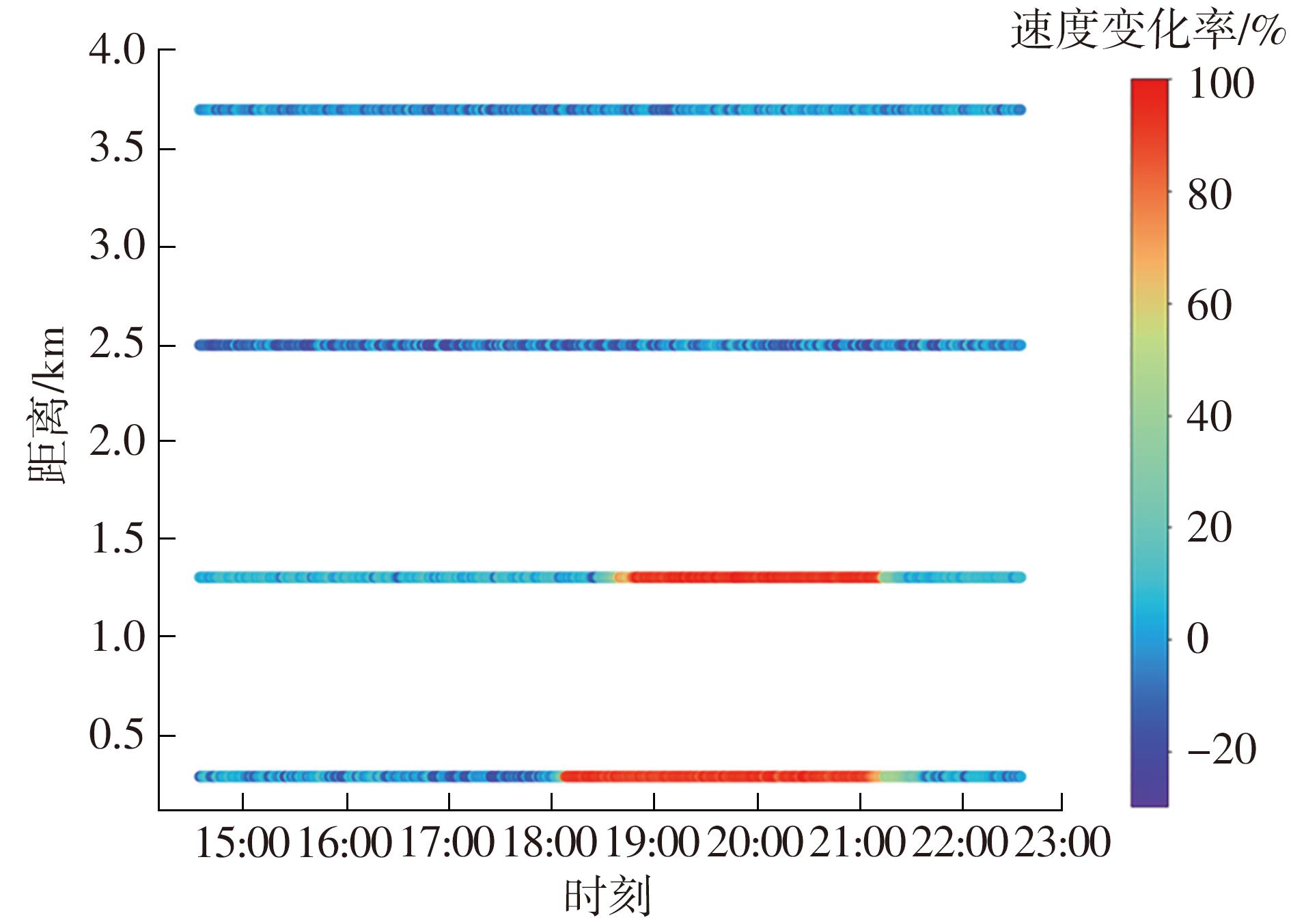
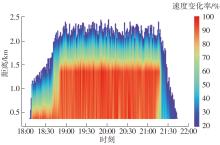
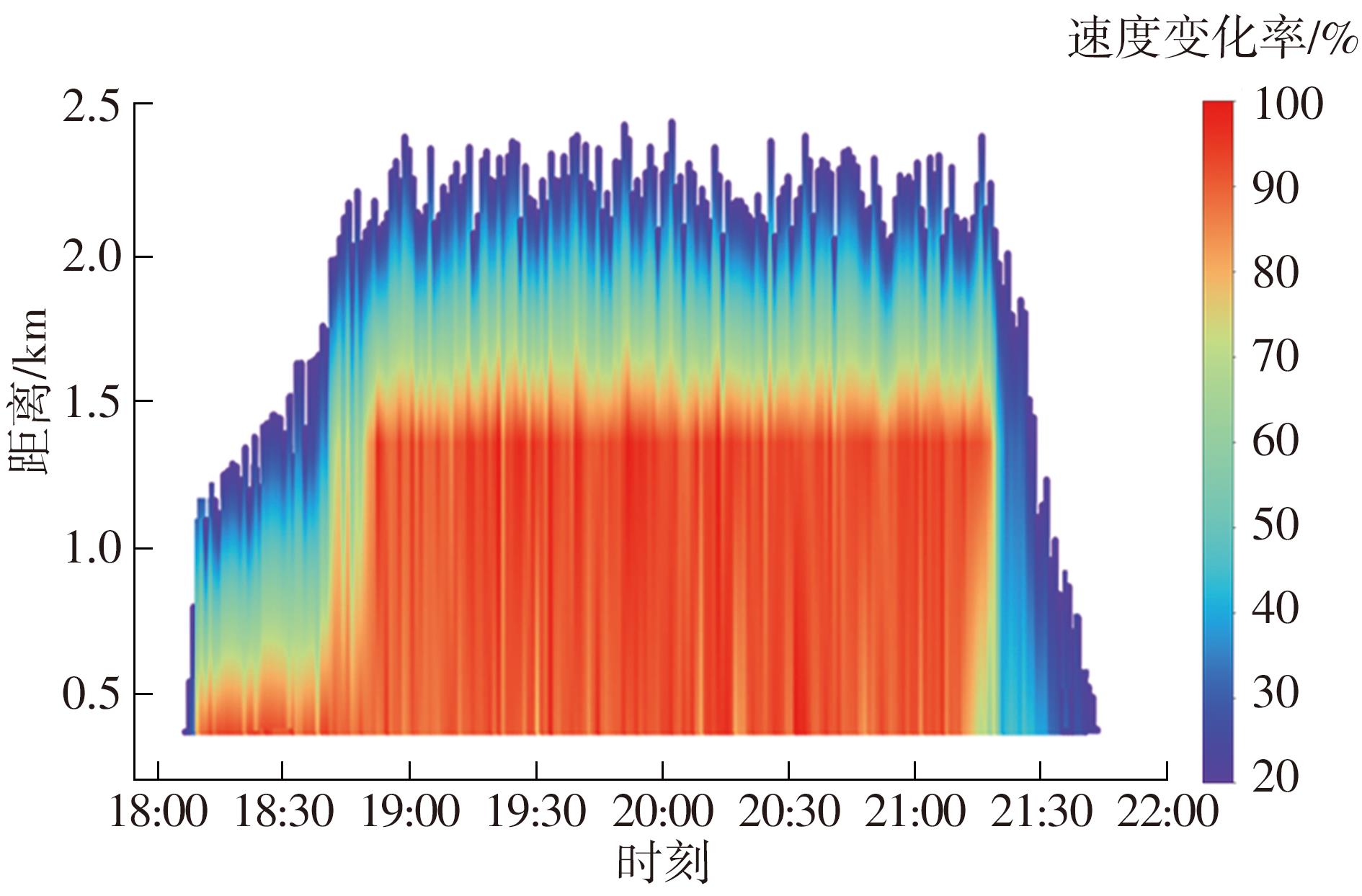
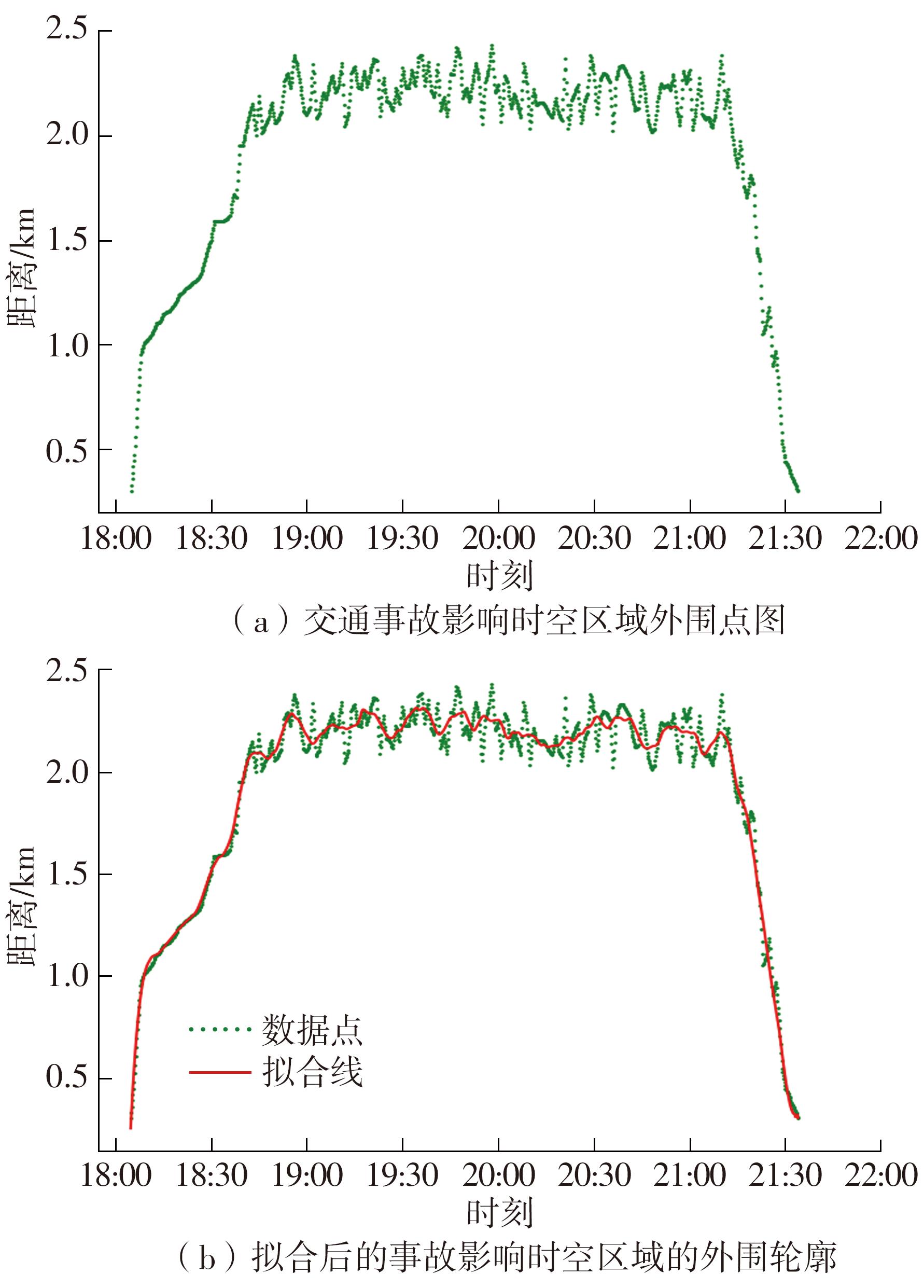
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 123-133.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220353
Special Issue: 2023年交通运输工程
• Traffic & Transportation Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis on Propagation of Spatio-Temporal Dynamic Effects Towards Freeway Traffic Crash
YANG Yang1,2 HU Yanran3 YUAN Zhenzhou3 WANG Yunpeng1,2
- 1.School of Transportation Science and Engineering,Beihang University,Beijing 100191,China
2.Beijing Key Laboratory for Cooperative Vehicle Infrastructure Systems and Safety Control,Beihang University,Beijing 100191,China
3.School of Traffic and Transportation,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China