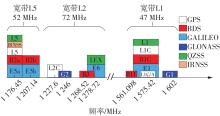
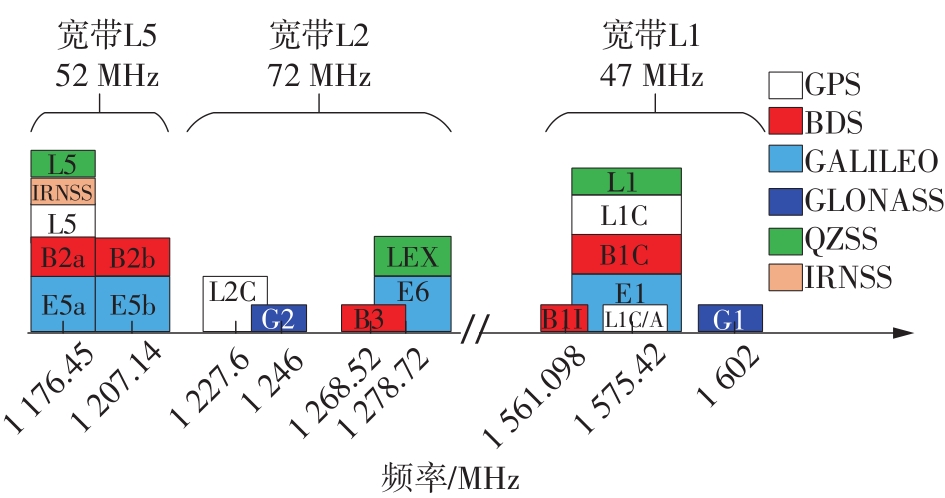
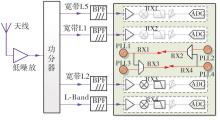
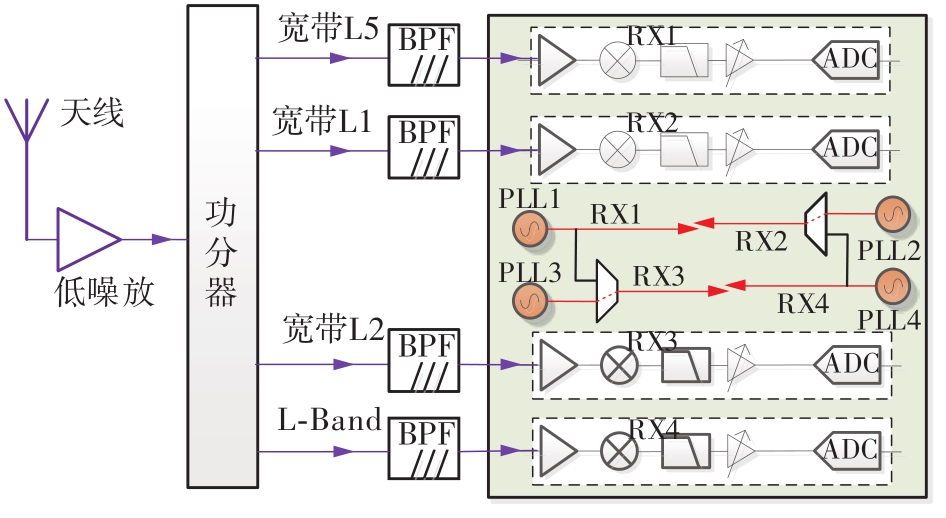
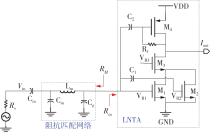
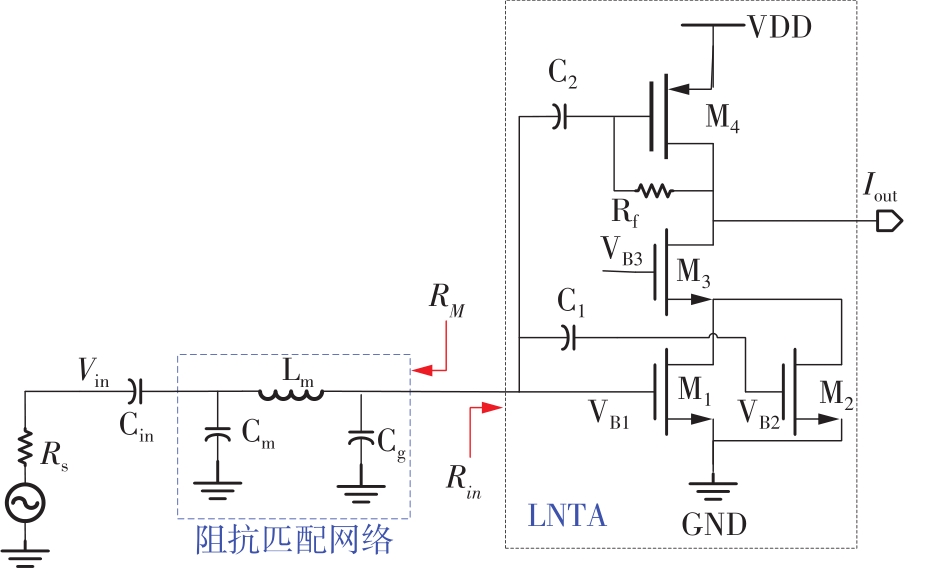
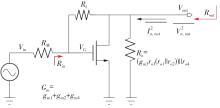
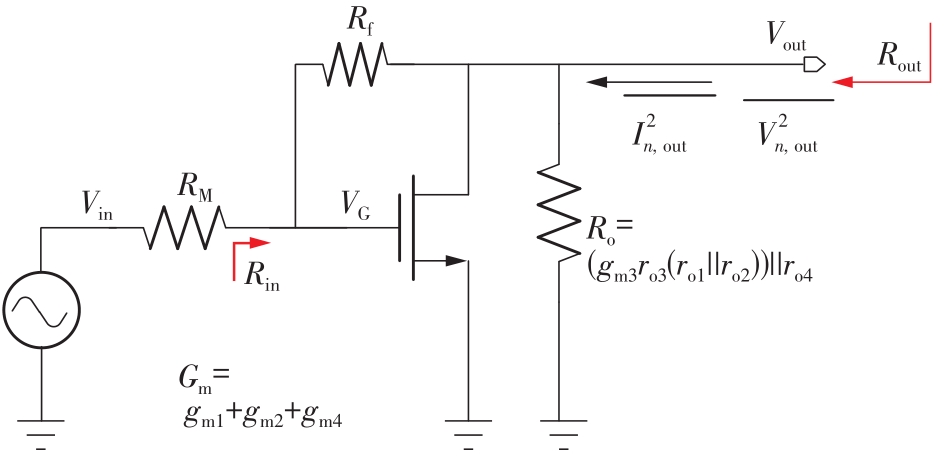
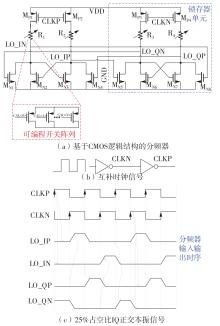
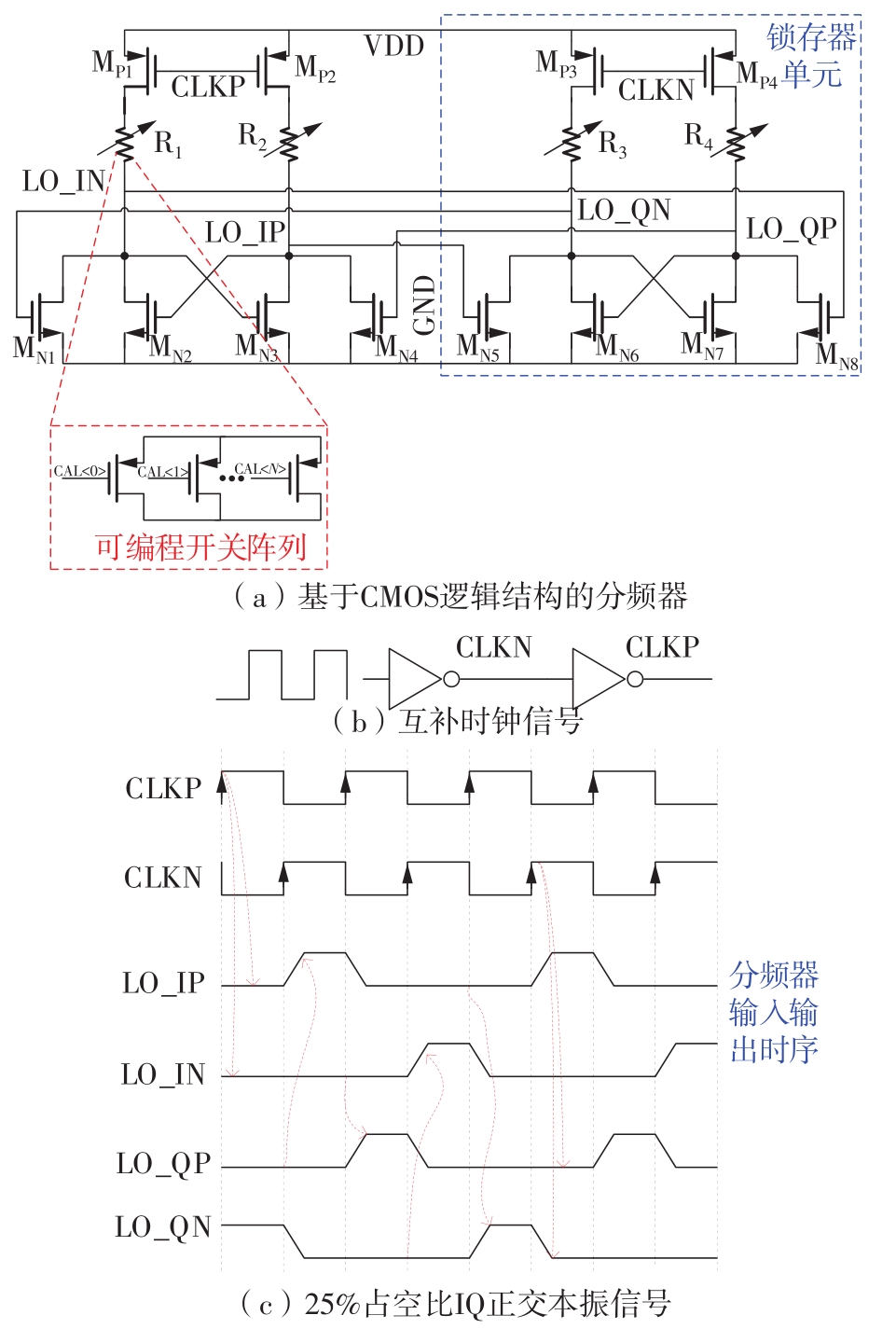
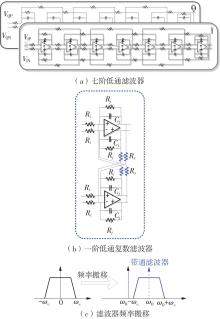
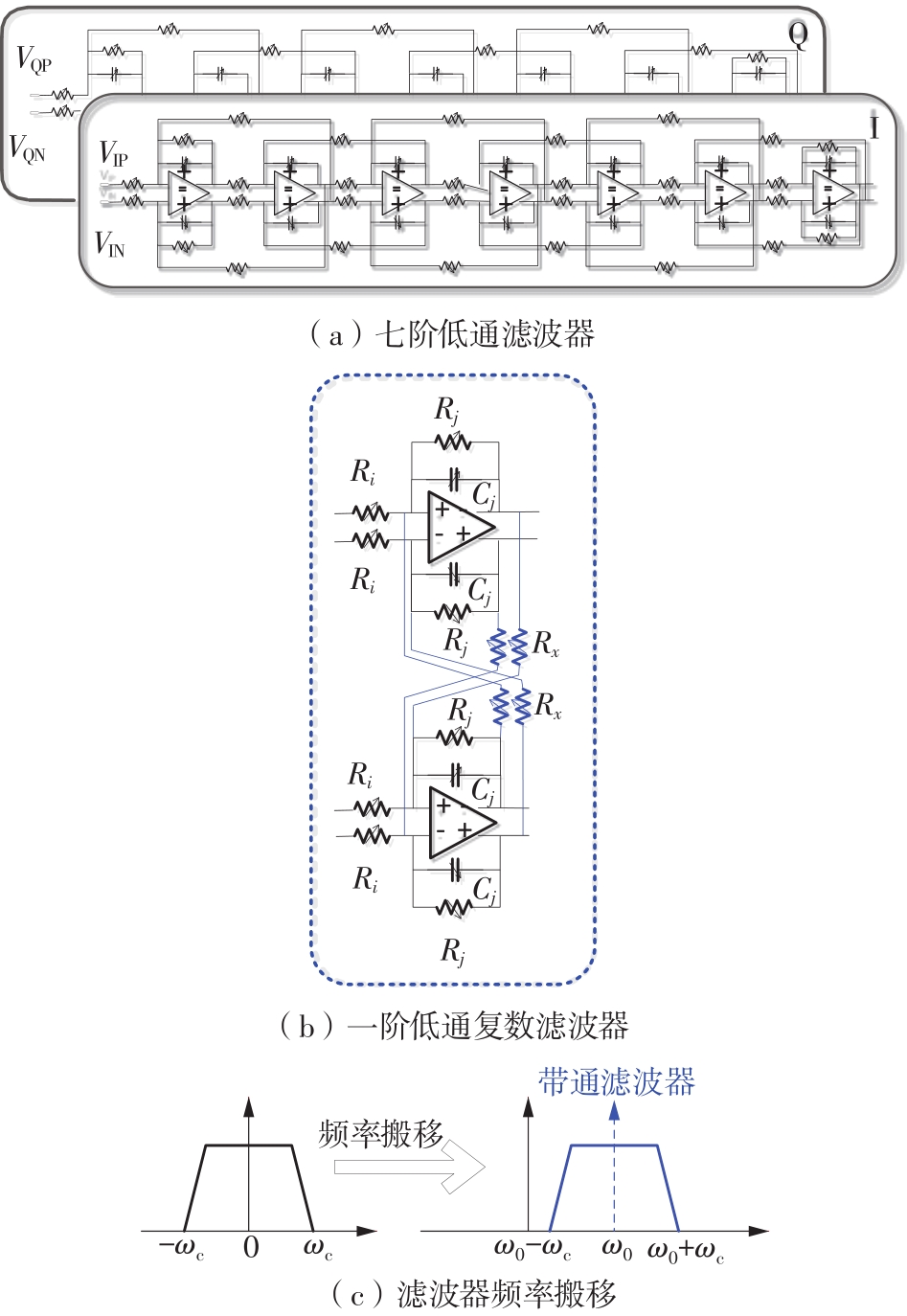
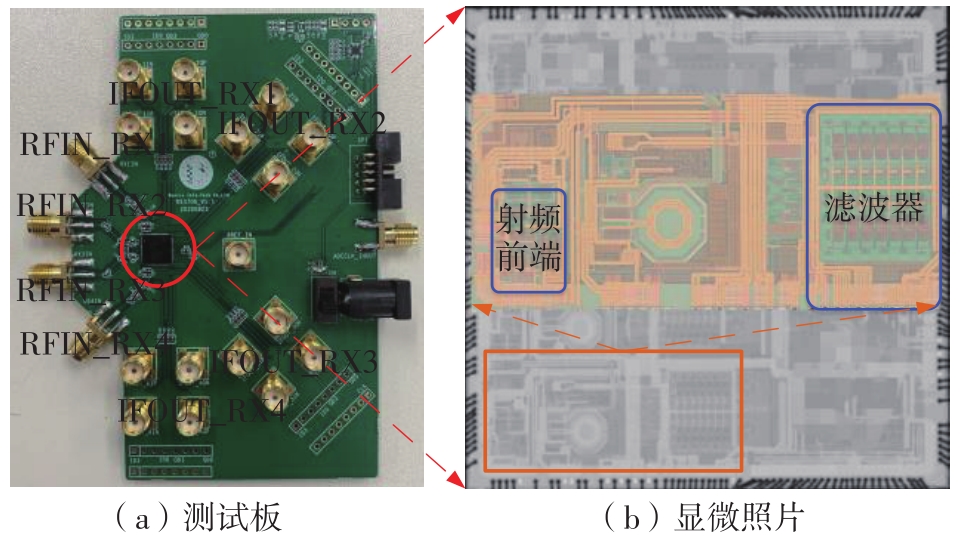
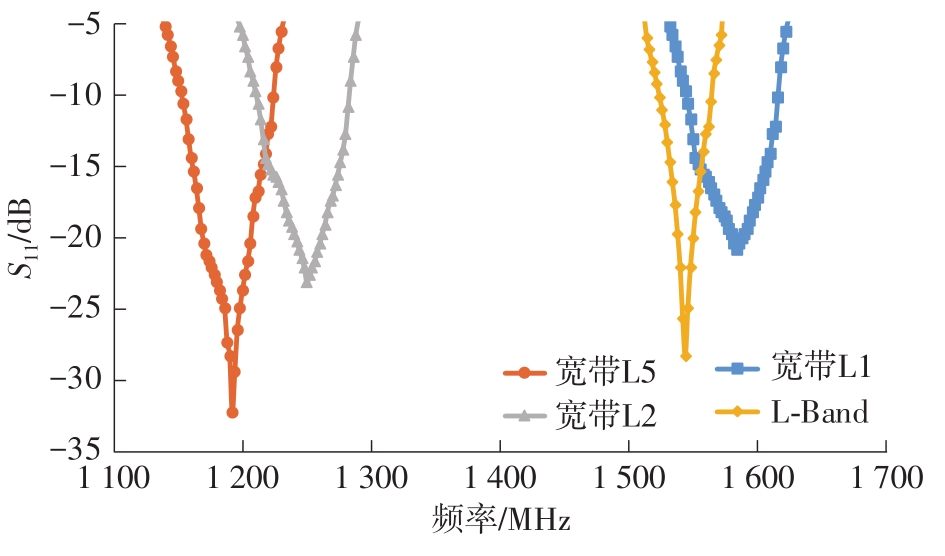
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 89-97.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220177
Special Issue: 2023年电子、通信与自动控制
• Electronics, Communication & Automation Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Reconfigurable GNSS RF Receiver for High-Precision Positioning and Orientation
LI Bin1 WANG Riyan1,2 CHEN Zhijian1 ZHONG Shiguang2 PENG Heng2 ZHANG Fangfang2 HE Hongyin2 YANG Kunming2
- 1.School of Microelectronics,South China University of China,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangzhou Runxin Information Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510663,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-04-05Online:2023-08-25Published:2023-02-08 -
Contact:陈志坚(1979-),男,博士,高级工程师,主要从事射频和毫米波集成电路研究。 E-mail:chenzhijian@scut.edu.cn -
About author:李斌(1967-),女,博士,教授,主要从事模拟和射频集成电路研究。E-mail:phlibin@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province of China(2019B010141002)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Bin, WANG Riyan, CHEN Zhijian, et al. Reconfigurable GNSS RF Receiver for High-Precision Positioning and Orientation[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(8): 89-97.
share this article
Table 1
Measurement summary and comparison"
| 参数 来源 | 特征尺寸/μm | 射频/GHz | 中频滤波 | 带宽/MHz | 增益/dB | 噪声系数/dB | OIP3/(dBm) | 1 dB压缩点/dBm | 镜像抑制/dB | 隔离/dB | 功耗/mW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 0.18 | 1.2~1.6 | BPF | 33 | — | — | 25.8 | — | +59.3 | — | 54.4 |
| 文献[ | 0.13 | 1.55/1.61 | BPF | 2/4 | 95 | 3.5~3.7 | — | — | +36.9 | — | 30.0 |
| 文献[ | 0.18 | 1.20/1.57 | BPF | 2/4/20 | <110 | 2.5~2.7 | — | -58 | +28.0 | — | 45.0 |
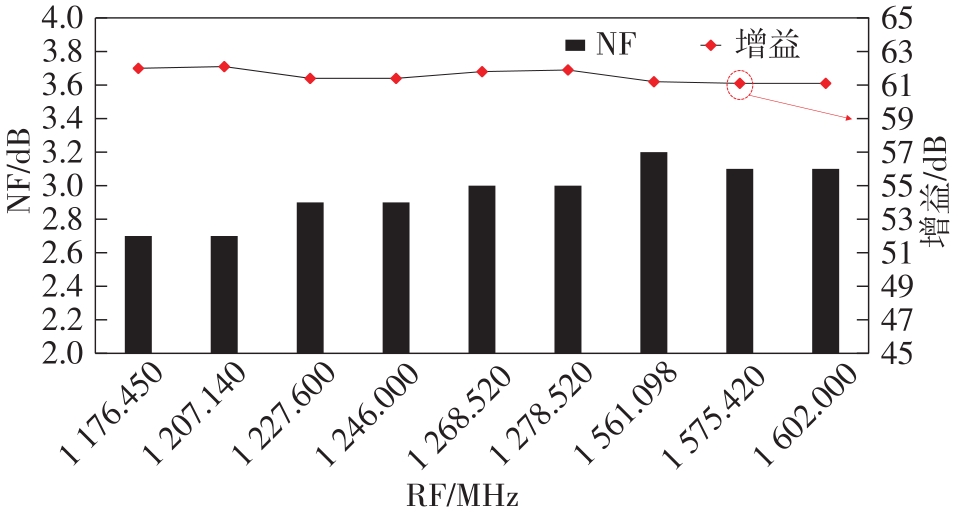
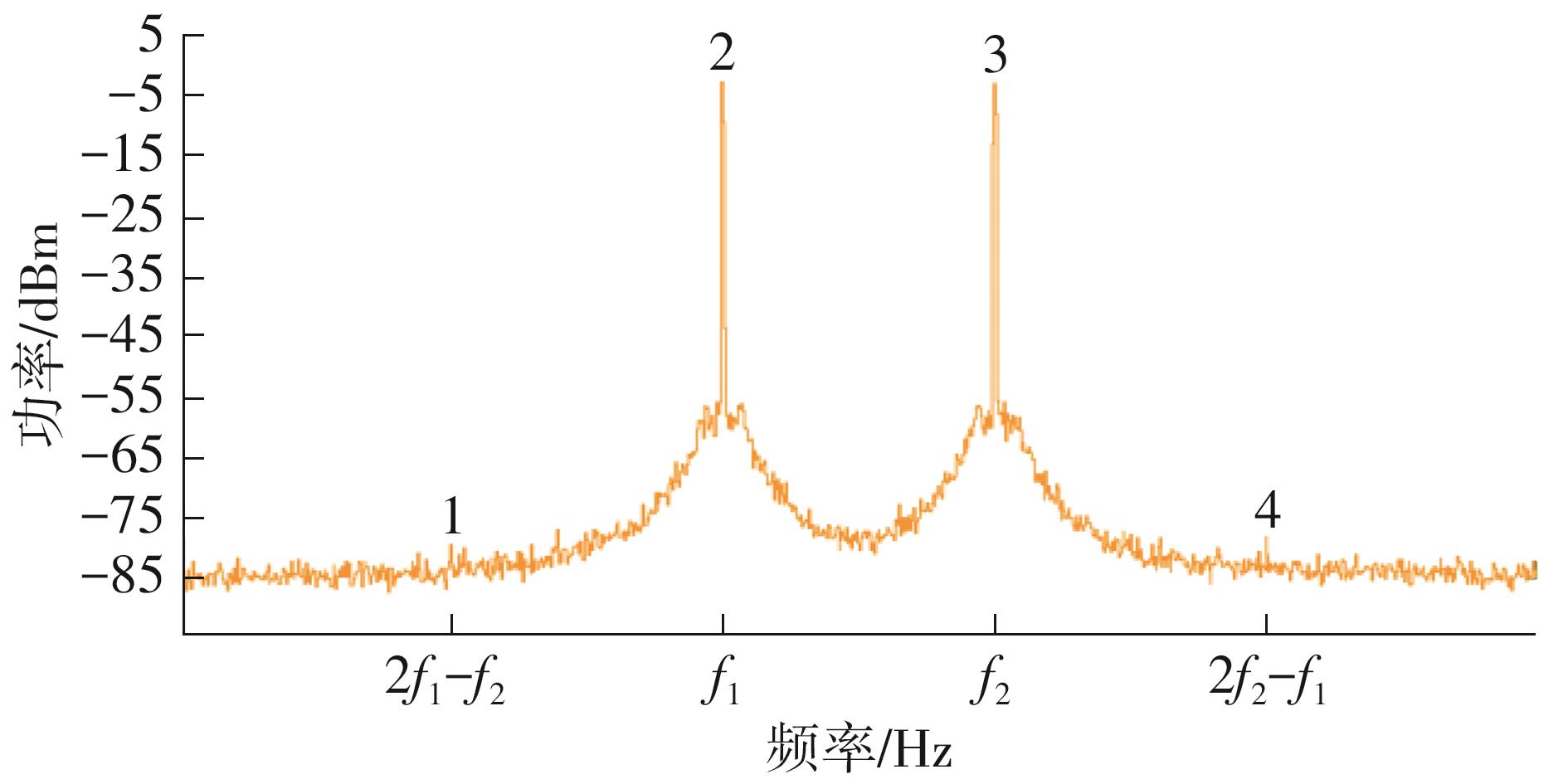
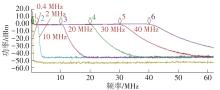
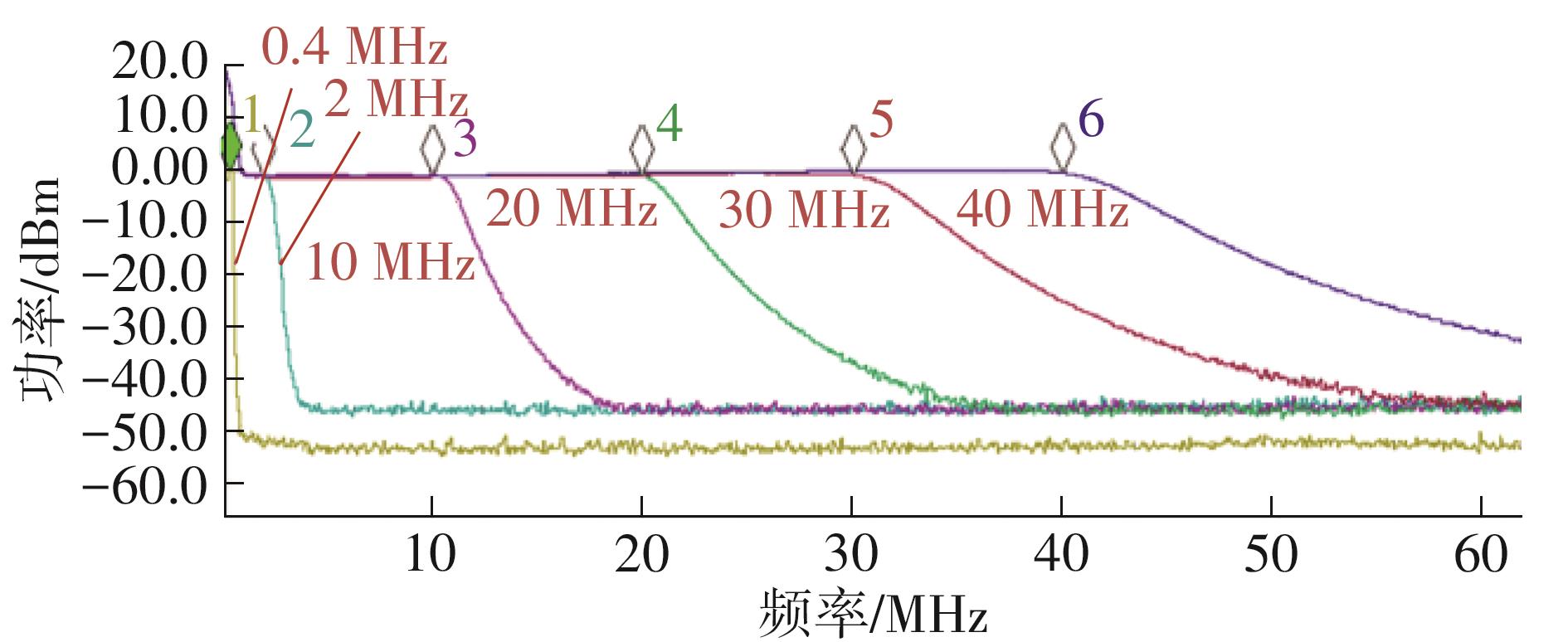
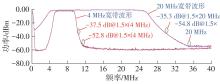
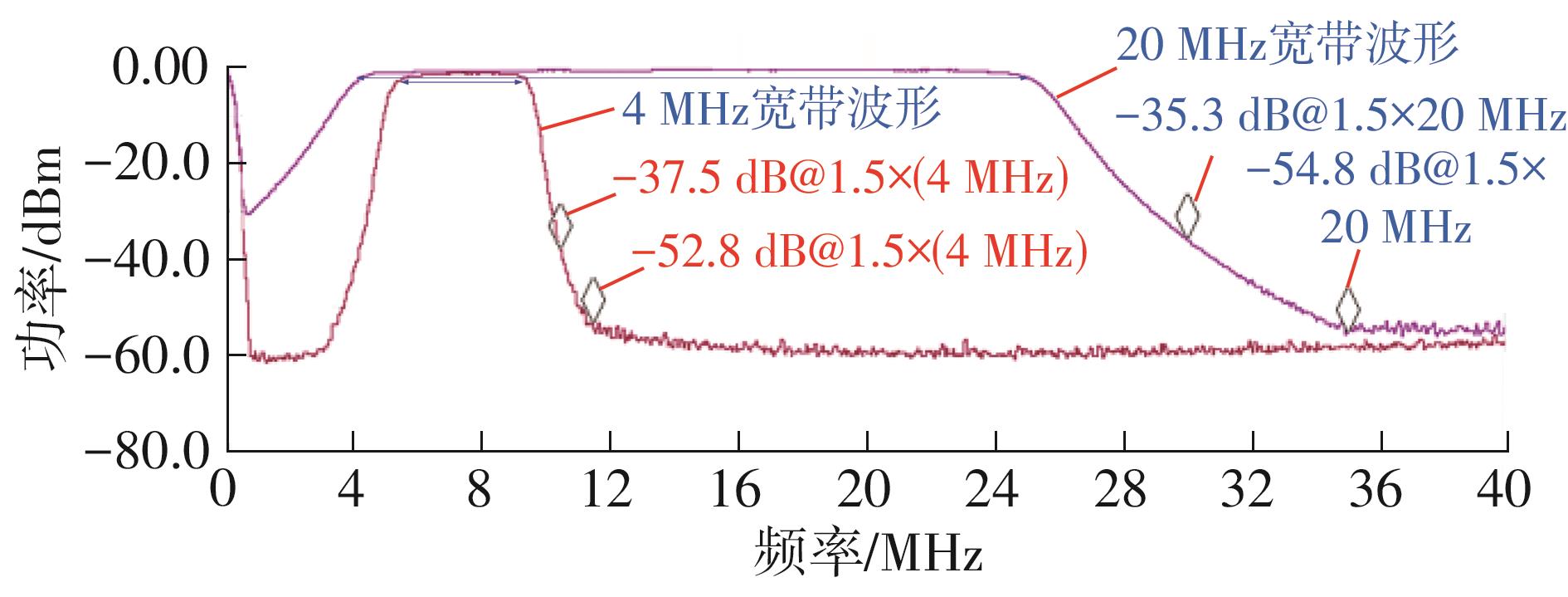
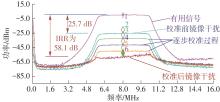
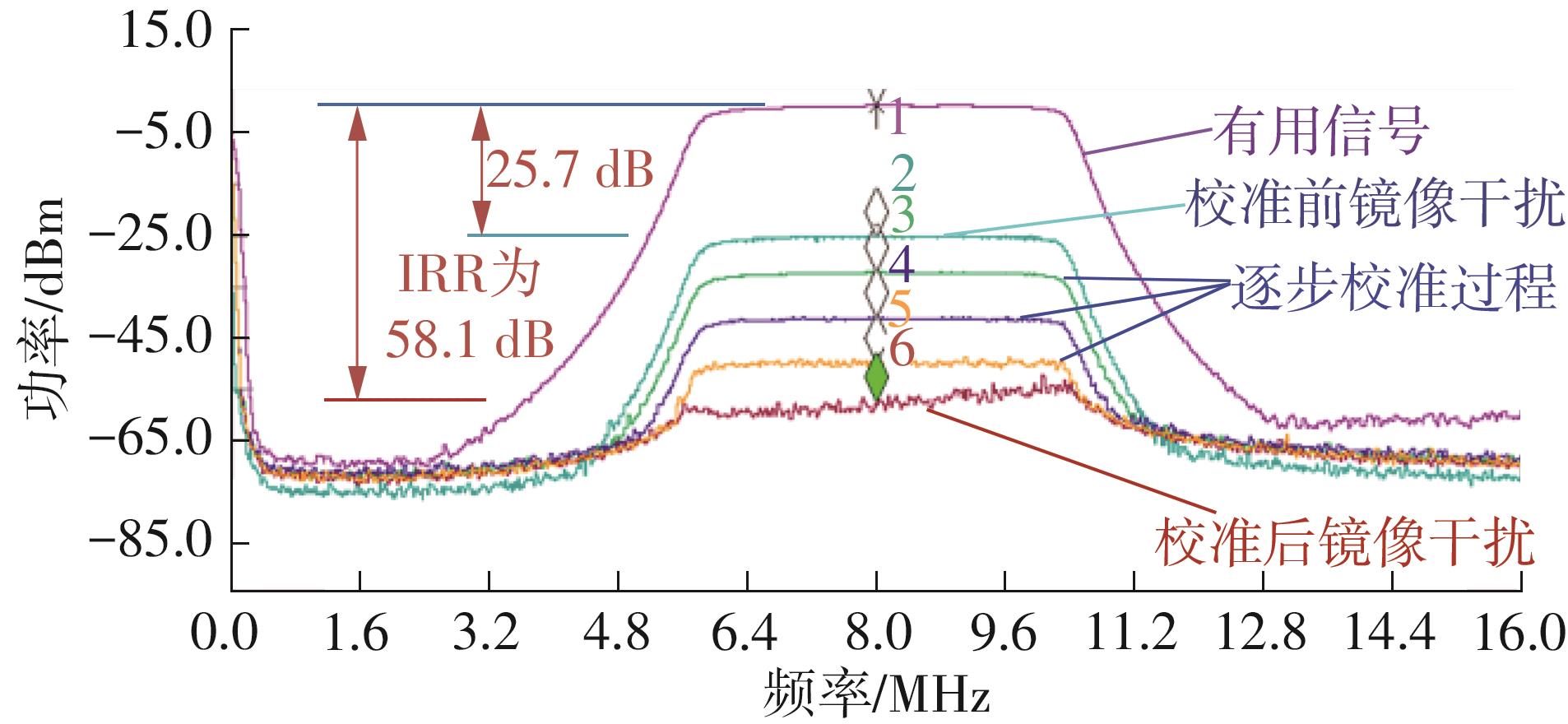
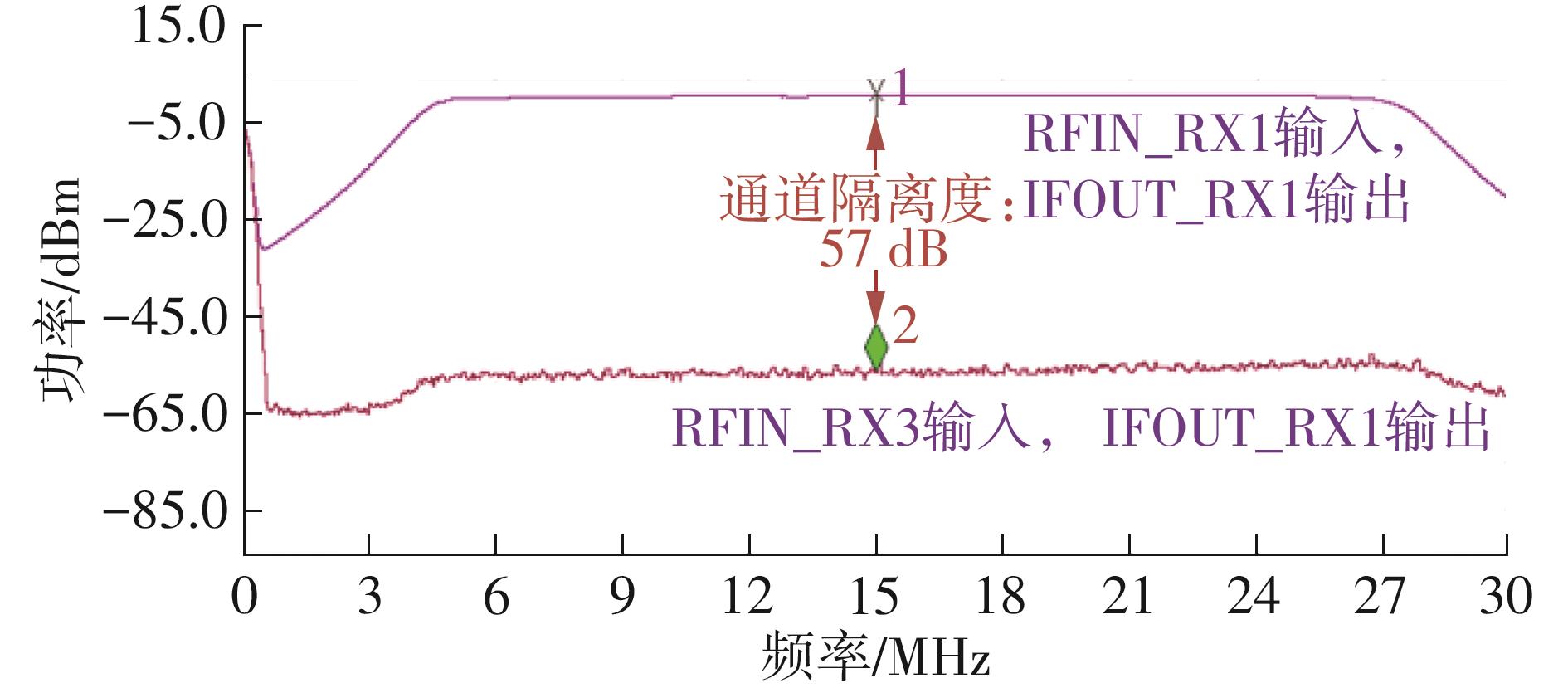
| 本文 | 0.13 | 1.15~1.65 | LPF/BPF | 0.8~80 | 20~110 | 2.7~3.2 | 34.7 | -14 | +58.1 | 57 | 24.7 |
| 1 | MAHATO S, SHAW G, SATRA A,et al .Low cost GNSS receiver RTK performance in forest environment [C]∥ Proceedings of the 2020 URSI Regional Confe-rence on Radio Science.Varanasi:IEEE,2020:1-4. |
| 2 | WU Z, ZHANG Y, YANG Y,et al .Spoofing and anti-spoofing technologies of global navigation satellite system:a survey [J].IEEE Access,2020,8:165444-165496. |
| 3 | XIN S, LI X, GENG J,et al .The implementation of multi-GNSS real-time precise point positioning service system:GPS/GLONASS [C]∥ Proceedings of the 2017 Forum on Cooperative Positioning and Service (CPGPS).Harbin:IEEE,2017:202-207. |
| 4 | ZHANG J, XU Y, ZHANG Z,et al .A 10-b fourth-order quadrature bandpass continuous-time modulator with 33-MHz bandwidth for a dual-channel GNSS receiver [J].IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques,2017,65(4):1303-1314. |
| 5 | LYU Y, ZOU W, CHEN S .A dual-channel GNSS receiver for GPS and Beidou applications [C]∥ Proceedings of the 2017 2nd IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits and Microsystems (ICICM).Nanjing:IEEE,2017:326-329. |
| 6 | 金晶,杨照霖,刘力僮,等 .基于CMOS工艺的全集成高线性度可重构全球卫星导航系统射频接收机[J].上海交通大学学报,2018,52(10):1226-1233. |
| JIN Jing, YANG Zhaolin, LIU Litong,et al .Fully-integrated reconfigurable CMOS global navigation satellite system receivers with high-Linearity [J].Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2018,52(10):1226-1233. | |
| 7 | SCAVINI P, CASTRO M, SUSINO E,et al .RF FE for multi-frequency/multi-constellation GNSS receiver for ASIL-grade applications [C]∥ Proceedings of the 2019 European Microwave Conference in Central Europe.[S.l.]:EuMCE,2019:315-318. |
| 8 | KANCHETLA V, KHARALKAR A, JAIN S,et al .A compact reconfigurable CMOS RF receiver for NavIC/GPS/Galileo/BeiDou [J].IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques,2022,70(7):3361-3373. |
| 9 | 彭旭飞,李立功 .北斗2机载双天线定向接收机研究与设计[J].兵器装备工程学报,2017,38(5):110-113. |
| PENG Xufei, LI Ligong .Research and design of onboard double antenna orientation BD2 receiver [J].Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering,2017,38(5):110-113. | |
| 10 | JIANG J, KIM J, KARSILAYAN A I,et al .A 3-6-GHz highly linear I-channel receiver with over +3.0-dBm in-band P1dB and 200-MHz baseband bandwidth suitable for 5G wireless and cognitive radio applications [J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers,2019,66(8):3134-3147. |
| 11 | ILYAS F, IRTEZA S, SHOAIB N,et al .A frequency agile dual-band gnss receiver front end with anti-jamming capabilities [C]∥ Proceedings of the 2020 European Navigation Conference,Bonn,Germany,2020:1-6. |
| 12 | KIM D, JANG S, LEE J,et al .A broadband pvt-insensitive all-nmos noise-canceling balun-lna for subgigahertz wireless communication applications [J].IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters.2021,31(2):165-168. |
| 13 | 陈志坚,蔡敏 .抗干扰高线性射频前端设计[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(1):37-43. |
| CHEN Zhi-jian, CAI Min .Design of anti-interference high-linearity RF front-end [J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,44(1):37-43. | |
| 14 | MASNADI SHIRAZI A H, LAVASANI H M, SHARIFZADEH M,et al .An ultralow-power current-reused direct-conversion bluetooth-low-energy receiver front-end in 40-nm cmos [J].IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques,2021,69(5):2697-2711. |
| 15 | LAVALLE-AVILES F, SÁNCHEZ-SINENCIO E .A 0.6-v power-efficient active-RC analog low-pass filter with cutoff frequency selection [J]∥ IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems,2020,28(8):1757-1769. |
| [1] | ZHUANG Ling, LIU Yuhang. Research on Transmission Scheme Based on Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface in Dense Urban Agglomeration [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(3): 112-118. |
| [2] | ZHENG Juanyi, DONG Jiahao, ZHANG Qingjue, et al. Reconfigurable Intelligence Surface Channel Estimation Algorithm Based on RDN [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(3): 102-111. |
| [3] | HU Qingchun, HUANG Si, CHEN Xingbin, et al. Research on Redundant Strapdown Inertial Navigation Information Fusion for eVTOL Aircraft [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(10): 1-8. |
| [4] | BIAN Yang, YU Jie ZHAO, Xiaohua, et al. Research on the Comprehensive Influence of Navigation BroadcastWording on Driving Behavior [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 30-37,54. |
| [5] |
YAO Ruohe HE Xiaomeng .
Broadband Low Noise Amplifier Architecture Based on Coupling and Negative Feedback
|
| [6] | CHEN Yongjun, LIU Qing, WAN Chengpeng, et al. Brittle Nodes Identification of Navigation System in Traffic Flow Intensive Waters in Emergency Situations [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(11): 54-61,70. |
| [7] | HE Wei ZHU Liang-sheng HU Jin-peng. Impact of Lingding Navigation Channel on Fresh Salt-Water Mixing in Dry Season [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(4): 138-144. |
| [8] | XIONG Wei WANG Qing-hui LI Jing-rong. A Hierarchical Method of Interaction Hand Gesture for Virtual Assembly [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(1): 78-84. |
| [9] | Zhang Feng Wang Zuo-jian Wu Yang Yu Fang Liu Zhong-li. Boolean Matching of Wide Functions and Its Application to Resynthesis of FPGA [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(5): 34-42. |
| [10] | Liu Jie Liu Chao Zong Chang- fu Zheng Hong- yu Liu Ming- hui. Fault- Tolerant Control of 4WID/4WIS Electric Vehicles Based on Reconfigurable Control Allocation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(11): 125-131. |
| [11] | Yu Jun Lou Pei-huang Qian Xiao-ming Wu Xing. Recognition and Accurate Measurement of Vision-Guided Path of Automatic Guided Vehicle [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(3): 143-149. |
| [12] | Zhang Quan Wen Hui-ying Sun Bo. Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm of Ergodic Model for Routing Planning of Delivery Vehicle Navigation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(8): 109-112,117. |
| [13] | Xu Yu-bin Ding Zhe Sha Xue-jun. Genetic Algorithm-Based Dynamic Planning and Management of Reconfigurable System [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(9): 13-19. |
| [14] | Zhang Dan Zuo Dun-wen Jiao Guang-ming Xue Shan-liang Li Jian-ping Zhou Hua-lin. Interactive Aid Technology for Virtual Assembly Manipulation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(5): 127-132. |
| [15] | Zhang Tao Xu Xiao-su. Initial Alignment for Integrated Navigation System Based on Neural Network and Wavelet [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(12): 73-78,89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||