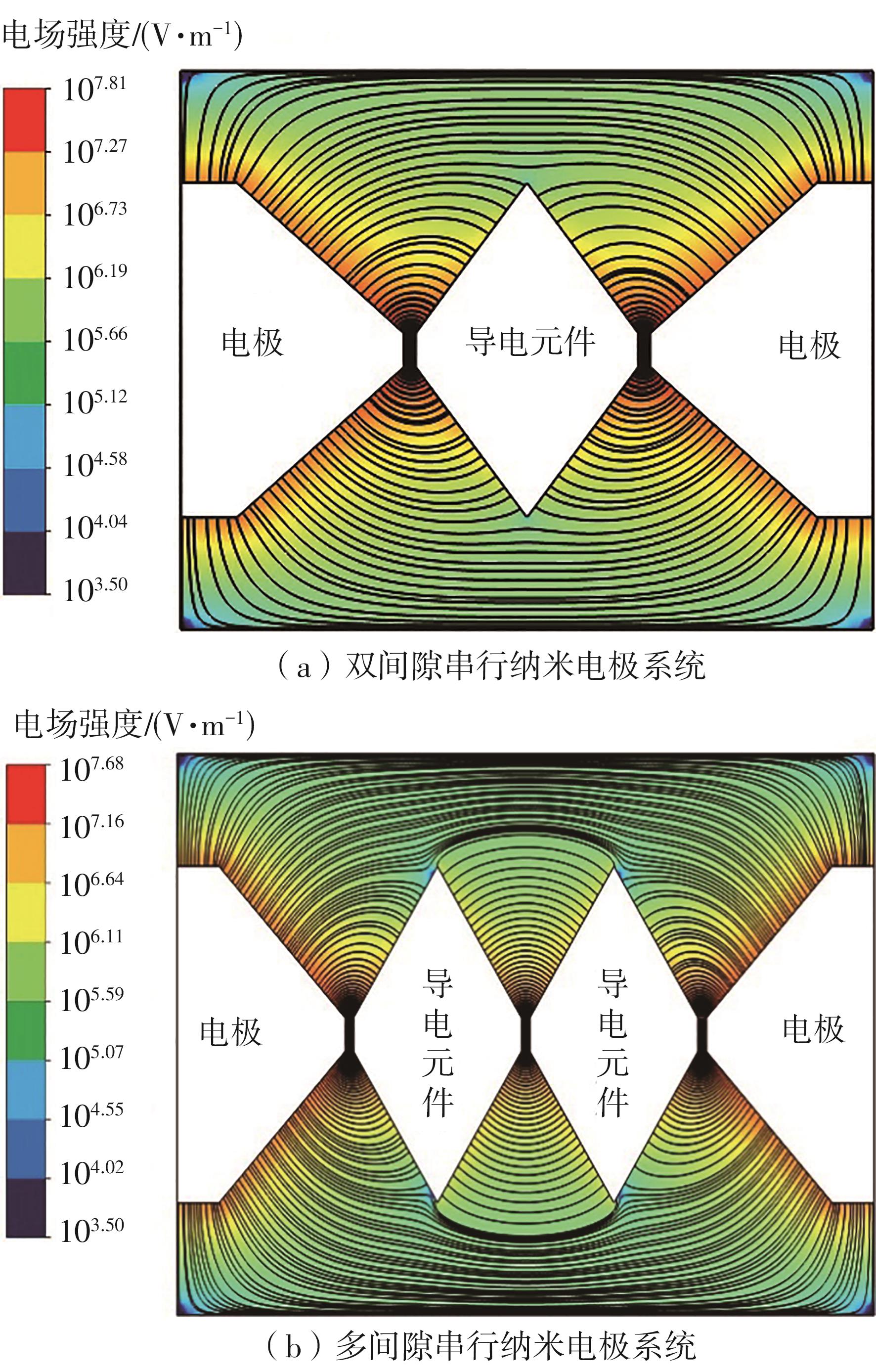
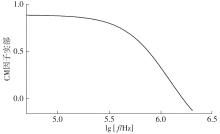
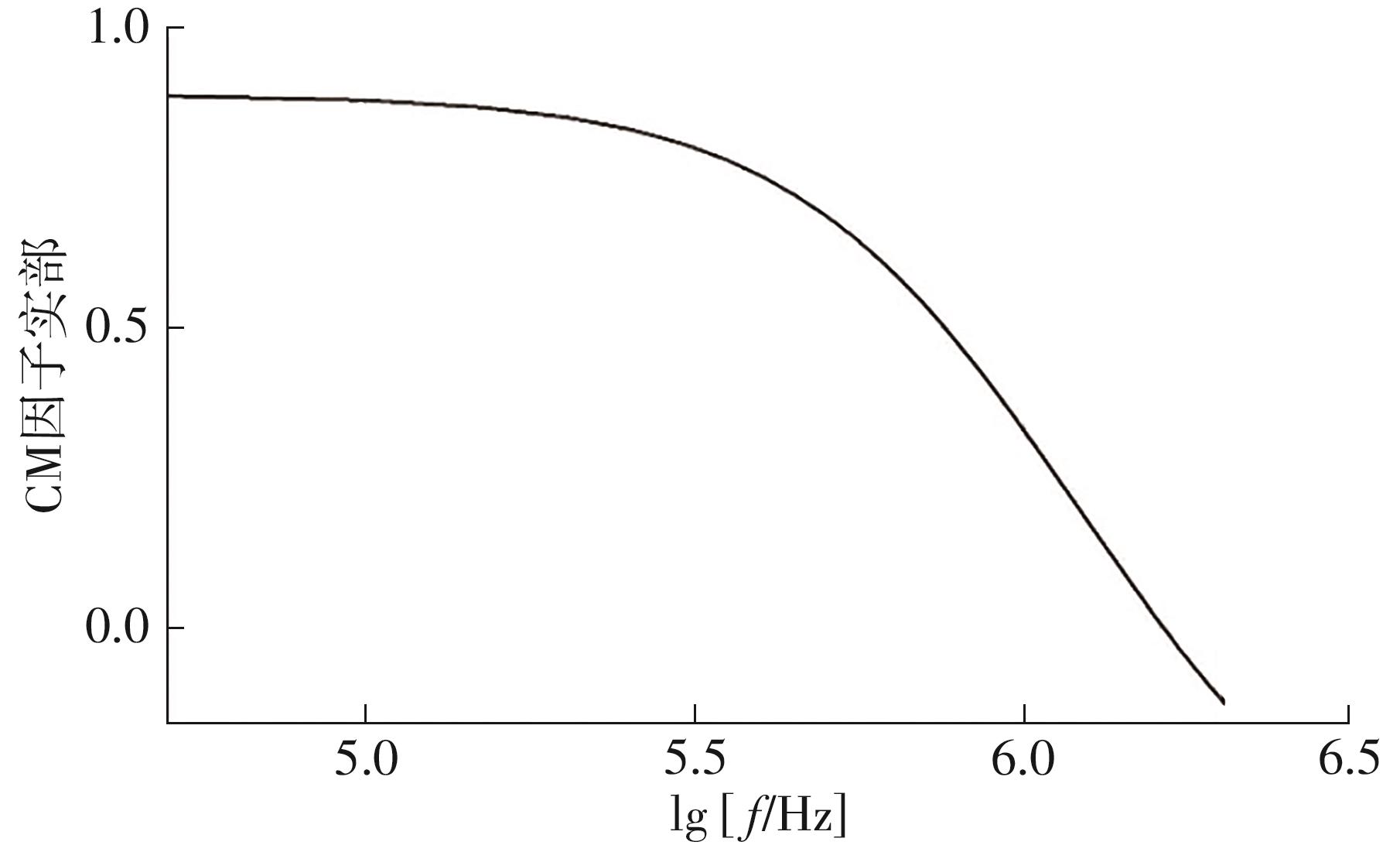
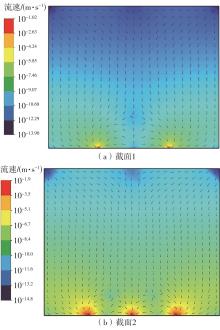
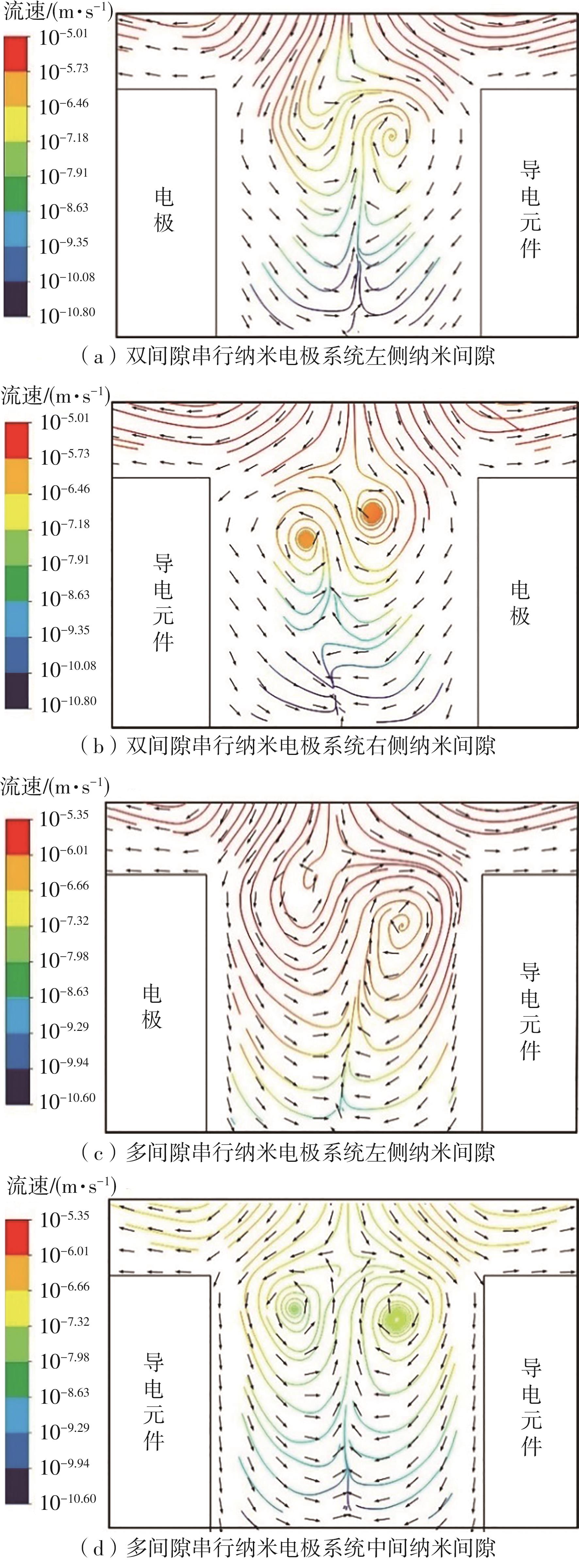
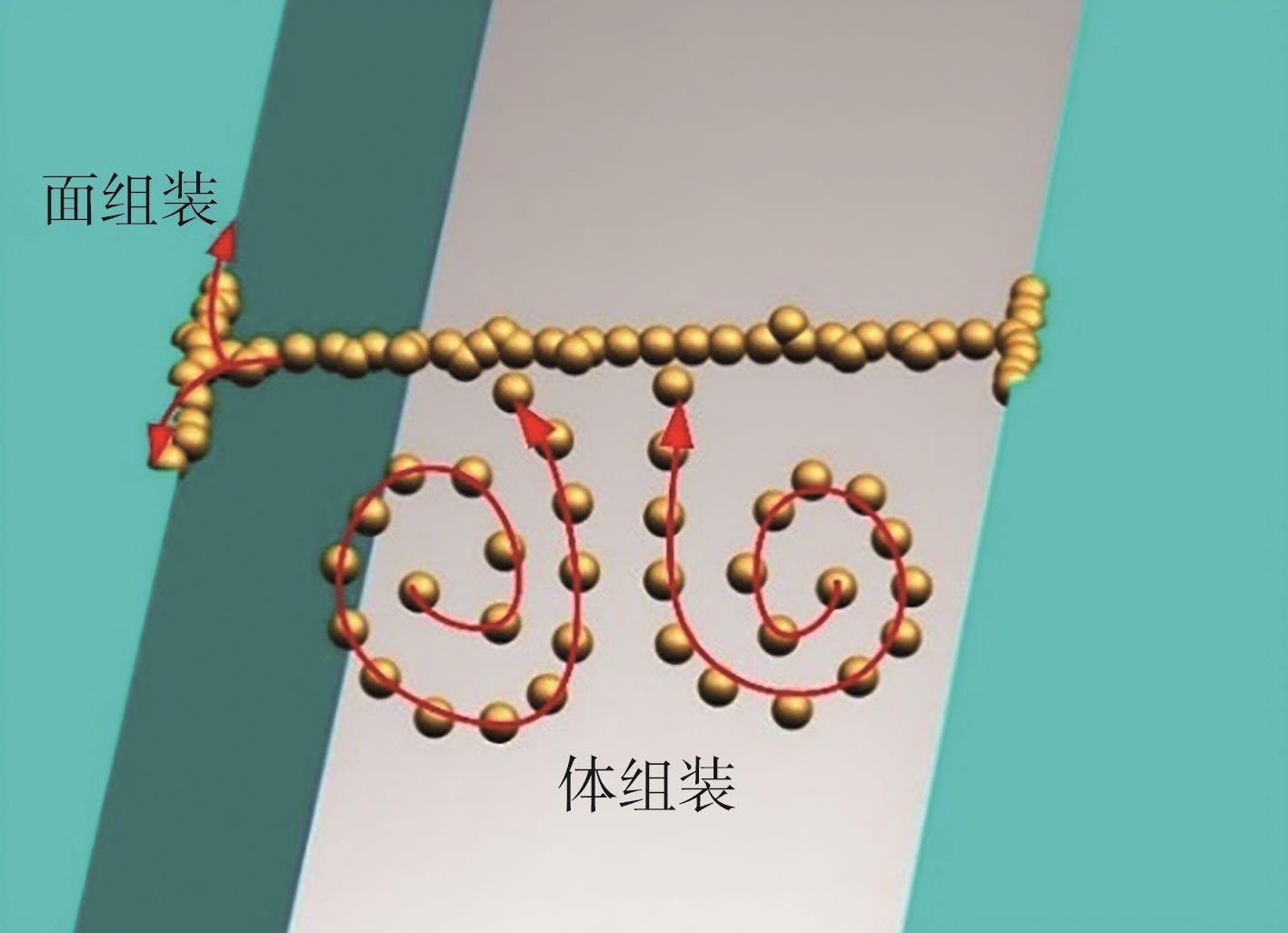
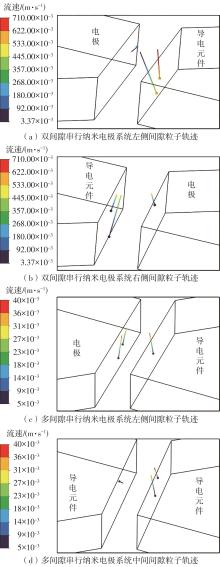
| 1 |
CHEN J, WU T, ZHANG L,et al .Fabrication of flexible organic electronic microcircuit pattern using near-field electrohydrodynamic direct-writing method[J].Journal of Materials Science:Materials in Electronics,2019,30(19):17863-17871.
|
| 2 |
MCGAHAY V .Porous dielectrics in microelectronic wiring applications[J].Materials,2010,3(1):536-562.
|
| 3 |
JEONG G S, BAEK D H, JUNG H C,et al .Solderable and electroplatable flexible electronic circuit on a porous stretchable elastomer[J].Nature Communications,2012,3:977/1-8.
|
| 4 |
SUN C, MIKHAYLOV R, FU Y,et al .Flexible printed circuit board as novel electrodes for acoustofluidic devices[J].IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices,2020,68(1):393-398.
|
| 5 |
MA R, GORDON D, YUSHIN G,et al .Robust and flexible micropatterned electrodes and micro-supercapacitors in grapheme-silk biopapers[J].Advanced Materials Interfaces,2018,5(24):1801203/1-8.
|
| 6 |
HASHIMOTO Y, MOGI K, YAMAMOTO T,et al .Nanoscale three-dimensional optical visualization method for a deformation of elastomer printing plate to realize soft nano-printing technology[J].Surface and Interface Analysis,2015,47(6):723-727.
|
| 7 |
REN Y, TAO Y, HOU L,et al .Automatic microcircuit formation based on gold-coated SU-8 microrods via dielectrophoresis[J].Chinese Physics B,2013,22(8):636-640.
|
| 8 |
LIU W, ZHU J, WANG Z,et al .Fabrication and characterization of a novel wafer-level micro-electrode system for dielectrophoresis manipulation[J].Physica E:Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures,2010,42(5):1653-1658.
|
| 9 |
DELEON C, TABIBI T, ALAGIC A .Characterization and electrochemical analysis of microelectrodes and the interface with a fabricated 3D-printed microfluidic chip in an upper-division analytical course[J].Journal of Chemical Education,2020,97(12):4453-4461.
|
| 10 |
DING H, LIU W, DING Y,et al .Particle clustering during pearl chain formation in a conductive-island based dielectrophoretic assembly system[J].RSC Advances,2015,5(8):5523-5532.
|
| 11 |
HERMANSON K, LUMSDON S, WILLIAMS J,et al .Dielectrophoretic assembly of electrically functional microwires from nanoparticle suspensions[J].Science,2001,294(5544):1082-1086.
|
| 12 |
ZHANG G, YU G, CHANG F,et al .Influence of the AC field intensity and frequency on composition and growth mechanism of Au-Pd alloy nanowires[J].Journal of Nanoscience & Nanotechnology,2013,13(10):6940-6947.
|
| 13 |
PETHIG R .Review article—dielectrophoresis:status of the theory,technology,and applications[J].Biomicrofluidics,2010,4(2):022811/1-35.
|
| 14 |
GANGWAL S, CAYRE O, VELEV O .Dielectrophoretic assembly of metallodielectric Janus particles in AC electric fields[J].Langmuir,2008,24(23):13312-13320.
|
| 15 |
TONER M, IRIMIA D .Blood-on-a-chip[J].Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering,2005,7(1):77-103.
|
| 16 |
SHAALAN N, YAMAZAKI T, KIKUTA T .Effect of micro-electrode geometry on NO2 gas-sensing characteristics of one-dimensional tin dioxide nanostructure microsensors[J].Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical,2011,156(2):784-790.
|
| 17 |
ZHANG C, KHOSHMANESH K, MITCHELL A,et al .Dielectrophoresis for manipulation of micro/nano particles in microfluidic systems[J].Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry,2010,396(1):401-420.
|
| 18 |
LEE K M, SMITH R P, CHOI T Y .Positional controlling of dielectric particles using a probe-typed micromanipulator with electrostatic mechanism[J].Applied Physics A,2020,126(3):219.
|
| 19 |
KIM D, SONKER M,ROS A .Dielectrophoresis:from molecular to micrometer-scale analytes[J].Analytical Chemistry,2018,91(1):277-295.
|
| 20 |
KIM D, MIN S, LEE Y,et al .Transparent flexible nanoline field-effect transistor (NL-FET) array with high-integration in large-area[J].ACS Nano,2020,14(1):907-918.
|
| 21 |
CHEON D, KUMAR S, KIM G .Assembly of gold nanoparticles of different diameters between nanogap electrodes[J].Applied Physics Letters,2010,96(1):013101/1-3.
|
| 22 |
GASCOYNE P, VYKOUKAL J .Particle separation by dielectrophoresis[J].Electrophoresis,2002,23(13):1973-1983.
|
| 23 |
PENG Y, LEI J .Fabrication,electrical characterization,and detection application of graphene-sheet-based electrical circuits[J].Nanoscale Research Letters,2014,9(1):1-9.
|
| 24 |
VIJAYARAGHAVAN A, SCIASCIA C, DEHM S,et al .Dielectrophoretic assembly of high-density arrays of individual graphene devices for rapid screening[J].ACS Nano,2009,3(7):1729-1734.
|
| 25 |
HASHEMI M, NIKFARJAM A, RAJI H .Novel fabrication of extremely high aspect ratio and straight nanogap and array nanogap electrodes[J].Microsystem Technologies,2019,25(2):541-549.
|
| 26 |
KUZYK A .Dielectrophoresis at the nanoscale[J].Electrophoresis,2011,32(17):2307-2313.
|
| 27 |
PESCH G, DU F .A review of dielectrophoretic separation and classification of non-biological particles[J].Electrophoresis,2021,42(1/2):134-152.
|
| 28 |
崔祥干,丁海涛,杜山 .交流电热流对导电岛纳米电极介电组装的影响[J].西安交通大学学报,2020,54(2):127-136.
|
|
CUI Xianggan, DING Haitao, DU Shan .Influence of AC electrothermal flow on dielectro-phoretic assembly in a conductive-island nanogap electrode system[J].Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2020,54(2):127-136.
|
| 29 |
LEE T, KIM T, YOON J,et al .Investigation of hemoglobin/gold nanoparticle heterolayer on micro-gap for electrochemical biosensor application[J].Sensors,2016,16(5):660/1-11.
|
| 30 |
DING H, SHAO J, DING Y,et al .Effect of island shape on dielectrophoretic assembly of metal nanoparticle chains in a conductive-island-based microelectrode system[J].Applied Surface Science 2015,330:178-184.
|
| 31 |
赵强 .聚合物溶胀诱导的纳米间隙电极断裂成形及其传感应用[D].西安:西安交通大学,2018:17-63.
|
| 32 |
ZHAKIN A .Electrohydrodynamics[J].Physics-Uspekhi,2012,55(5):465-488.
|
| 33 |
DU E, MANOOCHEHRI S .Electrohydrodynamic-mediated dielectrophoretic separation and transport based on asymmetric electrode pairs[J].Electrophoresis,2008,29(24):5017-5025.
|
| 34 |
KHOSHMANESH K, ZHANG C, TOVAR-LOPEZ F,et al .Dielectrophoretic manipulation and separation of microparticles using curved microelectrodes[J].Electrophoresis,2009,30(21):3707-3717.
|